本文主要是介绍配图详解链表冒泡排序(交换指针域),希望对大家解决编程问题提供一定的参考价值,需要的开发者们随着小编来一起学习吧!
冒泡排序的核心是从头开始相邻数据两两比较,如果要升序,前比后大则交换,下面用图讲解链表交换指针域的原理。

代码实现:
node* bubble_sort(node *head){node *tail=NULL,*q,*p=(node*)malloc(sizeof(node));for(p->next=head,head=p/*增加头结点*/;head->next!=tail;tail=q/*最后一个数已经排好了,所以尾部前移*/){for(p=head,q=p->next/*指针重新指向起始位置*/;q->next!=tail;p=p->next,q=p->next/*p,q同时后移,准备下一组交换*/){if(p->next->data>q->next->data){p->next=q->next;q->next=q->next->next;p->next->next=q;}}}head=head->next;//不要头结点free(p);return head;
}
排序效果如图:
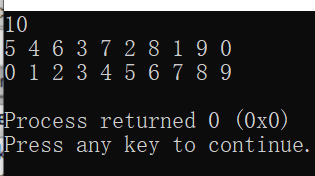
下面是整体的可运行代码:
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
typedef struct node
{int data;struct node* next;
}node;
node *create_list(int n)
{node *head=NULL,*q,*p;int i;for(i=0;i<n;i++){p=(node*)malloc(sizeof(node));scanf("%d",&(p->data));if(head==NULL){head=p;}else{q->next=p;}q=p;}p->next=NULL;return head;
}
node* bubble_sort(node *head){node *tail=NULL,*q,*p=(node*)malloc(sizeof(node));for(p->next=head,head=p/*增加头结点*/;head->next!=tail;tail=q/*最后一个数已经排好了,所以尾部前移*/){for(p=head,q=p->next/*指针重新指向起始位置*/;q->next!=tail;p=p->next,q=p->next/*p,q同时后移,准备下一组交换*/){if(p->next->data>q->next->data){p->next=q->next;q->next=q->next->next;p->next->next=q;}}}head=head->next;//不要头结点free(p);return head;
}
void print_list(node *head)
{node *p;for(p=head;p!=NULL;p=p->next){printf("%d ",p->data);}printf("\n");
}
int main()
{int n;scanf("%d",&n);node *head=create_list(n);head=bubble_sort(head);print_list(head);return 0;
}注意:
1.该交换方法只适用于相邻结点
2.交换前两个结点是特殊情况,所以需要加入头结点统一操作
下面推荐一些我的其他博文:
对动态链表的创建不太熟悉的同学请看https://blog.csdn.net/tongjingqi_/article/details/105831323
想了解单链表的增删改的同学请看
https://blog.csdn.net/tongjingqi_/article/details/105873529
对交换数据域排序方法感兴趣的同学请点
https://blog.csdn.net/tongjingqi_/article/details/105927156
这篇关于配图详解链表冒泡排序(交换指针域)的文章就介绍到这儿,希望我们推荐的文章对编程师们有所帮助!




