本文主要是介绍【数据库】函数,谓词(LIKE,BETWEEN,IN),CASE,希望对大家解决编程问题提供一定的参考价值,需要的开发者们随着小编来一起学习吧!
6.1函数
算术函数
6.1 创建表格:
postgres=# CREATE TABLE SampleMath
postgres-# (m NUMERIC (10,3),
postgres(# n INTEGER,
postgres(# p INTEGER);
CREATE TABLE
postgres=# BEGIN TRANSACTION;
BEGIN
postgres=# INSERT INTO SampleMath(m, n, p) VALUES (500, 0, NULL);
INSERT 0 1
postgres=# INSERT INTO SampleMath(m, n, p) VALUES (-180, 0, NULL);
INSERT 0 1
postgres=# INSERT INTO SampleMath(m, n, p) VALUES (NULL, NULL, NULL);
INSERT 0 1
postgres=# INSERT INTO SampleMath(m, n, p) VALUES (NULL, 7, 3);
INSERT 0 1
postgres=# INSERT INTO SampleMath(m, n, p) VALUES (NULL, 5, 2);
INSERT 0 1
postgres=# INSERT INTO SampleMath(m, n, p) VALUES (NULL, 4, NULL);
INSERT 0 1
postgres=# INSERT INTO SampleMath(m, n, p) VALUES (8, NULL, 3);
INSERT 0 1
postgres=# INSERT INTO SampleMath(m, n, p) VALUES (2.27, 1, NULL);
INSERT 0 1
postgres=# INSERT INTO SampleMath(m, n, p) VALUES (5.555,2, NULL);
INSERT 0 1
postgres=# INSERT INTO SampleMath(m, n, p) VALUES (NULL, 1, NULL);
INSERT 0 1
postgres=# INSERT INTO SampleMath(m, n, p) VALUES (8.76, NULL, NULL);
INSERT 0 1
postgres=# COMMIT;
COMMIT
postgres=# SELECT * FROM SampleMath;m | n | p
----------+---+---500.000 | 0 |-180.000 | 0 || || 7 | 3| 5 | 2| 4 |8.000 | | 32.270 | 1 |5.555 | 2 || 1 |8.760 | |
(11 行记录)
6.2 求绝对值
postgres=# SELECT m,
postgres-# ABS(m) AS abs_col
postgres-# FROM SampleMath;m | abs_col
----------+---------500.000 | 500.000-180.000 | 180.000||||8.000 | 8.0002.270 | 2.2705.555 | 5.555|8.760 | 8.760
(11 行记录)6.3 求余数MOD
postgres=# SELECT n,p,
postgres-# MOD(n,p) AS mod_col
postgres-# FROM SampleMath;n | p | mod_col
---+---+---------0 | |0 | || |7 | 3 | 15 | 2 | 14 | || 3 |1 | |2 | |1 | || |
(11 行记录)
6.4 ROUND四舍五入,m时待处理数据,n是四舍五入之后的位数
postgres=# SELECT m,n,
postgres-# ROUND(m,n) AS round_col
postgres-# FROM SampleMath;m | n | round_col
----------+---+-----------500.000 | 0 | 500-180.000 | 0 | -180| || 7 || 5 || 4 |8.000 | |2.270 | 1 | 2.35.555 | 2 | 5.56| 1 |8.760 | |
(11 行记录)
6.5 创建字符串表
postgres=# CREATE TABLE SampleStr
postgres-# (str1 VARCHAR(40),
postgres(# str2 VARCHAR(40),
postgres(# str3 VARCHAR(40));
CREATE TABLE
postgres=# BEGIN TRANSACTION;
BEGIN
postgres=# INSERT INTO SampleStr (str1, str2, str3) VALUES ('opx', 'rt',NULL);
INSERT 0 1
postgres=# INSERT INTO SampleStr (str1, str2, str3) VALUES ('abc','def',NULL);
INSERT 0 1
postgres=# INSERT INTO SampleStr (str1, str2, str3) VALUES ('山田',' 太郎' ,'是我');
INSERT 0 1
postgres=# INSERT INTO SampleStr (str1, str2, str3) VALUES ('aaa',NULL ,NULL);
INSERT 0 1
postgres=# INSERT INTO SampleStr (str1, str2, str3) VALUES (NULL,'xyz', NULL);
INSERT 0 1
postgres=# INSERT INTO SampleStr (str1, str2, str3) VALUES ('@!#$%',NULL,NULL);
INSERT 0 1
postgres=# INSERT INTO SampleStr (str1, str2, str3) VALUES ('ABC',NULL,NULL);
INSERT 0 1
postgres=# INSERT INTO SampleStr (str1, str2, str3) VALUES ('aBC',NULL,NULL);
INSERT 0 1
postgres=# INSERT INTO SampleStr (str1, str2, str3) VALUES ('abc太郎','abc','ABC');
INSERT 0 1
postgres=# INSERT INTO SampleStr (str1, str2, str3) VALUES ('abcdefabc', 'abc','ABC');
INSERT 0 1
postgres=# INSERT INTO SampleStr (str1, str2, str3) VALUES ('micmic', 'i', 'I');;
INSERT 0 1
postgres=# COMMIT;
COMMIT
postgres=# SELECT * FROM SampleStr;str1 | str2 | str3
-----------+------+------opx | rt |abc | def |山田 | 太郎 | 是我aaa | || xyz |@!#$% | |ABC | |aBC | |abc太郎 | abc | ABCabcdefabc | abc | ABCmicmic | i | I
(11 行记录)
6.6 字符串拼接||
postgres=# SELECT str1,str2,
postgres-# str1||str2 AS str_concat
postgres-# FROM SampleStr;str1 | str2 | str_concat
-----------+------+--------------opx | rt | opxrtabc | def | abcdef山田 | 太郎 | 山田太郎aaa | || xyz |@!#$% | |ABC | |aBC | |abc太郎 | abc | abc太郎abcabcdefabc | abc | abcdefabcabcmicmic | i | micmici
(11 行记录)
6.7 拼接三个字符串
postgres=# SELECT str1,str2,str3,
postgres-# str1||str2||str3 AS str_concat
postgres-# FROM SampleStr
postgres-# WHERE str1='山田';str1 | str2 | str3 | str_concat
------+------+------+--------------山田 | 太郎 | 是我 | 山田太郎是我
(1 行记录)6.8 计算字符串长度LENGTH
postgres=# SELECT str1,
postgres-# LENGTH(str1) AS length_str
postgres-# FROM SampleStr;str1 | length_str
-----------+------------opx | 3abc | 3山田 | 2aaa | 3|@!#$% | 5ABC | 3aBC | 3abc太郎 | 5abcdefabc | 9micmic | 6
(11 行记录)
6.9 大小写转换 LOWER UPPER
postgres=# SELECT str1,
postgres-# LOWER(str1) AS low_str
postgres-# FROM SampleStr;str1 | low_str
-----------+-----------opx | opxabc | abc山田 | 山田aaa | aaa|@!#$% | @!#$%ABC | abcaBC | abcabc太郎 | abc太郎abcdefabc | abcdefabcmicmic | micmic
(11 行记录)
6.10 替换字符串REPLACE(对象字符串,替换前,替换后)
postgres=# SELECT str1,str2,str3,
postgres-# REPLACE(str1,str2,str3) AS replace_str
postgres-# FROM SampleStr;str1 | str2 | str3 | replace_str
-----------+------+------+-------------opx | rt | |abc | def | |山田 | 太郎 | 是我 | 山田aaa | | || xyz | |@!#$% | | |ABC | | |aBC | | |abc太郎 | abc | ABC | ABC太郎abcdefabc | abc | ABC | ABCdefABCmicmic | i | I | mIcmIc
(11 行记录)
6.11 字符串的截取SUBSTRING(对象字符串 FROM 第几位 FRO 截取长度)
postgres=# SELECT str1,
postgres-# SUBSTRING(str1 FROM 3 FOR 2) AS subs_str
postgres-# FROM SampleStr;str1 | subs_str
-----------+----------opx | xabc | c山田 |aaa | a|@!#$% | #$ABC | CaBC | Cabc太郎 | c太abcdefabc | cdmicmic | cm
(11 行记录)
日期函数:
6.13 获得当前日期CURRENT_DATE
postgres=# SELECT CURRENT_DATE
postgres-# ;date
------------2021-04-14
(1 行记录)
6.14获取当前时间 CURRENT_TIME
postgres=# SELECT CURRENT_TIME;timetz
--------------------11:18:22.191069+08
(1 行记录)
6.15 获取当前的日期和时间 CURRENT_TIMESTAMP
postgres=# SELECT CURRENT_TIMESTAMP;now
-------------------------------2021-04-14 11:19:16.623151+08
(1 行记录)
6.16 截取日期元素
postgres=# SELECT CURRENT_TIMESTAMP,
postgres-# EXTRACT(YEAR FROM CURRENT_TIMESTAMP) AS year,
postgres-# EXTRACT(MONTH FROM CURRENT_TIMESTAMP) AS month;now | year | month
-------------------------------+------+-------2021-04-14 11:25:10.543004+08 | 2021 | 4
(1 行记录)
转换函数
6.17 数据类型转换CAST
格式:CAST(待转换对象 AS 转换后的数据类型)
postgres=# SELECT CAST('0001' AS INTEGER) AS int_col;int_col
---------1
(1 行记录)
6.18 将字符串转换为日期类型
postgres=# SELECT CAST('2009-12-11' AS DATE) AS date_col;date_col
------------2009-12-11
(1 行记录)
6.19 将NULL值转换为其他值COALESCE
返回COALESCE括号内第一个不为0的索引。
postgres=# SELECT COALESCE(NULL,1) AS col_1,
postgres-# COALESCE(2) AS col_2,
postgres-# COALESCE(NULL,NULL,NULL,NULL,4) AS col_3;col_1 | col_2 | col_3
-------+-------+-------1 | 2 | 4
(1 行记录)
6.20 COALESCE作用于某一列
postgres=# SELECT COALESCE(str2,'大哥')
postgres-# FROM SampleStr;coalesce
----------rtdef太郎大哥xyz大哥大哥大哥abcabci
(11 行记录)
6.2 谓词
6.21创建SampleLike表
postgres=# CREATE TABLE SampleLike
postgres-# (strcol VARCHAR(6) NOT NULL,
postgres(# PRIMARY KEY (strcol));
CREATE TABLE
postgres=# BEGIN TRASACTION;
错误: 语法错误 在 "TRASACTION" 或附近的
第1行BEGIN TRASACTION;^
postgres=# BEGIN TRANSACTION;
BEGIN
postgres=# INSERT INTO SampleLike (strcol) VALUES ('abcddd');
INSERT 0 1
postgres=# INSERT INTO SampleLike (strcol) VALUES ('dddabc');
INSERT 0 1
postgres=# INSERT INTO SampleLike (strcol) VALUES ('abdddc');
INSERT 0 1
postgres=# INSERT INTO SampleLike (strcol) VALUES ('abcdd');
INSERT 0 1
postgres=# INSERT INTO SampleLike (strcol) VALUES ('ddabc');
INSERT 0 1
postgres=# INSERT INTO SampleLike (strcol) VALUES ('abddc');
INSERT 0 1
postgres=# COMMIT;
COMMITpostgres=# SELECT * FROM SampleLike;strcol
--------abcddddddabcabdddcabcddddabcabddc
(6 行记录)
6.22 用LIKE语句做前方一致查询
postgres=# SELECT *
postgres-# FROM SampleLike
postgres-# WHERE strcol LIKE 'ddd%';strcol
--------dddabc
(1 行记录)
注:%表示任意字符串
6.22 中间一致查询
postgres=# SELECT * FROM SampleLike
postgres-# WHERE strcol LIKE '%ddd%';strcol
--------abcddddddabcabdddc
(3 行记录)
注:中间的查询结果包含前后
6.23 后方一致查询
postgres=# SELECT * FROM SampleLike
postgres-# WHERE strcol LIKE '%ddd';strcol
--------abcddd
(1 行记录)
6.26 用下划线表示任意一个字符
postgres=# SELECT * FROM SampleLike
postgres-# WHERE strcol LIKE '___dd';strcol
--------abcdd
(1 行记录)
6.27 选取销售单价在100-5000之间的商品BETWEEN
postgres=# SELECT product_name,sale_price
postgres-# FROM Product
postgres-# WHERE sale_price BETWEEN 100 AND 5000;product_name | sale_price
--------------+------------T恤 | 1000打孔器 | 500运动T恤 | 4000菜刀 | 3000叉子 | 500擦菜板 | 880圆珠笔 | 100
(7 行记录)
注:默认是闭区间,想要开区间,在数据前加<或>
6.29 选取进价为NULL的数据 ISNULL
postgres=# SELECT product_name,purchase_price
postgres-# FROM Product
postgres-# WHERE purchase_price ISNULL;product_name | purchase_price
--------------+----------------叉子 |圆珠笔 |
(2 行记录)
6.30 选取不为NULL的数据 IS NOT NULL
postgres=# SELECT product_name,purchase_price
postgres-# FROM Product
postgres-# WHERE purchase_price IS NOT NULL;product_name | purchase_price
--------------+----------------T恤 | 500打孔器 | 320运动T恤 | 2800菜刀 | 2800高压锅 | 5000擦菜板 | 790
(6 行记录)注:注意写法,中间有空格
6.32 用IN 指定多个具体的数据
postgres=# SELECT product_name,purchase_price
postgres-# FROM Product
postgres-# WHERE purchase_price IN (500,320,790);product_name | purchase_price
--------------+----------------T恤 | 500打孔器 | 320擦菜板 | 790
(3 行记录)
6.33 返回不在IN集合的数据
postgres=# SELECT product_name,purchase_price
postgres-# FROM Product
postgres-# WHERE purchase_price NOT IN (500,320,790);product_name | purchase_price
--------------+----------------运动T恤 | 2800菜刀 | 2800高压锅 | 5000
(3 行记录)
注:NULL 数据不参与
6.34 创建ShopProduct表
postgres=# SELECT * FROM ShopProduct;shop_id | shop_name | product_id | quantity
---------+-----------+------------+----------000A | 东京 | 0001 | 30000A | 东京 | 0002 | 50000A | 东京 | 0003 | 15000B | 名古屋 | 0002 | 30000B | 名古屋 | 0003 | 120000B | 名古屋 | 0004 | 20000B | 名古屋 | 0006 | 10000B | 名古屋 | 0007 | 40000C | 大阪 | 0003 | 20000C | 大阪 | 0004 | 50000C | 大阪 | 0006 | 90000C | 大阪 | 0007 | 70000D | 福冈 | 0001 | 100
(13 行记录)
6.36 使用子查询作为IN的参数
postgres=# SELECT product_name,sale_price
postgres-# FROM Product
postgres-# WHERE product_id IN (SELECT product_id FROM ShopProduct
postgres(# WHERE shop_name='大阪');product_name | sale_price
--------------+------------叉子 | 500擦菜板 | 880运动T恤 | 4000菜刀 | 3000
(4 行记录)
注:EXIST了解,多数情况下可以用IN代替
6.41 通过CASE语句给种类加ABC
postgres=# SELECT product_name,
postgres-# CASE WHEN product_type='衣服'
postgres-# THEN 'A:'|| product_type
postgres-# WHEN product_type='办公用品'
postgres-# THEN 'B:'|| product_type
postgres-# WHEN product_type='厨房用具'
postgres-# THEN 'C:'|| product_type
postgres-# ELSE NULL
postgres-# END AS nayilie
postgres-# FROM Product;product_name | nayilie
--------------+------------T恤 | A:衣服打孔器 | B:办公用品运动T恤 | A:衣服菜刀 | C:厨房用具高压锅 | C:厨房用具叉子 | C:厨房用具擦菜板 | C:厨房用具圆珠笔 | B:办公用品
(8 行记录)
6.43 CASE表达式进行列转换
postgres=# SELECT SUM(CASE WHEN product_type='衣服'
postgres(# THEN sale_price ELSE 0 END) AS clothes,
postgres-# SUM(CASE WHEN product_type='厨房用具'
postgres(# THEN sale_price ELSE 0 END) AS kitchen,
postgres-# SUM(CASE WHEN product_type='办公用品'
postgres(# THEN sale_price ELSE 0 END) AS office
postgres-# FROM Product;clothes | kitchen | office
---------+---------+--------5000 | 11180 | 600
(1 行记录)
练习:
6.1 计算执行结果

product_name | purchase_price
--------------+----------------
(0 行记录)
注:IN 无法选取NULL或者NOT NULL数据。
6.2 CASE问题
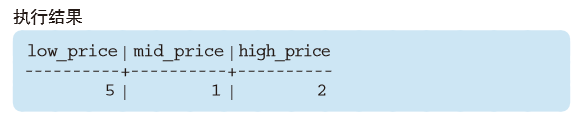
postgres=# SELECT SUM(CASE WHEN sale_price <= 1000 THEN 1 ELSE 0 END) AS low_price,
postgres-# SUM(CASE WHEN sale_price BETWEEN 1001 AND 3000 THEN 1 ELSE 0 END) AS mid_price,
postgres-# SUM(CASE WHEN sale_price >= 3001 THEN 1 ELSE 0 END) AS high_price
postgres-# FROM Product;low_price | mid_price | high_price
-----------+-----------+------------5 | 1 | 2
(1 行记录)
这篇关于【数据库】函数,谓词(LIKE,BETWEEN,IN),CASE的文章就介绍到这儿,希望我们推荐的文章对编程师们有所帮助!






