本文主要是介绍LeetCode第797题: 所有可能的路径,希望对大家解决编程问题提供一定的参考价值,需要的开发者们随着小编来一起学习吧!
目录
1.问题描述
2.问题分析
1.问题描述
给你一个有 n 个节点的有向无环图(DAG),请你找出所有从节点 0 到节点 n-1 的路径并输出(不要求按特定顺序)。
graph[i] 是一个从节点 i 可以访问的所有节点的列表(即从节点 i 到节点 graph[i][j]存在一条有向边)。
示例1:

输入:graph = [[1,2],[3],[3],[]]
输出:[[0,1,3],[0,2,3]]
解释:有两条路径 0 -> 1 -> 3 和 0 -> 2 -> 3
示例2:
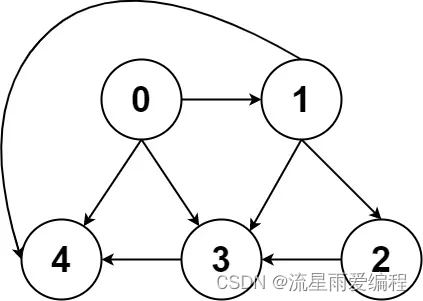
输入:graph = [[4,3,1],[3,2,4],[3],[4],[]]
输出:[[0,4],[0,3,4],[0,1,3,4],[0,1,2,3,4],[0,1,4]]
-
n == graph.length
-
2 <= n <= 15
-
0 <= graph[i][j] < n
-
graph[i][j] != i(即不存在自环)
-
graph[i] 中的所有元素互不相同
-
保证输入为有向无环图(DAG)
2.问题分析
思路分析:有向无环图(Directed acyclic graph, DAG)是图论中的一个概念,它指的是一个无回路的有向图。问题是要找到0节点到n − 1节点的所有路径,对于所有路径的问题,我们可以用深度优先搜索来做(广度优先搜索也可以)。
这题让在有向无环图中输出从顶点0到顶点n-1的所有路径,可以使用dfs,从顶点0开始搜索,搜索所有路径,因为是无环的,所以搜索的时候不会出现死循环。到顶点n-1的时候就把这条路径上所有的点都保存下来。因为是dfs搜索,往下走的时候选择节点,往回走的时候要记得撤销选择。
JAVA
public List<List<Integer>> allPathsSourceTarget(int[][] graph) {List<List<Integer>> ans = new ArrayList<>();ArrayList<Integer> path = new ArrayList<>();path.add(0);// 把起始节点0加进来dfs(graph, 0, ans, path);return ans;
}private void dfs(int[][] graph, int index, List<List<Integer>> ans, List<Integer> path) {// 到最后一个节点的时候,说明找了一个一条有效路径if (index == graph.length - 1) {ans.add(new ArrayList<>(path));return;}// 当前节点指向哪些节点(可以看做是n叉树的子节点,然后遍历他的子节点)int[] directs = graph[index];for (int i = 0; i < directs.length; i++) {path.add(directs[i]);// 把当前节点加入到路径中dfs(graph, directs[i], ans, path);// 递归path.remove(path.size() - 1); // 撤销选择}
}C++
public:vector<vector<int>> allPathsSourceTarget(vector<vector<int>> &graph) {vector<vector<int>> ans;vector<int> path;path.push_back(0);// 把起始节点0加进来dfs(graph, 0, ans, path);return ans;}void dfs(vector<vector<int>> &graph, int index, vector<vector<int>> &ans, vector<int> &path) {// 到最后一个节点的时候,说明找了一个一条有效路径if (index == graph.size() - 1) {ans.emplace_back(path);return;}// 当前节点指向哪些节点(可以看做是n叉树的子节点,然后遍历他的子节点)for (int g: graph[index]) {path.emplace_back(g);// 把当前节点加入到路径中dfs(graph, g, ans, path);// 递归path.pop_back(); // 撤销选择}}C
void dfs(int **graph, int graphSize, int *graphColSize, int *returnSize,int **returnColumnSizes, int **ans, int *path, int v, int count) {// 到最后一个节点的时候,说明找了一个一条有效路径if (v == graphSize - 1) {ans[*returnSize] = malloc(count * sizeof(int));memcpy(ans[*returnSize], path, count * sizeof(int));(*returnColumnSizes)[(*returnSize)++] = count;return;}// 当前节点指向哪些节点(可以看做是n叉树的子节点,然后遍历他的子节点)for (int i = 0; i < graphColSize[v]; ++i) {path[count++] = graph[v][i];// 把当前节点加入到路径中dfs(graph, graphSize, graphColSize, returnSize, returnColumnSizes, ans, path, graph[v][i], count);// 递归count--;// 撤销选择}
}int **allPathsSourceTarget(int **graph, int graphSize, int *graphColSize, int *returnSize, int **returnColumnSizes) {int **ans = malloc(20000 * sizeof(int *));int *path = malloc(15 * sizeof(int));int v = 0;int count = 0;*returnSize = 0;*returnColumnSizes = malloc(20000 * sizeof(int));path[count++] = v;// 把起始节点0加进来dfs(graph, graphSize, graphColSize, returnSize, returnColumnSizes, ans, path, v, count);return ans;
}Python
def allPathsSourceTarget(self, graph: List[List[int]]) -> List[List[int]]:def dfs(index):# 到最后一个节点的时候,说明找了一个一条有效路径if index == len(graph) - 1:ans.append(path[:])return# 当前节点指向哪些节点(可以看做是n叉树的子节点,然后遍历他的子节点)for direct in graph[index]:path.append(direct) # 把当前节点加入到路径中dfs(direct) # 递归path.pop() # 撤销选择ans = []path = [0]dfs(0)return ans复杂度分析

这篇关于LeetCode第797题: 所有可能的路径的文章就介绍到这儿,希望我们推荐的文章对编程师们有所帮助!






