本文主要是介绍Linux 6.文件属性(stat、fstat),希望对大家解决编程问题提供一定的参考价值,需要的开发者们随着小编来一起学习吧!
文件属性(stat、fstat)
- stat、fstat、lstat函数简介
- struct stat结构体简介
- stat
- 用代码判断文件类型
- 用代码判断文件权限设置
stat、fstat、lstat函数简介
-
每个文件中都附带了这个文件的一些属性(属性信息是存在于文件本身中的,但是它不像文件的内容一样可以被vi打开看到,属性信息只能被专用的API打开看到)
-
文件属性信息查看的API有三个:stat、fstat、lstat,三个作用一样,参数不同,细节略有不同。
-
linux命令行下还可以去用stat命令去查看文件属性信息,实际上stat命令内部就是使用stat系统调用来实现的。
-
stat这个API的作用就是让内核将我们要查找属性的文件的属性信息结构体的值放入我们传递给stat函数的buf中,当stat这个API调用从内核返回的时候buf中就被填充了文件的正确的属性信息,然后我们通过查看buf这种结构体变量的元素就可以得知这个文件的各种属性了。
-
fstat和stat的区别是 :stat是从文件名出发得到文件属性信息结构体,而fstat是从一个已经打开的文件fd出发得到一个文件的属性信息。所以用的时候如果文件没有打开(我们并不想打开文件操作而只是希望得到文件属性)那就用stat,如果文件已经被打开了然后要属性那就用fstat效率会更高(stat是从磁盘去读取文件的,而fstat是从内存读取动态文件的)。
-
stat/fstat的差别在于:lstat和对于符号链接文件,stat和fstat查阅的是符号链接文件指向的文件的属性,而lstat查阅的是符号链接文件本身的属性。
struct stat结构体简介
struct stat是内核定义的一个结构体,在<sys/stat.h>中声明,所以我们可以用。这个结构体中的所有元素加起来就是我们的文件属性信息。

stat
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <sys/stat.h>
#include <unistd.h> int stat(const char *pathname, struct stat *buf);
pathname:用于指定一个需要查看属性的文件路径。
buf:struct stat 类型指针,用于指向一个 struct stat 结构体变量。调用 stat 函数的时候需要传入一个 struct stat 变量的指针,获取到的文件属性信息就记录在 struct stat 结构体中。
返回值:成功返回 0;失败返回-1,并设置 error。
#include <sys/stat.h>
#include <stdio.h>
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <fcntl.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <stdlib.h>int main(int argc,char **argv)
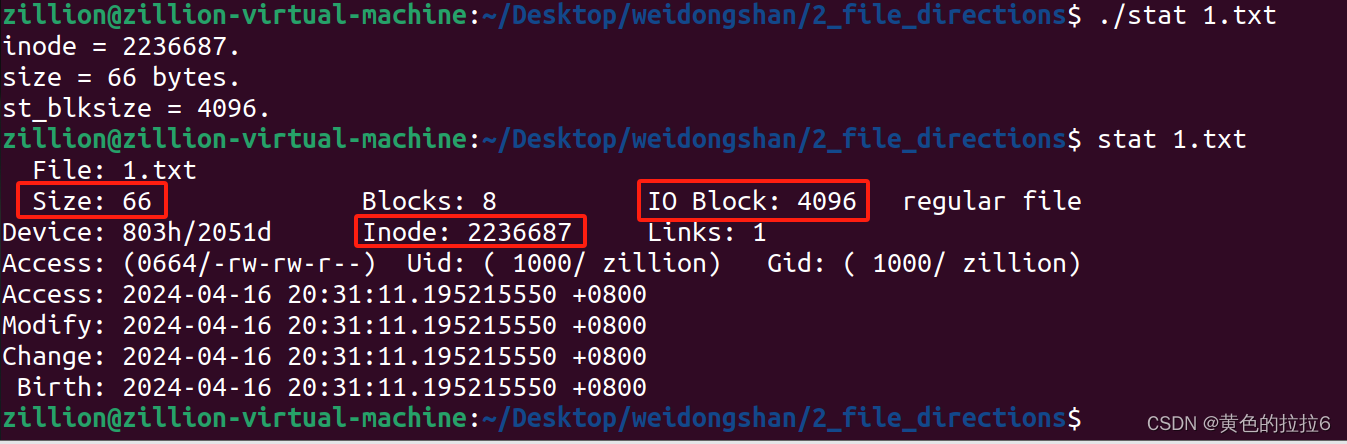
{if(argc != 2){printf("Usage: stat <file>\n");exit(-1);}int ret = -1;struct stat buf;memset(&buf, 0, sizeof(buf)); // memset后buf中全是0ret = stat(argv[1], &buf); // stat后buf中有内容了if (ret < 0){perror("stat");exit(-1);}// 成功获取了stat结构体,从中可以得到各种属性信息了printf("inode = %ld.\n", buf.st_ino);printf("size = %ld bytes.\n", buf.st_size);printf("st_blksize = %ld.\n", buf.st_blksize);return 0;
}
用代码判断文件类型
-
文件类型就是-、d、l····
-
文件属性中的文件类型标志在struct stat结构体的mode_t st_mode元素中,这个元素其实是一个按位来定义的一个位标志(有点类似于ARM CPU的CPSR寄存器的模式位定义)。这个东西有很多个标志位共同构成,记录了很多信息,如果要查找时按位&操作就知道结果了,但是因为这些位定义不容易记住,因此linux系统给大家事先定义好了很多宏来进行相应操作。
-
譬如S_ISREG宏返回值是1表示这个文件是一个普通文件,如果文件不是普通文件则返回值是0.
S_IFSOCK 0140000 socket(套接字文件)
S_IFLNK 0120000 symbolic link(链接文件)
S_IFREG 0100000 regular file(普通文件)
S_IFBLK 0060000 block device(块设备文件)
S_IFDIR 0040000 directory(目录)
S_IFCHR 0020000 character device(字符设备文件)
S_IFIFO 0010000 FIFO(管道文件)
用代码判断文件权限设置
-
st_mode中除了记录了文件类型之外,还记录了一个重要信息:文件权限。
-
linux并没有给文件权限测试提供宏操作,而只是提供了位掩码,所以我们只能用位掩码来自己判断是否具有相应权限。
可以使用 Linux 系统封装好的宏来进行判断属于什么文件,如下所示(m 是 st_mode 变 量):
S_ISREG(m) #判断是不是普通文件,如果是返回 true,否则返回 false
S_ISDIR(m) #判断是不是目录,如果是返回 true,否则返回 false
S_ISCHR(m) #判断是不是字符设备文件,如果是返回 true,否则返回 false
S_ISBLK(m) #判断是不是块设备文件,如果是返回 true,否则返回 false
S_ISFIFO(m) #判断是不是管道文件,如果是返回 true,否则返回 false
S_ISLNK(m) #判断是不是链接文件,如果是返回 true,否则返回 false
S_ISSOCK(m) #判断是不是套接字文件,如果是返回 true,否则返回 false /* 判断是不是普通文件 */
if (S_ISREG(st.st_mode)) { /* 是 */
} /* 判断是不是目录 */
if (S_ISDIR(st.st_mode)) { /* 是 */
} switch (file_stat.st_mode & S_IFMT) { case S_IFSOCK: printf("socket"); break; case S_IFLNK: printf("symbolic link"); break; case S_IFREG: printf("regular file"); break; case S_IFBLK: printf("block device"); break; case S_IFDIR: printf("directory"); break; case S_IFCHR: printf("character device"); break; case S_IFIFO: printf("FIFO"); break; } ————————————————版权声明:本文为博主原创文章,遵循 CC 4.0 BY-SA 版权协议,转载请附上原文出处链接和本声明。原文链接:https://blog.csdn.net/weixin_73901182/article/details/132072503
#include <sys/stat.h>
#include <stdio.h>
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <fcntl.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <stdlib.h>int main(int argc,char **argv)
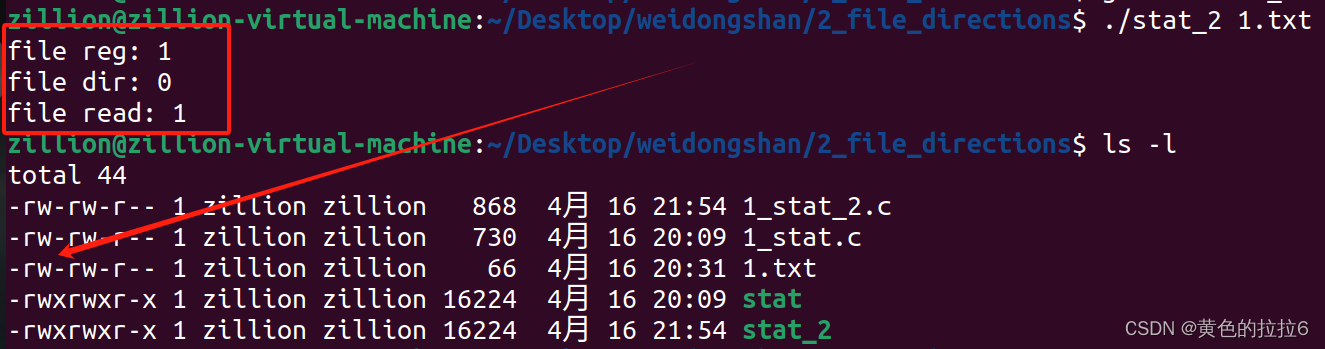
{if(argc != 2){printf("Usage: stat <file>\n");exit(-1);}int ret = -1;struct stat buf;memset(&buf, 0, sizeof(buf)); // memset后buf中全是0ret = stat(argv[1], &buf); // stat后buf中有内容了if (ret < 0){perror("stat");exit(-1);}int reg_result = ( S_ISREG(buf.st_mode) ? 1:0 );printf("file reg: %d\n",reg_result);int dir_result = ( S_ISDIR(buf.st_mode) ? 1:0 );printf("file dir: %d\n",dir_result);int read_result = (buf.st_mode & S_IRUSR) >> 8;printf("file read: %d\n",read_result);return 0;
}
这篇关于Linux 6.文件属性(stat、fstat)的文章就介绍到这儿,希望我们推荐的文章对编程师们有所帮助!







