本文主要是介绍【C++】unordered_set和unordered_map,希望对大家解决编程问题提供一定的参考价值,需要的开发者们随着小编来一起学习吧!
底层哈希结构
namespace hash_bucket
{template<class T>struct HashData{T _data;struct HashData* next = nullptr;HashData(const T& data):_data(data){}};//仿函数:这里直接用开散列仿函数template <class K>struct HashFunc{size_t operator()(const K& key){return (size_t)key;}};template <>struct HashFunc<string>//特化{size_t operator()(const string& key){size_t res = 0;for (auto e : key){res *= 131;res += e;}return res;}};//迭代器//前置声明template<class K, class T, class Hash, class KeyOfT>class HashTable;template<class K, class T, class Hash, class KeyOfT>struct _HashTableIterator{typedef HashData<T> Node;typedef HashTable<K, T, Hash, KeyOfT> Ht;typedef _HashTableIterator<K, T, Hash, KeyOfT> Self;Node* _node;Ht* _pht;_HashTableIterator(Node* node,Ht* pht):_node(node),_pht(pht){}T& operator*(){return _node->_data;}T* operator->(){return &_node->_data;}Self& operator++(){if (_node->next){//当前桶_node = _node->next;}else{//下一个桶KeyOfT kot;Hash hash;size_t i = hash(kot(_node->_data)) % _pht->_size;for (++i; i < _pht->_tables.size(); i++){if (_pht->_tables[i]){_node = _pht->_tables[i];if(node)break;}}if (i == _pht->_tables.size()){_node = nullptr;}}return *this;}bool operator!=(Self& s)const{return s._node != _node;}bool operator==(Self& s)const{return !operator!=(s);}};template<class K, class T, class Hash, class KeyOfT>class HashTable{typedef HashData<T> Node;typedef _HashTableIterator<K, T, Hash, KeyOfT> iterator;public:iterator begin(){for (size_t i = 0; i < _tables.size(); i++){if (_tables[i] != nullptr)return iterator(_tables[i], this);}return end();}iterator end(){return iterator(nullptr, this);}public:HashTable():_size(0),_tables(10, nullptr){}~HashTable()//这里的析构函数得自己添加,否则只会析构哈希表,导致节点数据没有被释放{//这里的操作和底下的打印有点像for (size_t i = 0; i < _tables.size(); i++){Node* cur = _tables[i];while (cur){Node* next = cur->next;delete cur;cur = next;}_tables[i] = nullptr;}}bool Insert(const T& data){Hash hash;KeyOfT kot;if (Find(kot(data)))return false;//负载因子到 1 就扩容if (_size == _tables.size())//扩容{size_t newSize = _tables.size() * 2;vector<Node*> newTables(newSize, nullptr);size_t hashi = 0;for (size_t i = 0; i < _tables.size(); i++){Node* cur = _tables[i];while (cur){Node* next = cur->next;hashi = hash(kot(cur->_data)) % newTables.size();cur->next = newTables[hashi];newTables[hashi] = cur;cur = next;}_tables[i] = nullptr;}_tables.swap(newTables);}size_t hashi = hash(kot(data)) % _tables.size();//头插Node* old = _tables[hashi];_tables[hashi] = new Node(data);_tables[hashi]->next = old;_size++;return true;}Node* Find(const K& key){if (_size == 0)return nullptr;Hash hash;KeyOfT kot;size_t hashi = hash(key) % _tables.size();Node* cur = nullptr;for (size_t i = 0; i < _tables.size(); i++){cur = _tables[i];while (cur){if (kot(cur->_data) == key){return cur;}cur = cur->next;}}return nullptr;}void Print(){KeyOfT kot;for (size_t i = 0; i < _tables.size(); i++){Node* cur = _tables[i];while (cur){cout << "[" << kot(cur->_data) << ": " << kot(cur->_data) << "]-->";cur = cur->next;}}cout << endl;}bool Erase(const K& key){Hash hash;KeyOfT kot;size_t hashi = hash(key) % _tables.size();Node* cur = _tables[hashi];Node* prev = nullptr;while (cur){if (kot(cur->_data) == key){if (prev){prev->next = cur->next;}else{_tables[hashi] = cur->next;}delete cur;cur = nullptr;return true;}else{prev = cur;cur = cur->next;}}return false;}size_t size(){return _size;}private:size_t _size = 0;//有效数据个数vector<Node*> _tables;};
}
unordered_set
namespace hash_bucket
{template<class K, class Hash = HashFunc<K>>class unordered_set{struct SetKeyOfT{const K& operator()(const K& key){return key;}};private:HashTable<K, K,Hash,SetKeyOfT> _ht;public:typedef typename HashTable<K, K, Hash, SetKeyOfT> ::iterator iterator;iterator begin(){return _ht.begin();}iterator end(){return _ht.end();}bool insert(const K& Node){return _ht.Insert(Node);}};void unorderedset_test1(){unordered_set<int> s;s.insert(2);s.insert(4);s.insert(9);s.insert(1);s.insert(2);s.insert(3);for (auto e : s){cout << e << " ";}}
}
unordered_map
namespace hash_bucket
{template<class K,class V, class Hash = HashFunc<K>>class unordered_map{struct MapKeyOfT{const K& operator()(const pair<K, V>& key){return key.first;}};private:HashTable<K, pair<K, V>, Hash, MapKeyOfT> _ht;public:typedef typename HashTable<K, pair<K, V>, Hash, MapKeyOfT>::iterator iterator;iterator begin(){return _ht.begin();}iterator end(){return _ht.end();}bool insert(const pair<K, V>& Node){return _ht.Insert(Node);}};void unorderedmap_test1(){unordered_map<string, string> dict;dict.insert(make_pair("insert", "插入"));dict.insert(make_pair("sort" , "排序"));dict.insert(make_pair("delete", "删除"));dict.insert(make_pair("string", "字符串"));dict.insert(make_pair("iterator", "迭代器"));unordered_map<string, string>::iterator umit = dict.begin();//while (umit != dict.end())//{// cout << umit->first << ":" << umit->second << endl;// ++umit;//}//cout << endl;}
}
此时编译:
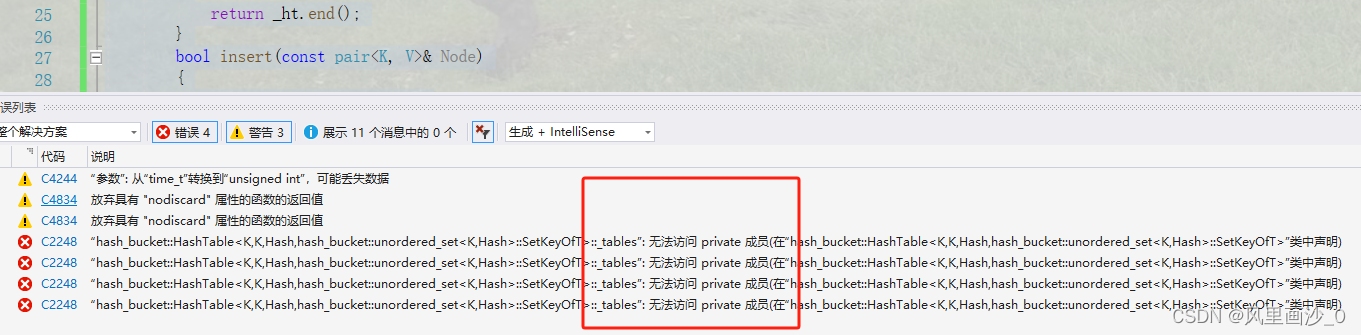 报错!
报错!
HashTable和其迭代器互相调用
从逻辑上讲,HashTable应该给迭代器开放权限,如下设置一个友元类即可
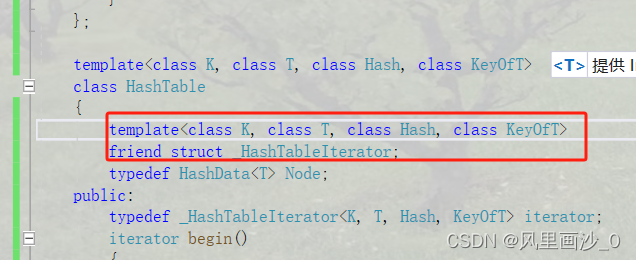
因为是模板故必须带参数。
经检测,以上代码有个小bug,可能会导致数据打印时无法跳出迭代器,形成死循环打印;
提示:错误点在该段代码中
Self& operator++(){if (_node->next){//当前桶_node = _node->next;}else{//下一个桶KeyOfT kot;Hash hash;size_t i = hash(kot(_node->_data)) % _pht->_size;for (++i; i < _pht->_tables.size(); i++){if (_pht->_tables[i]){_node = _pht->_tables[i];if(node)break;}}if (i == _pht->_tables.size()){_node = nullptr;}}return *this;}
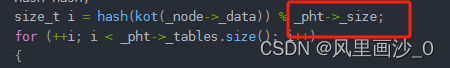
在这里我们是不是应该对哈希表的大小取模,而不是对现在的有效数据个数取模
size_t i = hash(kot(_node->_data)) % _pht->_tables.size();
完整代码
代码实现标准化,实现[ ]重载
#pragma once
#include "hash.h"
namespace hash_bucket
{template<class K, class Hash = HashFunc<K>>class unordered_set{struct SetKeyOfT{const K& operator()(const K& key){return key;}};private:HashTable<K, K,Hash,SetKeyOfT> _ht;public:typedef typename HashTable<K, K, Hash, SetKeyOfT> ::iterator iterator;iterator begin(){return _ht.begin();}iterator end(){return _ht.end();}pair<iterator, bool> insert(const K& Node){return _ht.Insert(Node);}};void unorderedset_test1(){unordered_set<int> s;s.insert(2);s.insert(4);s.insert(9);s.insert(1);s.insert(2);s.insert(3);for (auto e : s){cout << e << " ";}}
}
#pragma once
#include "hash.h"
namespace hash_bucket
{template<class K,class V, class Hash = HashFunc<K>>class unordered_map{struct MapKeyOfT{const K& operator()(const pair<K, V>& key){return key.first;}};private:HashTable<K, pair<K, V>, Hash, MapKeyOfT> _ht;public:typedef typename HashTable<K, pair<K, V>, Hash, MapKeyOfT>::iterator iterator;iterator begin(){return _ht.begin();}iterator end(){return _ht.end();}pair<iterator,bool> insert(const pair<K, V>& Node){return _ht.Insert(Node);}V& operator[](const K& key){pair<iterator, bool> ret = insert(make_pair(key, V()));return ret.first->second;}};void unorderedmap_test1(){unordered_map<string, string> dict;dict.insert(make_pair("insert", "插入"));dict.insert(make_pair("sort" , "排序"));dict.insert(make_pair("delete", "删除"));dict.insert(make_pair("string", "字符串"));dict.insert(make_pair("iterator", "迭代器"));unordered_map<string, string>::iterator umit = dict.begin();while (umit != dict.end()){cout << umit->first << ":" << umit->second << endl;++umit;}cout << endl;}void unorderedmap_test2(){string arr[] = { "梨子","苹果","猕猴桃","桃" ,"梨子","苹果", "猕猴桃","猕猴桃","猕猴桃","梨子","猕猴桃" };unordered_map<string, int> countMap;for (const auto& str : arr){countMap[str]++;}unordered_map<string, int>::iterator it = countMap.begin();while (it != countMap.end()){cout << (*it).first << ":" << (*it).second << endl;++it;}cout << endl << endl;for (auto e : countMap){cout << e.first << ":" << e.second << endl;}cout << endl;}
}
namespace hash_bucket
{template<class T>struct HashData{T _data;struct HashData* next = nullptr;HashData(const T& data):_data(data){}};//仿函数:这里直接用开散列仿函数template <class K>struct HashFunc{size_t operator()(const K& key){return (size_t)key;}};template <>struct HashFunc<string>//特化{size_t operator()(const string& key){size_t res = 0;for (auto e : key){res *= 131;res += e;}return res;}};//迭代器//前置声明template<class K, class T, class Hash, class KeyOfT>class HashTable;template<class K, class T, class Hash, class KeyOfT>struct _HashTableIterator{typedef HashData<T> Node;typedef HashTable<K, T, Hash, KeyOfT> Ht;typedef _HashTableIterator<K, T, Hash, KeyOfT> Self;Node* _node;Ht* _pht;_HashTableIterator(Node* node,Ht* pht):_node(node),_pht(pht){}T& operator*(){return _node->_data;}T* operator->(){return &_node->_data;}Self& operator++(){if (_node->next){//当前桶_node = _node->next;}else{//下一个桶KeyOfT kot;Hash hash;size_t i = hash(kot(_node->_data)) % _pht->_tables.size();for (++i; i < _pht->_tables.size(); i++){if (_pht->_tables[i]){_node = _pht->_tables[i];if (_node){break;}}}if (i == _pht->_tables.size()){_node = nullptr;}}return *this;}Self& operator++(int){Self tmp = this;if (_node->next){//当前桶_node = _node->next;}else{//下一个桶KeyOfT kot;Hash hash;size_t i = hash(kot(_node->_data)) % _pht->size();for (++i; i < _pht->_tables.size(); i++){if (_pht->_tables[i]){_node = _pht->_tables[i];break;}}if (i == _pht->_tables.size()){_node = nullptr;}}return tmp;}bool operator!=(const Self& s) const{return s._node != _node;}bool operator==(const Self& s) const{return s._node == _node;}};template<class K, class T, class Hash, class KeyOfT>class HashTable{template<class K, class T, class Hash, class KeyOfT>friend struct _HashTableIterator;typedef HashData<T> Node;public:typedef _HashTableIterator<K, T, Hash, KeyOfT> iterator;iterator begin(){for (size_t i = 0; i < _tables.size(); i++){if (_tables[i] != nullptr)return iterator(_tables[i], this);}return end();}iterator end(){return iterator(nullptr, this);}public:HashTable():_size(0),_tables(10, nullptr){}~HashTable()//这里的析构函数得自己添加,否则只会析构哈希表,导致节点数据没有被释放{//这里的操作和底下的打印有点像for (size_t i = 0; i < _tables.size(); i++){Node* cur = _tables[i];while (cur){Node* next = cur->next;delete cur;cur = next;}_tables[i] = nullptr;}}pair<iterator,bool> Insert(const T& data){Hash hash;KeyOfT kot;iterator ret = Find(kot(data));if (ret != end())return make_pair(ret, false); //负载因子到 1 就扩容if (_size == _tables.size())//扩容{size_t newSize = _tables.size() * 2;vector<Node*> newTables(newSize, nullptr);//这里为了减少调用,不像开散列那样采用复用insert的形式,而是直接将原表中的节点拿下来直接用//而且复用insert的时候会涉及空间的申请释放问题(申请新节点,将旧节点的值给新节点,然后释放新旧结点)size_t hashi = 0;//旧表数据移到新表//特别注意:一个一个数据移动,不可一串一串移动,那样的话会造成映射位置错误,最后使其数据不能被正常找到for (size_t i = 0; i < _tables.size(); i++){Node* cur = _tables[i];while (cur){Node* next = cur->next;hashi = hash(kot(cur->_data)) % newTables.size();cur->next = newTables[hashi];newTables[hashi] = cur;cur = next;}_tables[i] = nullptr;}_tables.swap(newTables);}size_t hashi = hash(kot(data)) % _tables.size();//头插Node* old = _tables[hashi];_tables[hashi] = new Node(data);_tables[hashi]->next = old;_size++;return make_pair(iterator(_tables[hashi], this), true);}iterator Find(const K& key){if (_size == 0)return iterator(nullptr, this);Hash hash;KeyOfT kot;size_t hashi = hash(key) % _tables.size();Node* cur = nullptr;for (size_t i = 0; i < _tables.size(); i++){cur = _tables[i];while (cur){if (kot(cur->_data) == key){return iterator(cur, this);}cur = cur->next;}}return end();}void Print(){KeyOfT kot;for (size_t i = 0; i < _tables.size(); i++){Node* cur = _tables[i];while (cur){cout << "[" << kot(cur->_data) << ": " << kot(cur->_data) << "]-->";cur = cur->next;}}cout << endl;}bool Erase(const K& key){Hash hash;KeyOfT kot;size_t hashi = hash(key) % _tables.size();Node* cur = _tables[hashi];Node* prev = nullptr;while (cur){if (kot(cur->_data) == key){if (prev){prev->next = cur->next;}else{_tables[hashi] = cur->next;}delete cur;cur = nullptr;return true;}else{prev = cur;cur = cur->next;}}return false;}size_t size(){return _size;}private:size_t _size = 0;//有效数据个数vector<Node*> _tables;};
}
这篇关于【C++】unordered_set和unordered_map的文章就介绍到这儿,希望我们推荐的文章对编程师们有所帮助!







