本文主要是介绍A Brief Introduction of the Tqdm Module in Python,希望对大家解决编程问题提供一定的参考价值,需要的开发者们随着小编来一起学习吧!
| Date | Author | Version | Note |
|---|---|---|---|
| 2024.02.28 | Dog Tao | V1.0 | Release the note. |
文章目录
- A Brief Introduction of the Tqdm Module in Python
- Introduction
- Key Features
- Installation
- Usage Examples
- Basic Usage
- Advanced Usage
A Brief Introduction of the Tqdm Module in Python
Introduction
Tqdm is a versatile Python library that provides a fast, extensible progress bar for loops and other iterable processes. The name tqdm is derived from the Arabic word “taqaddum” (تقدّم), meaning “progress,” and is pronounced as “ta-qe-dum.” Its simplicity and efficiency have made it a go-to choice for adding progress indicators to Python code, especially in data processing, file I/O, and long-running computations.
Key Features
- Easy to Use:
Tqdmcan be added to your loops with minimal code changes, instantly providing visual feedback on the progress. - Highly Customizable: While simple to implement with default settings,
tqdmalso offers a wide range of customization options, including custom messages, progress bar formatting, and manual control over the progress updates. - Lightweight with Minimal Dependencies: It is designed to be lightweight and requires no heavy dependencies, making it suitable for various projects.
- Versatile: Works with loops, iterable objects, and can even be used to track progress in pandas operations with
tqdm.pandas().
Installation
- Using
pip
To install tqdm using pip, open your terminal (or command prompt/PowerShell in Windows) and run the following command:
pip install tqdm
If you are working in a virtual environment (which is recommended to avoid conflicts between different projects), make sure it is activated before running the pip install command.
- Using
conda
To install tqdm using conda, you should have Anaconda or Miniconda installed on your system. Open your Anaconda Prompt (or terminal in Linux/macOS) and run the following command:
conda install -c conda-forge tqdm
Using the -c conda-forge flag specifies that conda should install tqdm from the conda-forge channel, which is a community-maintained collection of conda packages.
Usage Examples
Basic Usage
The most common use of tqdm is to wrap it around any iterable in a for loop.
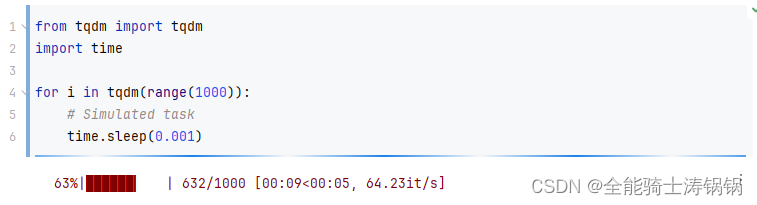
from tqdm import tqdm
import timefor i in tqdm(range(1000)):# Simulated tasktime.sleep(0.001)
The output example:
Advanced Usage
- Customization: You can customize the progress bar with various parameters such as
desc(description),total,leave,ncols(width),unit, and more.
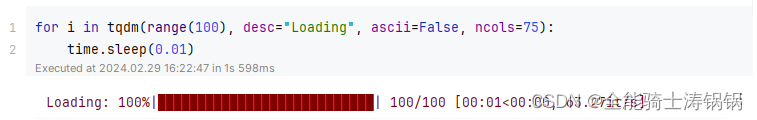
for i in tqdm(range(100), desc="Loading", ascii=False, ncols=75):time.sleep(0.01)
- Manual Updates: For tasks that don’t fit neatly into a loop,
tqdmcan be manually updated.
pbar = tqdm(total=100)
for i in range(10):time.sleep(0.1)pbar.update(10) # Manually update the progress bar by 10
pbar.close()
The output example:
- Integration with Pandas:
Tqdmcan be integrated with Pandas operations usingtqdm.pandas(). This is particularly useful for applying functions to DataFrame columns or rows and visualizing the progress.
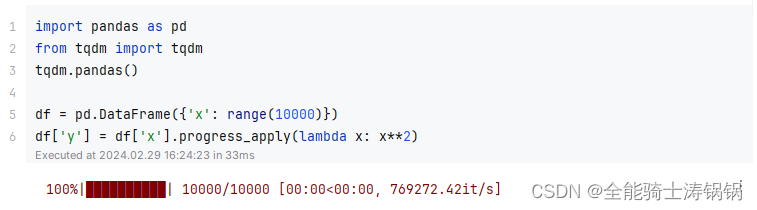
import pandas as pd
from tqdm import tqdm
tqdm.pandas()df = pd.DataFrame({'x': range(10000)})
df['y'] = df['x'].progress_apply(lambda x: x**2)
The output example:
- Working with Concurrent Futures:
Tqdmcan also be used with concurrent programming modules likeconcurrent.futuresfor tracking the progress of asynchronous tasks.
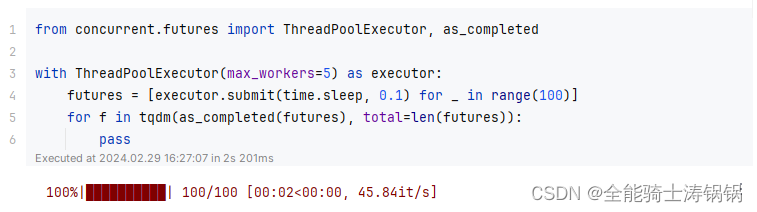
from concurrent.futures import ThreadPoolExecutor, as_completedwith ThreadPoolExecutor(max_workers=5) as executor:futures = [executor.submit(time.sleep, 0.1) for _ in range(100)]for f in tqdm(as_completed(futures), total=len(futures)):pass
The output example:
Tqdm’s simplicity, combined with its powerful features, makes it an invaluable tool for enhancing the user experience in command-line applications and Jupyter notebooks by providing clear and customizable progress indications.
这篇关于A Brief Introduction of the Tqdm Module in Python的文章就介绍到这儿,希望我们推荐的文章对编程师们有所帮助!




