本文主要是介绍.NET CORE使用Redis分布式锁续命(续期)问题,希望对大家解决编程问题提供一定的参考价值,需要的开发者们随着小编来一起学习吧!
结合上一期 .NET CORE 分布式事务(三) DTM实现Saga及高并发下的解决方案(.NET CORE 分布式事务(三) DTM实现Saga及高并发下的解决方案-CSDN博客)。有的小伙伴私信说如果锁内锁定的程序或者资源未在上锁时间内执行完,造成的使用资源冲突,需要如何解决。本来打算之后在发博文说明这个问题。那就先简短的说明一下。
这是一个Redis分布式锁续命或者称之为续期的问题。废话不多说,直接上代码。
using Microsoft.AspNetCore.DataProtection.KeyManagement;
using Newtonsoft.Json;
using Newtonsoft.Json.Linq;
using Redlock.CSharp;
using StackExchange.Redis;
using System.Diagnostics;
using System.Globalization;
using System.Net.Sockets;
using System.Runtime.CompilerServices;
using System.Threading;public class RedisService
{private readonly ConnectionMultiplexer _redis;private readonly IDatabase _database;/// <summary>/// 初始化 <see cref="RedisService"/> 类的新实例。/// </summary>/// <param name="connectionMultiplexer">连接多路复用器。</param>public RedisService(string connectionString){_redis = ConnectionMultiplexer.Connect(connectionString);_database = _redis.GetDatabase();}#region 分布式锁#region 阻塞锁/// <summary>/// 阻塞锁--加锁/// </summary>/// <param name="key">阻塞锁的键</param>/// <param name="expireSeconds">阻塞锁的缓存时间</param>/// <param name="timeout">加锁超时时间</param>/// <returns></returns>public bool AcquireLock(string key, int expireSeconds, int timeout){var script = @"local isNX = redis.call('SETNX', KEYS[1], ARGV[1])if isNX == 1 thenredis.call('PEXPIRE', KEYS[1], ARGV[2])return 1endreturn 0";RedisKey[] scriptkey = { key };RedisValue[] scriptvalues = { key, expireSeconds * 1000 };var stopwatch = Stopwatch.StartNew();while (stopwatch.Elapsed.TotalSeconds < timeout){if (_database.ScriptEvaluate(script, scriptkey, scriptvalues).ToString() == "1"){stopwatch.Stop();return true;}}Console.WriteLine($"[{DateTime.Now}]{key}--阻塞锁超时");stopwatch.Stop();return false;}Action<string, int, int, IDatabase> postponeAction = (string key, int expireSeconds, int postponetime, IDatabase database) =>{var stopwatchpostpone = Stopwatch.StartNew();while (true){//记录时钟大于锁的设置时间说明这个锁已经自动释放了,没必要再用lua脚本去判断了,直接提前退出if (stopwatchpostpone.Elapsed.TotalSeconds > expireSeconds) return;//提前三分之一时间续命,必须提前。要不真释放了if (stopwatchpostpone.Elapsed.TotalSeconds > expireSeconds * 0.66){var scriptpostpone = @"local isNX = redis.call('EXISTS', KEYS[1])if isNX == 1 thenredis.call('PEXPIRE', KEYS[1], ARGV[2])return 1endreturn 0";RedisKey[] scriptkey = { key };RedisValue[] scriptvalues = { key, postponetime * 1000 };if (database.ScriptEvaluate(scriptpostpone, scriptkey, scriptvalues).ToString() == "1")Console.WriteLine($"[{DateTime.Now}]{key}--阻塞锁续命成功");elseConsole.WriteLine($"[{DateTime.Now}]{key}--阻塞锁续命失败");return;}}};/// <summary>/// 阻塞续命锁/// </summary>/// <param name="key">阻塞锁的键</param>/// <param name="expireSeconds">阻塞锁的缓存时间</param>/// <param name="timeout">加锁超时时间</param>/// <param name="postponetime">续命时间</param>/// <returns></returns>public bool AcquireLock(string key, int expireSeconds, int timeout, int postponetime){var script = @"local isNX = redis.call('SETNX', KEYS[1], ARGV[1])if isNX == 1 thenredis.call('PEXPIRE', KEYS[1], ARGV[2])return 1endreturn 0";RedisKey[] scriptkey = { key };RedisValue[] scriptvalues = { key, expireSeconds * 1000 };var stopwatch = Stopwatch.StartNew();while (stopwatch.Elapsed.TotalSeconds < timeout){if (_database.ScriptEvaluate(script, scriptkey, scriptvalues).ToString() == "1"){stopwatch.Stop();//锁续命Thread postponeThread = new Thread(() =>{postponeAction.Invoke(key, expireSeconds, postponetime, _database);});postponeThread.Start();return true;}}Console.WriteLine($"[{DateTime.Now}]{key}--阻塞锁超时");stopwatch.Stop();return false;}/// <summary>/// 阻塞锁--释放锁/// </summary>/// <param name="key"></param>/// <returns></returns>public bool UnAcquireLock(string key){var script = @"local getLock = redis.call('GET', KEYS[1])if getLock == ARGV[1] thenredis.call('DEL', KEYS[1])return 1endreturn 0";RedisKey[] scriptkey = { key };RedisValue[] scriptvalues = { key };return _database.ScriptEvaluate(script, scriptkey, scriptvalues).ToString() == "1";}#endregion#endregion
}
.NET CORE中是没有现成的Redis锁续命的api,只能自己造轮子。续命同样使用了Redis的Lua脚本来实现,确保了原子性。获取了Redis锁之后,直接开启了一个新的线程,在设置时间还剩三分之一的时候进行了续命,这在程序中是有必要使用的,比如说因为网络原因造成的延时,本来我的这个接口执行完毕只需要3秒钟,但是有于网络延时造成了我的这个接口执行超过了3秒,这时候就需要Redis锁续命。以上代码就可以完美结局这个问题。
[HttpGet("AcquireLockPostpone")]public void AcquireLockPostpone(){string key = Guid.NewGuid().ToString();if (_redisService.AcquireLock("AcquireLockPostpone", 3, 100, 3)){Thread.Sleep(5000);_redisService.UnAcquireLock("AcquireLockPostpone");Console.WriteLine($"AcquireLockPostpone--释放锁");}}控制器API,调用可以续命的阻塞锁,缓存时间设置为3秒 续命时间也是延长3秒。我们走个100阻塞锁的并发试一下。
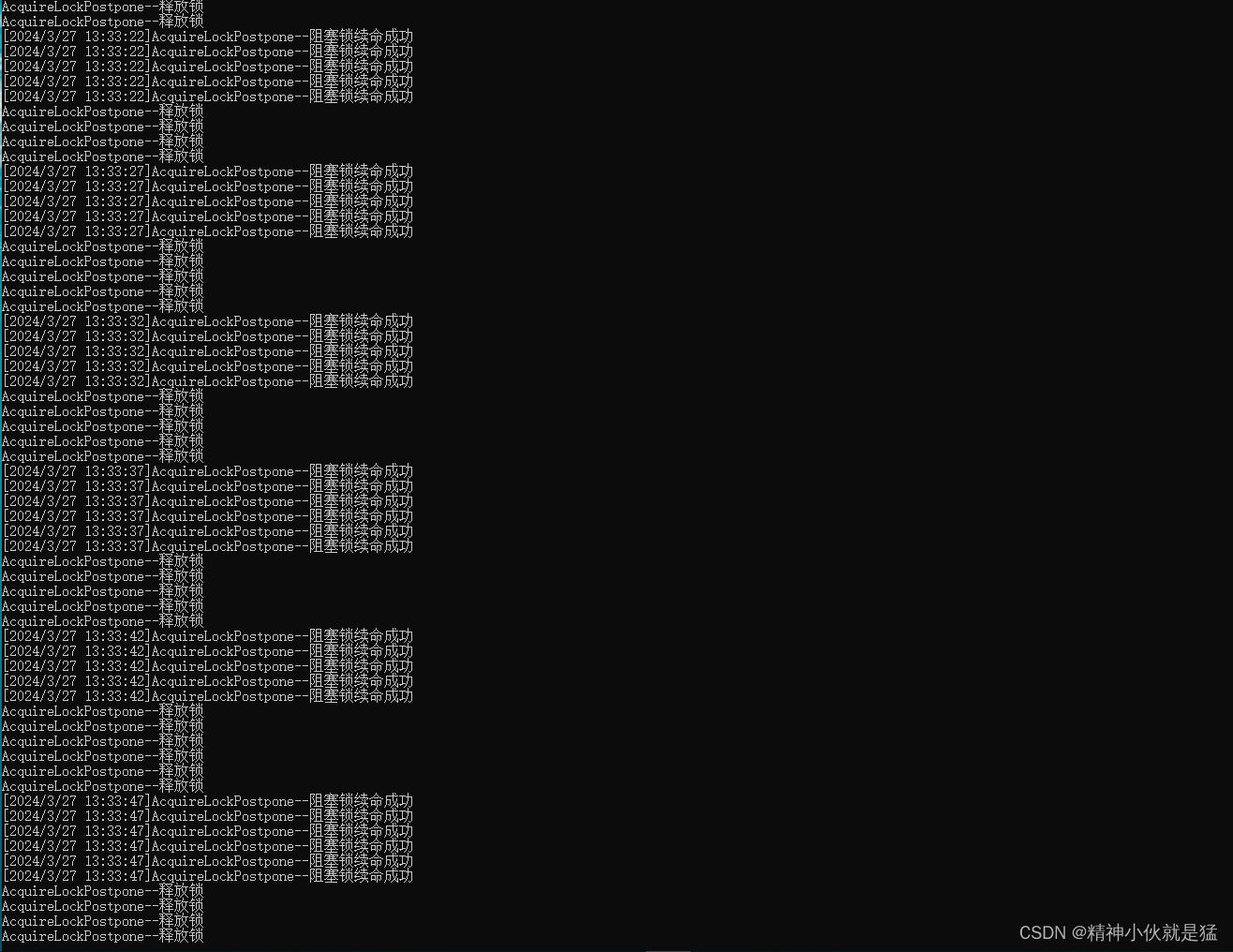
这100个阻塞锁均续命完成。也都正常执行完毕。
为什么不用Task进行循环监视?
因为Task是对ThreadPool线程池进行的封装。ASP.NET CORE 后端开发基本上所有的方法都在用Task。续命Redis还是一个耗时的操作,需要在一定时间内一直占用线程池里的线程。所有用了Thread。
为什么一个Redis阻塞锁一个Thread监视?
最开始也想着的是使用一个线程,这个线程贯穿整个进程,然后用线程安全数据类型ConcurrentDictionary<锁的key,时间>进行存储,线程监视ConcurrentDictionary里的数据然后进行续命。但是并发多的时候较短的Redis锁有于循环次数过多就导致续不上时间了,就是还没续上时间,就释放了...............(这就比较尴尬了)。所以一个锁起来了一个线程监视。
为什么需要续命?反正都要解锁,为什么不直接设置一个较长的时间?
我写了一个接口,正常情况下,比如是3秒执行完毕。但是有于网络超时或者服务宕机等原因,执行超过了3秒。5秒才执行完。这时候就需要对Redis锁进行续命。但是程序执行流程反正都要给Redis锁进行释放,为什么不直接设置一个长时间呢?因为如果这个服务还没对锁进行释放就宕机了,Redis锁还在,相同的服务实例在次执行这个接口就拿不到锁了,需要锁释放结束之后才能拿到。
这篇关于.NET CORE使用Redis分布式锁续命(续期)问题的文章就介绍到这儿,希望我们推荐的文章对编程师们有所帮助!





