本文主要是介绍algorithm 题集四 (16.06.10),希望对大家解决编程问题提供一定的参考价值,需要的开发者们随着小编来一起学习吧!
继2016.05.24续:
codeforces 651B. Beautiful Paintings-简单
http://codeforces.com/problemset/problem/651/B
大意:给出一个序列,求解其任意排列中满足ai + 1 > ai 的元素个数最大和。
分析:理想情况下,无重复元素的0从小到大的排列,满足条件的元素个数最多,是n-1.
非理想情况下还有重复元素,只要不断提取出重复的这些元素归到另一集合再这样讨论即可。
#include <iostream>
#include <cstdio>
#include <algorithm>
using namespace std;int s1[1009],s2[1009];int main()
{//freopen("cin.txt","r",stdin);int n;while(cin>>n){for(int i=0;i<n;i++) scanf("%d",&s1[i]);int top=n,ans=0;sort(s1,s1+n);while(top){int tp=0;for(int i=1;i<top;i++){if(s1[i]==s1[i-1]) s2[tp++]=s1[i];else ans++;}for(int i=0;i<tp;i++) s1[i]=s2[i];top=tp;}printf("%d\n",ans);}return 0;
}zoj 2343 Robbers-简单
http://acm.zju.edu.cn/onlinejudge/showProblem.do?problemCode=2343
大意:n个抢到分配赃物,要将总量是M的金币分配完全,每人得到ki,且误差|Xi/Y - Ki/M|的累计最小。
分析:误差式可以化成(XiM-KiY)/(YM),于是对于每一个金币,我给XiM最大的人即可。使用优先队列,每一模拟
#include <iostream>
#include <cstdio>
#include <queue>
#include <vector>
#include <algorithm>
using namespace std;
typedef long long LL;
LL n,m,y,xx;
struct node{LL x,k,dex;void show(){ cout<<x<<" "<<k<<" "<<dex<<endl; }
}p[1009];
struct cmp{bool operator()(node a,node b){return a.x<b.x;}
};
int cmp2(node a,node b){return a.dex<b.dex;
}
int main()
{//freopen("cin.txt","r",stdin);while(~scanf("%lld%lld%lld",&n,&m,&y)){priority_queue<node,vector<node>,cmp> que;for(int i=0;i<n;i++){scanf("%lld",&xx);node p;p.k=0;p.x=xx*m;p.dex=i;que.push(p);node t=que.top();}while(m>0){node temp=que.top();que.pop();temp.x-=y;temp.k++;que.push(temp);m--;}int top=0;while(!que.empty()){p[top++]=que.top();que.pop();}sort(p,p+top,cmp2);for(int i=0;i<top-1;i++) printf("%lld ",p[i].k);printf("%lld\n",p[top-1].k);}return 0;
}或者,先按比例分配,然后对于x[i]/Y - k[i]/M,谁最大我分给谁。注意,不是绝对值。这种解法更容易编码。
codeforces 651A. Joysticks-简单贪心
http://codeforces.com/problemset/problem/651/A
大意:两个操作杆,一个充电器,每一分钟可以选择一个操作杆充电,增加 1 percent,没有充电的减少2 percent。原来两者的电量是a,b。求解能维持两者电量都大于0的分钟数。
分析:木桶原理,保证两者都要大于0,那么谁少就给谁充电。
#include <iostream>
#include <cstdio>
#include <algorithm>
using namespace std;int main()
{int a1,a2;while(cin>>a1>>a2){int sec=0;if(a1>a2) swap(a1,a2);while(a1>=1 && a2>=2){a1++;a2-=2;if(a1>a2) swap(a1,a2);sec++;}printf("%d\n",sec);}return 0;
}acdream 1220 Hyperhuffman-哈夫曼编码简单题
http://acdream.info/problem?pid=1220
大意:给出每一个字符出现的次数,问哈弗曼编码的带权路径长度。
分析:关于哈弗曼编码,将每一个字符出现的次数作为树的结点的值,然后每一次取集合中最小的两个值合并,持续下去,直到剩下一个值,作为根节点。
相关博文:
http://www.cnblogs.com/Jezze/archive/2011/12/23/2299884.html
http://blog.csdn.net/thearcticocean/article/details/46597773
本题自然是模拟中间两两合并的过程即可。要求输出length of text, bits. 那么所有的结点的值之和即是所求。
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
#include <queue>
#include <cstdio>
using namespace std;
typedef long long LL;
struct cmp{bool operator ()(const LL a,const LL b){return a>b;}
};
int main()
{int n;LL a;while(cin>>n){priority_queue<LL,vector<LL>,cmp> que;for(int i=0;i<n;i++){scanf("%lld",&a);que.push(a);}LL sum=0,t1=0,t2=0;//while(!que.empty()) { cout<<que.top()<<" "; que.pop(); } cout<<endl;while(!que.empty()){t1=que.top();que.pop();if(que.empty()) break;t2=que.top();que.pop();sum+=t2+t1;que.push(t1+t2);}printf("%lld\n",sum);}return 0;
}codeforces 650B. Image Preview-二分 好题
http://codeforces.com/problemset/problem/650/B
大意:n张相片,从第一张相片开始,可以向左或向右滑动查看不同的相片,手机的方向是vertical,相片可能vertical,也可能horizontal,查看过的相片不再查看,不过要计算滑动的时间。在总时间T秒内最多能查看多少张相片?
分析:感觉变化好多啊,翻页花费的时间,调整方向花费的时间,看相片花费的时间。仿佛没有规律。
暴力是个好东西,专门解决没有规律的问题。不过暴力也要有技巧的暴力,比如,二进制枚举,二分查找等。
分析发现,最终的结果也就是向左、向右查看了多少相片。所以我们可以一个方向上直接枚举,另一个方向上二分加速。
工具好不好用,能发挥多大的威力完全在于使用它的人啊。此题再次说明了这个道理。一般来讲,寻找极限值使用三分查找的,但是三分往往针对浮点数有效。此题是整数问题,我见识到了用二分解决整数极值问题。
#include <iostream>
#include <cstdio>
#include <cstring>
using namespace std;const int N=5e5+10;
char str[N];
int sum[N];
int n,a,b,t;
bool check(int w){int ans=0,temp=0;for(int i=1;i<=w;i++){ans=sum[i]+sum[n]-sum[n-(w-i)]; // 前缀和能求出任意段值temp=min(a*(i-1)*2+(w-i)*a,a*(w-i)*2+a*(i-1)); //右右左、左左右ans=ans+temp;if(ans<=t) return 1;}return 0;
}
int main()
{//freopen("cin.txt","r",stdin);while(~scanf("%d%d%d%d",&n,&a,&b,&t)){scanf("%s",str+1);for(int i=1;i<=n;i++){sum[i]=sum[i-1]+1;if(str[i]=='w') sum[i]+=b;}int ans=0,l=1,r=n,mid; // binary search for number of photo(answer)!while(l<=r){mid=(l+r)>>1;if(check(mid)){ ans=ans>mid?ans:mid; l=mid+1; }else r=mid-1;}printf("%d\n",ans);}return 0;
}codeforces 652B. z-sort -简单
http://codeforces.com/problemset/problem/652/B
大意:给出n个数字,求解其满足这样的排列。
ai ≥ ai - 1 for all even i,
ai ≤ ai - 1 for all odd i > 1.
分析:先把前n/2个数字放在偶数位,然后在奇数位上放入剩下的数字。
#include <iostream>
#include <cstdio>
#include <algorithm>
using namespace std;
int a[1009],b[1009];
int cmp(int t1,int t2){return t1>t2;
}
int main()
{//freopen("cin.txt","r",stdin);int n;while(cin>>n){for(int i=0;i<n;i++){scanf("%d",&a[i]);}sort(a,a+n,cmp);int len=n>>1,top=0;for(int i=0;i<len;i++){int j=2*i+1;b[j]=a[i];}for(int i=len;i<n;i++){b[top]=a[i];top+=2;}for(int i=0;i<n-1;i++){printf("%d ",b[i]);}printf("%d\n",b[n-1]);}return 0;
}ACdream - 1195 Sudoku Checker-递归 or math
http://acdream.info/problem?pid=1195
大意:检测一个矩阵是否满足数独的特征。
Each row contains each number from 1 to N2, once each.
Each column contains each number from 1 to N2, once each.
Divide the N2×N2 matrix into N2 non-overlapping N×N sub-matrices. Each sub-matrix contains each number from 1 to N2, once each.
分析:
用一维数组做,易出错啊,交了四次。直接计算每一个起点和起点对应的小矩阵里的每一个元素的位置。即用纯数学思维,找每一个元素的位置。
#include <iostream>
#include <cstdio>
#include <cstring>
using namespace std;
int g[1600];
bool tag[1050];
bool check(int s,int N,int n){memset(tag,0,sizeof(tag));for(int i=0;i<n;i++){int x=i*N+s,y;for(int j=0;j<n;j++){y=x+j;tag[g[y]]=1;}}for(int i=1;i<=N;i++){if(tag[i]==0) {return false;}}return true;
}
int main()
{//freopen("cin.txt","r",stdin);int t,n,ca=1;cin>>t;while(t--){scanf("%d",&n);int N=n*n;for(int i=0;i<N;i++){for(int j=1;j<=N;j++){scanf("%d",&g[i*N+j]);}}int s=1,len=N*N;bool ok=1;while(s<=len){for(int i=0;i<n;i++){if(i) s+=n;//cout<<s<<" ";if(check(s,N,n)==false) {ok=0;break;}}if(ok==0) break;s+=(n-1)*N+n-1+1;} //cout<<endl;for(int i=0;i<N;i++){ // 横着memset(tag,0,sizeof(tag));for(int j=1;j<=N;j++){tag[g[i*N+j]]=1;}for(int j=1;j<=N;j++){if(tag[j]==0){ ok=0; break; }}if(ok==0) break;}for(int j=1;j<=N;j++){ //竖着memset(tag,0,sizeof(tag));for(int i=0;i<N;i++){tag[g[j+i*N]]=1;}for(int i=1;i<=N;i++){if(tag[i]==0){ ok=0; break; }}if(ok==0) break;}if(ok) printf("Case #%d: Yes\n",ca++);else printf("Case #%d: No\n",ca++);}return 0;
}用二维数组做,归纳的思想,不易出错。将每一个n*n的小部分看做n^4的一个格子。即:
那么我们令大格子的迭代器x: i, y: j 每一个小格子n*n部分的左上角位置就是(i-1)n+1, (j-1)n+1 (设数组各维的起点是1)
#include <iostream>
#include <cstdio>
#include <cstring>
using namespace std;
int g[40][40];
bool vis[1009];
int main()
{int t,n,ca=1;cin>>t;while(t--){scanf("%d",&n);int N=n*n;for(int i=1;i<=N;i++){for(int j=1;j<=N;j++){scanf("%d",&g[i][j]);}}bool ok=1;for(int i=1;i<=n;i++){for(int j=1;j<=n;j++){int start_x=(i-1)*n+1,x_step=n;int start_y=(j-1)*n+1,y_step=n;memset(vis,0,sizeof(vis));for(int ii=start_x;x_step>0;ii++,x_step--){y_step=n;for(int jj=start_y;y_step>0;jj++,y_step--){vis[g[ii][jj]]=1;}}for(int ii=1;ii<=N;ii++){if(vis[ii]==0) { ok=0; break; }}}}for(int i=1;i<=N;i++){memset(vis,0,sizeof(vis));for(int j=1;j<=N;j++){vis[g[i][j]]=1;}for(int j=1;j<=N;j++) if(vis[j]==0) ok=0;}for(int j=1;j<=N;j++){memset(vis,0,sizeof(vis));for(int i=1;i<=N;i++){vis[g[i][j]]=1;}for(int i=1;i<=N;i++) if(vis[i]==0) ok=0;}if(ok==0) printf("Case #%d: No\n",ca++);else printf("Case #%d: Yes\n",ca++);}return 0;
}ACdream - 1187 Rational Number Tree -tree 规律
http://acdream.info/problem?pid=1187
大意:有一颗分子树是这样的:
1/1______|______| |1/2 2/1___|___ ___|___| | | |
1/3 3/2 2/3 3/1
...left and right childs of node p/q are p/(p+q) and (p+q)/q, respectively
现在有两种问法,一种是给出一个数字,作为结点的位置,求解结点的分子和分母。另一种是给出结点的分子和分母,求解它在树中的位置(层次遍历)。
分析:解题思路一定和路径相关。这听起来是一句废话,但是确实能起很大作用。通过观察发现,
1______|______| |2 3___|___ ___|___| | | |4 5 6 7位置是偶数的相对父节点而言是在左边,且是父节点位置的2倍;是奇数的相对父节点而言是在右边,位置比左兄弟大1。
分支规律:
a/b______|______| |a/(a+b) (a+b)/b 那么我们对位置dex分解,用一个栈存储分解信息。
char sta[1000]; int top=0;
void solve(dex){if(dex is odd) {sta.push('B'); // 右边dex--;}else {sta.push('A'); // 左边dex>>=1;}
}再根据路径信息寻找分子。
work(a,b,key){if(key=='A') return(a,a+b);else return (b,b-a);
}由a/b寻找位置dex,观察容易发现,只有根结点分子和分母是相等的。再结合这颗树的分支特征,我们不断向上直达根部,存储路径信息,最后由路径信息计算位置.
while(a!=b){if(a>b){LL t=b; b=a; a=a-t;sta.push('B');}else {b=b-a;sta.push('A');}
}最后,信息先进后出,计算位置.
while(top>0){if(sta[top-1]=='A') ans<<=1;else ans++;top--;
}code:
#include <iostream>
#include <cstdio>
using namespace std;typedef unsigned long long LL;
struct node{LL a,b;node(LL t1,LL t2){ a=t1; b=t2; }void show(){ cout<<" ("<<a<<","<<b<<") ";}
};
char sta[1000];
int top;node work(node p,char key){if(key=='A') return node(p.a,p.a+p.b);else if(key=='B') return node(p.b,p.b-p.a);
}int main()
{//freopen("cin.txt","r",stdin);int t,ca=1,key;cin>>t;while(t--){scanf("%d",&key);LL dex,a,b;if(key==1) {scanf("%llu",&dex);node p(1,1);top=0;while(dex>1){if(dex&1) {dex--;sta[top++]='B';}else {dex>>=1;sta[top++]='A';}}while(top>0){p=work(p,sta[--top]);//p.show();}printf("Case #%d: %llu %llu\n",ca++,p.a,p.b);}else {scanf("%llu %llu",&a,&b);top=0;LL ans=1;while(a!=b){if(a>b){LL t=b; b=a; a=a-t;sta[top++]='B';}else {b=b-a;sta[top++]='A';}}while(top>0){if(sta[top-1]=='A') ans=ans<<1;else ans++;top--;}printf("Case #%d: %llu\n",ca++,ans);}}return 0;
}codeforces 659A. Round House - math
http://codeforces.com/problemset/problem/659/A
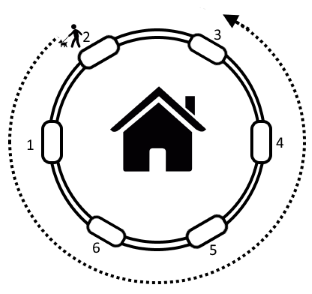
大意:给出圆环上结点的个数n,起点a,和运动距离b(b<0则代表逆时针运动,b>0则代表顺时针运动),问结果的位置。
分析:虽然只是A题,但仍然错了一次。一开始写出的答案是ans=(a-1+n+b)%n+1,错了不知道为何,模拟过了。后期明白了,真实的结果是ans=((a-1+b+n)%n+n)+1 注意b可能小于0,且绝对值远大于n。
#include <iostream>
#include <cstdio>
#include <cmath>
using namespace std;int main()
{int n,a,b;while(~scanf("%d%d%d",&n,&a,&b)){/*int bb=abs(b);while(bb>0){if(b>0){ a=a+1; if(a==n+1) a=1; }if(b<0){ a=a-1; if(a==0) a=n; }bb--;}printf("%d\n",a); */int ans=((a-1+n+b)%n+n)%n;printf("%d\n",ans+1);}return 0;
}codeforces 659C. Tanya and Toys - hash STL
http://codeforces.com/problemset/problem/659/C
大意:给出n个数字(1——1e9),求出剩下尽可能多的数字(在1——1e9内)使得他们的和不大于m。
分析:hash标记出现过的数字,再由小到大遍历没有出现的数字,和不大于m即可。
#include <iostream>
#include <cstdio>
#include <algorithm>
#include <map>
using namespace std;
const int N=1e5+10;
int sta[N];
int main()
{int n,m,a;while(cin>>n>>m){map<int,int> mp;for(int i=0;i<n;i++){scanf("%d",&a);mp[a]=1;}int top=0;for(int i=1;i<=m;i++){if(mp[i]==0){sta[top++]=i;m-=i;}}printf("%d\n",top);if(top==0) continue;for(int i=0;i<top-1;i++){printf("%d ",sta[i]);}printf("%d\n",sta[top-1]);}return 0;
}codeforces 659G. Fence Divercity - dp
http://codeforces.com/problemset/problem/659/G
大意:有一堵墙,给出一列列的高度,现在要除去一部分的高度,要求不能把某一部分的高度变成0,且除去部分需要连着,或者就除去一列。
分析:从中间过程入手,假设要降低某一列i的高度,要么和前面是连着的降低的,要么是单独降低的。为了方便思考,将所有的高度减去1,单独的就是高度1,2,3…… 连着降低的就是
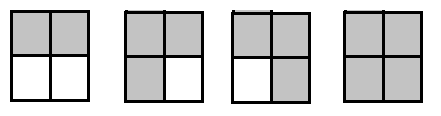
高度方案是乘的关系。
即:ans=ans+h[i]*last(i)+h[i]
ans=ans+min(h[i],h[i-1]) last[i]+h[i].
然后现在就是解决这个last。
分析容易知道last是和h[i]连着的,为了保证是连着的,右边的高度不能大于h[i]。所以最右边的高度应该是H=min(h[i-1],h[i]).
同时我们还需要保证last有所有的和h[i]相连的方案情况。
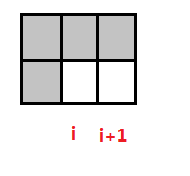
观察上图,可以发现last(i+1)含有的方案属于ans(i). 这其中含有递推关系。但ans(i)是含有独立h[i]的,last[i]必须考虑能和h[i]连接。所以last[i]有和ans[i]相似的性质,但是没有独立的h[i],且h[i]要么和前面多个相连要么单个相连。
last[i]=last[i-1]*min(h[i-1],h[i],h[i+1])+min(h[i],h[i+1]);
综上,写出递推式子:
dp[i][1]=dp[i-1][1]+min(h[i],h[i-1])*dp[i-1][0]+h[i]
dp[i][0]=dp[i-1]*min(min(h[i-1],h[i]),h[i+1])+min(h[i],h[i+1]);cout<<dp[n][1]<<endl;code:
#include <iostream>
#include <cstdio>
#include <algorithm>
using namespace std;
typedef long long LL;
const int mod=1e9+7,N=1e6+10;
LL h[N],dp[N][2];
int main()
{//freopen("cin.txt","r",stdin);int n;LL a;while(cin>>n){for(int i=1;i<=n;i++) {scanf("%I64d",&h[i]);h[i]--;}for(int i=1;i<=n;i++){dp[i][1]=(dp[i-1][1]+min(h[i],h[i-1])*dp[i-1][0]%mod+h[i])%mod;dp[i][0]=(dp[i-1][0]*min(min(h[i-1],h[i]),h[i+1])%mod+min(h[i],h[i+1]))%mod;}cout<<dp[n][1]<<endl;}return 0;
}acdream 1408 Money, Money, Money - 规律
http://acdream.info/problem?pid=1408
大意:给出一个数字x,求解是否存在a,b,使得它们的组合>x。 即t1a+t1b=y>x. (y=x+1, y=x+2, y=x+3…… t1>=0, t2>=0)
分析:不要用正常的数字思路分析,不然会发现几个变量组成的等式没有解。
暴力查出前几个数字的解,然后看出规律即可。答案是2, x+2. 当x是偶数时,这个答案失效了。恩,偶数就是没有答案。
code:
#include <iostream>
#include <cstdio>
using namespace std;
typedef long long LL;
bool check(LL a,LL b,LL g){for(LL t1=0;t1<100;t1++){for(LL t2=0;t2<100;t2++){if(t1*a+t2*b==g) return true;}}return false;
}
int main()
{LL x;while(cin>>x){/*for(LL a=1;a<x+10;a++){for(LL b=1;b<x+10;b++){bool ok=1;for(LL g=x+1;g<x+1000;g++){if(!check(a,b,g)){ ok=0; break; }}if(ok){ cout<<a<<" "<<b<<endl; }//else cout<<"0 0\n";}}*/if((x&1)==0) {puts("0 0"); continue;}printf("%lld %lld\n",2LL,x+2LL);}return 0;
}codeforces 650A. Watchmen - 去重
http://codeforces.com/problemset/problem/650/A
大意:求解哈弗曼距离和欧式距离相等的点对个数。
分析:想要让两种距离相等,那么两个点要么x相等,要么y相等,或者全等。于是我们发现还有点重复的问题,
理想情况下仅仅有一维坐标相等,那么增加的点对个数就是(设k是点的个数)k(k-1)/2。那么非理想情况下,就需要我们去重:
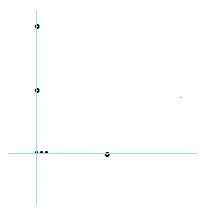
先对y排序: ∑y(y−1)2
再对x排序: ∑x(x−1)2
但是y维和x维都把相同位置点的配对情况统计了一次,所以要再减去一次。
消除相同位置点的影响: ∑q(q−1)2
#include <iostream>
#include <cstdio>
#include <algorithm>
using namespace std;
const int N=2e5+10,inf=1<<30;
typedef long long LL;
struct node{LL x,y;void show(){ printf("(%I64d %I64d) ",x,y); }
}p[N];
int cmpx(node a,node b){return a.x<b.x || (a.x==b.x && a.y<b.y);
}
int cmpy(node a,node b){return a.y<b.y || (a.y==b.y && a.x<b.x);
}
void show(int n){for(int i=1;i<=n;i++) p[i].show();puts("");
}
int main()
{//freopen("cin.txt","r",stdin);int n;while(cin>>n){for(int i=1;i<=n;i++){scanf("%I64d%I64d",&p[i].x,&p[i].y);}sort(p+1,p+n+1,cmpy);p[0].x=inf; p[0].y=inf;LL same=0,temp=1; // 计算出位置一样的点的组合个数和for(int i=1;i<=n;i++){if(p[i].x==p[i-1].x && p[i].y==p[i-1].y) temp++;else {same+=(temp*(temp-1)>>1);temp=1;}}same+=(temp*(temp-1)>>1);temp=1;LL ans=0;for(int i=1;i<=n;i++){if(p[i].y==p[i-1].y) temp++;else {ans=ans+(temp*(temp-1)>>1);temp=1;}}ans=ans+(temp*(temp-1)>>1);sort(p+1,p+1+n,cmpx);temp=1;for(int i=1;i<=n;i++){if(p[i].x==p[i-1].x) temp++;else {ans=ans+(temp*(temp-1)>>1);temp=1;}}ans=ans+(temp*(temp-1)>>1);ans=ans-same;printf("%I64d\n",ans);}return 0;
}但是在解完后,我在网上看到了更美的解法:
http://blog.csdn.net/why850901938/article/details/51078267
一种中间思想,每一次加入一个新点,就增加新的点对,一直循环下去。
scanf("%d%d",&x,&y);ans+=a[x]+b[y]-c[make_pair(x,y)];//注意减去重复的++a[x];++b[y];++c[make_pair(x,y)];
codeforces 676B. Pyramid of Glasses - 递归 or 递推 好题
http://codeforces.com/problemset/problem/676/B
大意:如下图所示,每一秒钟从上倒一杯的水,问n秒后有多少个杯子装满了水
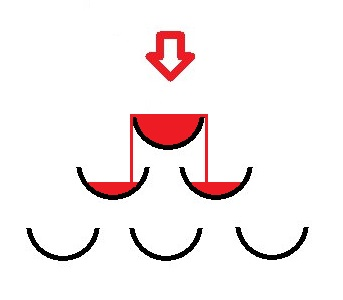
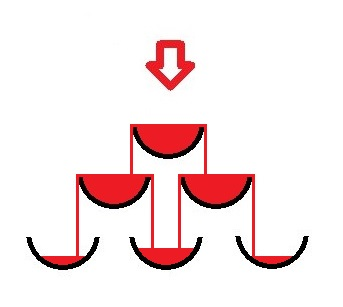
分析:
(1) 可以发现层和层之间有递推关系,直接联系到pascal三角形。可以用数学+递归完成这道题。
2^9=512。为了避免浮点数的影响,设一个杯子的容积是512.
#include <iostream>
#include <cstdio>
#include <algorithm>
#include <cstring>
using namespace std;
int h[15][15],h3[15][15];
int ans;
int mymin(int t1,int t2,int t3){return min(min(t1,t2),t3);
}
void flow(int vol,int x,int y,int n){if(vol==0 || x>n) return;if(h3[x][y]==0) {flow(vol>>1,x+1,y,n);flow(vol>>1,x+1,y+1,n);}if(vol>0 && h3[x][y]>0){int w=mymin(h3[x][y],h[x][y],vol);h3[x][y]-=w;vol-=w;if(h3[x][y]==0) ans++;}
}
int main()
{for(int i=1;i<=10;i++){h[i][1]=h[i][i]=1;}for(int i=3;i<=10;i++){for(int j=2;j<i;j++){h[i][j]=h[i-1][j-1]+h[i-1][j];}}int vol=512;for(int i=1;i<=10;i++){for(int j=1;j<=i;j++){h[i][j]*=vol;}vol>>=1;}int n,t;while(cin>>n>>t){for(int i=1;i<=10;i++){for(int j=1;j<=10;j++) h3[i][j]=512;}ans=0;for(int time=0;time<t;time++){vol=512;flow(vol,1,1,n);}printf("%d\n",ans);}return 0;
}(2) 如果不受动态过程的干扰,静态分析,那么我们就可以不用递归,而是单纯的使用递推即可。将所有的水vol倒入第一个杯子,假设水溢出没向下流(当然这在现实生活中是不可能的),那么分析它是否超过容积,超过了就ans++, vol-=v. 继续向下分析。这种思路成功是因为水一定是从高层水杯流向低处水杯的,直接抹去时间带来的影响。
#include <iostream>
#include <cstdio>
using namespace std;
int dp[15][15];
void show(){for(int i=1;i<=6;i++){for(int j=1;j<=i;j++){printf("%6d",dp[i][j]);} cout<<endl;}
}
int main()
{int n,t;while(cin>>n>>t){int ans=0;dp[1][1]=512*t;if(dp[1][1]>=512){dp[1][1]-=512;ans++;}else dp[1][1]=0; //避免影响下一层for(int i=2;i<=n;i++){for(int j=1;j<=i;j++){dp[i][j]=(dp[i-1][j]+dp[i-1][j-1])>>1;if(dp[i][j]>=512) {ans++;dp[i][j]-=512;}else dp[i][j]=0;}}printf("%d\n",ans);}return 0;
}对比可以发现,第一种方案容易想编码稍复杂,第二种方法容易实现但不易想到。
codeforces 652C. Foe Pairs - hash, dp,atom
http://codeforces.com/problemset/problem/652/C
大意:求解区间个数,区间内没有给出的点对。
我们需要考虑如下情况,有包含的,有重叠的,有分离的。
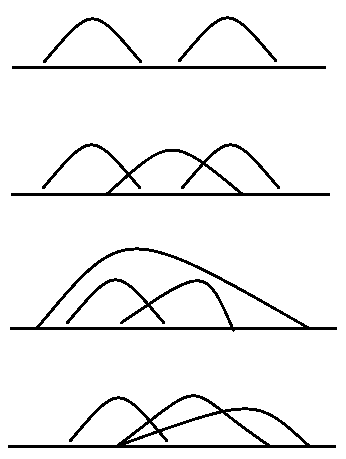
直接排个序,然后分段求解容易少算或者多算区间,这往往是由于计数的方式不对。可以针对每一个数字计算合理的区间数,然后累加起来。合理的区间数是可以和数字配对的右边数字的个数。
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
typedef long long LL;
const LL N=3e5+10;
LL mp[N],dp[N];int main()
{//freopen("cin.txt","r",stdin);LL n,m,t1,t2;while(cin>>n>>m){for(int i=1;i<=n;i++){scanf("%I64d",&t1);mp[t1]=i;dp[i]=n+1;}for(int i=0;i<m;i++){scanf("%I64d%I64d",&t1,&t2);LL d1=mp[t1], d2=mp[t2];if(d1>d2) swap(d1,d2);dp[d1]=min(dp[d1],d2);}for(int i=n-1;i>0;i--){dp[i]=min(dp[i],dp[i+1]);}LL ans=0;for(int i=1;i<=n;i++){ans=ans+dp[i]-i;} printf("%I64d\n",ans);}return 0;
}codeforces 645E.Intellectual Inquiry - 去重问题
http://codeforces.com/problemset/problem/645/E
大意:给出长度是n的字符串的前m部分,所有的字符从前k英文字符中选择,问怎样安排后的字符部分使得字符子串的个数最多?
分析:单纯用数学方法计算具有重复字符的子串个数似乎算不出来。向着中间状态思考——dp.
每增加一个字符会发生什么?
1.如果和前面没有字符重复,那么结果新增加的字符串个数就是前面原串的字符子串个数(原子串加上新的字符就是新串)。即dp[i]=dp[i-1]+dp[i-1]。
2.如果有重复,设字符q上一次出现的位置是last[q],那么重复次数就是dp[last[q]-1]
由1和2得到:dp[i]=2*dp[i-1]-dp[last[q]-1]
最后的答案就是dp[n+m]
由实际意义可以知道dp[]是一个递增数组,且前缀子串种类越多,那么总的子串个数越多。
所以我们需要dp[last[q]-1]小,也即是last[q]小
#include <iostream>
#include <cstdio>
#include <cstring>
using namespace std;const int N=2e6+10,mod=1e9+7;
char str[N];
int last[30];
int dp[N];
int n,k;
struct node{int last,ch;
};
node chfind(){ // find minist last[i]node ans;ans.last=last[0];ans.ch=0;for(int i=1;i<k;i++){if(ans.last>last[i]){ans.last=last[i];ans.ch=i;}}return ans;
}
int main()
{//freopen("cin.txt","r",stdin);while(cin>>n>>k){scanf("%s",str+1);memset(last,0,sizeof(last));int m=strlen(str+1);dp[0]=1; // set of nothing dp[1]=2;last[str[1]-'a']=1;for(int i=2;str[i];i++){int tlast=last[str[i]-'a'];if(tlast>=1) dp[i]=(2*dp[i-1]%mod-dp[tlast-1]+mod)%mod;else dp[i]=2*dp[i-1]%mod;last[str[i]-'a']=i;//cout<<i<<": "<<dp[i]<<endl;}for(int i=1;i<=n;i++){node temp=chfind();int ii=i+m;if(temp.last>=1) {dp[ii]=(2*dp[ii-1]%mod-dp[temp.last-1]+mod)%mod;}else {dp[ii]=2*dp[ii-1]%mod;}last[temp.ch]=ii;// cout<<ii<<": "<<dp[ii]<<endl;}printf("%d\n",dp[n+m]);}return 0;
}
最后送上一首优美的音乐谢谢你的阅读:
名人堂 Hall of Fame
这篇关于algorithm 题集四 (16.06.10)的文章就介绍到这儿,希望我们推荐的文章对编程师们有所帮助!





![[Algorithm][综合训练][栈和排序][加减]详细讲解](https://i-blog.csdnimg.cn/direct/7df413c28a644b6097dcfa5df3fb027c.png)
![[Algorithm][综合训练][四个选项][接雨水]详细讲解](https://i-blog.csdnimg.cn/direct/9e062d23fecc4cdc937d86b7f56aad5b.png)

