本文主要是介绍fstat函数的使用,希望对大家解决编程问题提供一定的参考价值,需要的开发者们随着小编来一起学习吧!
今天在排查一个问题,在使用select函数的时候,返回-1,errno=EBADF,表示的错误字符为:An invalid file descriptor was given in one of the sets. (Perhaps a file descriptor that was already closed, or one on which an error has occurred.),源码里加了一点打印,如下:

设置完select的参数后马上调用了select,然后就返回错误了。于是找到了函数fstat,在设置fd后,调用fstat获取文件状态,如果获取失败可能是导致select失败的原因,但这里只记录fstat的用法,不纠结select失败的原因。
#include <sys/socket.h>
#include <arpa/inet.h>
#include <stdint.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <sys/stat.h>
#include <errno.h>int main()
{int32_t fd = socket(AF_INET, SOCK_STREAM, 0);struct stat fdStat;if(fstat(fd, &fdStat) == 0){printf("select set fd = %d, type = %07o, isSock? = %d\n", fd, fdStat.st_mode & S_IFMT, S_ISSOCK(fdStat.st_mode));}else{printf("fstat error msg = %s\n", strerror(errno));}close(fd);return 0;
}函数成功时,打印了该fd的类型,及判断是否是socket类型。
涉及到的相关宏:用于判断是否是指定类型
#define S_ISBLK(m) (((m)&_IFMT) == _IFBLK)
#define S_ISCHR(m) (((m)&_IFMT) == _IFCHR)
#define S_ISDIR(m) (((m)&_IFMT) == _IFDIR)
#define S_ISFIFO(m) (((m)&_IFMT) == _IFIFO)
#define S_ISREG(m) (((m)&_IFMT) == _IFREG)
#define S_ISLNK(m) (((m)&_IFMT) == _IFLNK)
#define S_ISSOCK(m) (((m)&_IFMT) == _IFSOCK)具体是何种类型的宏定义:这里是八进制表示形式
#define _IFMT 0170000 /* type of file */
#define _IFDIR 0040000 /* directory */
#define _IFCHR 0020000 /* character special */
#define _IFBLK 0060000 /* block special */
#define _IFREG 0100000 /* regular */
#define _IFLNK 0120000 /* symbolic link */
#define _IFSOCK 0140000 /* socket */
#define _IFIFO 0010000 /* fifo */很显明要判断是何种类型,即用st_mode & _IFMT 即可。而_IFMT又被定义为宏:
#define S_IFMT _IFMT
#define S_IFDIR _IFDIR
#define S_IFCHR _IFCHR
#define S_IFBLK _IFBLK
#define S_IFREG _IFREG
#define S_IFLNK _IFLNK
#define S_IFSOCK _IFSOCK
#define S_IFIFO _IFIFO所以:fdStat.st_mode & S_IFMT 得到该fd的类型,运行结果如:
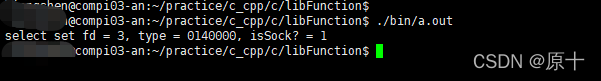
type = 0140000,根据上面的宏定义,即为socket类型。
这篇关于fstat函数的使用的文章就介绍到这儿,希望我们推荐的文章对编程师们有所帮助!




