本文主要是介绍Mint_21.3 drawing-area和goocanvas的FB笔记(六),希望对大家解决编程问题提供一定的参考价值,需要的开发者们随着小编来一起学习吧!
FreeBASIC gfx 基本 graphics 绘图
一、旧故事
DOS时代PC技术将各类硬插卡限制在 640K到1MB的空间范围内,BIOS负责在相关位置写读测试卡的存在,那时期的Color Video在0xB800,Monochrome Video在0xB000,这是显卡的内存地址,字符方式下通常用2个byte共16位显示一个字符,首字节是ASCII值,另外一个字节(8BIT)为属性字节,高4位表示背景色、低4位表示前景色。因为用4位颜色表示,0xF种色彩就是16种颜色,编号 0 - 15。
QuickBASIC示例 - 白字蓝底:
Color 15, 1: Locate 12, 32: Print "Hello World!"

二、FreeBASIC进化
随着视窗的发展,一些复杂的内存管理交给了CPU处理,不再是原来与卡密切相关的固定显存地址,取而代之的是可大可小的窗口。FreeBASIC保留了原有的13种显示模式,同时增加到了21种,达到1280x1024, 160列x128行,256K颜色。

除此之外,继续演进,增加了screenres 指令,可以任意定义窗口尺寸,比如: screenres 1920, 1080, 32, 5, 0, 0 或简写为 screenres 1920, 1080, 32 , 其它参数均为 default 值。它创建一个 1920x1080像素的屏幕(不是实际意义上的屏幕,但仍称其为screen,是个绘图用的surface而已),用32位颜色,5个页面(一个活动可见页面,其它的在内存中不可见,考贝到可见页即可见), 接着的0表示全屏或显示驱动的选择。由于相关定义变得复杂,此时编程需使用 gfxlib 支持。
三、屏幕变为窗口后的编程
1、示例一:屏幕变为窗口
screen 9是640x480标准模式。过去,设置完屏幕方式后即可print或line绘图; 现在,它是一个窗口,因此,可以设置它的标题 WindowTitle "FreeBASIC example program",还可加一句非常简便的无限等待 sleep 语句,直到有按键动作时退出。
Locate 和 Line 都是传统 QBasic 使用的绘图语句。
'' examples/manual/gfx/windowtitle.bas
''
'' Example extracted from the FreeBASIC Manual
'' from topic 'WINDOWTITLE'
''
'' See Also: https://www.freebasic.net/wiki/wikka.php?wakka=KeyPgWindowtitle
'' --------
'' Modified: Mongnewer 9, March 2024'Set screen mode
Screen 9'Set the window title
WindowTitle "FreeBASIC example program"Locate 12, 35: Print "Hello World!"
line (200, 100) - (440, 220), 4, bSleep
2、绘图锁定与缩放
在屏幕绘图前先 screenlock, 绘图后 screenunlock, 并通过 window 函数改变座标系而circle本身的参数则无需变化。屏幕上显示一个连续缩放的黄色填充的圆形,锁定的目的是绘图完成后一次性显示到屏幕上,避免了绘制过程的拖慢效果。
'' examples/manual/gfx/window2.bas
''
'' Example extracted from the FreeBASIC Manual
'' from topic 'WINDOW'
''
'' See Also: https://www.freebasic.net/wiki/wikka.php?wakka=KeyPgWindow
'' --------'' The program shows how changing the view coordinates mapping for the current viewport changes the size of a figure drawn on the screen.
'' The effect is one of zooming in and out:
'' - As the viewport coordinates get smaller, the figure appears larger on the screen, until parts of it are finally clipped,
'' because they lie outside the window.
'' - As the viewport coordinates get larger, the figure appears smaller on the screen.
'' ---------------------------------
'' Modified: Mongnewer 9, March 2024Declare Sub Zoom (ByVal X As Integer)
Dim As Integer X = 500, Xdelta = 50Screen 12
DoDo While X < 525 And X > 50X += Xdelta '' Change window size.Zoom(X)If Inkey <> "" Then Exit Do, Do '' Stop if key pressed.Sleep 100LoopX -= XdeltaXdelta *= -1 '' Reverse size change.
LoopSub Zoom (ByVal X As Integer)Window (-X,-X)-(X,X) '' Define new window.ScreenLockClsCircle (0,0), 60, 14, , , 0.7, F '' Draw ellipse with x-radius 60.ScreenUnlock
End Sub

3 、view and window, draw string
view 是在screen窗口中创建视图区,而window 语句是视图区的新座标系、不带参数时取消所建立的座标系,Draw string 与 print 类似但又不同, 它不同按行显示字符串,是按 x, y 位置绘制字符串。
'' examples/manual/gfx/window.bas
''
'' Example extracted from the FreeBASIC Manual
'' from topic 'WINDOW'
''
'' See Also: https://www.freebasic.net/wiki/wikka.php?wakka=KeyPgWindow
'' --------Screen 13'' define clipping area
View ( 10, 10 ) - ( 310, 150 ), 1, 15 '' set view coordinates
Window ( -1, -1 ) - ( 1, 1 ) '' Draw X axis
Line (-1,0)-(1,0),7
Draw String ( 0.8, -0.1 ), "X"'' Draw Y axis
Line (0,-1)-(0,1),7
Draw String ( 0.1, 0.8 ), "Y"Dim As Single x, y, s'' compute step size (corresponds to a step of 1 pixel on x coordinate)
s = 2 / PMap( 1, 0 )'' plot the function
For x = -1 To 1 Step sy = x ^ 3PSet( x, y ), 14
Next x'' revert to screen coordinates
Window'' remove the clipping area
View'' draw title
Draw String ( 120, 160 ), "Y = X ^ 3"Sleep

4、在内存中绘像素后显示在屏幕窗口
image pixel , 简写 ip,ip = ImageCreate(64, 64),在内存中创建一个64x64像素的像素块,ip是它的指针。
QBasic原有的PSet后面带上参数 ip, 表示在 ip 内存块pset像素点
screensync 是等待场同步信号,在换场的间隙中把图显示在屏幕窗口上,从而最大限度地减小抖动发生(这个语句的受限点是变换速度被限定在了场频之内),在等待场同步时screenlock后绘图,绘好后screenunlock,将图显示到屏幕上,最后要imagedestroy(ip)销毁创建的像素块。因为在蓝框内有个view, 在view中显示的像素块。
'' examples/manual/gfx/view.bas
''
'' Example extracted from the FreeBASIC Manual
'' from topic 'VIEW (GRAPHICS)'
''
'' See Also: https://www.freebasic.net/wiki/wikka.php?wakka=KeyPgViewgraphics
'' --------Screen 12
Dim ip As Any Ptr
Dim As Integer x, y'simple sprite
ip = ImageCreate(64,64)
For y = 0 To 63For x = 0 To 63PSet ip, (x, y), (x\4) Xor (y\4)Next x
Next y'viewport with blue border
Line (215,135)-(425,345), 1, bf
View (220,140)-(420,340)'move sprite around the viewport
Dox = 100*Sin(Timer*2.0)+50y = 100*Sin(Timer*2.7)+50ScreenSyncScreenLock'clear viewport and put imageCls 1Put (x, y), ip, PSetScreenUnlockLoop While Inkey = ""ImageDestroy(ip)

5、显示内存的考贝
screenres 创建屏幕窗口。screenset 1, 0 设置工作页为1页(0页为正在显示的画面)。screensync等待场同步信号。screencopy 将工作页面1考贝到显示页面0,完成显示一个移动的红方块。如果将一个跑步者的不同像素块放在不同的工作页面,然后随场同步显示,则是一幅跑步画面。
'' examples/manual/gfx/screenset.bas
''
'' Example extracted from the FreeBASIC Manual
'' from topic 'SCREENSET'
''
'' See Also: https://www.freebasic.net/wiki/wikka.php?wakka=KeyPgScreenset
'' --------' Open graphics screen (320*200, 8bpp) with 2 pages
ScreenRes 320, 200, 8, 2' Work on page 1 while displaying page 0
ScreenSet 1, 0Dim As Integer x = -40Do'' Clear the screen, draw a box, update xClsLine (x, 80)-Step(39, 39), 4, BFx += 1: If (x > 319) Then x = -40' Wait for vertical sync: only used to control refresh rate, can be put anywhere in the Do loopScreenSync' Copy work page to visible pageScreenCopyLoop While Inkey = ""

6、显示窗口指针
一个正在显示的窗口,实际是一张像素块,它有对应的内存,而内存地址就是显示窗口的指针,在freebasic中用screenptr获得。screeninfo w, h, , bypp, pitch获得屏幕窗口的长、宽、色彩模式和一行的像素数(因此才能知道什么时候换行),在cairo绘图时也会看到这个参数的使用。移动指针、放置数据,即得到欲显示的图像。
'' examples/manual/gfx/screenptr2.bas
''
'' Example extracted from the FreeBASIC Manual
'' from topic 'SCREENPTR'
''
'' See Also: https://www.freebasic.net/wiki/wikka.php?wakka=KeyPgScreenptr
'' --------'Const SCREEN_WIDTH = 256, SCREEN_HEIGHT = 256
Const SCREEN_WIDTH = 1024, SCREEN_HEIGHT = 768
Dim As Long w, h, bypp, pitch'' Make 32-bit screen.
ScreenRes SCREEN_WIDTH, SCREEN_HEIGHT, 32'' Get screen info (w and h should match the constants above, bypp should be 4)
ScreenInfo w, h, , bypp, pitch'' Get the address of the frame buffer. An Any Ptr
'' is used here to allow simple pointer arithmetic
Dim buffer As Any Ptr = ScreenPtr()
If (buffer = 0) ThenPrint "Error: graphics screen not initialized."SleepEnd -1
End If'' Lock the screen to allow direct frame buffer access
ScreenLock()'' Set row address to the start of the bufferDim As Any Ptr row = buffer'' Iterate over all the pixels in the screen:For y As Integer = 0 To h - 1'' Set pixel address to the start of the row'' It's a 32-bit pixel, so use a ULong PtrDim As ULong Ptr pixel = rowFor x As Integer = 0 To w - 1'' Set the pixel value*pixel = RGB(x, x Xor y, y) '' Get the next pixel address '' (ULong Ptr will increment by 4 bytes)pixel += 1Next x'' Go to the next rowrow += pitchNext y'' Unlock the screen.
ScreenUnlock()'' Wait for the user to press a key before closing the program
Sleep

7、获得鼠标和键盘事件
需要 fbgfx.bi 支持,event 是freebasic中的一个type类,它含有事件的名称和附带参数。 Dim e as event 定义 e 为 event 类 ; if (screenEvent(@e)) then 是如果有事件发生; e.type 是查看发生的事件。 e.scancode 是查看键盘扫描码; e.ascii 是按下键的ascii值; e.dx, e.dy是鼠标的位置; e.button是按的左键或右键, 如果左右键同时按,被视为中间键。
'' examples/manual/gfx/screenevent.bas
''
'' Example extracted from the FreeBASIC Manual
'' from topic 'SCREENEVENT'
''
'' See Also: https://www.freebasic.net/wiki/wikka.php?wakka=KeyPgScreenevent
'' --------'' include fbgfx.bi for some useful definitions
#include "fbgfx.bi"
#if __FB_LANG__ = "fb"
Using fb '' constants and structures are stored in the FB namespace in lang fb
#endifDim e As EventScreenRes 640, 480
DoIf (ScreenEvent(@e)) ThenSelect Case e.typeCase EVENT_KEY_PRESSIf (e.scancode = SC_ESCAPE) ThenEndEnd IfIf (e.ascii > 0) ThenPrint "'" & e.ascii & "'";ElsePrint "unknown key";End IfPrint " was pressed (scancode " & e.scancode & ")"Case EVENT_KEY_RELEASEIf (e.ascii > 0) ThenPrint "'" & e.ascii & "'";ElsePrint "unknown key";End IfPrint " was released (scancode " & e.scancode & ")"Case EVENT_KEY_REPEATIf (e.ascii > 0) ThenPrint "'" & e.ascii & "'";ElsePrint "unknown key";End IfPrint " is being repeated (scancode " & e.scancode & ")"Case EVENT_MOUSE_MOVEPrint "mouse moved to " & e.x & "," & e.y & " (delta " & e.dx & "," & e.dy & ")"Case EVENT_MOUSE_BUTTON_PRESSIf (e.button = BUTTON_LEFT) ThenPrint "left";ElseIf (e.button = BUTTON_RIGHT) ThenPrint "right";ElsePrint "middle";End IfPrint " button pressed"Case EVENT_MOUSE_BUTTON_RELEASEIf (e.button = BUTTON_LEFT) ThenPrint "left";ElseIf (e.button = BUTTON_RIGHT) ThenPrint "right";ElsePrint "middle";End IfPrint " button released"Case EVENT_MOUSE_DOUBLE_CLICKIf (e.button = BUTTON_LEFT) ThenPrint "left";ElseIf (e.button = BUTTON_RIGHT) ThenPrint "right";ElsePrint "middle";End IfPrint " button double clicked"Case EVENT_MOUSE_WHEELPrint "mouse wheel moved to position " & e.zCase EVENT_MOUSE_ENTERPrint "mouse moved into program window"Case EVENT_MOUSE_EXITPrint "mouse moved out of program window"Case EVENT_WINDOW_GOT_FOCUSPrint "program window got focus"Case EVENT_WINDOW_LOST_FOCUSPrint "program window lost focus"Case EVENT_WINDOW_CLOSEEndCase EVENT_MOUSE_HWHEELPrint "horizontal mouse wheel moved to position " & e.wEnd SelectEnd IfSleep 1
Loop
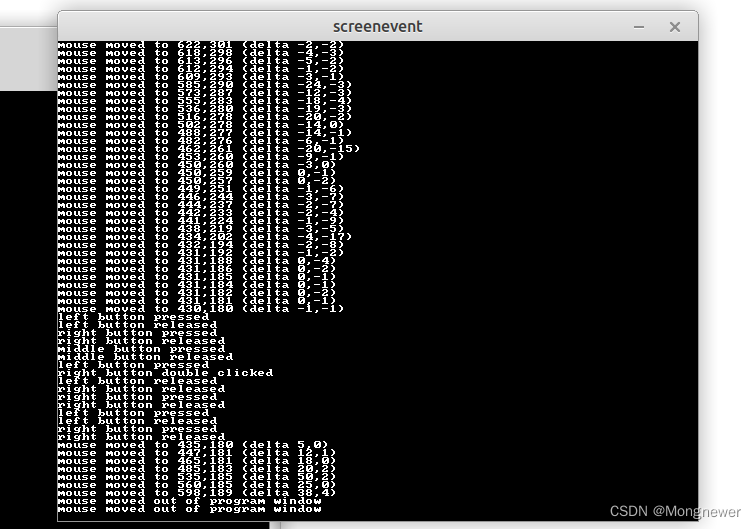
至此,应该可以写个简单的石头剪刀布游戏了。
这篇关于Mint_21.3 drawing-area和goocanvas的FB笔记(六)的文章就介绍到这儿,希望我们推荐的文章对编程师们有所帮助!









