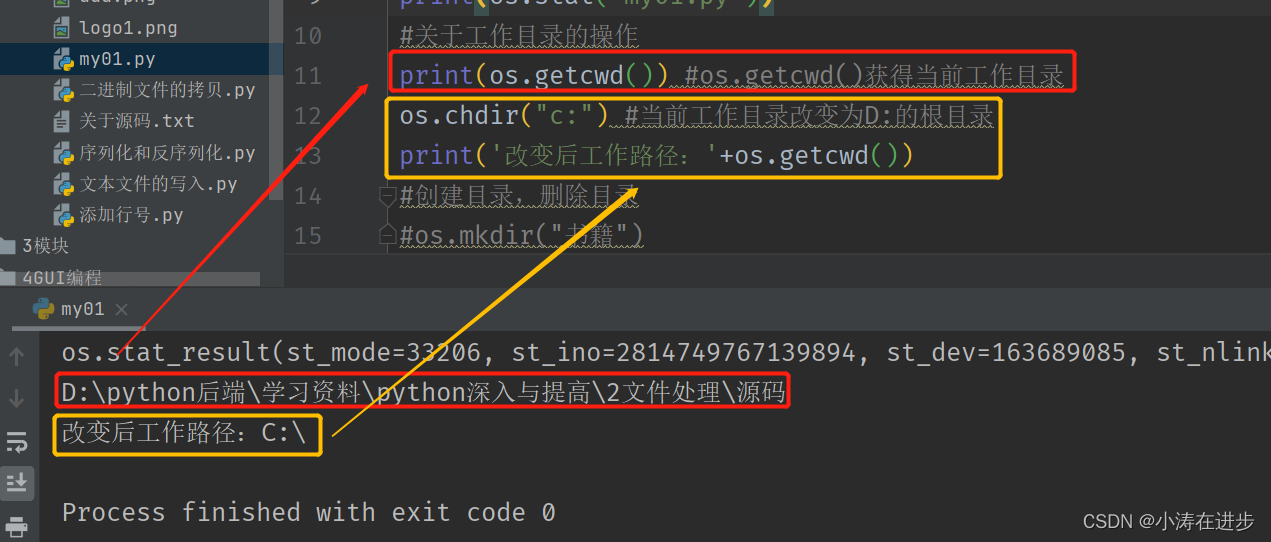
本文主要是介绍chdir与getcwd,希望对大家解决编程问题提供一定的参考价值,需要的开发者们随着小编来一起学习吧!
chdir(改变当前的工作目录)
相关函数 getcwd,chroot
表头文件 #include<unistd.h>
定义函数 int chdir(const char * path);
函数说明 chdir()用来将当前的工作目录改变成以参数path所指的目录。
返回值 执行成功则返回0,失败返回-1,errno为错误代码。
范例
#include<unistd.h>
main()
{
chdir(“/tmp”);
printf(“current working directory: %s”,getcwd(NULL,NULL));
}
执行
current working directory :/tmp
相关函数 getcwd,chroot
表头文件 #include<unistd.h>
定义函数 int chdir(const char * path);
函数说明 chdir()用来将当前的工作目录改变成以参数path所指的目录。
返回值 执行成功则返回0,失败返回-1,errno为错误代码。
范例
#include<unistd.h>
main()
{
chdir(“/tmp”);
printf(“current working directory: %s”,getcwd(NULL,NULL));
}
执行
current working directory :/tmp
fchdir(改变当前的工作目录)
相关函数 getcwd,chroot
表头文件 #include<unistd.h>
定义函数 int fchdir(int fd);
函数说明 fchdir()用来将当前的工作目录改变成以参数fd所指的文件描述
词。
返回值 执行成功则返回0,失败返回-1,errno为错误代码。
附加说明
范例
#include<sys/types.h>
#include<sys/stat.h>
#include<fcntl.h>
#include<unistd.h>
main()
{
int fd;
fd = open(“/tmp”,O_RDONLY);
fchdir(fd);
printf(“current working directory : %s ”,getcwd(NULL,NULL));
close(fd);
}
相关函数 getcwd,chroot
表头文件 #include<unistd.h>
定义函数 int fchdir(int fd);
函数说明 fchdir()用来将当前的工作目录改变成以参数fd所指的文件描述
词。
返回值 执行成功则返回0,失败返回-1,errno为错误代码。
附加说明
范例
#include<sys/types.h>
#include<sys/stat.h>
#include<fcntl.h>
#include<unistd.h>
main()
{
int fd;
fd = open(“/tmp”,O_RDONLY);
fchdir(fd);
printf(“current working directory : %s ”,getcwd(NULL,NULL));
close(fd);
}
执行
current working directory : /tmp
getcwd(取得当前的工作目录)
相关函数 get_current_dir_name,getwd,chdir
表头文件 #include<unistd.h>
定义函数 char * getcwd(char * buf,size_t size);
函数说明 getcwd()会将当前的工作目录绝对路径复制到参数buf所指的内
存空间,参数size为buf的空间大小。在调用此函数时,buf所指的
内存空间要足够大,若工作目录绝对路径的字符串长度超过参数
size大小,则回值NULL,errno的值则为ERANGE。倘若参数buf
为 NULL,getcwd()会依参数 size 的大小自动配置内存(使用
malloc()),如果参数size也为0,则getcwd()会依工作目录
绝对路径的字符串程度来决定所配置的内存大小,进程可以在使用
完此字符串后利用free()来释放此空间。
返回值 执行成功则将结果复制到参数buf所指的内存空间,或是返回自动
配置的字符串指针。失败返回NULL,错误代码存于errno。
相关函数 get_current_dir_name,getwd,chdir
表头文件 #include<unistd.h>
定义函数 char * getcwd(char * buf,size_t size);
函数说明 getcwd()会将当前的工作目录绝对路径复制到参数buf所指的内
存空间,参数size为buf的空间大小。在调用此函数时,buf所指的
内存空间要足够大,若工作目录绝对路径的字符串长度超过参数
size大小,则回值NULL,errno的值则为ERANGE。倘若参数buf
为 NULL,getcwd()会依参数 size 的大小自动配置内存(使用
malloc()),如果参数size也为0,则getcwd()会依工作目录
绝对路径的字符串程度来决定所配置的内存大小,进程可以在使用
完此字符串后利用free()来释放此空间。
返回值 执行成功则将结果复制到参数buf所指的内存空间,或是返回自动
配置的字符串指针。失败返回NULL,错误代码存于errno。
范例
#include<unistd.h>
main()
{
char buf[80];
getcwd(buf,sizeof(buf));
printf(“current working directory : %s”,buf);
}
执行
current working directory :/tmp
#include<unistd.h>
main()
{
char buf[80];
getcwd(buf,sizeof(buf));
printf(“current working directory : %s”,buf);
}
执行
current working directory :/tmp
这篇关于chdir与getcwd的文章就介绍到这儿,希望我们推荐的文章对编程师们有所帮助!
![os.getcwd(),os.path.realpath(__file__),sys.path[0]与绝对路径](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/20181121011047203.png)