本文主要是介绍JAVA中Arrays.sort()使用两种方式(Comparable和Comparator接口)对对象或者引用进行排序,希望对大家解决编程问题提供一定的参考价值,需要的开发者们随着小编来一起学习吧!
一、描述
自定义的类要按照一定的方式进行排序,比如一个Person类要按照年龄进行从小到大排序,比如一个Student类要按照成绩进行由高到低排序。
这里我们采用两种方式,一种是使用Comparable接口:让待排序对象所在的类实现Comparable接口,并重写Comparable接口中的compareTo()方法,缺点是只能按照一种规则排序。
另一种方式是使用Comparator接口:编写多个排序方式类实现Comparator接口,并重写新Comparator接口中的compare()方法,在调用Arrays的sort()时将排序类对象作为参数传入:public static <T> void sort(T[] a,Comparator<? super T> c),根据指定比较器产生的顺序对指定对象数组进行排序。数组中的所有元素都必须是通过指定比较器可相互比较的(也就是说,对于数组中的任何 e1 和 e2 元素而言,c.compare(e1, e2) 不得抛出 ClassCastException)。
优点是可以按照多种方式排序,你要按照什么方式排序,就创建一个实现Comparator接口的排序方式类,然后将该排序类的对象传入到Arrays.sort(待排序对象,该排序方式类的对象)
二、源代码
方式1:使用Comparable接口
package tong.day4_27.systemUse;import java.util.Arrays;
/*** 使用Comparable接口:让待排序对象所在的类实现Comparable接口,并重写Comparable接口中的compareTo()方法* 缺点是只能按照一种规则排序* @author tong**/
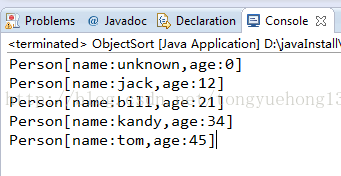
public class ObjectSort {public static void main(String[] args) {Person[] persons = new Person[5];persons[0] =new Person("tom",45);persons[1] =new Person("jack",12);persons[2] =new Person("bill",21);persons[3] =new Person("kandy",34);persons[4] =new Person();Arrays.sort(persons);for (Person person:persons) {System.out.println(person);}}}
class Person implements Comparable<Person>{private String name;private int age;public Person(String name,int age){this.name = name;this.age = age;}public Person(){this("unknown", 0);}//重写该类的compareTo()方法,使其按照从小到大顺序排序@Overridepublic int compareTo(Person o) {return age-o.age;}//重写Student类的toString()方法,在输入对象时按照以下方式输出@Overridepublic String toString() { return "Person[name:"+name+",age:"+age+"]";}}
方式2:使用Comparator接口
package tong.day4_27.systemUse;import java.util.Arrays;
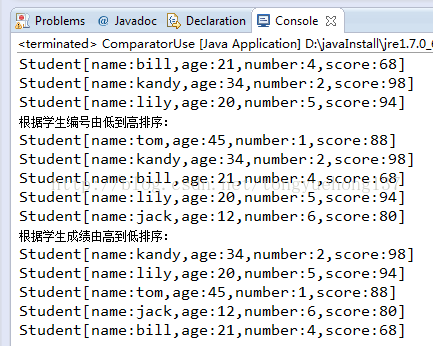
import java.util.Comparator;/*** 使用Comparator接口:编写多个排序方式类实现Comparator接口,并重写新Comparator接口中的compare()方法* public static <T> void sort(T[] a,Comparator<? super T> c),根据指定比较器产生的顺序对指定对象数组进行排序。数组中的所有元素都必须是通过指定比较器可相互比较的* (也就是说,对于数组中的任何 e1 和 e2 元素而言,c.compare(e1, e2) 不得抛出 ClassCastException)。* 优点是可以按照多种方式排序,你要按照什么方式排序,就创建一个实现Comparator接口的排序方式类,然后将该排序类的对象传入到Arrays.sort(待排序对象,该排序方式类的对象)* @author tong**/public class ComparatorUse {public static void main(String[] args) {Student[] persons = new Student[5];persons[0] =new Student("tom",1,88,45);persons[1] =new Student("jack",6,80,12);persons[2] =new Student("bill",4,68,21);persons[3] =new Student("kandy",2,98,34);persons[4] =new Student("lily",5,94,20);System.out.println("排序前的数据:");for (Student student:persons) {System.out.println(student);}//创建SortByNumber对象,将其作为参数传入Arrays.sort(persons,sortByNumber)方法中SortByNumber sortByNumber = new SortByNumber();Arrays.sort(persons,sortByNumber);System.out.println("根据学生编号由低到高排序:");for (Student student:persons) {System.out.println(student);}SortByScore sortByScore = new SortByScore();Arrays.sort(persons,sortByScore);System.out.println("根据学生成绩由高到低排序:");for (Student student:persons) {System.out.println(student);}}}class Student {private String name;private int number;private int score;private int age;public Student(String name,int number,int score,int age){this.name = name;this.number = number;this.score = score;this.age = age;}//重写Student类的toString()方法,在输入对象时按照以下方式输出@Overridepublic String toString() { return "Student[name:"+name+",age:"+age+",number:"+number+",score:"+score+"]";}public String getName() {return name;}public void setName(String name) {this.name = name;}public int getNumber() {return number;}public void setNumber(int number) {this.number = number;}public int getScore() {return score;}public void setScore(int score) {this.score = score;}public int getAge() {return age;}public void setAge(int age) {this.age = age;}}
//按照学号由低到高排列,创建SortByNumber类,该类实现Comparator,重写该接口的compare()
class SortByNumber implements Comparator<Student>{//重写该接口的compare()使其按照学号由小到大排序(前者减去后者)@Overridepublic int compare(Student o1, Student o2) {return o1.getNumber()-o2.getNumber();}}
//按照分数由高到低排列,创建SortByScore类,该类实现Comparator,重写该接口的compare()
class SortByScore implements Comparator<Student>{//重写该接口的compare()使其按照分数由高到低排序(后者减去前者)@Overridepublic int compare(Student o1, Student o2) {return o2.getScore()-o1.getScore();}}
这篇关于JAVA中Arrays.sort()使用两种方式(Comparable和Comparator接口)对对象或者引用进行排序的文章就介绍到这儿,希望我们推荐的文章对编程师们有所帮助!