本文主要是介绍poj 1426 Find The Multiple(dfs || 二进制枚举),希望对大家解决编程问题提供一定的参考价值,需要的开发者们随着小编来一起学习吧!
题目:http://poj.org/problem?id=1426
大意是:给定一个数字n,求出数字m,其中m是n的倍数,且m是只由0,1构成的十进制数。
Sample Input
2 6 19 0
Sample Output
10 100100100100100100 111111111111111111开始我一直往数论方向想呢···使用单纯的枚举肯定是要超时的,
TLE:
#include <iostream>
#include<cstdio>
#include<cstring>
#include<cmath>
/* run this program using the console pauser or add your own getch, system("pause") or input loop */
using namespace std;
typedef unsigned long long ull;
ull pow(ull a){ //自己定义函数,不要用pow,防止精度问题。ull ans=1;while(a--){ans=ans*10;}return ans;
}
int main(int argc, char *argv[]) {//freopen("cin.txt","r",stdin);int n;ull t=1;while(cin>>n&&n){bool judge=0;for(ull i=1;i<(t<<63);i++){ //所有变量全用ull表示,不然1<<63的结果会超过int的表示范围,会发生怪事儿。ull temp=0;if(judge)break;for(ull j=0;j<63;j++){if((t<<j)&i){temp+=pow(j);if(temp>0&&temp%n==0){printf("%I64u\n",temp);judge=1;break;}}}}}return 0;
}#include<iostream>
#include<stdio.h>
#include<queue>
using namespace std;
typedef unsigned long long ull;
void bfs(ull n)
{queue<ull>q;q.push(1);while(!q.empty()){ull x;x=q.front();q.pop();if(x%n==0){printf("%I64u\n",x);return ;}if(x*10>(ull(1)<<63))return ;q.push(x*10);q.push(x*10+1);}
}
int main()
{ull n;while(cin>>n&&n){bfs(n);}return 0;
}正确的代码:
#include <iostream>
#include <cstdio>
using namespace std;
typedef unsigned long long ull;
bool flag=0;
void dfs(ull number,int n,int count){if(count>19 || flag )return ;if(number%n==0){flag=1;cout<<number<<endl;return ;}dfs(number*10,n,count+1);dfs(number*10+1,n,count+1);
}
int main()
{int n;while(cin>>n&&n){flag=0;dfs(1,n,0);}return 0;
}#include <iostream>
#include<cstdio>
#include<cstring>
#include<cmath>
/* run this program using the console pauser or add your own getch, system("pause") or input loop */
using namespace std;
typedef unsigned long long ull;
int p[30],top;
void turn(ull a){cout<<"turn: \n";top=0;memset(p,0,sizeof(p));while(a){p[top++]=a%2;a=a/2;}for(int i=top-1;i>=0;i--)cout<<p[i]; cout<<endl;
}
ull pow(ull a){ull ans=1;while(a--){ans=ans*10;}return ans;
}
int main(int argc, char *argv[]) {//freopen("cout.txt","w",stdout);int n;while(cin>>n&&n){ull t=1;for(ull i=(t<<19)-1;i>=n;i--){ull temp=0;//turn(i);for(ull j=18;j>=0&&j<19;j--){ //当j==0后再减1就变成了-1的补码:18446744073709551615if((t<<j)&i){temp+=pow(j);}}if(temp>=n&&temp%n==0){printf("%I64u\n",temp);break;}}}return 0;
}ull maxn=1111111111111111111;
void bfs(ull n)
{
queue<ull>q;
q.push(maxn);
q.push(maxn-1);
while(!q.empty())
{
ull x;
x=q.front();
q.pop();
if(x<n)return ;
if(x%n==0)
{
printf("%I64u\n",x);
return ;
}
q.push(x/10);
q.push(x/10-1);
}
}
------------------------------------------
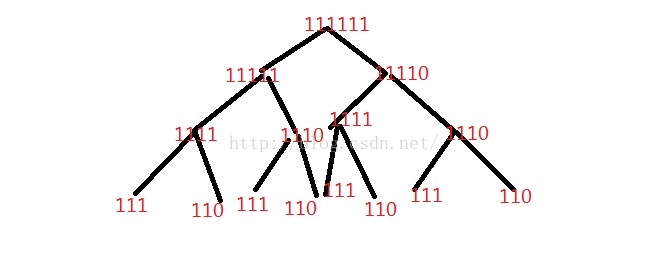
很遗憾是吧,它缺乏DFS和二进制枚举的灵活性还浪费空间。
这篇关于poj 1426 Find The Multiple(dfs || 二进制枚举)的文章就介绍到这儿,希望我们推荐的文章对编程师们有所帮助!



