本文主要是介绍Android14 InputManager-InputReader的处理,希望对大家解决编程问题提供一定的参考价值,需要的开发者们随着小编来一起学习吧!
IMS启动时会调用InputReader.start()方法
InputReader.cpp
status_t InputReader::start() {if (mThread) {return ALREADY_EXISTS;}mThread = std::make_unique<InputThread>("InputReader", [this]() { loopOnce(); }, [this]() { mEventHub->wake(); });return OK;
}当线程开始运行后,将会在内建的线程循环中不断地调用threadLoop(),直到此函数返回false,则退出线程循环,从而结束线程。
InputReader的一次线程循环的工作思路非常清晰,一共三步:
□首先从EventHub中抽取未处理的事件列表。这些事件分为两类,一类是从设备节点中读取的原始输入事件,另一类则是输入设备可用性变化事件,简称为设备事件。
□通过processEventsLocked()对事件进行处理。对于设备事件,此函数对根据设备的可用性加载或移除设备对应的配置信息。对于原始输入事件,则在进行转译、封装与加工后将结果暂存到mQueuedListener中。
□所有事件处理完毕后,调用mQueuedListener.flush()将所有暂存的输入事件一次性地交付给InputDispatcher。
void InputReader::loopOnce() {int32_t oldGeneration;int32_t timeoutMillis;// Copy some state so that we can access it outside the lock later.bool inputDevicesChanged = false;std::vector<InputDeviceInfo> inputDevices;std::list<NotifyArgs> notifyArgs;{ // acquire lockstd::scoped_lock _l(mLock);oldGeneration = mGeneration;timeoutMillis = -1;auto changes = mConfigurationChangesToRefresh;if (changes.any()) {mConfigurationChangesToRefresh.clear();timeoutMillis = 0;refreshConfigurationLocked(changes);} else if (mNextTimeout != LLONG_MAX) {nsecs_t now = systemTime(SYSTEM_TIME_MONOTONIC);timeoutMillis = toMillisecondTimeoutDelay(now, mNextTimeout);}} // release lockstd::vector<RawEvent> events = mEventHub->getEvents(timeoutMillis);{ // acquire lockstd::scoped_lock _l(mLock);mReaderIsAliveCondition.notify_all();
// 如果有事件信息,调用processEventsLocked()函数对事件进行加工处理if (!events.empty()) {notifyArgs += processEventsLocked(events.data(), events.size());}if (mNextTimeout != LLONG_MAX) {nsecs_t now = systemTime(SYSTEM_TIME_MONOTONIC);if (now >= mNextTimeout) {if (debugRawEvents()) {ALOGD("Timeout expired, latency=%0.3fms", (now - mNextTimeout) * 0.000001f);}mNextTimeout = LLONG_MAX;notifyArgs += timeoutExpiredLocked(now);}}if (oldGeneration != mGeneration) {inputDevicesChanged = true;inputDevices = getInputDevicesLocked();notifyArgs.emplace_back(NotifyInputDevicesChangedArgs{mContext.getNextId(), inputDevices});}} // release lock// Send out a message that the describes the changed input devices.if (inputDevicesChanged) {mPolicy->notifyInputDevicesChanged(inputDevices);}// Notify the policy of the start of every new stylus gesture outside the lock.for (const auto& args : notifyArgs) {const auto* motionArgs = std::get_if<NotifyMotionArgs>(&args);if (motionArgs != nullptr && isStylusPointerGestureStart(*motionArgs)) {mPolicy->notifyStylusGestureStarted(motionArgs->deviceId, motionArgs->eventTime);}}notifyAll(std::move(notifyArgs));// Flush queued events out to the listener.// This must happen outside of the lock because the listener could potentially call// back into the InputReader's methods, such as getScanCodeState, or become blocked// on another thread similarly waiting to acquire the InputReader lock thereby// resulting in a deadlock. This situation is actually quite plausible because the// listener is actually the input dispatcher, which calls into the window manager,// which occasionally calls into the input reader.mQueuedListener.flush();
}processEventsLocked()会分别处理原始输入事件与设备增删事件。
对于原始输入事件,由于EventHub会将属于同一输入设备的原始输入事件放在一起,因此processEventsLocked()可以使processEventsForDeviceLocked()同时处理来自同一输入设备的一批事件。
std::list<NotifyArgs> InputReader::processEventsLocked(const RawEvent* rawEvents, size_t count) {std::list<NotifyArgs> out;for (const RawEvent* rawEvent = rawEvents; count;) {int32_t type = rawEvent->type;size_t batchSize = 1;if (type < EventHubInterface::FIRST_SYNTHETIC_EVENT) {int32_t deviceId = rawEvent->deviceId;while (batchSize < count) {if (rawEvent[batchSize].type >= EventHubInterface::FIRST_SYNTHETIC_EVENT ||rawEvent[batchSize].deviceId != deviceId) {break;}batchSize += 1;}if (debugRawEvents()) {ALOGD("BatchSize: %zu Count: %zu", batchSize, count);}out += processEventsForDeviceLocked(deviceId, rawEvent, batchSize);} else {switch (rawEvent->type) {case EventHubInterface::DEVICE_ADDED:addDeviceLocked(rawEvent->when, rawEvent->deviceId);break;case EventHubInterface::DEVICE_REMOVED:removeDeviceLocked(rawEvent->when, rawEvent->deviceId);break;case EventHubInterface::FINISHED_DEVICE_SCAN:handleConfigurationChangedLocked(rawEvent->when);break;default:ALOG_ASSERT(false); // can't happenbreak;}}count -= batchSize;rawEvent += batchSize;}return out;
}std::list<NotifyArgs> InputReader::processEventsForDeviceLocked(int32_t eventHubId,const RawEvent* rawEvents,size_t count) {auto deviceIt = mDevices.find(eventHubId);if (deviceIt == mDevices.end()) {ALOGW("Discarding event for unknown eventHubId %d.", eventHubId);return {};}std::shared_ptr<InputDevice>& device = deviceIt->second;if (device->isIgnored()) {// ALOGD("Discarding event for ignored deviceId %d.", deviceId);return {};}return device->process(rawEvents, count);
}InputDevice.cpp
std::list<NotifyArgs> InputDevice::process(const RawEvent* rawEvents, size_t count) {// Process all of the events in order for each mapper.// We cannot simply ask each mapper to process them in bulk because mappers may// have side-effects that must be interleaved. For example, joystick movement events and// gamepad button presses are handled by different mappers but they should be dispatched// in the order received.std::list<NotifyArgs> out;for (const RawEvent* rawEvent = rawEvents; count != 0; rawEvent++) {if (debugRawEvents()) {const auto [type, code, value] =InputEventLookup::getLinuxEvdevLabel(rawEvent->type, rawEvent->code,rawEvent->value);ALOGD("Input event: eventHubDevice=%d type=%s code=%s value=%s when=%" PRId64,rawEvent->deviceId, type.c_str(), code.c_str(), value.c_str(), rawEvent->when);}if (mDropUntilNextSync) {if (rawEvent->type == EV_SYN && rawEvent->code == SYN_REPORT) {mDropUntilNextSync = false;ALOGD_IF(debugRawEvents(), "Recovered from input event buffer overrun.");} else {ALOGD_IF(debugRawEvents(),"Dropped input event while waiting for next input sync.");}} else if (rawEvent->type == EV_SYN && rawEvent->code == SYN_DROPPED) {ALOGI("Detected input event buffer overrun for device %s.", getName().c_str());mDropUntilNextSync = true;out += reset(rawEvent->when);} else {for_each_mapper_in_subdevice(rawEvent->deviceId, [&](InputMapper& mapper) {out += mapper.process(rawEvent);});}--count;}return out;
}InputMapper是InputReader中实际进行原始输入事件加工的场所,它有一系列的子类,分别用于加工不同类型的原始输入事件。而InputDevice的process()函数使用InputMapper的方式是一个简化了的职责链(chain of responsibility)设计模式。InputDevice不需要知道哪一个InputMapper可以处理一个原始输入事件,只须将一个事件逐个交给每一个InputMapper尝试处理,如果InputMapper可以接受这个事件则处理之,否则什么都不做。
根据设备的类型,将设备做如下分配
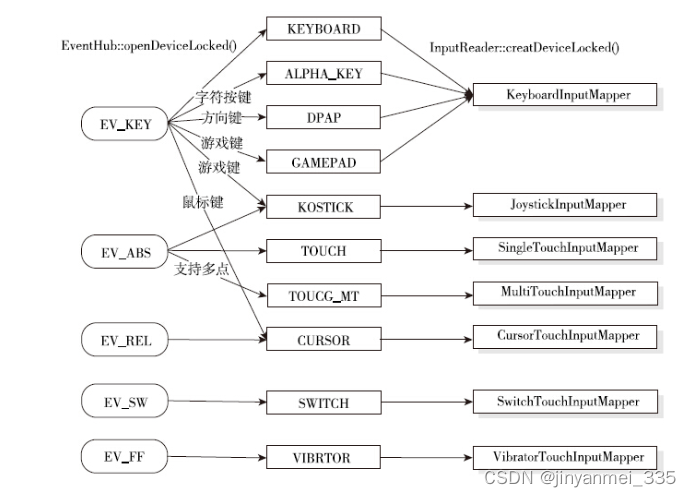
InputMapper的种类实在很多,对所有类型都进行详细分析并不现实。选择KeyboardInputMapper和MultiTouchInputMapper两个常用并且具有代表性的InputMapper进行探讨
键盘事件的处理
KeyboardInputMapper的process()函数比较简单
□通过processKey()按键事件做进一步处理。
mQueuedListener.flush();
根据扫描码获取虚拟键值以及功能值后,KeyboardInputMapper::process()调用了processKey()函数对按键事件做进一步处理。
将键盘信息转化为NotifyKeyArgs,返回到loopOnce的loopOnce中,通知事件分发
触摸事件的处理
触摸事件的处理
std::list<NotifyArgs> MultiTouchInputMapper::process(const RawEvent* rawEvent) {std::list<NotifyArgs> out = TouchInputMapper::process(rawEvent);mMultiTouchMotionAccumulator.process(rawEvent);return out;
}事件处理完成后回到最初的
mQueuedListener.flush(); // 将事件交给inputDispatcher的过程
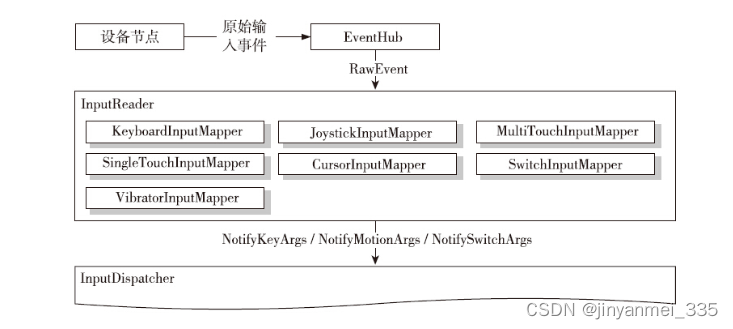
InputDispatcher继承了InputDispatcherInterface接口
class InputDispatcher : public android::InputDispatcherInterface {
void InputListenerInterface::notify(const NotifyArgs& generalArgs) {Visitor v{[&](const NotifyInputDevicesChangedArgs& args) { notifyInputDevicesChanged(args); },[&](const NotifyConfigurationChangedArgs& args) { notifyConfigurationChanged(args); },[&](const NotifyKeyArgs& args) { notifyKey(args); },[&](const NotifyMotionArgs& args) { notifyMotion(args); },[&](const NotifySwitchArgs& args) { notifySwitch(args); },[&](const NotifySensorArgs& args) { notifySensor(args); },[&](const NotifyVibratorStateArgs& args) { notifyVibratorState(args); },[&](const NotifyDeviceResetArgs& args) { notifyDeviceReset(args); },[&](const NotifyPointerCaptureChangedArgs& args) { notifyPointerCaptureChanged(args); },};std::visit(v, generalArgs);
}
以motion事件为例
void InputDispatcher::notifyMotion(const NotifyMotionArgs& args) {if (debugInboundEventDetails()) {ALOGD("notifyMotion - id=%" PRIx32 " eventTime=%" PRId64 ", deviceId=%d, source=%s, ""displayId=%" PRId32 ", policyFlags=0x%x, ""action=%s, actionButton=0x%x, flags=0x%x, metaState=0x%x, buttonState=0x%x, ""edgeFlags=0x%x, xPrecision=%f, yPrecision=%f, xCursorPosition=%f, ""yCursorPosition=%f, downTime=%" PRId64,args.id, args.eventTime, args.deviceId, inputEventSourceToString(args.source).c_str(),args.displayId, args.policyFlags, MotionEvent::actionToString(args.action).c_str(),args.actionButton, args.flags, args.metaState, args.buttonState, args.edgeFlags,args.xPrecision, args.yPrecision, args.xCursorPosition, args.yCursorPosition,args.downTime);for (uint32_t i = 0; i < args.pointerCount; i++) {ALOGD(" Pointer %d: id=%d, toolType=%s, x=%f, y=%f, pressure=%f, size=%f, ""touchMajor=%f, touchMinor=%f, toolMajor=%f, toolMinor=%f, orientation=%f",i, args.pointerProperties[i].id,ftl::enum_string(args.pointerProperties[i].toolType).c_str(),args.pointerCoords[i].getAxisValue(AMOTION_EVENT_AXIS_X),args.pointerCoords[i].getAxisValue(AMOTION_EVENT_AXIS_Y),args.pointerCoords[i].getAxisValue(AMOTION_EVENT_AXIS_PRESSURE),args.pointerCoords[i].getAxisValue(AMOTION_EVENT_AXIS_SIZE),args.pointerCoords[i].getAxisValue(AMOTION_EVENT_AXIS_TOUCH_MAJOR),args.pointerCoords[i].getAxisValue(AMOTION_EVENT_AXIS_TOUCH_MINOR),args.pointerCoords[i].getAxisValue(AMOTION_EVENT_AXIS_TOOL_MAJOR),args.pointerCoords[i].getAxisValue(AMOTION_EVENT_AXIS_TOOL_MINOR),args.pointerCoords[i].getAxisValue(AMOTION_EVENT_AXIS_ORIENTATION));}}Result<void> motionCheck = validateMotionEvent(args.action, args.actionButton,args.pointerCount, args.pointerProperties);if (!motionCheck.ok()) {LOG(ERROR) << "Invalid event: " << args.dump() << "; reason: " << motionCheck.error();return;}uint32_t policyFlags = args.policyFlags;policyFlags |= POLICY_FLAG_TRUSTED;android::base::Timer t;mPolicy.interceptMotionBeforeQueueing(args.displayId, args.eventTime, policyFlags);if (t.duration() > SLOW_INTERCEPTION_THRESHOLD) {ALOGW("Excessive delay in interceptMotionBeforeQueueing; took %s ms",std::to_string(t.duration().count()).c_str());}bool needWake = false;{ // acquire lockmLock.lock();if (!(policyFlags & POLICY_FLAG_PASS_TO_USER)) {// Set the flag anyway if we already have an ongoing gesture. That would allow us to// complete the processing of the current stroke.const auto touchStateIt = mTouchStatesByDisplay.find(args.displayId);if (touchStateIt != mTouchStatesByDisplay.end()) {const TouchState& touchState = touchStateIt->second;if (touchState.deviceId == args.deviceId && touchState.isDown()) {policyFlags |= POLICY_FLAG_PASS_TO_USER;}}}if (shouldSendMotionToInputFilterLocked(args)) {ui::Transform displayTransform;if (const auto it = mDisplayInfos.find(args.displayId); it != mDisplayInfos.end()) {displayTransform = it->second.transform;}mLock.unlock();MotionEvent event;event.initialize(args.id, args.deviceId, args.source, args.displayId, INVALID_HMAC,args.action, args.actionButton, args.flags, args.edgeFlags,args.metaState, args.buttonState, args.classification,displayTransform, args.xPrecision, args.yPrecision,args.xCursorPosition, args.yCursorPosition, displayTransform,args.downTime, args.eventTime, args.pointerCount,args.pointerProperties, args.pointerCoords);policyFlags |= POLICY_FLAG_FILTERED;if (!mPolicy.filterInputEvent(event, policyFlags)) {return; // event was consumed by the filter}mLock.lock();}// Just enqueue a new motion event.std::unique_ptr<MotionEntry> newEntry =std::make_unique<MotionEntry>(args.id, args.eventTime, args.deviceId, args.source,args.displayId, policyFlags, args.action,args.actionButton, args.flags, args.metaState,args.buttonState, args.classification, args.edgeFlags,args.xPrecision, args.yPrecision,args.xCursorPosition, args.yCursorPosition,args.downTime, args.pointerCount,args.pointerProperties, args.pointerCoords);if (args.id != android::os::IInputConstants::INVALID_INPUT_EVENT_ID &&IdGenerator::getSource(args.id) == IdGenerator::Source::INPUT_READER &&!mInputFilterEnabled) {const bool isDown = args.action == AMOTION_EVENT_ACTION_DOWN;mLatencyTracker.trackListener(args.id, isDown, args.eventTime, args.readTime);}needWake = enqueueInboundEventLocked(std::move(newEntry));mLock.unlock();} // release lockif (needWake) {mLooper->wake();}
}到达InputDispatcher的Motion事件被保存在MotionEntry类中
bool InputDispatcher::enqueueInboundEventLocked(std::unique_ptr<EventEntry> newEntry) {bool needWake = mInboundQueue.empty();mInboundQueue.push_back(std::move(newEntry));EventEntry& entry = *(mInboundQueue.back());traceInboundQueueLengthLocked();switch (entry.type) {case EventEntry::Type::KEY: {LOG_ALWAYS_FATAL_IF((entry.policyFlags & POLICY_FLAG_TRUSTED) == 0,"Unexpected untrusted event.");// Optimize app switch latency.// If the application takes too long to catch up then we drop all events preceding// the app switch key.const KeyEntry& keyEntry = static_cast<const KeyEntry&>(entry);if (isAppSwitchKeyEvent(keyEntry)) {if (keyEntry.action == AKEY_EVENT_ACTION_DOWN) {mAppSwitchSawKeyDown = true;} else if (keyEntry.action == AKEY_EVENT_ACTION_UP) {if (mAppSwitchSawKeyDown) {if (DEBUG_APP_SWITCH) {ALOGD("App switch is pending!");}mAppSwitchDueTime = keyEntry.eventTime + APP_SWITCH_TIMEOUT;mAppSwitchSawKeyDown = false;needWake = true;}}}// If a new up event comes in, and the pending event with same key code has been asked// to try again later because of the policy. We have to reset the intercept key wake up// time for it may have been handled in the policy and could be dropped.if (keyEntry.action == AKEY_EVENT_ACTION_UP && mPendingEvent &&mPendingEvent->type == EventEntry::Type::KEY) {KeyEntry& pendingKey = static_cast<KeyEntry&>(*mPendingEvent);if (pendingKey.keyCode == keyEntry.keyCode &&pendingKey.interceptKeyResult ==KeyEntry::InterceptKeyResult::TRY_AGAIN_LATER) {pendingKey.interceptKeyResult = KeyEntry::InterceptKeyResult::UNKNOWN;pendingKey.interceptKeyWakeupTime = 0;needWake = true;}}break;}case EventEntry::Type::MOTION: {LOG_ALWAYS_FATAL_IF((entry.policyFlags & POLICY_FLAG_TRUSTED) == 0,"Unexpected untrusted event.");if (shouldPruneInboundQueueLocked(static_cast<MotionEntry&>(entry))) {mNextUnblockedEvent = mInboundQueue.back();needWake = true;}break;}case EventEntry::Type::FOCUS: {LOG_ALWAYS_FATAL("Focus events should be inserted using enqueueFocusEventLocked");break;}case EventEntry::Type::TOUCH_MODE_CHANGED:case EventEntry::Type::CONFIGURATION_CHANGED:case EventEntry::Type::DEVICE_RESET:case EventEntry::Type::SENSOR:case EventEntry::Type::POINTER_CAPTURE_CHANGED:case EventEntry::Type::DRAG: {// nothing to dobreak;}}return needWake;
}通过这两个函数可以看出,到达InputDispatcher的Motion事件被保存在MotionEntry类中,然后排在mInboundQueue列表的队尾,这个mInboundQueue就是InputDispatcher的派发队列。MotionEntry是EventEntry的一个子类,保存了Motion事件的信息。Key事件也有一个KeyEntry与之对应。EventEntry是输入事件在InputDispatcher中的存在形式。另外,由于InputDispatcher在没有事件可以派发时(mInboundQueue为空),将会进入休眠状态,因此在将事件放入派发队列时,需要将派发线程唤醒。
上述过程运行在inputReader线程中,至此inputReader的处理完成
这篇关于Android14 InputManager-InputReader的处理的文章就介绍到这儿,希望我们推荐的文章对编程师们有所帮助!







