本文主要是介绍蓝桥杯第101题 拉马车 C++ Java Python,希望对大家解决编程问题提供一定的参考价值,需要的开发者们随着小编来一起学习吧!
目录
题目
思路和解题方法
复杂度:
c++ 代码
Java 版本(仅供参考)
Python 版本(仅供参考)
代码细节
C++ 版本:
Java 版本:
Python 版本:
题目


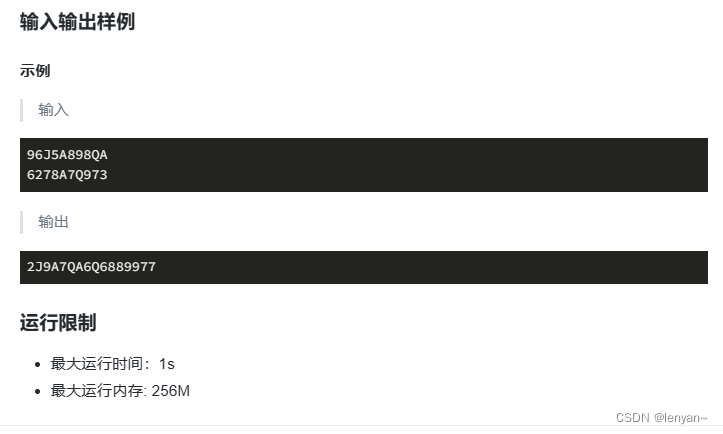
思路和解题方法
这个游戏是一个简单的纸牌游戏,两个玩家轮流出牌,每个玩家从自己的牌堆中选择一张牌出牌,直到没有牌为止。具体步骤如下:
- 定义两个队列来存储玩家A和玩家B的牌堆。
- 玩家轮流出牌,每次出一张牌。
- 当任一玩家的牌堆为空时,游戏结束。
- 输出剩余的牌堆。
复杂度:
- 时间复杂度: 代码只需遍历字符串一次,时间复杂度为 O(n),其中 n 是字符串的长度。
- 空间复杂度: 使用了队列、栈和数组来存储字符,因此空间复杂度为 O(n)。
c++ 代码
#include <iostream>
#include <queue>
#include <stack>
#include <string>
#include <cstring> // 添加这一行来包含 <cstring> 头文件以使用 memset 函数
using namespace std;queue<char> a, b; // 修改为队列存储字符
stack<char> s;
int check[256]; // 修改为使用数组存储字符出现情况int main() {string aa, bb;int who = 1;cin >> aa >> bb;// 将字符串转换为队列for (int i = 0; i < aa.size(); i++) {a.push(aa[i]);}for (int i = 0; i < bb.size(); i++) {b.push(bb[i]);}while (!a.empty() && !b.empty()) {if (who == 1) {s.push(a.front());a.pop();if (check[s.top()]) {who = 1;char tmp = s.top();a.push(tmp); // 修正为将字符 tmp 压入队列 as.pop();while (s.top() != tmp) {a.push(s.top());check[s.top()] = 0;s.pop();}a.push(tmp);check[tmp] = 0;s.pop();}else {who = 2;check[s.top()] = 1;}}else {s.push(b.front());b.pop();if (check[s.top()]) {who = 2;char tmp = s.top();b.push(tmp); // 修正为将字符 tmp 压入队列 bs.pop();while (s.top() != tmp) {b.push(s.top());check[s.top()] = 0;s.pop();}b.push(tmp);check[tmp] = 0;s.pop();}else {who = 1;check[s.top()] = 1;}}}while (!a.empty()) {cout << a.front();a.pop();}while (!b.empty()) {cout << b.front();b.pop();}return 0;
}
Java 版本(仅供参考)
import java.util.*;public class Main {public static void main(String[] args) {Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in);Queue<Character> a = new LinkedList<>();Queue<Character> b = new LinkedList<>();Stack<Character> s = new Stack<>();int[] check = new int[256];String aa = scanner.next();String bb = scanner.next();int who = 1;for (char c : aa.toCharArray())a.offer(c);for (char c : bb.toCharArray())b.offer(c);while (!a.isEmpty() && !b.isEmpty()) {if (who == 1) {s.push(a.poll());if (check[s.peek()] != 0) {who = 1;char tmp = s.peek();a.offer(tmp);s.pop();while (s.peek() != tmp) {a.offer(s.peek());check[s.peek()] = 0;s.pop();}a.offer(tmp);check[tmp] = 0;s.pop();} else {who = 2;check[s.peek()] = 1;}} else {s.push(b.poll());if (check[s.peek()] != 0) {who = 2;char tmp = s.peek();b.offer(tmp);s.pop();while (s.peek() != tmp) {b.offer(s.peek());check[s.peek()] = 0;s.pop();}b.offer(tmp);check[tmp] = 0;s.pop();} else {who = 1;check[s.peek()] = 1;}}}while (!a.isEmpty())System.out.print(a.poll());while (!b.isEmpty())System.out.print(b.poll());}
}
Python 版本(仅供参考)
from collections import dequeaa = input()
bb = input()a = deque(aa)
b = deque(bb)
s = []
check = [0] * 256
who = 1while a and b:if who == 1:s.append(a.popleft())if check[ord(s[-1])] != 0:who = 1tmp = s[-1]a.append(tmp)s.pop()while s[-1] != tmp:a.append(s[-1])check[ord(s[-1])] = 0s.pop()a.append(tmp)check[ord(tmp)] = 0s.pop()else:who = 2check[ord(s[-1])] = 1else:s.append(b.popleft())if check[ord(s[-1])] != 0:who = 2tmp = s[-1]b.append(tmp)s.pop()while s[-1] != tmp:b.append(s[-1])check[ord(s[-1])] = 0s.pop()b.append(tmp)check[ord(tmp)] = 0s.pop()else:who = 1check[ord(s[-1])] = 1print(''.join(a) + ''.join(b))
代码细节:
C++ 版本:
- 使用
std::queue<char>和std::stack<char>分别代表队列和栈。这些数据结构需要包含<queue>和<stack>头文件。 - 使用
std::string类型代表输入的字符串,字符串的读取使用cin。 - 使用
std::memset函数需要包含<cstring>头文件。 - 使用
std::cout输出结果。
Java 版本:
- 使用
java.util.Queue<Character>和java.util.Stack<Character>分别代表队列和栈。 - 使用
java.util.Scanner类型进行输入。 - 使用
System.out.println()输出结果。
Python 版本:
- 使用
collections.deque代表队列。 - 使用列表代表栈。
- 使用
input()函数进行输入。 - 使用
print()函数输出结果。
觉得有用的话可以点点赞,支持一下。
如果愿意的话关注一下。会对你有更多的帮助。
每天都会不定时更新哦 >人< 。
这篇关于蓝桥杯第101题 拉马车 C++ Java Python的文章就介绍到这儿,希望我们推荐的文章对编程师们有所帮助!





