本文主要是介绍正确使用@RequestMapping(包含属性详解),希望对大家解决编程问题提供一定的参考价值,需要的开发者们随着小编来一起学习吧!
目录
- 一、基本认知
- 二、@RequestMapping的基本使用
- 三、深入学习@RequestMapping
- 1、@RequestMapping的源码
- 2、@RequestMapping的属性
- 2.1 path
- 2.2 method
- 2.3 params
- 2.4 headers
- 2.5 consumes
- 2.6 produces
- 2.7 name
一、基本认知
- 客户端发起Http请求,会提供一个URL [
协议://域名{/path}]。
- 协议通常是https
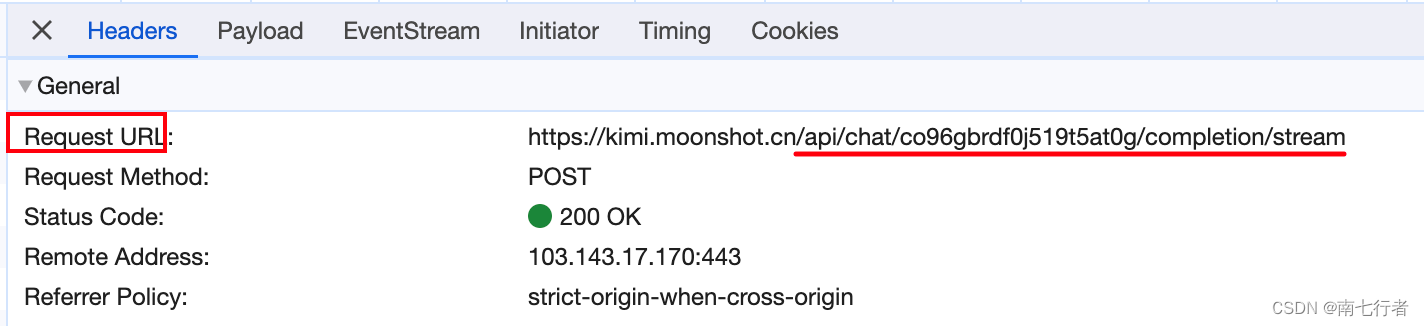
- 域名,例如:kimi.moonshot.cn
- 路径(path),例如:/api/chat/co96gbrdf0j519t5at0g/completion/stream
- 通过域名和端口(https的默认端口是443)可以定位服务器的进程。
- 通过路径来确定由进程的哪个方法来处理请求。【这个是本文的重点,也是@RequestMapping发光发热的领域】
二、@RequestMapping的基本使用
- 示例:
@RestController
@RequestMapping("/api/chat")
public class ChatController {@PostMapping("/{chatId}/completion/stream")public String completionStream(@PathVariable String chatId, @RequestBody ChatInput chatInput) {return "/" + chatId + "/completion/stream : " + chatInput.getPrompt();}
}
curl 'http://127.0.0.1:8080/api/chat/co96gbrdf0j519t5at0g/completion/stream' \
-H 'Content-Type: application/json' \
-d '{"prompt": "你好~"
}'
/co96gbrdf0j519t5at0g/completion/stream : 你好~
- Http请求的路径(
/api/chat/co96gbrdf0j519t5at0g/completion/stream)由ChatController.completionStream方法来处理了。
三、深入学习@RequestMapping
1、@RequestMapping的源码
@Target({ElementType.TYPE, ElementType.METHOD})
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Documented
@Mapping
public @interface RequestMapping {String name() default "";@AliasFor("path")String[] value() default {};@AliasFor("value")String[] path() default {};RequestMethod[] method() default {};String[] params() default {};String[] headers() default {};String[] consumes() default {};String[] produces() default {};
}
2、@RequestMapping的属性
2.1 path
- 示例:
@RequestMapping("/api/chat")
public class ChatController {@PostMapping("/{chatId}/completion/stream")public String completionStream(@PathVariable String chatId, @RequestBody ChatInput chatInput) {...}
- 没有指定属性,直接填属性值。相当于:value=“xxx”。根据@RequestMapping的定义可知,value和path是等价的。(@AliasFor的作用)
- 我们在类上设定了path(
/api/chat),这是完整path的前缀,即:/api/chat/xxx。 - 我们在方法上设定“xxx”(
/{chatId}/completion/stream),如果使用了占位符{a},那么可以在入参中,通过注解@PathVariable来获取。 - SpringMVC会根据Http请求的URL的路径(
/api/chat/co96gbrdf0j519t5at0g/completion/stream)来找到对应的处理方法(ChatController.completionStream)。【path属性的核心作用】
2.2 method
- Http请求,不仅有URL,还有方法,常用的是:GET、POST。
- 示例:
@RequestMapping("/api/chat")
public class ChatController {...@RequestMapping(path = "/hello", method = RequestMethod.GET)public String sayHello() {return "hello world!";}@RequestMapping(path = "/hello", method = RequestMethod.POST)public String sayHello(@RequestBody ChatInput chatInput) {return "Hello: " + chatInput.getPrompt();}...
}
- 如果路径都是
/api/chat/hello,SpringMVC就搞不清楚到底要映射到哪个Java方法上了。这时候,可以进一步设置method属性。 - method属性的核心作用:通过设定请求方法,进一步来明确映射到哪个Java方法上。
- 实际开发中,一般不设定method属性,而是直接用对应的xxxMapping。
@GetMapping
@PostMapping
@PutMapping
@DeleteMapping以@GetMapping为例,无非就是指定了method的@RequestMapping而已
@Target({ElementType.METHOD})
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Documented
@RequestMapping(method = {RequestMethod.GET}
)
public @interface GetMapping {...
}
2.3 params
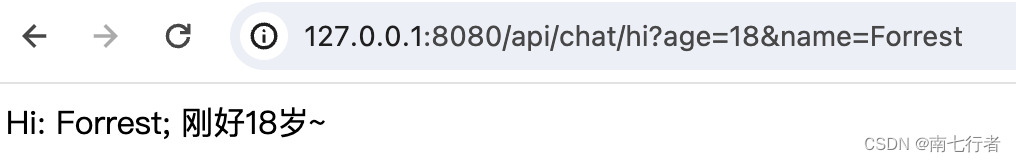
- 我们见过这样的URL:http://127.0.0.1:8080/api/chat/hi?name=Forrest&age=18
?后面的kv对(name=Forrest、age=18)便是参数名=参数值,并用&进行连接。
- 那怎么让SpringMVC识别这种路径,并映射到一个Java方法呢?
- 这就要用到params属性了,示例:
@GetMapping(path = "/hi", params = "name")
public String sayHi(@RequestParam String name, @RequestParam Integer age) {return "Hi: " + name + "; 刚好" + age + "岁~";
}
- 咦,咋只涉及name,而没有age?
- 这个的含义是:路径是
/api/chat/hi?xxx,xxx必须包含name,才会映射到sayHi方法。然后这个方法的入参有@RequestParam Integer age,因此,路径中也必须包含age参数。
- 这个的含义是:路径是
- params属性的核心作用:根据路径中的参数,进一步来明确映射到哪个Java方法上。
- 有4种表达方式:
params = "chatId":参数中必须包含chatId。params = "!chatId":参数中不包含chatId。params = "manager=Forrest":manager参数等于Forrestparams = "manager!=Forrest":manager参数不等于Forrest
- 示例:
// 用户传了chatId,那就查这个chatId信息
@GetMapping(path = "/chatIds", params = "chatId")
public String gotChatId(@RequestParam String chatId) {return "chatId: " + chatId;
}// 用户没指定某个chatId,那就查所有chatId信息
@GetMapping(path = "/chatIds", params = "!chatId")
public String gotChatId() {return "chatIdList";
}
@GetMapping(path = "/administrator", params = "manager=Forrest")
public String gotManager() {return "manager=Forrest";
}@GetMapping(path = "/administrator", params = "manager!=Forrest")
public String gotEmployee() {return "manager!=Forrest";
}/*
很鸡肋,完全可以接受一个maneger参数,在方法中来做特殊处理。
@GetMapping(path = "/employee")
public String gotEmployee(@RequestParam String name) {if (name != null && name.equals("Forrest")) {// 领导return "leader";} else {// 员工return "employee";}
}*/
2.4 headers
- headers属性的核心作用:通过Http的请求头,过滤出满足条件的请求。
@GetMapping(path = "/login", headers = "Host=127.0.0.1:8080")
public String login() {return "login";
}
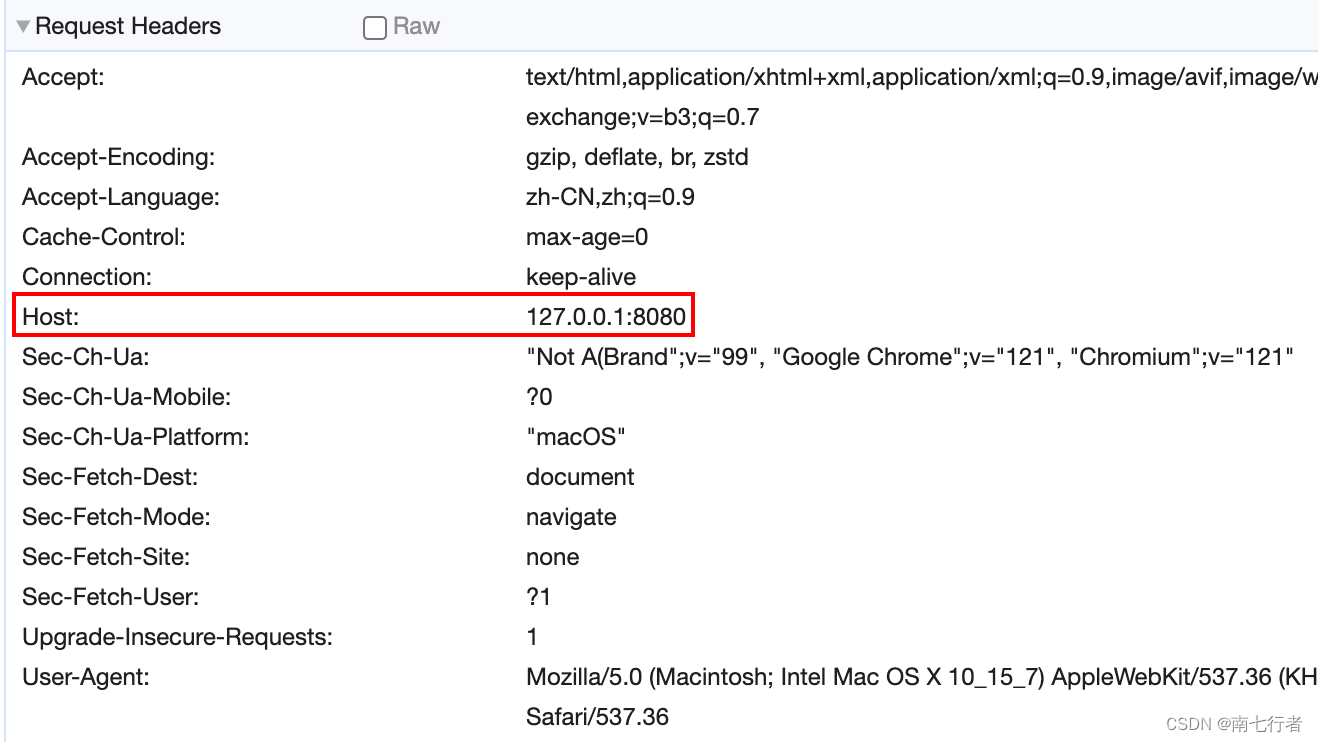
- 如果Host不是127.0.0.1:8080,那么Spring MVC就不会让login方法进行处理。
2.5 consumes
- consumes属性的核心作用:要求请求体必须是某种媒体类型。
- 示例:
@PostMapping(path = "/stream", consumes = MediaType.APPLICATION_JSON_VALUE)
public String stream(@RequestBody ChatInput chatInput) {return "stream: " + chatInput.getPrompt();
}
- 如果用户传入的请求体不是json,那么会报错:
{"timestamp": "2024-04-14T09:53:43.430+00:00","status": 415,"error": "Unsupported Media Type","path": "/api/chat/stream"
}
- 是json格式,才能正常处理:

- 当然了,也可以用
!,表示请求体不能是某种类型。 - 示例:
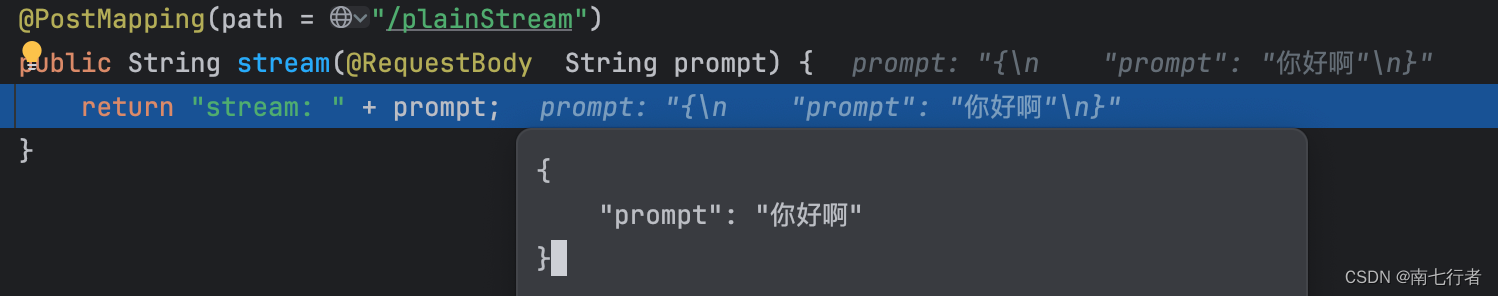
@PostMapping(path = "/plainStream", consumes = "!" + MediaType.APPLICATION_JSON_VALUE)
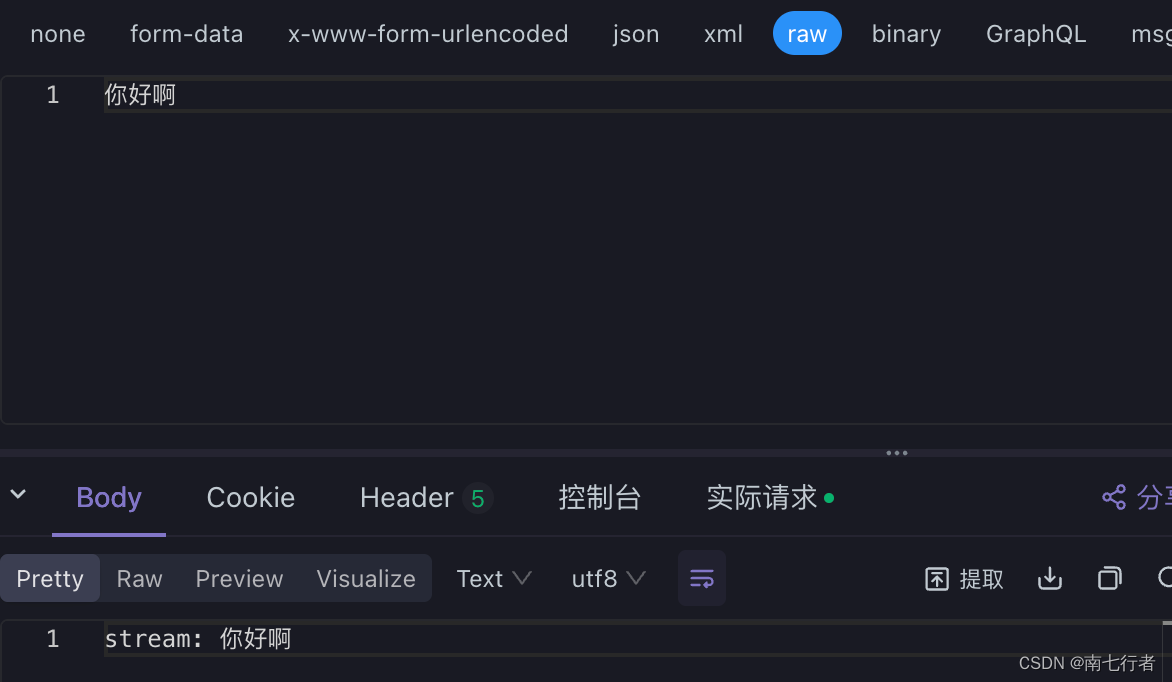
public String stream(@RequestBody String prompt) {return "stream: " + prompt;
}
- 当请求体为json格式时:

- 当请求体为不是json格式时,可以正常调用:
如果没设置consumes,就可以:
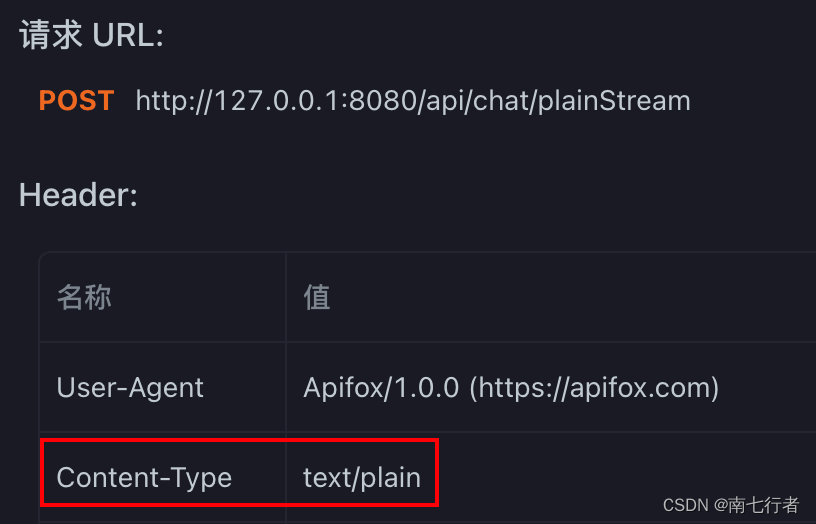
- 怎么判断请求体的类型呢?–>
Content-Type
2.6 produces
- 有些客户端对服务器返回的内容类型有要求,如果不满足这个要求,那也没必要处理了。
- produces属性的核心作用:通过请求头的Accept,判断是否包含返回的内容类型。包含则处理该请求。
- 示例:
@GetMapping(path = "/completion", produces = MediaType.APPLICATION_JSON_VALUE)
public ChatOutput completion() {return new ChatOutput("你好啊~");
}@Data
@AllArgsConstructor
public class ChatOutput {private String completion;
}
- 当客户端发送Http请求,并且请求头的Accept为text/plain时,会报错:
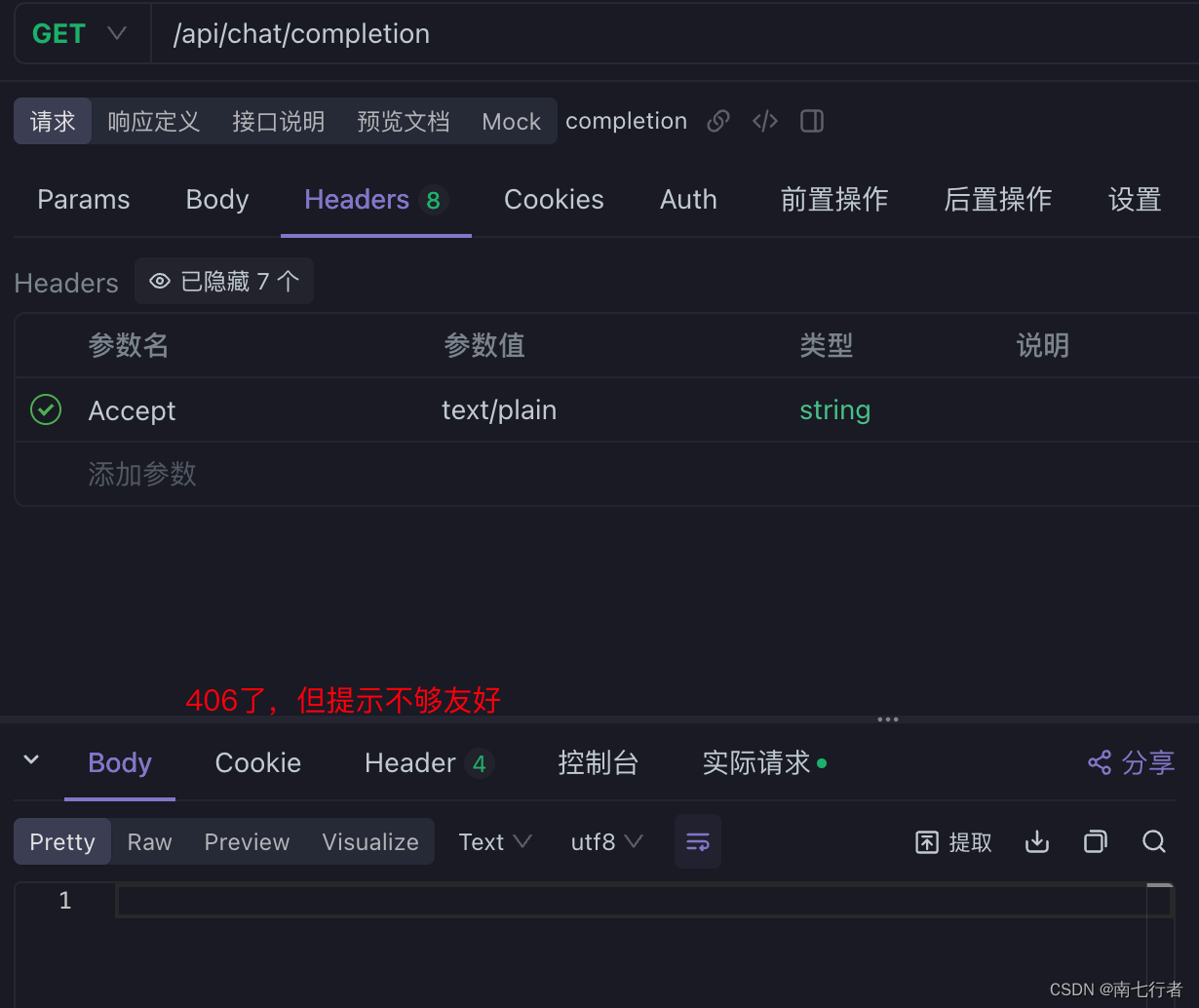
服务端报错:Resolved [org.springframework.web.HttpMediaTypeNotAcceptableException: Could not find acceptable representation]
- 自定义异常处理器,让提示友好点~
@ControllerAdvice
public class GlobalExceptionHandler {@ExceptionHandler(HttpMediaTypeNotAcceptableException.class)@ResponseBodypublic ResponseEntity<Map<String, String>> handleHttpMediaTypeNotAcceptable(HttpMediaTypeNotAcceptableException ex) {Map<String, String> responseBody = new HashMap<>();responseBody.put("message", "Unsupported media type. Please accept JSON format.");return ResponseEntity.status(HttpStatus.NOT_ACCEPTABLE).contentType(MediaType.APPLICATION_JSON).body(responseBody);}
}
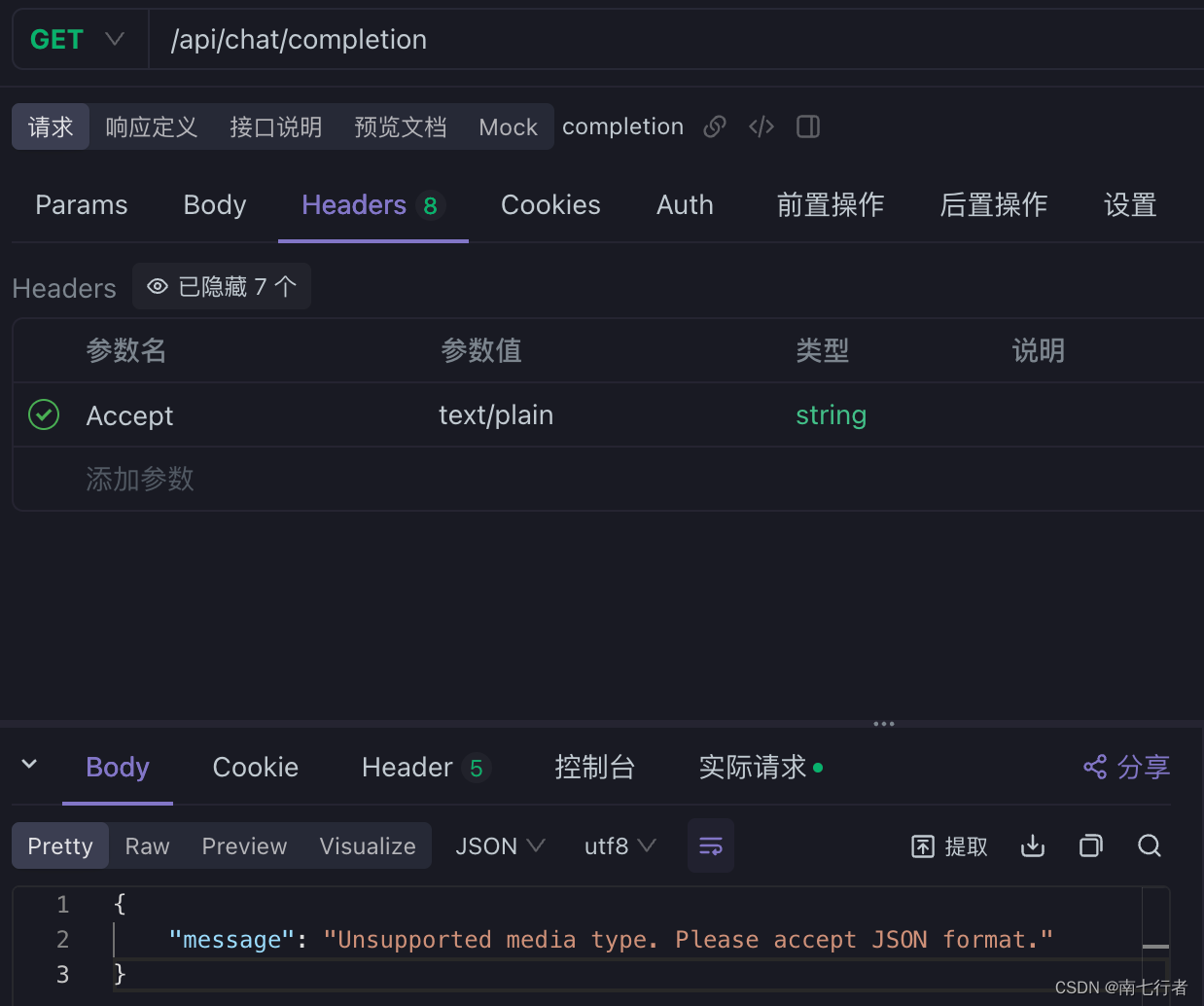
- 我们将请求头的Accept改为application/json,便能被服务端正常处理了:
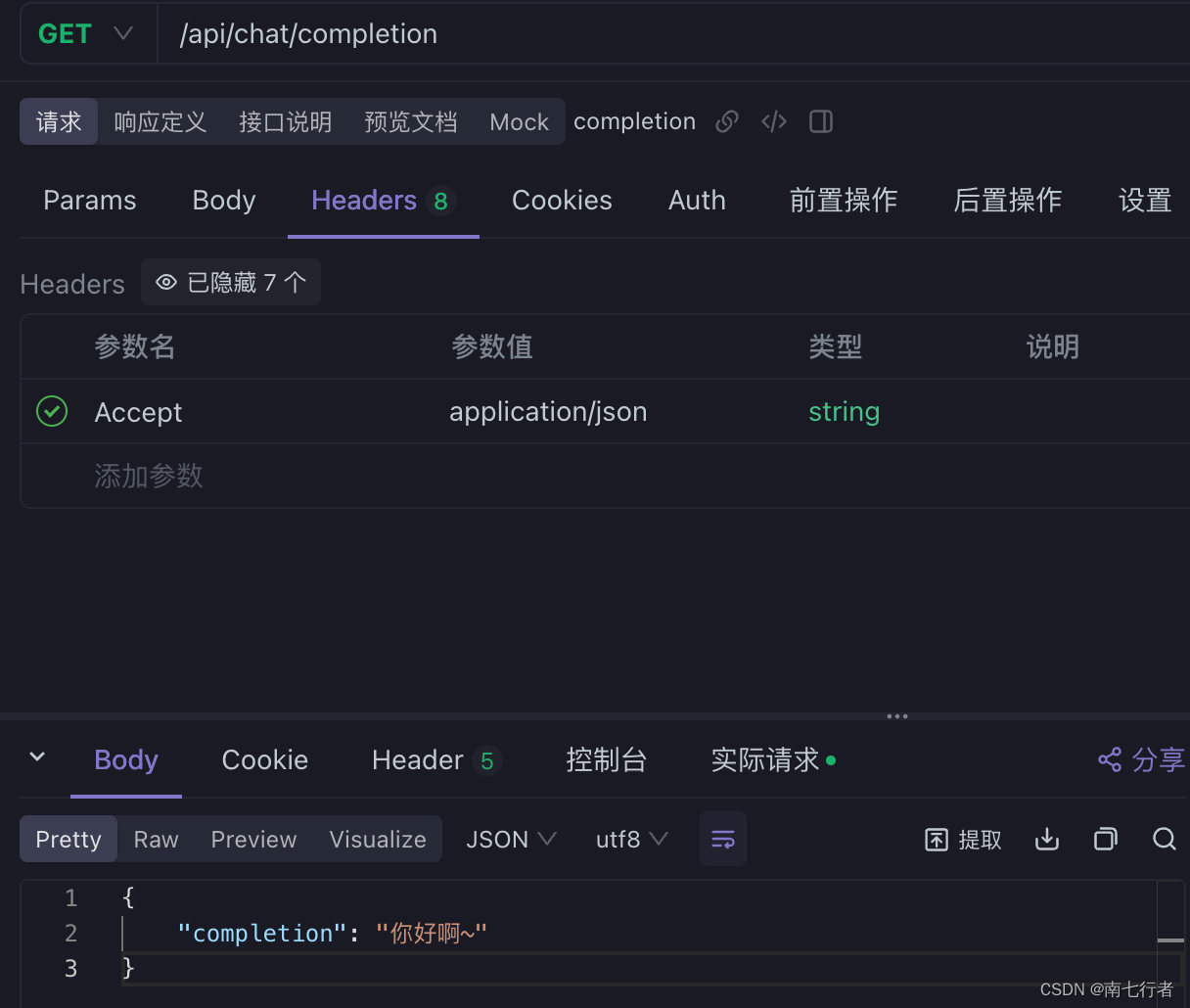
默认情况下:请求头的Accept为
*/*
- 还可以指定编码方式:
@GetMapping(path = "/completion", produces = MediaType.APPLICATION_JSON_UTF8_VALUE)
public static final String APPLICATION_JSON_UTF8_VALUE = “application/json;charset=UTF-8”;
2.7 name
为啥把这个属性放到最后?并不是last but not least,而是这个属性真不重要。
- 相当于对方法的注释。
- 但实际开发中,一般用的是swagger提供的注解
@ApiOperation。
这篇关于正确使用@RequestMapping(包含属性详解)的文章就介绍到这儿,希望我们推荐的文章对编程师们有所帮助!