本文主要是介绍Linux-MDK can电机带导轨 C++封装,希望对大家解决编程问题提供一定的参考价值,需要的开发者们随着小编来一起学习吧!
我使用的是MKS的52D can电机带导轨,现在我要根据电机说明书将运动指令封装,有一个限位开关, 闭合时高电平
滑块需要运动在限位开关左侧,所以限位归零的方向为顺时针
根据说明书,我要设置的命令应该是:
cansend can0 001#900100004001D3将滑块运动到适当位置,执行限位归零命令 :
cansend can0 001#9192滑块就会回到限位开关的位置了
但是限位归零后,再给电机发送命令它就没有反应了;原因是我设置的归零方向是顺时针,所以电机只能向逆时针方向运动了...这应该是电机问题了,先放一边
我直接用按照脉冲数相对运动封装运动控制
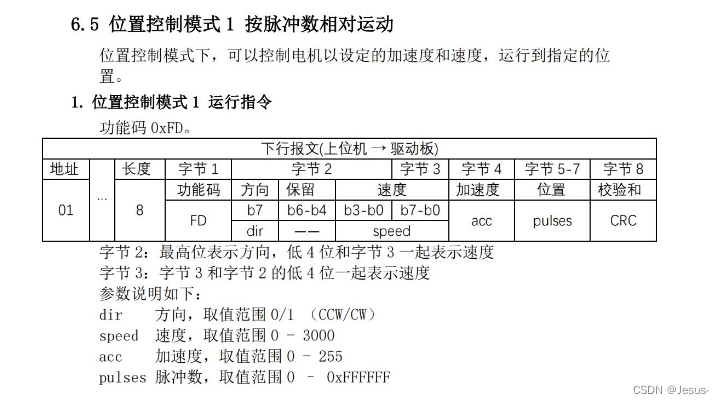
采用C++编写代码
#include <iostream>
#include <sstream>
#include <iomanip>
#include <string>// Function to convert integer to a zero-padded hexadecimal string
std::string intToHex(int value, int width) {std::stringstream stream;stream << std::setfill('0') << std::setw(width) << std::hex << value;return stream.str().substr(0, width); // Ensure the string is of the correct width
}// Function to calculate checksum
std::string calculateChecksum(const std::string &command) {int sum = 1; // Starting with the value of byte 1 (01)for (int i = 0; i < command.length(); i += 2) {std::string byteString = command.substr(i, 2);sum += std::stoi(byteString, nullptr, 16);}return intToHex(sum % 256, 2);
}int main(int argc, char *argv[]) {if (argc != 2) {std::cout << "Usage: " << argv[0] << " <number of rotations>\n";return 1;}const int stepsPerRotation = 16; // Assuming 16 steps per rotation// Convert rotations to steps and then to hexadecimalint rotations = std::stoi(argv[1]);int steps = rotations * stepsPerRotation;std::string stepsHex = intToHex(steps, 4); // Convert steps to 4-character hexadecimal// Construct the CAN commandstd::string command = "FD014002" + stepsHex + "00"; // Assuming the steps need to be placed in the middle// Calculate checksumstd::string checksum = calculateChecksum(command);// Complete CAN commandstd::string canCommand = "cansend can0 001#" + command + checksum;// Print and execute the CAN commandstd::cout << "Executing command: " << canCommand << std::endl;system(canCommand.c_str());return 0;
}执行为可编译文件
g++ test.cpp -o thefirst代码分析
//其功能是将一个整数(int)转换成它的十六进制(hex)字符串表示,并确保字符串的宽度(长度)为指定的宽度。 std::string intToHex(int value, int width) {//创建一个stringstream对象stream。stringstream是C++中一种方便的流类,用于字符串的格式化 操作std::stringstream stream;//std::setfill('0')设置填充字符为'0',std::setw(width)设置字段宽度为width,std::hex设置流的格式为十六进制,最后value是要转换的整数值。stream << std::setfill('0') << std::setw(width) << std::hex << value;//stream.str()将流内容转换为字符串。然后,substr(0, width)函数从这个字符串的开头开始截取长度为width的子字符串。这是为了确保即使生成的字符串长度超过了width,也只返回长度为width的部分。return stream.str().substr(0, width); }//它的功能是计算输入字符串的校验和,具体实现方法是将字符串中的每两个字符视为一个16进制数,然后求和,最后将和转换为两个字符的16进制数。 std::string calculateChecksum(const std::string &command) {int sum = 1; //在指令中001就是电机的ID,不会变for (int i = 0; i < command.length(); i += 2) {//使用substr方法从command中提取两个字符(从索引i开始)。这两个字符被视为一个16进制的字节,并存储在byteString字符串中。std::string byteString = command.substr(i, 2);//将byteString从16进制转换为整数(使用std::stoi函数),并加到sum上。std::stoi函数的第三个参数指定了基数,这里是16,表示输入字符串是16进制的。sum += std::stoi(byteString, nullptr, 16);}return intToHex(sum % 256, 2); }int main(int argc, char *argv[]) {//检查命令行参数的数量。如果不等于2(argc是参数总数,包括程序名),则输出使用说明并返回1,表示错误。if (argc != 2) {std::cout << "Usage: " << argv[0] << " <number of rotations>\n";return 1;}//定义细分步数为16const int stepsPerRotation 16;//将命令行中的第二个参数(旋转次数)转换为整数。int rotations = std::atoi(argv[1]);//计算总步骤数,即旋转次数乘以每次旋转的步骤数。int steps = rotations * stepsPerRotation;//将步骤数转换为4字符长的16进制数。std::string stepsHex = inToHex(steps, 4);//其中FD014002和00是固定的命令部分,stepsHex是可变的部分,表示步骤数std::string command = "FD014002" + stepsHex + "00";//计算检验和std::string checksum = calculateChecksum(command);//组合can命令std::string canCommand = "cansend can0 001#" + command + checksum;std::cout << "Executing command: " << canCommand << std::endl;//使用system函数执行命令。canCommand.c_str()将C++字符串转换为C风格的字符串。system(canCommand.c_str());return 0; }
上面的程序只有旋转次数是可变的,现在修改代码使得速度,加速度,位置都是可变的
#include <iostream>
#include <sstream>
#include <iomanip>
#include <string>
#include <vector>// Function to convert integer to a zero-padded hexadecimal string
std::string intToHex(int value, int width) {std::stringstream stream;stream << std::setfill('0') << std::setw(width) << std::hex << value;return stream.str();
}// Function to calculate checksum
std::string calculateChecksum(const std::vector<int> &bytes_values) {int sum = 0x01 + 0xFD; // Starting sum with the motor ID (01) and function code (FD)for (int value : bytes_values) {sum += value;}return intToHex(sum % 256, 2);
}int main(int argc, char *argv[]) {if (argc != 5) {std::cout << "Usage: " << argv[0] << " <direction (0 for CCW, 1 for CW)> <speed (0-3000)> <acceleration (0-255)> <number of rotations>\n";return 1;}int direction = std::stoi(argv[1]);int speed = std::stoi(argv[2]);int acceleration = std::stoi(argv[3]);int rotations = std::stoi(argv[4]);// Total pulses calculation modified as per the new requirementint totalPulses = rotations * 3200;// Constructing the CAN commandint speedHigh = (speed >> 8) & 0x0F; // Extract high 4 bits of speedif (direction == 0) {speedHigh |= 0x80; // Set high bit for CCW direction}int speedLow = speed & 0xFF; // Low part of the speedstd::vector<int> bytes_values = {speedHigh, speedLow, acceleration, (totalPulses >> 16) & 0xFF, (totalPulses >> 8) & 0xFF, totalPulses & 0xFF};std::string checksum = calculateChecksum(bytes_values);// Combine all parts into the final CAN command with motor ID and function codestd::string canCommand = "cansend can0 001#FD";for (size_t i = 0; i < bytes_values.size(); ++i) {canCommand += intToHex(bytes_values[i], 2);}canCommand += checksum;// Print and execute the CAN commandstd::cout << "Executing command: " << canCommand << std::endl;system(canCommand.c_str());return 0;
}
上面的代码可以实现用户输入方向,速度,加速度,和旋转次数
这篇关于Linux-MDK can电机带导轨 C++封装的文章就介绍到这儿,希望我们推荐的文章对编程师们有所帮助!







