本文主要是介绍Java“树结构TreeNode”用法详解,二叉树用法实现代码!!!,希望对大家解决编程问题提供一定的参考价值,需要的开发者们随着小编来一起学习吧!
一、TreeNode用法
在Java中,TreeNode通常用于表示树结构中的节点。在树结构中,每个节点可以有零个或多个子节点,而TreeNode就是这个树结构中的一个节点。通常,树结构是通过链式结构实现的,每个节点有指向其子节点的引用。
下面是一个简单的示例,展示了如何定义一个简单的TreeNode类以及如何使用它:
// TreeNode 类表示二叉树中的一个节点
class TreeNode {int val; // 节点的值TreeNode left; // 左子节点TreeNode right; // 右子节点// 构造函数TreeNode(int x) {val = x;}
}public class BinaryTreeExample {// 二叉树的根节点private TreeNode root;// 构造函数public BinaryTreeExample() {root = null;}// 插入节点public void insert(int value) {root = insertRec(root, value);}// 递归方法插入节点private TreeNode insertRec(TreeNode root, int value) {// 如果树为空,则创建一个新节点作为根节点if (root == null) {root = new TreeNode(value);return root;}// 否则,向左或向右递归地插入节点if (value < root.val) {root.left = insertRec(root.left, value);} else if (value > root.val) {root.right = insertRec(root.right, value);}// 返回根节点return root;}public static void main(String[] args) {BinaryTreeExample tree = new BinaryTreeExample();// 插入节点tree.insert(50);tree.insert(30);tree.insert(20);tree.insert(40);tree.insert(70);tree.insert(60);tree.insert(80);}
}
在这个示例中,我们定义了一个 BinaryTreeExample 类来表示一个二叉排序树,其中包含了 TreeNode 类来表示二叉树的节点。我们实现了插入节点的方法 insert()。然后,在 main 方法中创建了一个二叉树实例,并插入了一些节点。
向二叉搜索树中插入节点的递归方法 insertRec()理解过程
首先,让我们假设有一个空树,然后开始向树中插入节点。我们将以插入值为50、30、20、40、70、60、80的顺序进行演示。
插入节点 50:由于树为空,因此将节点 50 插入为根节点。
50插入节点 30:因为根节点的值为 50,且 30 小于 50,所以我们将节点 30 插入根节点的左子树。
50/30插入节点 20:因为根节点的值为 50,且 20 小于 50,所以我们继续向左子树插入节点 20小于30,则在30的左子树插入节点20。
50/30/ 20插入节点 40:因为根节点的值为 50,且 40 小于 50,所以我们向50的左子树插入,40>30故在30的右子树插入节点 40。
50/30/ \ 20 40插入节点 70:因为根节点的值为 50,且 70 大于 50,所以我们将节点 70 插入根节点的右子树。
50/ \30 70/ \ 20 40插入节点 60:因为根节点的值为 50,且 60 大于50小于 70,所以我们向右子树的左子树插入节点 60。
50/ \30 70/ \ / 20 40 60插入节点 80:因为根节点的值为 50,且 80 大于 70,所以我们继续向右子树插入节点 80。
50/ \30 70/ \ / \ 20 40 60 80
注意啊!!!树结构基本都要用到递归 ,所以一定要好好理解递归算法。
二、二叉树的先,中,后序遍历
// TreeNode 类表示二叉树中的一个节点
class TreeNode {int val; // 节点的值TreeNode left; // 左子节点TreeNode right; // 右子节点// 构造函数TreeNode(int x) {val = x;}
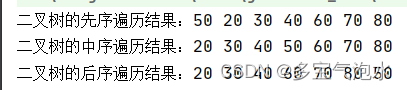
}public class BinaryTreeExample {// 二叉树的根节点private TreeNode root;// 构造函数public BinaryTreeExample() {root = null;}// 插入节点public void insert(int value) {root = insertRec(root, value);}// 递归方法插入节点private TreeNode insertRec(TreeNode root, int value) {// 如果树为空,则创建一个新节点作为根节点if (root == null) {root = new TreeNode(value);return root;}// 否则,向左或向右递归地插入节点if (value < root.val) {root.left = insertRec(root.left, value);} else if (value > root.val) {root.right = insertRec(root.right, value);}// 返回根节点return root;}// 先序遍历二叉树public void firstorderTraversal(TreeNode root) {if (root != null) {System.out.print(root.val + " ");inorderTraversal(root.left);inorderTraversal(root.right);}}// 中序遍历二叉树public void inorderTraversal(TreeNode root) {if (root != null) {inorderTraversal(root.left);System.out.print(root.val + " ");inorderTraversal(root.right);}}// 后序遍历二叉树public void postorderTraversal(TreeNode root) {if (root != null) {inorderTraversal(root.left);inorderTraversal(root.right);System.out.print(root.val + " ");}}public static void main(String[] args) {BinaryTreeExample tree = new BinaryTreeExample();// 插入节点tree.insert(50);tree.insert(30);tree.insert(20);tree.insert(40);tree.insert(70);tree.insert(60);tree.insert(80);// 先序遍历二叉树System.out.print("二叉树的先序遍历结果:");tree.firstorderTraversal(tree.root);System.out.println();// 中序遍历二叉树System.out.print("二叉树的中序遍历结果:");tree.inorderTraversal(tree.root);System.out.println();// 后序遍历二叉树System.out.print("二叉树的后序遍历结果:");tree.postorderTraversal(tree.root);System.out.println();}
}
三、二叉树层序遍历
层序遍历是一种广度优先搜索(BFS)的方法,它从根节点开始逐层遍历二叉树,先遍历完一层节点,再遍历下一层节点,直到遍历完整棵树。在层序遍历中,我们通常使用队列来辅助实现。
关于在Java中如何使用队列,待我更新一篇…… (可关注我主页,如果我忘了踢踢我~)
import java.util.LinkedList;
import java.util.Queue;class TreeNode {int val;TreeNode left;TreeNode right;// 构造函数public TreeNode(int val) {this.val = val;}
}public class BinaryTreeExample {// 二叉树的根节点private TreeNode root;// 构造函数public BinaryTreeExample() {root = null;}// 插入节点public void insert(int value) {root = insertRec(root, value);}// 递归方法插入节点private TreeNode insertRec(TreeNode root, int value) {// 如果树为空,则创建一个新节点作为根节点if (root == null) {root = new TreeNode(value);return root;}// 否则,向左或向右递归地插入节点if (value < root.val) {root.left = insertRec(root.left, value);} else if (value > root.val) {root.right = insertRec(root.right, value);}// 返回根节点return root;}// 层序遍历二叉树public void levelOrderTraversal(TreeNode root) {if (root == null)return;// 创建一个队列用于辅助层序遍历Queue<TreeNode> queue = new LinkedList<>();queue.offer(root);while (!queue.isEmpty()) {TreeNode node = queue.poll();System.out.print(node.val + " ");if (node.left != null)queue.offer(node.left);if (node.right != null)queue.offer(node.right);}}public static void main(String[] args) {BinaryTreeExample tree = new BinaryTreeExample();// 插入节点tree.insert(50);tree.insert(30);tree.insert(20);tree.insert(40);tree.insert(70);tree.insert(60);tree.insert(80);// 层序遍历二叉树System.out.println("二叉树的层序遍历结果:");tree.levelOrderTraversal(tree.root);}
}
四、根据所给遍历顺序构造二叉树
如果给出二叉树的先序遍历和中序遍历或者给出二叉树的后序遍历和中序遍历都能唯一的确定一颗二叉树,但是若是给出先序遍历和后序遍历则无法唯一的确定一颗二叉树。
以下示例是根据先序遍历和中序遍历构造的二叉树:
import java.util.HashMap;class TreeNode {int val;TreeNode left;TreeNode right;// 构造函数public TreeNode(int val) {this.val = val;}
}public class BinaryTreeBuilder {// 构建二叉树public TreeNode buildTree(int[] preorder, int[] inorder) {// 使用 HashMap 存储中序遍历结果中每个节点的索引HashMap<Integer, Integer> map = new HashMap<>();for (int i = 0; i < inorder.length; i++) {map.put(inorder[i], i);}// 调用递归函数构建二叉树return buildTreeHelper(preorder, 0, preorder.length - 1, inorder, 0, inorder.length - 1, map);}// 递归函数构建二叉树private TreeNode buildTreeHelper(int[] preorder, int preStart, int preEnd, int[] inorder, int inStart, int inEnd, HashMap<Integer, Integer> map) {// 如果先序遍历的起始索引大于结束索引,则表示子树为空,返回 nullif (preStart > preEnd) {return null;}// 获取根节点的值int rootVal = preorder[preStart];TreeNode root = new TreeNode(rootVal);// 获取根节点在中序遍历结果中的位置int index = map.get(rootVal);// 计算左子树的长度int leftTreeSize = index - inStart;// 递归构建左子树和右子树root.left = buildTreeHelper(preorder, preStart + 1, preStart + leftTreeSize, inorder, inStart, index - 1, map);root.right = buildTreeHelper(preorder, preStart + leftTreeSize + 1, preEnd, inorder, index + 1, inEnd, map);return root;}// 中序遍历二叉树(用于验证结果)public void inorderTraversal(TreeNode root) {if (root != null) {inorderTraversal(root.left);System.out.print(root.val + " ");inorderTraversal(root.right);}}public static void main(String[] args) {int[] preorder = {3, 9, 20, 15, 7};int[] inorder = {9, 3, 15, 20, 7};BinaryTreeBuilder builder = new BinaryTreeBuilder();TreeNode root = builder.buildTree(preorder, inorder);System.out.println("构建的二叉树中序遍历结果:");builder.inorderTraversal(root);}
}
以下示例是根据后序遍历和中序遍历构造的二叉树:
import java.util.HashMap;class TreeNode {int val;TreeNode left;TreeNode right;// 构造函数public TreeNode(int val) {this.val = val;}
}public class ConstructBinaryTree {// 构造二叉树public TreeNode buildTree(int[] inorder, int[] postorder) {// 使用HashMap存储中序遍历结果中每个节点的索引HashMap<Integer, Integer> map = new HashMap<>();for (int i = 0; i < inorder.length; i++) {map.put(inorder[i], i);}// 调用递归函数构建二叉树return buildTreeHelper(inorder, 0, inorder.length - 1, postorder, 0, postorder.length - 1, map);}// 递归函数构建二叉树private TreeNode buildTreeHelper(int[] inorder, int inStart, int inEnd, int[] postorder, int postStart, int postEnd, HashMap<Integer, Integer> map) {// 如果中序遍历的起始索引大于结束索引,则表示子树为空,返回 nullif (inStart > inEnd || postStart > postEnd) {return null;}// 获取根节点的值int rootVal = postorder[postEnd];TreeNode root = new TreeNode(rootVal);// 获取根节点在中序遍历结果中的位置int index = map.get(rootVal);// 递归构建左子树和右子树root.left = buildTreeHelper(inorder, inStart, index - 1, postorder, postStart, postStart + index - inStart - 1, map);root.right = buildTreeHelper(inorder, index + 1, inEnd, postorder, postStart + index - inStart, postEnd - 1, map);return root;}// 中序遍历二叉树(用于验证)public void inorderTraversal(TreeNode root) {if (root != null) {inorderTraversal(root.left);System.out.print(root.val + " ");inorderTraversal(root.right);}}public static void main(String[] args) {ConstructBinaryTree solution = new ConstructBinaryTree();int[] inorder = {4, 2, 5, 1, 3};int[] postorder = {4, 5, 2, 3, 1};// 构建二叉树TreeNode root = solution.buildTree(inorder, postorder);// 验证中序遍历结果System.out.println("中序遍历结果:");solution.inorderTraversal(root);}
}
五、二叉树找某一节点的父节点
在二叉树中,要找到一个节点的父节点,需要从根节点开始向下遍历,直到找到该节点。具体方法如下:
- 从根节点开始,递归地向下遍历二叉树。
- 如果当前节点的左子节点或右子节点等于目标节点,则当前节点就是目标节点的父节点。
- 如果目标节点不是根节点,并且当前节点不是叶子节点,则继续递归地向下遍历左子树和右子树,直到找到目标节点。
以下是一个示例的 Java 代码,演示了如何找到二叉树中某个节点的父节点:
class TreeNode {int val;TreeNode left;TreeNode right;// 构造函数public TreeNode(int val) {this.val = val;}
}public class BinaryTree {// 找到节点的父节点public TreeNode findParent(TreeNode root, TreeNode target) {// 如果根节点为空或者目标节点为根节点,则返回 nullif (root == null || root == target) {return null;}// 如果目标节点是当前节点的左子节点或右子节点,则返回当前节点if (root.left == target || root.right == target) {return root;}// 递归在左子树中寻找目标节点的父节点TreeNode leftParent = findParent(root.left, target);// 如果在左子树中找到了,则直接返回结果if (leftParent != null) {return leftParent;}// 递归在右子树中寻找目标节点的父节点TreeNode rightParent = findParent(root.right, target);// 如果在右子树中找到了,则直接返回结果if (rightParent != null) {return rightParent;}// 如果左右子树都没有找到,则返回 nullreturn null;}public static void main(String[] args) {BinaryTree tree = new BinaryTree();// 构建二叉树TreeNode root = new TreeNode(1);root.left = new TreeNode(2);root.right = new TreeNode(3);root.left.left = new TreeNode(4);root.left.right = new TreeNode(5);root.right.left = new TreeNode(6);root.right.right = new TreeNode(7);// 找到目标节点TreeNode target = root.left.right;// 找到目标节点的父节点TreeNode parent = tree.findParent(root, target);if (parent != null) {System.out.println("节点 " + target.val + " 的父节点是 " + parent.val);} else {System.out.println("节点 " + target.val + " 没有父节点");}}
}
这篇关于Java“树结构TreeNode”用法详解,二叉树用法实现代码!!!的文章就介绍到这儿,希望我们推荐的文章对编程师们有所帮助!


