本文主要是介绍linux:du和df区别,希望对大家解决编程问题提供一定的参考价值,需要的开发者们随着小编来一起学习吧!
文章目录
- 1. 概述
- 2. du 命令
- 2. df 命令
- 3. 区别总结
1. 概述
du 和 df 都是 Linux 系统中用于查看磁盘空间使用情况的命令,但它们的功能和用法有所不同。
2. du 命令
du 是 “disk usage” 的缩写,用于显示文件或目录的磁盘使用情况。du 命令用于查看指定文件或目录的磁盘空间使用情况,可以递归地查看目录下所有文件和子目录的大小。
详细用法查看这里。
du [OPTION]... [FILE]...
常用OPTION:
-h:以人类可读的格式显示磁盘使用量,如 KB、MB、GB 等。-s:显示指定目录的总大小,而不显示其子目录的大小。-c:显示总计磁盘使用量。-a:显示所有文件和目录的大小,包括隐藏文件。-k、-m、-g:以 KB、MB、GB 等单位显示磁盘使用量。
2. df 命令
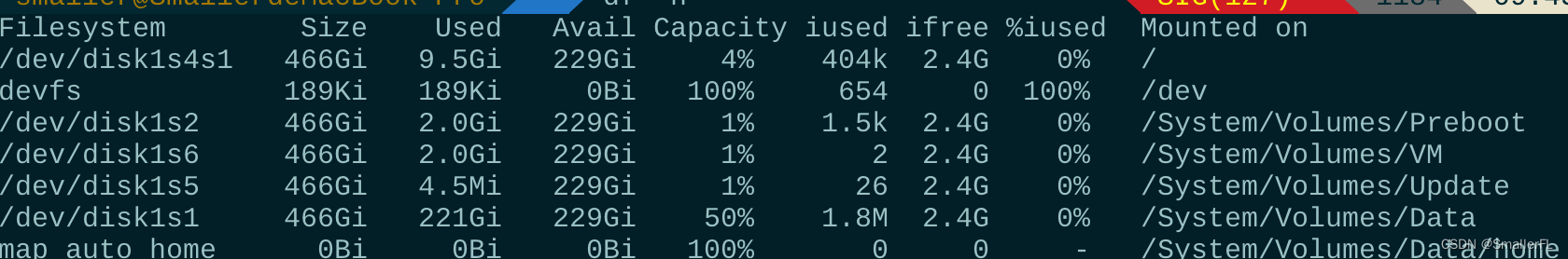
df 是 “disk free” 的缩写,用于显示文件系统的磁盘空间使用情况。df 命令用于查看系统中所有挂载的文件系统的磁盘空间使用情况,包括每个文件系统的总大小、已用空间、可用空间以及文件系统类型等信息。
df [OPTION]... [FILE]...[OPTION]:-a, --all include pseudo, duplicate, inaccessible file systems-B, --block-size=SIZE scale sizes by SIZE before printing them; e.g.,'-BM' prints sizes in units of 1,048,576 bytes;see SIZE format below-h, --human-readable print sizes in powers of 1024 (e.g., 1023M)-H, --si print sizes in powers of 1000 (e.g., 1.1G)-i, --inodes list inode information instead of block usage-k like --block-size=1K-l, --local limit listing to local file systems--no-sync do not invoke sync before getting usage info (default)--output[=FIELD_LIST] use the output format defined by FIELD_LIST,or print all fields if FIELD_LIST is omitted.-P, --portability use the POSIX output format--sync invoke sync before getting usage info--total elide all entries insignificant to available space,and produce a grand total-t, --type=TYPE limit listing to file systems of type TYPE-T, --print-type print file system type-x, --exclude-type=TYPE limit listing to file systems not of type TYPE-v (ignored)--help display this help and exit--version output version information and exit
常用OPTION:
-h:以人类可读的格式显示磁盘空间信息,如 KB、MB、GB 等。-T:显示文件系统类型。-t:仅显示指定类型的文件系统,如 ext4、tmpfs 等。-i:显示 inode 的使用情况。
3. 区别总结
du 和 df 是两个不同的命令,用于查看不同层次的磁盘空间使用情况。
du用于查看指定文件或目录的磁盘使用情况,而df用于查看系统中所有挂载的文件系统的磁盘空间使用情况。du只显示指定文件或目录的大小,而df显示文件系统的总大小、已用空间、可用空间等信息。du是针对文件或目录的,而df是针对文件系统的。
这篇关于linux:du和df区别的文章就介绍到这儿,希望我们推荐的文章对编程师们有所帮助!









