本文主要是介绍Netty进阶:自顶向下解析FastThreadLocal,希望对大家解决编程问题提供一定的参考价值,需要的开发者们随着小编来一起学习吧!
文章目录
- FastThreadLocalThread 分析
- 优雅的使用 FastThreadLocal
- 1. InternalThreadLocalMap 底层数据结构
- 2. FastThreadLocal
- 3. set
- 3.1 获取map
- 3.2 设置value
- 4. get
- 5. remove
FastThreadLocalThread 分析
我们知道EventLoopGroup相当于线程池,而EventLoop是其中的线程,用来执行IO任务和一些handler中的业务逻辑。在Netty进阶:Netty核心NioEventLoop原理解析文章中详解的介绍了EventLoopGroup和EventLoop的构造过程,以及他们如何去执行IO任务等。但是关于NioEventLoop中持有的Executor引用并没有做过多的解释。Executor是JDK提供的一个线程池接口,只有一个execte方法。下面对Netty对Executor的实现做一个详细的阐述。
NioEventLoopGroup的父类MultithreadEventExecutorGroup的构造函数中对Executor的赋值语句如下:
executor = new ThreadPerTaskExecutor(newDefaultThreadFactory());
ThreadPerTaskExecutor是Netty对JDK Exectuor的实现类。这个类的实现非常简单
public final class ThreadPerTaskExecutor implements Executor {// 每一个EventLoopGroup对应一个ThreadPerTaskExecutorprivate final ThreadFactory threadFactory;// 构造函数public ThreadPerTaskExecutor(ThreadFactory threadFactory) {if (threadFactory == null) {throw new NullPointerException("threadFactory");}this.threadFactory = threadFactory;}// 实现Executor的方法@Overridepublic void execute(Runnable command) {threadFactory.newThread(command).start();}
}
这里有一个疑惑,Netty为什么不用JDK提供的Exector接口的多个实现(Executors有对ThreadFactory的实现)?
可以看到threadFactory.newThread(command).start();的意思是创建一个新的线程并且启动。我们继续跟进ThreadFactory的实现;
@Override
public Thread newThread(Runnable r) {Thread t = newThread(FastThreadLocalRunnable.wrap(r), prefix + nextId.incrementAndGet());// 一般daemon为false,意思是不设置为守护线程if (t.isDaemon() != daemon) {t.setDaemon(daemon);}// 优先级 默认为5if (t.getPriority() != priority) {t.setPriority(priority);}return t;
}protected Thread newThread(Runnable r, String name) {return new FastThreadLocalThread(threadGroup, r, name);
}
可以看到创建了一个FastThreadLocalThread类型的线程。FastThreadLocalThread继承自Thread类,看它的两个属性
// 任务执行完,是否清除FastThreadLocal的标记
private final boolean cleanupFastThreadLocals;
// 类似于Thread类中ThreadLocalMap,为了实现FastThreadLocal
private InternalThreadLocalMap threadLocalMap;
说了这么多终于讲到本文的主题,前面所说的这个过程是为了让大家明白EventLoop中的线程都是FastThreadLocalThread类型的。并且在此类型的线程中有一个属性叫做InternalThreadLocalMap,该属性是为了实现FastThreadLocal。
优雅的使用 FastThreadLocal
下面演示两种方式,分别是Netty提供的ThreadFactory和手动创建FastThreadLoalThread。
FastThreadLocal<String> threadLocal = new FastThreadLocal() {@Overrideprotected String initialValue() throws Exception {return "hello netty";}@Overrideprotected void onRemoval(Object value) throws Exception {System.out.println("value has be removed");}
};new DefaultThreadFactory("FastThread-Pool").newThread(() -> {System.out.println(threadLocal.get());}
).start();new FastThreadLocalThread(() -> {threadLocal.set("hello FastThreadLocalThread");System.out.println(threadLocal.get());}
).start();/** 输出
hello netty
value has be removed
hello FastThreadLocalThread
value has be removed
*/
首先重写FastThreadLocal的initValue方法很容易理解,和ThreadLocal中的一样,那么重写的onRemoval方法看样子应该是FastThreadLocal移除是会被调用。
在JDK的ThreadLocal中一般我们通过ThreadLocal.remove方法移除value。在这里似乎当线程把任务执行完毕后会自动的调用类似于remove的方法。
这个逻辑是在创建线程的过程添加进去的,Netty把Runnable的匿名类封装成一个FastThreadLocalRunnable类型,该类的实现如下:
final class FastThreadLocalRunnable implements Runnable {private final Runnable runnable;private FastThreadLocalRunnable(Runnable runnable) {this.runnable = ObjectUtil.checkNotNull(runnable, "runnable");}@Overridepublic void run() {try {runnable.run();} finally {// 任务执行完之后,清除当前线程所有FastThreadLocal,removeAll方法中会调用我们实现的onRemoval方法FastThreadLocal.removeAll();}}static Runnable wrap(Runnable runnable) {return runnable instanceof FastThreadLocalRunnable ? runnable : new FastThreadLocalRunnable(runnable);}
}
看到这里就明白了为什么重写的onRemoval方法会被执行了,线程池中的线程由于会被复用,所以线程池中的每一条线程在执行task结束后,要清理掉其InternalThreadLocalMap和其内的FastThreadLocal信息,否则InternalThreadLocalMap信息还存储着上一次被使用时的信息;另外,假设这条线程不再被使用,但是这个线程有可能不会被销毁(与线程池的类型和配置相关),那么线程上的FastThreadLocal将发生资源泄露。
1. InternalThreadLocalMap 底层数据结构
InternalThreadLocalMap的父类是UnpaddedInternalThreadLocalMap,该类中指定了保存数据的结构。
// SlowMap
static final ThreadLocal<InternalThreadLocalMap> slowThreadLocalMap = new ThreadLocal<InternalThreadLocalMap>();// FastMap
static final AtomicInteger nextIndex = new AtomicInteger();
Object[] indexedVariables;
有些情况下,我们自己创建的线程并没有使用FastThreadLocalThread,为了适配这种情况,Netty通过Thread原生的ThreadLocal来保存InternalThreadLocalMap。关系图如下:

即Thread中的属性threadLocalMap中key是上面定义的:ThreadLocal<InternalThreadLocalMap> slowThreadLocalMap,注意这是一个静态变量。
如果使用了FastThreadLocalThread,那么存储数据的结构直接使用Netty定义的InternalThreadLocalMap,通过Object[] indexedVariables保存key(FastThreadLocal)和value。nextIndex是一个自增的数组下表。JDK的ThreadLocal是通过Hash计算到下表,遇到冲突通过线性探测法解决。Netty确定了每一个key对应的value在数组中的下标,因此不会有冲突发生。
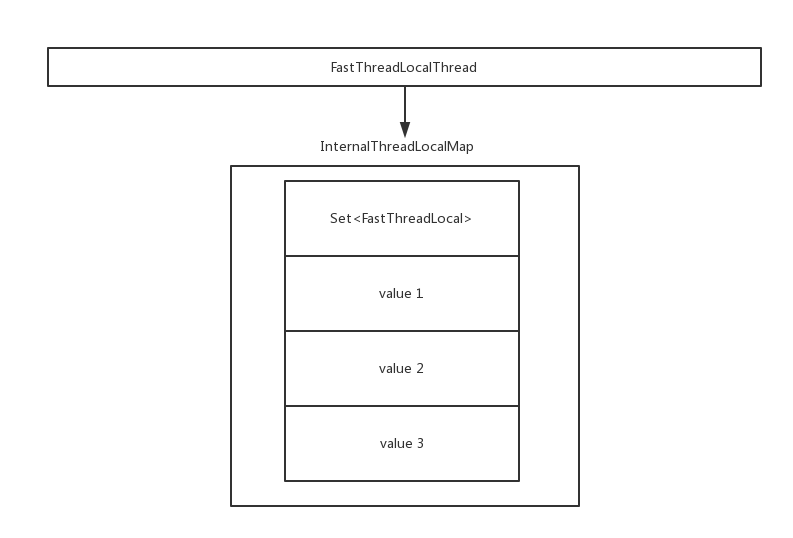
下面看一下它的构造方法
private InternalThreadLocalMap() {super(newIndexedVariableTable());
}
private static Object[] newIndexedVariableTable() {// 创建数据,填充Object对象Object[] array = new Object[32];Arrays.fill(array, UNSET);return array;
}
2. FastThreadLocal
在前面也介绍到FastThreadLocal的用法,和JDK提供的ThreadLcal几乎没出入。下面就一起探索它的内部实现细节。
// 常量0,存放FastThreadLocal集合的下标
private static final int variablesToRemoveIndex = InternalThreadLocalMap.nextVariableIndex();
// 每一个FastThreadLocal对应的Value的下标
private final int index;
private final int cleanerFlagIndex;
构造方法为:
public FastThreadLocal() {// 每一个FastThreadLocal对象的index都是不同的,因此确定了 value在数组中的位置index = InternalThreadLocalMap.nextVariableIndex();// 清除标记位cleanerFlagIndex = InternalThreadLocalMap.nextVariableIndex();
}
构造完成之后,进入set和get方法
3. set
set方法的目的是以当前FastThreadLocal为key,设置value到当前FastThreadLocalThread类型线程的 InternalThreadLocalMap实例中。
public final void set(V value) {// UNSET为空的Object对象,不允许为空if (value != InternalThreadLocalMap.UNSET) {InternalThreadLocalMap threadLocalMap = InternalThreadLocalMap.get();setKnownNotUnset(threadLocalMap, value);} else {remove();}
}
前面说到有两种情况,即线程类型是否为FastThreadLocalThread
- 根据不同的线程类型获取不同的InternalThreadLocalMap
- 设置value
3.1 获取map
InternalThreadLocalMap.get实现如下:
public static InternalThreadLocalMap get() {Thread thread = Thread.currentThread();if (thread instanceof FastThreadLocalThread) {return fastGet((FastThreadLocalThread) thread);} else {return slowGet();}
}
判断当前线程的类型,如果是FastThreadLocalThread类型,则使用该类内部属性InternalThreadLocalMap,否则使用原生Thread对象中的ThreadLocalMap属性来,然后在此
map中保存key为JDK中的ThreadLocal对象,value为InternalThreadLocalMap(Netty中的类)。
fastGet的逻辑是获取InternalThreadLocalMap,如果不存在那么新创建一个。
private static InternalThreadLocalMap fastGet(FastThreadLocalThread thread) {InternalThreadLocalMap threadLocalMap = thread.threadLocalMap();if (threadLocalMap == null) {// 设置到FastThreadLocalThread对象内部的属性中thread.setThreadLocalMap(threadLocalMap = new InternalThreadLocalMap());}return threadLocalMap;
}
slowGet获取当前线程ThreadLocaMap中key为slowThreadLocalMap(定义声明在UnpaddedInternalThreadLocalMap的常量),value是InternalThreadLocalMap。
private static InternalThreadLocalMap slowGet() {ThreadLocal<InternalThreadLocalMap> slowThreadLocalMap = UnpaddedInternalThreadLocalMap.slowThreadLocalMap;InternalThreadLocalMap ret = slowThreadLocalMap.get();if (ret == null) {ret = new InternalThreadLocalMap();slowThreadLocalMap.set(ret);}return ret;
}
3.2 设置value
当 InternalThreadLocalMap.get() 返回了 一个 InternalThreadLocalMap,接下来就可以保存数据了。
private boolean setKnownNotUnset(InternalThreadLocalMap threadLocalMap, V value) {// 设置valueif (threadLocalMap.setIndexedVariable(index, value)) {//将key(FastThreadLoca)添加到数组的第一个元素(Set集合)中addToVariablesToRemove(threadLocalMap, this);return true;}return false;
}
下面还是逐一分析,分析一下设置value的内部逻辑:
public boolean setIndexedVariable(int index, Object value) {// indexedVariables是构造函数中创建的Object数组Object[] lookup = indexedVariables;// index是从FastThreadLcal中传入的值,初始为1(自增),因为0被静态变量variablesToRemoveIndex抢占了if (index < lookup.length) {Object oldValue = lookup[index];lookup[index] = value;return oldValue == UNSET;} else {expandIndexedVariableTableAndSet(index, value);return true;}
}
整体逻辑比较直观,如果index没有越界,那么进行覆盖,如果old value为 UNSET,那么返回true,否则返回false。如果越界则进行扩容并返回true。这里有一个小细节。只有一种情况会返回fasle,即某个元素已经被赋值过了。那么返回false直接影响的是addToVariablesToRemove方法不会执行。即key不会再次被添加到Set集合中。因为已经被添加过了。下面看一下经典的扩容方式:
private void expandIndexedVariableTableAndSet(int index, Object value) {Object[] oldArray = indexedVariables;final int oldCapacity = oldArray.length;int newCapacity = index;newCapacity |= newCapacity >>> 1;newCapacity |= newCapacity >>> 2;newCapacity |= newCapacity >>> 4;newCapacity |= newCapacity >>> 8;newCapacity |= newCapacity >>> 16;newCapacity ++;Object[] newArray = Arrays.copyOf(oldArray, newCapacity);Arrays.fill(newArray, oldCapacity, newArray.length, UNSET);newArray[index] = value;indexedVariables = newArray;
}
这段代码的作用就是按原来的容量扩容2倍。并且保证结果是2的幂次方。JDK中HashMap的扩容也类似。扩容完成之后填充UNSET,并且将保存value。至此保存value的操作已经完毕。下面分析保存key的过程:
private static void addToVariablesToRemove(InternalThreadLocalMap threadLocalMap, FastThreadLocal<?> variable) {// 获取到下表为0的数组元素Object v = threadLocalMap.indexedVariable(variablesToRemoveIndex);Set<FastThreadLocal<?>> variablesToRemove;// 如果未设置过或者为nullif (v == InternalThreadLocalMap.UNSET || v == null) {// 创建一个IdentityHashMap的实现,IdentityHashMap和HashMap类似,只是key的相同判断方式以 ‘==’来决定variablesToRemove = Collections.newSetFromMap(new IdentityHashMap<FastThreadLocal<?>, Boolean>());// 将这个 Set 放到这个 Map 数组的下标 0 处threadLocalMap.setIndexedVariable(variablesToRemoveIndex, variablesToRemove);} else {// 如果拿到的不是 UNSET ,说明这是第二次操作了,因此可以强转为 SetvariablesToRemove = (Set<FastThreadLocal<?>>) v;}// 将 FastThreadLocal 放置到 Set 中variablesToRemove.add(variable);
}
这个方法的目的是将一条线程的所有FastThreadLocal对象保存到一个 Set 中,静态方法 removeAll 就需要使用到这个 Set,可以快速的删除线程 Map 里的所有 FTL 对应的 Value。如果不使用 Set,那么就需要遍历 InternalThreadLocalMap。
4. get
get方法极为简单,实现如下:
public final V get() {InternalThreadLocalMap threadLocalMap = InternalThreadLocalMap.get();Object v = threadLocalMap.indexedVariable(index);if (v != InternalThreadLocalMap.UNSET) {return (V) v;}V value = initialize(threadLocalMap);registerCleaner(threadLocalMap);return value;
}首先获取当前线程的map,然后根据 FastThreadLocal的index 获取value,然后返回,如果是空对象,则通过 initialize 返回,initialize 方法会将返回值设置到 map 的槽位中,并放进 Set 中。最后,尝试注册一个清洁器。
我们跟进初始化操作
private V initialize(InternalThreadLocalMap threadLocalMap) {V v = null;try {//1、获取初始值v = initialValue();} catch (Exception e) {throw new RuntimeException(e);}// 2、设置value到InternalThreadLocalMap中threadLocalMap.setIndexedVariables(index, v);// 3、添加当前的FastThreadLocal到InternalThreadLocalMap的Set<FastThreadLocal<?>>中addToVariablesToRemove(threadLocalMap, this);return v;
}//初始化参数:由子类复写
protected V initialValue() throws Exception {return null;
}
initialize过程和set过程几乎一样,此处不再赘述。
5. remove
FastThreadLocal有两种删除操作,删除当前线程上的InternalThreadLocalMap中的每一个value以及threadLocalMap本身。单个删除当前的FastThreadLocal对象的值。
public static void removeAll() {// 获取到mapInternalThreadLocalMap threadLocalMap = InternalThreadLocalMap.getIfSet();if (threadLocalMap == null) {return;}try {// 获取到Set<FastThreadLocal>集合Object v = threadLocalMap.indexedVariable(variablesToRemoveIndex);if (v != null && v != InternalThreadLocalMap.UNSET) {@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")Set<FastThreadLocal<?>> variablesToRemove = (Set<FastThreadLocal<?>>) v;// 将Set转换为数组FastThreadLocal<?>[] variablesToRemoveArray =variablesToRemove.toArray(new FastThreadLocal[variablesToRemove.size()]);// 遍历数组,删除每一个FastThreadLocal对应的valuefor (FastThreadLocal<?> tlv: variablesToRemoveArray) {tlv.remove(threadLocalMap);}}} finally {// 删除当前线程的InternalThreadLocalMapInternalThreadLocalMap.remove();}
}
tlv.remove单个删除过程如下:
private void remove() {remove(InternalThreadLocalMap.getIfSet());
}private void remove(InternalThreadLocalMap threadLocalMap) {if (threadLocalMap == null) {return;}// 从 InternalThreadLocalMap 中删除当前的FastThreadLocal对应的valueObject v = threadLocalMap.removeIndexedVariable(index);// 从 InternalThreadLocalMap 中的Set<FastThreadLocal<?>>中删除当前的FastThreadLocal对象removeFromVariablesToRemove(threadLocalMap, this);// 如果删除的是有效值,则进行onRemove方法的回调if (v != InternalThreadLocalMap.UNSET) {try {// 回调子类复写的onRemoved方法,默认为空实现onRemoved((V) v);} catch (Exception e) {throw new RuntimeException(e);}}
}
代码非常直观,继续分析删除map的操作
public static void remove() {Thread thread = Thread.currentThread();if (thread instanceof FastThreadLocalThread) {// 将FastThreadLocalThread 内部的map置位null((FastThreadLocalThread) thread).setThreadLocalMap(null);} else {// 将 ThreadLocal内部ThreadLocalMap 中的value置位nullslowThreadLocalMap.remove();}
}
removeAll操作会在FastThreadLocal线程自动的执行,但是普通类型的线程只能通过手动的remove/removeAll,但是Netty作者提供了另外一个神器ObjectCleaner。
专门对普通线程中FastThreadLocal的回收操作。
总结 FastThreadLocal使用的数组替代JDK中的线性探测发法的Map,如果是Netty内部创建的线程不用担心内存泄漏的,如果开发者使用了普通的线程,Netty 仍然会借助 JDK 的 ThreadLocal,只是只借用一个槽位,放置 Netty的Map
这篇关于Netty进阶:自顶向下解析FastThreadLocal的文章就介绍到这儿,希望我们推荐的文章对编程师们有所帮助!





