本文主要是介绍ICANN备稿时debug遇到的问题,希望对大家解决编程问题提供一定的参考价值,需要的开发者们随着小编来一起学习吧!
包问题
- 装包:先用fastai
- 出现单击没有跳转的情况:安装pylance即可
- 出现了用
pip3 uninstall后pip3 list还有原来的numpy,然后用conda uninstall之后就行了。pip, pip3, conda这几个来回用。
精度问题
打印tensor数组自动保留后四位:
是精度缩减了吗?其实是因为print访问的为_str_方法打印出来的小数只有四位,用torch.set_printoptions(precision=15)(设置小数精度显示)即可显示原来数据。
visio图片转PDF
overleaf插入去白边的Visio图:
https://www.cnblogs.com/doubleyue/p/15684697.html
如果使用visio,在保存为PDF图片时候点下选项,把打钩的都不选就好了
保存latest和best model函数
def main(if valid_loss < best_loss:is_best = Truebest_epoch = epochbest_prec = min(valid_loss,best_loss)save_checkpoint({'epoch': epoch + 1,'state_dict': model.state_dict(),'best_prec': best_prec,'optimizer': optimizer.state_dict(),}, is_best, fdir)def save_checkpoint(state, is_best, fdir):filepath = os.path.join(fdir, 'checkpoint.pth')torch.save(state, filepath) # latestif is_best: # bestshutil.copyfile(filepath, os.path.join(fdir, 'model_best.pth.tar'))
extra_repr
extra_repr 是 Python 中一种特殊的方法。在 PyTorch 中,它通常用于自定义类的字符串表示形式,特别是在打印对象时。当你使用 print 函数打印一个对象时,Python 会调用该对象的 str 方法来生成可读的字符串表示形式。但是,有时 str 方法可能不够详细或不够清晰,这时可以定义 extra_repr 方法来提供额外的信息。当你使用 print 函数打印对象时,Python 会检查是否定义了 extra_repr 方法,如果定义了,则会使用该方法返回的字符串来丰富对象的字符串表示形式。
return -> str一定要return的是string
例子:
class QuantReLU(nn.ReLU):def __init__(self, inplace: bool = False):super(QuantReLU, self).__init__(inplace)def extra_repr(self) -> str:return 'clipping threshold activation alpha: {:.3f}'.format(self.act_alpha)
当你print(QuantReLU)或者print的model里面含有他时,会输出:
Dummy(
(block): Sequential(
(0): Conv1d(12, 16, kernel_size=(5,), stride=(3,))
(1): QuantReLU(clipping threshold activation alpha: 7.832)
)
)
关于torch.size():
1.相加操作要掌握
import torchsize1 = torch.Size([3, 4])
size2 = torch.Size([5, 6, 7])# 将 size1 和 size2 进行相加操作
result_size = size1 + size2print(result_size) # 输出: torch.Size([3, 4, 5, 6, 7])
2..shape返回的是torch.size()类型。
综合上述两点就可以写出以下代码:
spike_train = torch.zeros(membrane.shape[:1] + torch.Size([self.T]) + membrane.shape[1:],device=membrane.device)
state_dict
model.state_dict() 返回的是模型的参数字典,其中键是参数的名称,值是参数的张量
state_dict.pop(k) 是 Python 字典(dictionary)的一个方法,用于移除字典中键为 k 的项,并返回该项的值。
for key in checkpoint:print(key, checkpoint[key].shape)
for key in model.state_dict():print(key, model.state_dict()[key].size() or .shape)# 在 PyTorch 中,.size() 和 .shape 是等价的,两者都可以用于获取张量的形状信息。#conv1.weight torch.Size([6, 3, 5, 5])
#conv1.bias torch.Size([6])
原来是用的relu.thresh
要改成relu.up
keys = list(checkpoint.keys())
for key in keys:if 'thresh' in key:checkpoint[key[:-6] + 'up'] = checkpoint.pop(key)
state_dict.pop(k) 是 Python 字典(dictionary)的一个方法,用于移除字典中键为 k 的项,并返回该项的值。
由于在 Python 中字典的迭代器在遍历时不允许修改字典的结构,所以必须用keys来作为迭代。
例子二:
#Remove DataParallel wrapper 'module'
for name in list(checkpoint['state_dict'].keys()):checkpoint['state_dict'][name[7:]] = checkpoint['state_dict'].pop(name)
torch.optim模块中的Optimizer优化器对象也存在一个state_dict对象,此处的state_dict字典对象包含state和param_groups的字典对象
for var_name in optimizer.state_dict():print(var_name,'\t',optimizer.state_dict()[var_name])
输出:
state {}
param_groups [{'lr': 0.001, 'momentum': 0.9, 'dampening': 0, 'weight_decay': 0, 'nesterov': False, 'params': [367949288, 367949432, 376459056, 381121808, 381121952, 381122024, 381121880, 381122168, 381122096, 381122312]}]
网络,对不同网络层的操作
虽然表面上是说对网络以及网络层的操作,但本质上是对象和索引对象属性的问题。
有一些内置函数用来索引到对象属性:
内置函数: getattr(), setattr()
value = getattr(obj, 'attr')
setattr(obj, 'attr', 42)
e.g.: 用于遍历索引到对象属性。
for i in range(2, num_layers + 1):getattr(model, 'layer' + str(i)).idem = Truegetattr(snn, 'layer' + str(i)).idem = True
当没有sequential时:
print(net.fc2)
有sequential时:
print(net.fc[2])
梯度
torch.clamp是有梯度的,只有round函数需要单独考虑梯度(即写backward function)
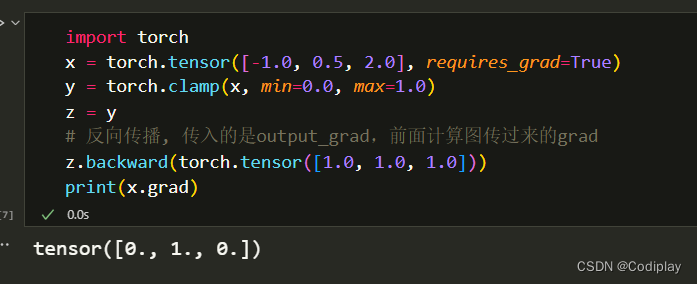
round的梯度是和clip一样的。他俩都是treats the quantization and de-quantization function as if it were identity function in the clipping range and constant function outside the clipping range.
grad只要不低到0都是可以的,1e-4,1e-5,也会更新。lr * grad
alpha_new = alpha_old - learning_rate * grad_alpha
Bug
因为不懂optimizer原理犯的错误:
optimizer一定要在model settled 好之后再调用,因为有model.parameters()作为参数
这下对整个梯度的从开始到更新一轮应该比较了解了:
final_model #需要梯度的用parameter或tensor(require_grad)
optimizer = optim.Adam(final_model.parameters(), lr=0.0001)
model.train()
optimizer.zero_grad() #把optimizer存的grad清空
loss.backward() # 根据模型输出的损失值计算梯度。它会自动地沿着网络的参数计算梯度,并将梯度存储在参数的.grad属性中
nn.utils.clip_grad_norm_(model.parameters(), max_norm=10) # 会计算所有参数的梯度的范数,并根据指定的max_norm进行裁剪
optimizer.step() # 这一步是利用优化器来更新模型的参数。优化器根据梯度和指定的优化算法(如SGD、Adam等)来更新模型参数。它会使用loss.backward()计算得到的梯度来更新模型参数,通常使用学习率和其他超参数来控制更新的步长和方向。
优化器在训练过程中会存储并使用梯度来更新模型参数。每次调用optimizer.step()时,优化器会使用之前存储的梯度信息来更新模型参数。
0-d tensor 就是 scalar,不能输出他的shape
UserWarning: Detected call of lr_scheduler.step() before optimizer.step().
#scheduler.step() 不要放在这
train_acc, trian_loss= train_one_epoch(args, model, dset, optimizer, data_loader, epoch)
scheduler.step()
Loss
分类问题就无脑CE,比MSE要好。
nn.CrossEntropyLoss()=nn.LogSoftmax()+nn.NLLLoss().
optimizer
要手动将load下来的参数放到GPU上。
optimizer.load_state_dict(checkpoint['optimizer'])
for state in optimizer.state.values():for k, v in state.items():if isinstance(v, torch.Tensor):state[k] = v.cuda()
许愿第一次论文
这篇关于ICANN备稿时debug遇到的问题的文章就介绍到这儿,希望我们推荐的文章对编程师们有所帮助!







