本文主要是介绍USB - USB Gadget on Linux,希望对大家解决编程问题提供一定的参考价值,需要的开发者们随着小编来一起学习吧!
February, 2012. Embedded Linux Conference 2012.
Agenda
- Introduction to USB
- USB Gadget API
- Existing Gadgets
- Design your own Gadget
- Demo
- Conclusio
About the Author
Software engineer at Adeneo Embedded
- Linux, Android
- Main activities:
– BSP adaptation
– Driver development
– System integration
Context and objectives
General knowledge of the API
- Focused on USB not general driver development
- Nothing on the host side
Case study
- Using a generic embedded device, see how we cancreate a USB Gadget
Show potential
- How to fulfill every need
Universal Serial Bus

- Industry standard developed in the mid-1990s
- Defines the cables, connectors and protocols used forconnection, communication and power supplybetween computers and electronic devices
- 2 billion USB devices were sold each year (as of 2008)
Benefits:
- Replace lots of old buses
- Automatic configuration
- Multiple speeds
- Reliable
Limits:
- Distance
- Peer-To-Peer
- Broadcasting
Architecture:
- Master-Slave protocol
- Up to 127 devices addressable
- Can be hot-plugged
- Identification to the host
- Supports high speeds
- Supports high speeds
Description:
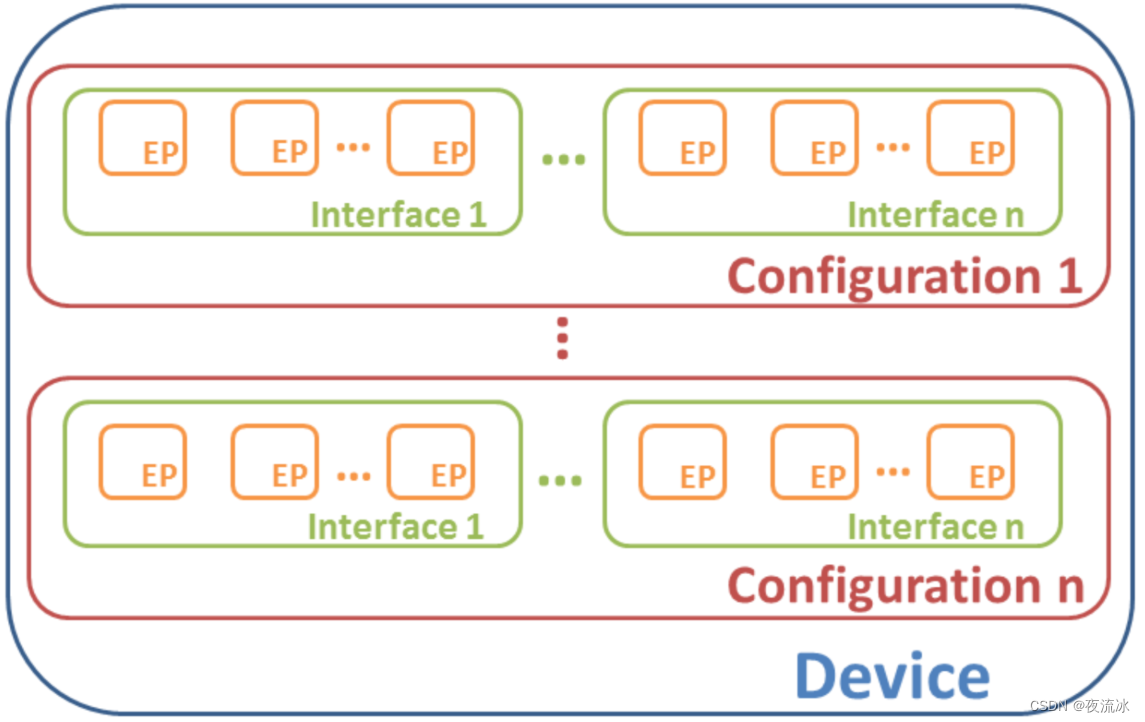
Endpoints
- Source and Sink of data
- Uniquely identifiable
- Unique direction (except setup)
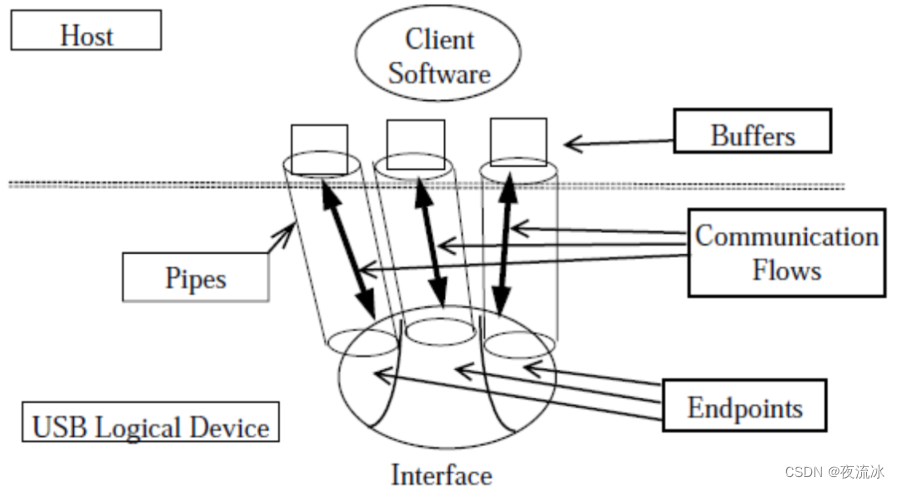
4 transfer types:
- ControlConfiguration and control information
- InterruptSmall quantities time-sensitive data
- BulkLarge quantities time-insensitive data
- IsochronousReal-time data at predictable bit rates
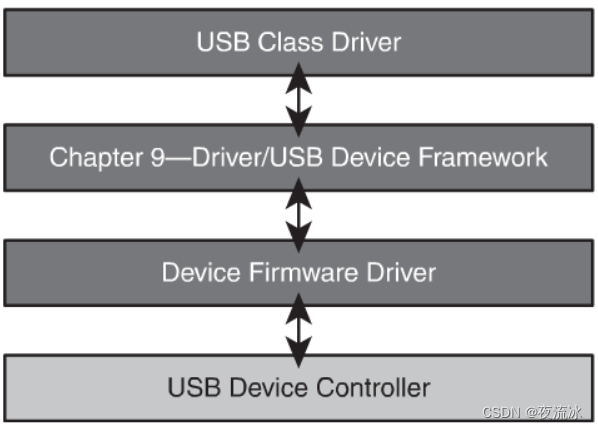
Typical Device Driver
- Device Firmware Driver
- Hardware specific routines
- USB interrupts/events
-
- Chapter 9
- Enumeration process
- Transfer data to upper layer
-
- USB Class Driver
- Defines the behavior
- Provides configuration
-
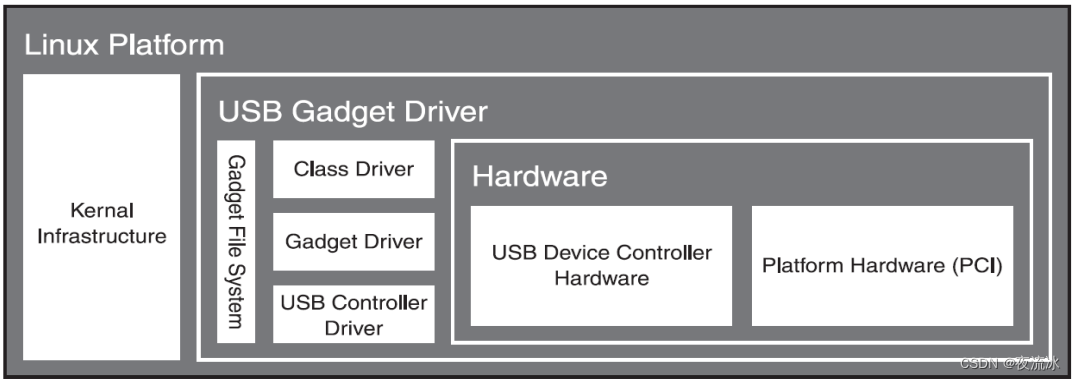
Gadget API
- Provides essential infrastructure
- Similar to Chapter 9 in typical USB device software
- Handles USB protocol specific requirements
- Flexible enough to expose more complex USB devicecapabilities
Gadget API vs. Linux-USB API
- Similarities
- Share common definitions for the standard USB messages,structures and constants
- Use queues of request objects to package I/O buffers
- Both APIs bind and unbind drivers to devices
-
- Differences
- Control transfers
- Configuration management
-
=> Thanks to similarities, Gadget API supports OTG
Gadget API
Lower boundary:
- handling setup requests (ep0 protocol responses)possibly including class-specific functionality
- returning configuration and string descriptors
- (re)setting configurations and interface alternate settings, including enabling and configuring endpoints
- handling life cycle events, such as managing bindingsto hardware, USB suspend/resume, remote wakeup,and disconnection from the USB host
- managing IN and OUT transfers on all currentlyenabled endpoints
Upper layer:
- user mode code, using generic (gadgetfs) or applicationspecific files in /dev
- networking subsystem (for network gadgets, like theCDC Ethernet Model gadget driver)
- data capture drivers, perhaps video4Linux or a scannerdriver; or test and measurement hardware
- input subsystem (for HID gadgets)
- sound subsystem (for audio gadgets)
- file system (for PTP gadgets)
- block i/o subsystem (for usb-storage gadgets)
Gadget API – Main structures
struct usb_gadget – represents a gadget device
> usb_gadget_ops – contains callbacks for hardware operations
struct usb_ep – device hardware management
> usb_ep_ops – contains callbacks for endpoints operations
struct usb_gadget_driver – device functions management (bind, unbind, suspend etc...)
struct usb_request – USB transfers management
Gadget API – Main functions
General operations (usb_gadget_x()):
- probe_driver / unregister_driver
- set_selfpowered / clear_selfpowered
- vbus_connect / vbus_disconnect
- connect / disconnect
- frame_number
Endpoint operations (usb_ep_x()):
- autoconf / autoconf_reset
- enable / disable
- alloc / free
- queue / dequeue
- set_halt / clear_halt
- fifo_status / fifo_flush
Descriptor operations:
- usb_descriptor_fillbuf
- usb_gadget_config_buf
Gadget API
Driver life cycle:
- Register driver for a particular device controller
- Register gadget driver (bind)
- Hardware powered, enumeration starts
- Gadget driver returns descriptors (setup)
- Gadget driver returns interfaces configuration
- Do real work (data transfer) until disconnect
- Gadget driver unloaded (unbind)
Existing Gadgets
Ethernet
- Enumerate to the host as an Ethernet device
- Can easily be bridging, routing, or firewalling access to other networks
- Interoperability with hosts running Linux, MS Windows among others
- Possibility to set parameters such as MAC address,IP configuration or DHCP use thanks to the bootargs if using a boot firmware like U-Boot
GadgetFS
- Provides User-Mode API
- Each endpoint presented as single I/O file descriptor
- Normal read() and write() calls
- Async I/O supported
- Configuration and descriptors written into files
Note that user mode gadget drivers do not neccesarily need to be licensed according to the GPL.
File-backed Storage
- Implements the USB Mass Storage Class
- Up to 8 disk drives can be set
- Store file or block device is called the “backing storage”
- Backing storage requires preparation
- If a file is used, it must created with its desired size before launching the driver
- If a block device, it must match host requirements (DOS partition for MS-Windows host)
-
- The backing storage must not change while FBS is running, only the host should access it
Webcam
- Acts as a composite USB Audio and Video Class device
- Provides a user space API to process UVC control requests and stream video data
Serial Gadget
- Useful for TTY style operation
- Supports a CDC-ACM module option
MIDI
- Exposes an ALSA MIDI interface
- Both recording and playback support
GadgetZero
- Useful to test device controller driver
- Helps verify that the driver stack pass USB-IF (forUSB branding)
- On the host side, useful to test USB stack
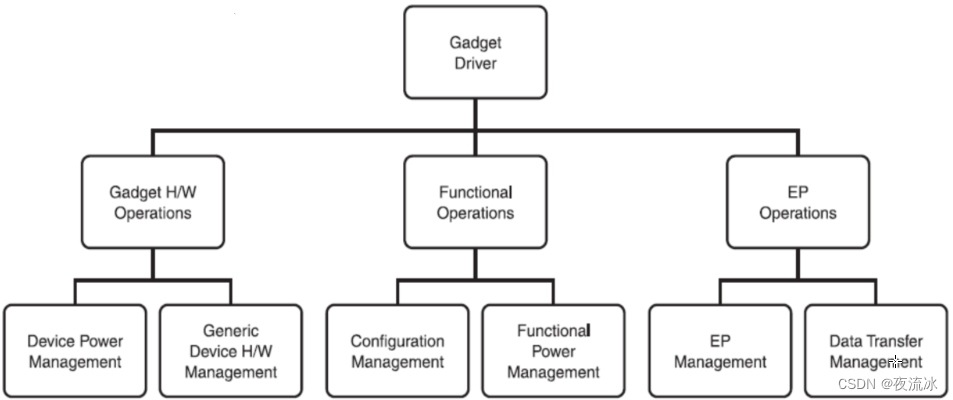
Design your own Gadget
3 main operations to consider
- Hardware
- Functional
- Endpoints
- First implement the register/unregister functions
- usb_gadget_probe_driver
- Resgistration of the usb_gadget_driver
- Responsible for binding the gadget driver and powering upthe device
-
- usb_gadget_unregister_driver
- Responsible for unbinding the gadget from the functionaldriver and powering down the device
-
-
- Then define callbacks hardware related
- Fill usb_ep_ops and usb_gadget_ops
- Not necessary to support all functions
-
- Implement the control request handles (ep0)
- Gadget driver handles only a part of it
- The rest is routed to the class driver
-

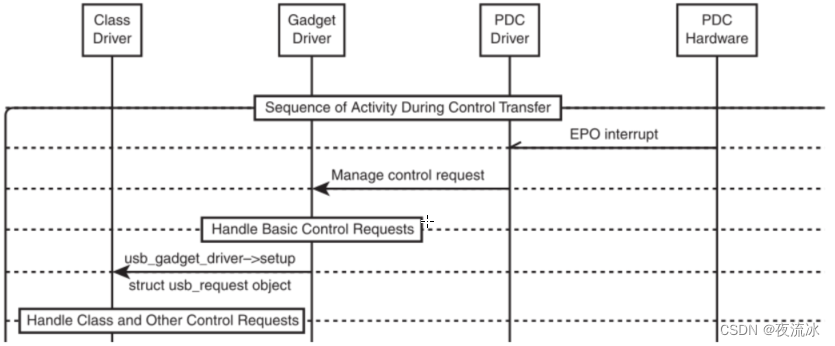
- Power Management requests
- Comes from the PDC to the Gadget
- The Gadget must pass the events to the class driver
-
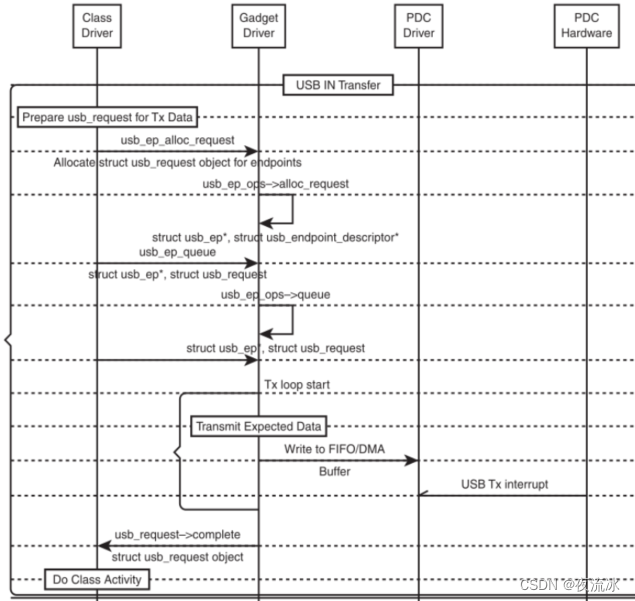
- Once enumeration is done, class driver requests usb_request structure for IN/OUT transfers
- Gadget receives data in interrupt routine (OUT)
- Only when the expected amount is received the Gadgetcalls the complete function
-
- Gadget sends data to the PDC (IN)
- Wait send completion to inform the class driver
-
-
Demo: Hardware
BeagleBoard xM
- ARM™ Cortex™-A8 1000 MHz
- USB connectivity:
- 4 host ports
- 1 OTG port (used as device)
-

Demo: Software
- Bootloader
- U-boot 2011.12 r4
-
- Kernel
- 3.0.17 r115c
-
- Root filesystem
- Console image
- Custom recipe (lighttpd)
-
- Additional modules
-
Conclusion
- Easy to implement
- Hardware independent
- Scalability
- Large panel of existing gadgets
- Awareness of limitations
Appendix: References
- Linux-USB Gadget API Framework: Generalpresentation.Linux-USB Gadget API Framework
- USB Gadget API for Linux: Full description of the API.https://archive.kernel.org/oldlinux/htmldocs/gadget/index.html
- Essential Linux Device Drivers (SreekrishnanVenkateswaran) : General device driver bookcontaining a useful USB section.
- Bootstrap Yourself with Linux-USB Stack (RajaramRegupathy): Very detailed and easy-to-read book aboutLinux-USB.
Other resources
- USB Raw Gadget — The Linux Kernel documentation
- USB Gadget API for Linux — The Linux Kernel documentation (Current newest version docs)
参考:
1, eLinux
https://elinux.org/images/8/81/Useful_USB_Gadgets_on_Linux.pdf
这篇关于USB - USB Gadget on Linux的文章就介绍到这儿,希望我们推荐的文章对编程师们有所帮助!







