本文主要是介绍MQ之Spring AMQP学习,希望对大家解决编程问题提供一定的参考价值,需要的开发者们随着小编来一起学习吧!
Spring AMQP学习
Spring AMQP
AMQP是Advanced Message Queuing Protocol的缩写。AMQP是用于在应用程序之间传递消息的开放标准,该协议与语言和平台无关,更符合微服务中独立性的要求。
Spring AMQP是基于AMQP协议定义的一套API规范,提供了模版来发送和接收消息,包含两部分,其中spring-amqp是基础抽象,spring-rabbit是底层的默认实现。
SpringAMQP提供了三个功能:
- 自动声明队列、交换机及其绑定关系
- 基于注解的监听器模式,异步接收消息
- 封装了RabbitTemplate工具,用于发送消息
Spring AMQP使用
首先需要引入依赖
<dependency><groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId><artifactId>spring-boot-starter-amqp</artifactId></dependency>RabbitMQ配置:
spring:rabbitmq:port: 5672 # mq server 端口号,注意:部署15672virtual-host: /test #虚拟主机host: 192.168.200.215 # mq server ipusername: testuser1 # mq管理后台用户名password: testuser1 # mq管理后台密码
简单队列
work queue(工作队列)
work queue简单来说就是让多个消费者绑定到一个队列,共同消费队列中的消息。
当消息处理比较耗时的时候,可能生产消息的速度会远远大于消费的速度。如果一直这样,消息就会堆积越来越多,无法及时处理。
此时就可以使用work模型,多个消费者共同处理消息,这样消费速度就能大大提高了。
work queu默认是采用预取模式去消费消息的,也就是如果有多个消费者,则会先预分配给每个消费一个消息,消费完以后,再给每个消费者继续分配。
消息生产代码如下:
@RequestMapping("/work-queue")public String testWorkQueue() {// 消息String message = "hello, spring amqp!";for (int i = 0; i < 50; i++) {// 发送消息rabbitTemplate.convertAndSend(SIMPLE_QUEUE_NAME, message + i);}log.info("消息发送成功: {}", message);return "success";}
消费者代码如下:
@Component
@Slf4j
public class SimpleQueueListener {@RabbitListener(queues = "simple.queue")public void listenerWorkQueue1(String message) {log.info("消费者1接收到的消息: {}", message);Thread.sleep(5);}@RabbitListener(queues = "simple.queue")public void listenerWorkQueue2(String message) {log.info("消费者2接收到的消息: {}", message);Thread.sleep(200);}}
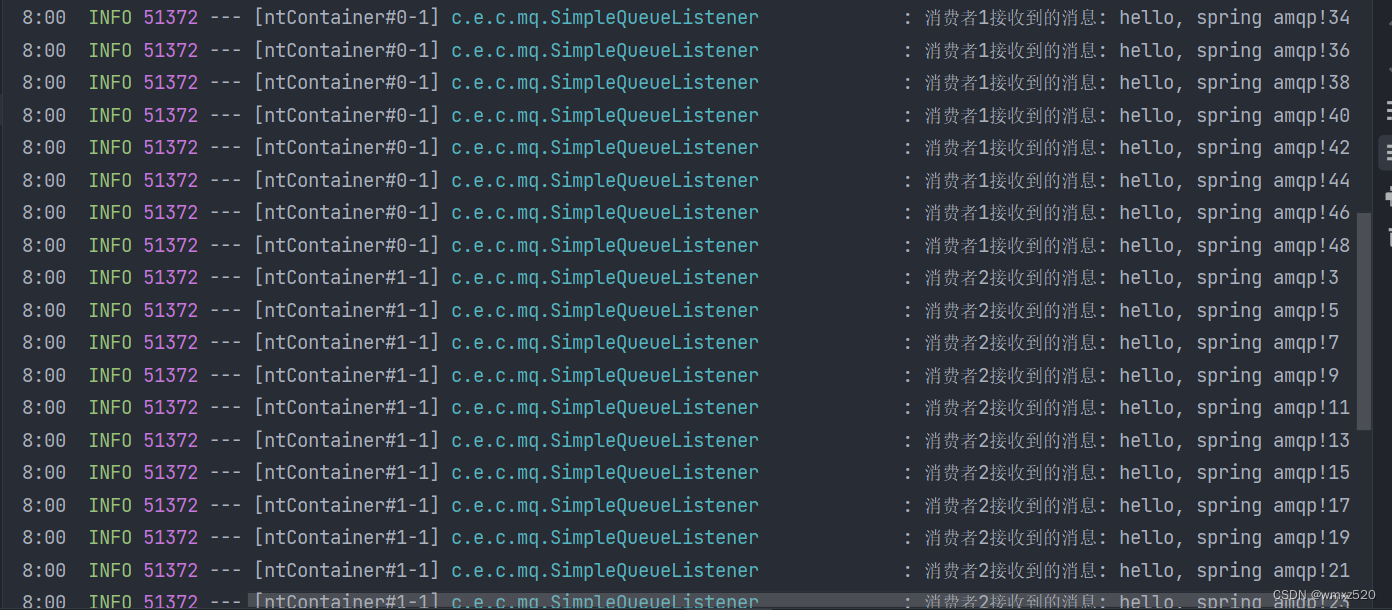
结果如下图所示,可以看到两个消费者消费消息是均匀分配的。
如果想实现“能者多劳”,消费消息快的消费者多消费,可以使用下面的配置
rabbitmq:host: 192.168.200.215username: testuser1password: testuser1port: 5672 #这里的端口是5762,不是15762virtual-host: /testlistener:simple:prefetch: 1 #每次只能得到一条消息,处理完ACK之后,才能获取下一个消息
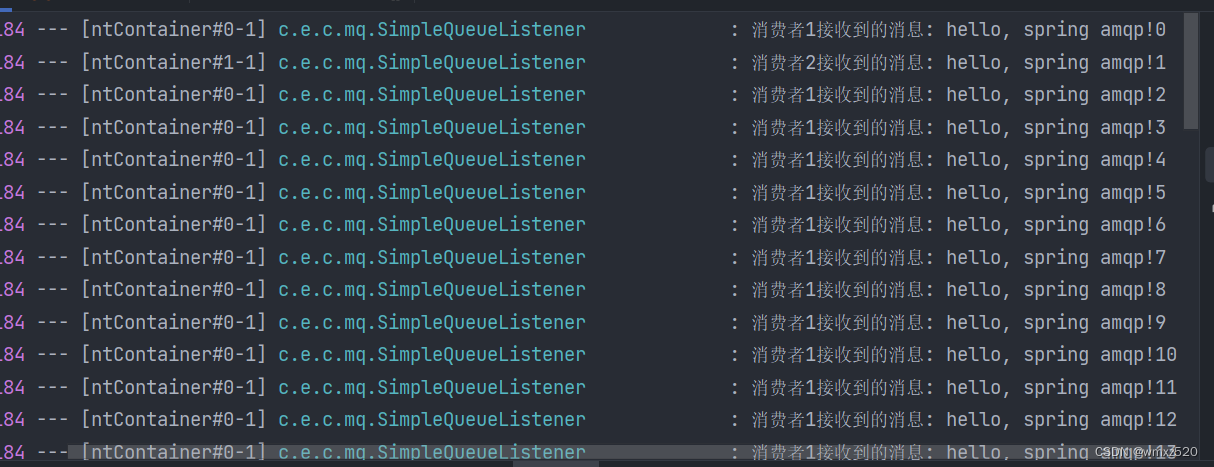
加入配置以后,可以看到消费者2消费的消息比消费者1多。
发布订阅
发布订阅的模型如下图所示:
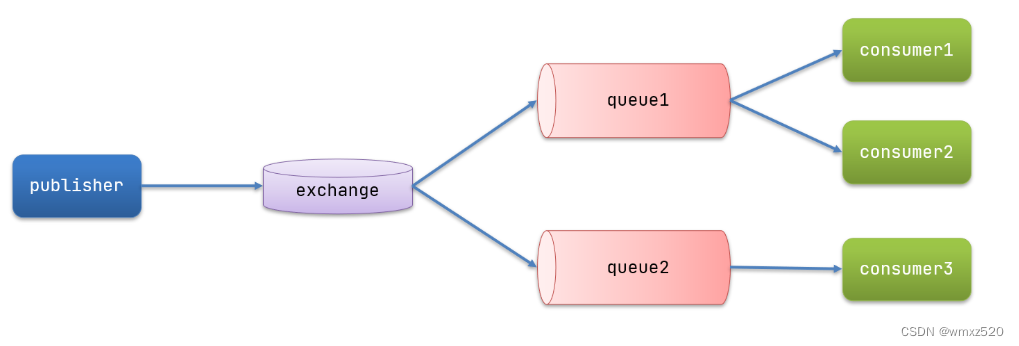
在订阅模型中,多了一个exchange角色,而且过程略有变化:
- Publisher:生产者,也就是要发送消息的程序,但是不再发送到队列中,而是发给X(交换机)
- Exchange:交换机,图中的X。一方面,接收生产者发送的消息。另一方面,知道如何处理消息,例如递交给某个特别队列、递交给所有队列、或是将消息丢弃。到底如何操作,取决于Exchange的类型。Exchange有以下3种类型:
- Fanout:广播,将消息交给所有绑定到交换机的队列
- Direct:定向,把消息交给符合指定routing key 的队列
- Topic:通配符,把消息交给符合routing pattern(路由模式) 的队列
- Consumer:消费者,与以前一样,订阅队列,没有变化
- Queue:消息队列也与以前一样,接收消息、缓存消息
Fanout模式示例
声明交换机,绑定队列和交换机。这个代码需要和消息发送者在同一个服务中。
@Configuration
public class FanoutConfiguration {/*** 声明交换机**/@Beanpublic FanoutExchange fanoutExchange() {return new FanoutExchange("demo.fanout");}@Beanpublic Queue fanoutQueue1() {return new Queue("fanout.queue1");}/*** 绑定队列和交换机*/@Beanpublic Binding bindingQueue1(@Autowired Queue fanoutQueue1, @Autowired FanoutExchange fanoutExchange) {return BindingBuilder.bind(fanoutQueue1).to(fanoutExchange);}/*** 第2个队列*/@Beanpublic Queue fanoutQueue2(){return new Queue("fanout.queue2");}/*** 绑定队列和交换机*/@Beanpublic Binding bindingQueue2(Queue fanoutQueue2, FanoutExchange fanoutExchange){return BindingBuilder.bind(fanoutQueue2).to(fanoutExchange);}}
发送消息。注意:convertAndSend方法中指定了交换机的名称
@GetMapping("/fanout")public String testFanoutQueue() {// 消息String message = "hello, fanout queue!";//交换机名称String exchange = "demo.fanout";rabbitTemplate.convertAndSend(exchange, "", message);log.info("消息发送成功: {}", message);return "success";}
消费者接收消息,接收消息和前面简单队列是一样的。
@Component
@Slf4j
public class SimpleQueueListener {@RabbitListener(queues = "fanout.queue1")public void fanoutQueue1(String message) throws InterruptedException {log.info("消费者1接收到的消息: {}", message);}@RabbitListener(queues = "fanout.queue2")public void fanoutQueue2(String message) throws InterruptedException {log.info("消费者2接收到的消息: {}", message);}}
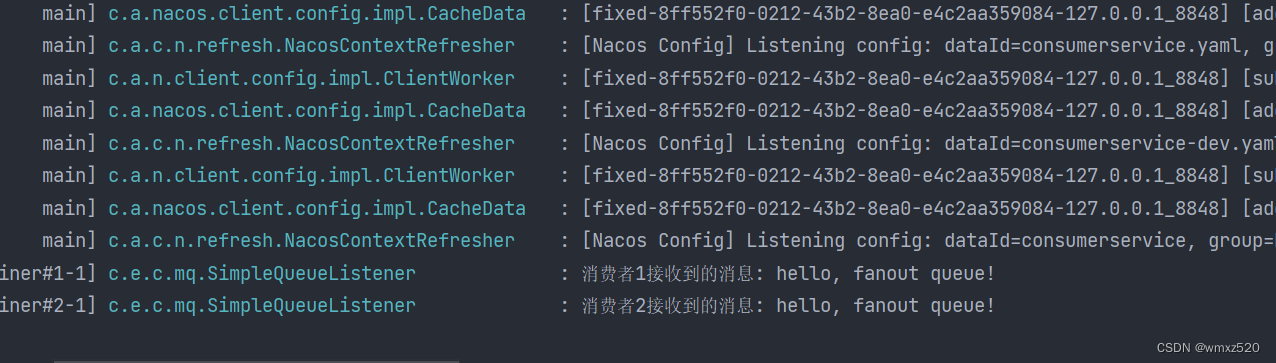
结果如下图所示:
Topic模式
在fanout模式下,一条消息会被所有订阅的队列消费,但是有时候,我们想让消息被不同的队列消费,这时候就需要用到direct类型的Exchange。
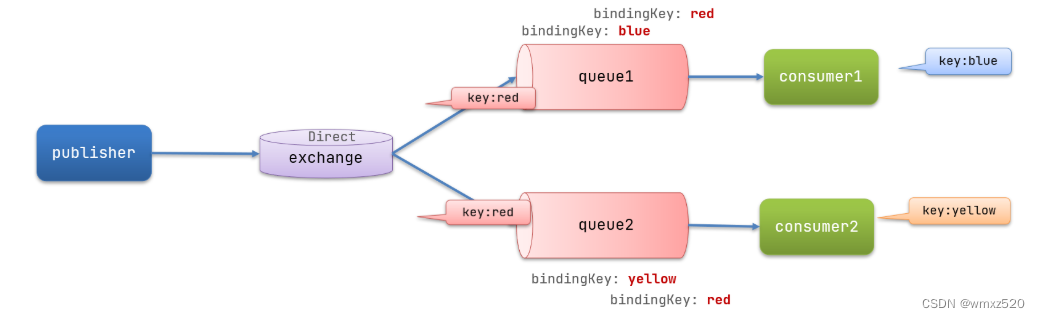
消息监听,这里使用的注解的方式,使用@Queue指定队列,@Exchange指定交换机,key指定路由的key,数组类型,可以指定多个
@RabbitListener(bindings = @QueueBinding(value = @Queue(name = "direct.queue1"),exchange = @Exchange(name = "direct", type = ExchangeTypes.DIRECT),key = {"blue"}))public void listenDirectQueue1(String message) {log.info("消费者1接收到的消息: {}", message);}@RabbitListener(bindings = @QueueBinding(value = @Queue(name = "direct.queue2"),exchange = @Exchange(name = "direct", type = ExchangeTypes.DIRECT), key = {"yellow"}))public void listenDirectQueue2(String message) {log.info("消费者2接收到的消息: {}", message);}
发送消息,发送消息时需要指定路由key,这样消息才能被指定的队列收到
// 消息String message = "hello, direct queue!";//交换机名称String exchange = "direct";rabbitTemplate.convertAndSend(exchange, "yellow", message);
Topic模式
Topic类型的Exchange与Direct相比,都是可以根据RoutingKey把消息路由到不同的队列。只不过Topic类型Exchange可以让队列在绑定Routing key 的时候使用通配符!
接收消息监听
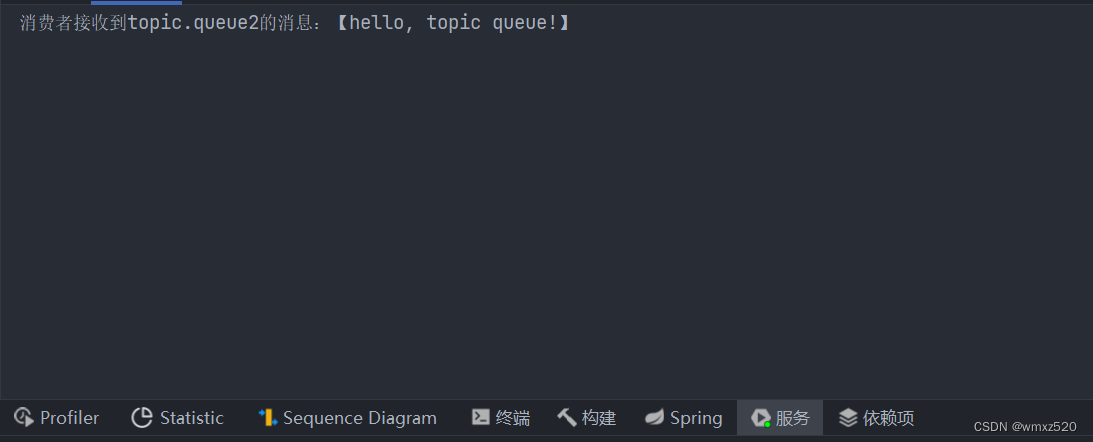
@RabbitListener(bindings = @QueueBinding(value = @Queue(name = "topic.queue1"),exchange = @Exchange(name = "topic", type = ExchangeTypes.TOPIC),key = "china.#"))public void listenTopicQueue1(String msg){System.out.println("消费者接收到topic.queue1的消息:【" + msg + "】");}@RabbitListener(bindings = @QueueBinding(value = @Queue(name = "topic.queue2"),exchange = @Exchange(name = "topic", type = ExchangeTypes.TOPIC),key = "#.news"))public void listenTopicQueue2(String msg){System.out.println("消费者接收到topic.queue2的消息:【" + msg + "】");}
发送消息,需要匹配通配符,这样才能收到消息
// 消息String message = "hello, topic queue!";//交换机名称String exchange = "topic";rabbitTemplate.convertAndSend(exchange, "chiana.news", message);
结果如下:
参考
- Spring AMQP 官方文档
这篇关于MQ之Spring AMQP学习的文章就介绍到这儿,希望我们推荐的文章对编程师们有所帮助!






