本文主要是介绍kubectl命令小本本,希望对大家解决编程问题提供一定的参考价值,需要的开发者们随着小编来一起学习吧!
kubectl命令小本本
- 1、kubectl 概述
- 2、kubectl 命令的语法
- 3、常用帮助文档
- 4、kubectl 常用子命令
- 5、kubectl 帮助文档详情
- 6、yaml资源清单文件
- 7、快速编写yaml资源清单
- 8、k8s命令练习记录
1、kubectl 概述
kubectl 是Kubernetes 集群的命令行工具,通过kubectl 能够对集群本身进行管理,并能
够在集群上进行容器化应用的安装部署。
2、kubectl 命令的语法
kubectl [command] [TYPE] [NAME] [flags]
(1)comand:指定要对资源执行的操作,例如create、get、describe 和delete;
(2)TYPE:指定资源类型,资源类型是大小写敏感的,开发者能够以单数、复数和缩略的
形式。例如:pod、pods、po;
(3)NAME:指定资源的名称,名称也大小写敏感的。如果省略名称,则会显示所有的资源;
(4)flags:指定可选的参数。例如:-s 或者 -server 参数指定Kubernetes API
server 的地址和端口;
kubectl get pods
kubectl get pod
kubectl get pods nginx-f89759699-48qvm
kubectl get pod nginx-f89759699-48qvm
kubectl get po nginx-f89759699-48qvm
kubectl get cs
kubectl get pod,cs,svc
kubectl get nodes
3、常用帮助文档
kubectl <command> --help
4、kubectl 常用子命令
(1)基础命令
| comman | desc |
|---|---|
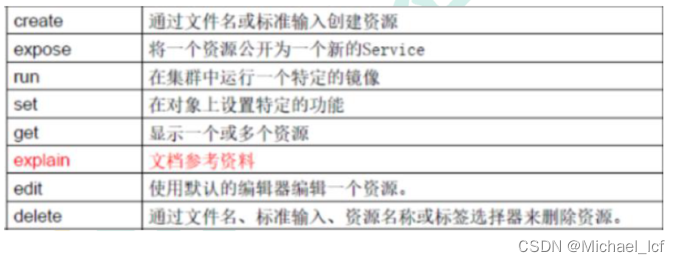
(2)部署和集群管理命令
| comman | desc |
|---|---|
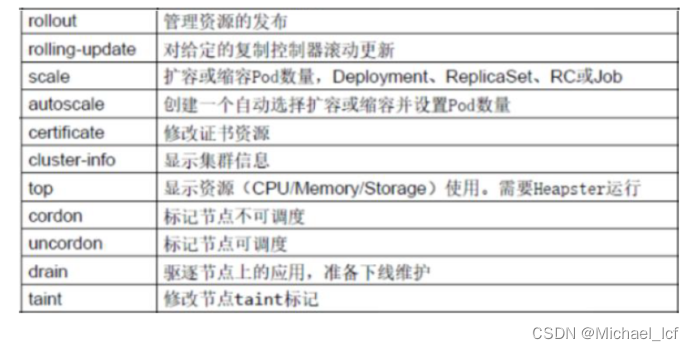
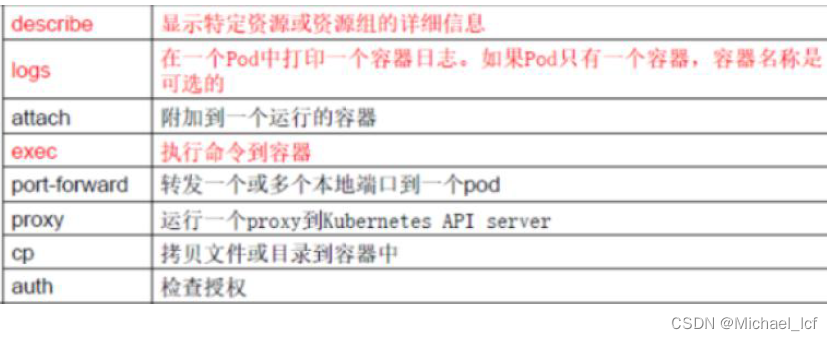
(3)故障和调试命令
| comman | desc |
|---|---|
(4)其他命令
| comman | desc |
|---|---|
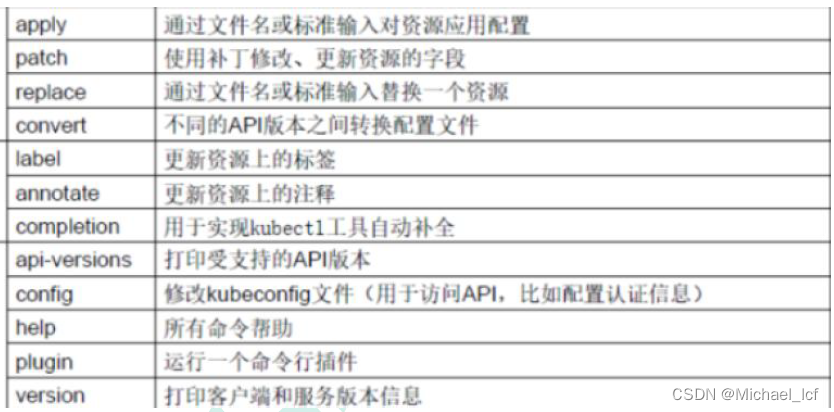
5、kubectl 帮助文档详情
kubectl --help
kubectl controls the Kubernetes cluster manager.Find more information at: https://kubernetes.io/docs/reference/kubectl/overview/Basic Commands (Beginner):create Create a resource from a file or from stdin.expose Take a replication controller, service, deployment or pod and expose it as a new Kubernetes Service 使用replication controller, service, deployment or pod并暴露它作为一个新的Kubernetes Servicerun Run a particular image on the cluster 在集群中运行一个指定的镜像set Set specific features on objects为objects设置一个指定的特征Basic Commands (Intermediate):explain Documentation of resources查看资源的文档get Display one or many resources显示一个或更多resourcesedit Edit a resource on the server在服务器上编辑一个资源delete Delete resources by filenames, stdin, resources and names, or by resources and label selectorDeploy Commands:rollout Manage the rollout of a resourcescale Set a new size for a Deployment, ReplicaSet or Replication Controller为Deployment, ReplicaSet or ReplicationController设置一个新的副本数量autoscale Auto-scale a Deployment, ReplicaSet, or ReplicationController自动调整Deployment, ReplicaSet or ReplicationController的副本数量Cluster Management Commands:certificate Modify certificate resources.修改 certificate 资源cluster-info Display cluster info显示集群信息top Display Resource (CPU/Memory/Storage) usage.cordon Mark node as unschedulable标记 node 为unschedulableuncordon Mark node as schedulable标记 node 为schedulabledrain Drain node in preparation for maintenancetaint Update the taints on one or more nodes更新一个或多个 node 上的taints Troubleshooting and Debugging Commands:describe Show details of a specific resource or group of resources显示一个指定 resource 或 resources组 的详情 logs Print the logs for a container in a pod打印容器在pod中的日志attach Attach to a running containerattach到一个运行中的containerexec Execute a command in a container在一个container中执行一个命令port-forward Forward one or more local ports to a podproxy Run a proxy to the Kubernetes API server运行一个proxy到the Kubernetes API servercp Copy files and directories to and from containers.复制files and directories到containers 或者 从containers复制files and directoriesauth Inspect authorizationAdvanced Commands:diff Diff live version against would-be applied versionapply Apply a configuration to a resource by filename or stdin通过文件名或标准输入流stdin对资源进行配置patch Update field(s) of a resource using strategic merge patch使用strategic merge patch更新一个资源的field(s)replace Replace a resource by filename or stdin通过filename or stdin替换一个资源wait Experimental: Wait for a specific condition on one or many resources.convert Convert config files between different API versions在不同的API versions转换配置文件kustomize Build a kustomization target from a directory or a remote url.Settings Commands:label Update the labels on a resource更新这个资源上的labelsannotate Update the annotations on a resource更新一个资源的注释completion Output shell completion code for the specified shell (bash or zsh)Other Commands:alpha Commands for features in alphaapi-resources Print the supported API resources on the serverapi-versions Print the supported API versions on the server, in the form of "group/version"config Modify kubeconfig filesplugin Provides utilities for interacting with plugins.version Print the client and server version informationUsage:kubectl [flags] [options]Use "kubectl <command> --help" for more information about a given command.
Use "kubectl options" for a list of global command-line options (applies to all commands).6、yaml资源清单文件
k8s 集群中的资源管理和资源对象编排部署都可以通过kubectl命令直接使用声明式YAML资源清单文件来解决。
(1)YAML 基本语法
1 使用空格做为缩进;
2 缩进的空格数目不重要,只要相同层级的元素左侧对齐即可;
3 低版本缩进时不允许使用 Tab 键,只允许使用空格;
4 使用#标识注释,从这个字符一直到行尾,都会被解释器忽略;
5 一般行首缩进2个空格;冒号后缩进1个空格
6 使用---表示一个新的文件的开始
-- 对象:键值对集合,又称为映射mapping、哈希hash、字典dictionary
# 对象类型:对象的一组键值对使用冒号结构表示
name: michael
age: 18
# 也允许将所有键值对写成一个行内对象
hash: { name: michael, age: 18 }
===========================================================
-- 数组:一组按次序排列的值,又称为序列sequence / 列表list
# 数组可以使用一组连词线开头的行表示
student:- michael- michelle
# 数组也可以使用行内表示法
student: [michael, michelle]
===========================================================
-- 纯量scalars:单个的、不可再分的值
# 数值字面量
order_money: 666.66
# 布尔值true、false
orderflag: true
# null用 ~ 表示
name: ~
# 时间采用ISO8601格式
iso8601: 2022-05-15T08:14:55+08:00
#日期采用复合ISO8601格式的年月日
date: 1976-07-31
# 使用连个感叹号,强制转换数据类型
var1: !!str 123
var2: !!str true
# 字符串默认不用使用引号包裹,如果有空格或特殊字符需要引号包裹
str1: 我是一行字符串
str2: "i am michael!"
# 单引号和双引号都可以使用,双引号不会对特殊字符转义
str3: '我字符串\n内容'
str4: "我字符串\n内容"
# 单引号之中如果还有单引号,必须使用连续的两个单引号转义
str5: 'michael''day'
# 字符串可以写多行,从第二行开始必须有一个单空格缩进,“换行符”会被转为“空格”
str6: 这是一行字符字符字符串
# 多行字符串可以使用 | 保留换行符,也可以使用 > 折叠换行
this: |7、快速编写yaml资源清单
1)kubectl create生成yaml文件
kubectl create deployment myweb --image=nginx -o yaml --dry-run=client > myweb.yaml
2)kubectl get导出yaml文件
kubectl get deploy
kubectl get deploy nginx -o=yaml --export > my2.yaml
8、k8s命令练习记录
hostnamectl set-hostname hadoop114
kubectl get nodes
kubectl get pods -n kube-system
kubectl expose deployment nginx --port=80 --type=NodePort
kubectl get pod
kubectl get pods -n
kubectl get pods -n kube-system
route -n
kubectl get pods -o wide
kubectl get pods
modprobe --help
man modprobe
kubectl get cs
kubectl apply --help
kubectl create --help
kubectl api-versions
kubectl --help
kubectl api-versions
kubectl version
kubectl create deployment web --image=nginx -o yaml --dry-run
kubectl get deploy
kubectl get deploy nginx -o=yaml --export > my2.yaml
kubectl get node,svc,cs,pod
kubectl get po,svc,rc,deploy,rs
kubectl get pod,service,replicationcontroller,deployment,replicaset
=============================================
kubectl label nodes hadoop112 my_env_role=prod
kubectl label --overwrite nodes hadoop112 my_env_role=dev
kubectl get nodes hadoop112 --show-labels=true
kubectl label nodes hadoop112 my_env_role-kubectl label pods mynginx-7f596f64f7-j8mcc unhealthy=true123456
kubectl label --overwrite pods mynginx-7f596f64f7-j8mcc unhealthy=false123456
kubectl label pods mynginx-7f596f64f7-j8mcc unhealthy-=============================================
kubectl create deployment mynginx --image=nginx -o yaml --dry-run > mynginx.yaml
kubectl apply -f mynginx.yaml
kubectl expose deployment mynginx --port=80 --type=NodePort --target-port=80 --name=mynginx-expose -o yaml --dry-run=client > mynginx-expose.yaml
kubectl apply -f mynginx-expose.yaml
kubectl get po,svc,rc,deploy,rs
wget http://192.168.6.112:30626
kubectl delete service/nginx
=======================================================
[root@hadoop114 ~]# vim mynginx1.4.yaml
metadata:creationTimestamp: nulllabels:app: mynginxname: mynginx
spec:replicas: 1selector:matchLabels:app: mynginxstrategy: {}template:metadata:creationTimestamp: nulllabels:app: mynginxspec:containers:- image: nginx:1.14name: nginxresources: {}
status: {}
-------------------------------------
kubectl create deployment mynginx --image=nginx
kubectl expose deployment mynginx --port=80 --type=NodePort --target-port=80 --name=mynginx-expose
-------------------------------------
kubectl set image deployment mynginx nginx=nginx:1.15
kubectl rollout status deployment mynginx
kubectl rollout history deployment mynginx
kubectl rollout history deployment mynginx --show-labels
kubectl rollout history --help
kubectl rollout undo deployment mynginx
kubectl rollout undo deployment mynginx --to-revision=2
kubectl scale deployment mynginx --replicas=5
=============================================
kubectl get node
kubectl get pod
kubectl get nodes hadoop114
kubectl get nodes hadoop114 --show-labels
kubectl get nodes --help
kubectl get nodes hadoop114 --show-labels=false
kubectl get nodes hadoop114 --show-labels=true
kubectl get nodes hadoop114 --show-kind
kubectl get nodes hadoop114 --show-kind=true
kubectl get nodes hadoop114 --server-print
kubectl get nodes --server-print
kubectl describe node
kubectl describe node hadoop114
kubectl describe node | grep Taint
kubectl get pods
kubectl create deployment myredis --image=redis
kubectl get node
kubectl get pod
kubectl scale deployment myredis --replicas=3
kubectl get pod -o wide
kubectl delete deployment myredis
====================================================
kubectl taint node hadoop113 my_env_taint=yes:NoSchedule
kubectl taint node hadoop113 my_env_taint=yes:PreferNoSchedule
kubectl taint node hadoop113 my_env_taint=yes:NoExecute
kubectl describe node hadoop113 | grep Taint
kubectl taint node hadoop113 my_env_taint:NoSchedule-
====================================================
kubectl taint nodes hadoop112 dedicated=special-user:NoSchedule
kubectl taint nodes hadoop112 dedicated:NoSchedule-
kubectl taint nodes hadoop112 dedicated-
====================================================生成yaml文件
kubectl create deployment myredis --image=redis --dry-run -o yaml > myredis.yaml
kubectl create deployment myredis --image=redis --dry-run=client -o yaml > myredis.yaml
使用yaml文件部署应用
kubectl apply -f myredis.yaml
对外发布(暴露端口)
kubectl expose deployment myredis --port=6379 --type=NodePort --target-port=6379 --name=myredis-name
kubectl expose deployment myredis --port=6379 --type=NodePort --target-port=6379 --name=myredis-name --dry-run=client -o yaml > myredis-expose.yaml
查看服务
kubectl get svc应用升级
kubectl set image deployment myredis redis=redis:6.0.16
kubectl set image deployment my-nginx-web nginx=nginx:1.15
查看升级状态
kubectl rollout status deployment myredis
查看历史版本
kubectl rollout history deployment myredis
回滚到上一个版本
kubectl rollout undo deployment myredis
回滚到指定的版本
kubectl rollout undo deployment myredis --to-revision=2
弹性伸缩
kubectl scale deployment myredis --replicas=5
kubectl scale deployment myredis --replicas=1=========================================================kubectl exec -it myredis-6cbccc7496-wd4ws bash
kubectl exec [POD] [COMMAND] is DEPRECATED and will be removed in a future version. Use kubectl
kubectl exec [POD] -- [COMMAND] instead.kubectl logs nginx-f89759699-6rtjhkubectl delete Pod --all—— 尚硅谷视频k8s教程 学习笔记
这篇关于kubectl命令小本本的文章就介绍到这儿,希望我们推荐的文章对编程师们有所帮助!





