本文主要是介绍STM32CbueMX之SPI_FLASH + FATFS + USB MSC + 虚拟扩容,希望对大家解决编程问题提供一定的参考价值,需要的开发者们随着小编来一起学习吧!
前言:
做一个在spi flash 上挂一个文件系统,然后板子用USB线连接电脑能识别读出spi flash上的文件。
背景:
因为spi flash容量比较小,我使用的是32MB的,插上电脑,感觉不好看,显示容量太小了。
所以我打算虚拟扩容一下变成1GB,但是实际可用的还是32MB。把电脑的写权限取消,只读。
fatfs调用写函数
FRESULT f_write (
FIL* fp, /* Pointer to the file object */
const void* buff, /* Pointer to the data to be written */
UINT btw, /* Number of bytes to write */
UINT* bw /* Pointer to number of bytes written */
)
返回值正常,然后*bw = 0;表示无空间写入。
主要是我下面实现了在MCU的fatfs文件系统分配超过32MB的空间都会提示已满,不再写入数据。
毕竟真实物理空间是32MB.这样不会破坏文件系统的文件表,导致文件系统出错。
为什么取消电脑写权限呢?是因为电脑写入fatfs文件系统的数据超过32MB的时候会破坏文件系统的文件表。
或者可以再改进一下,可以自我尝试。
STM32CbueMX配置图





USB pack 大小 = 4096;包越大速度越快。
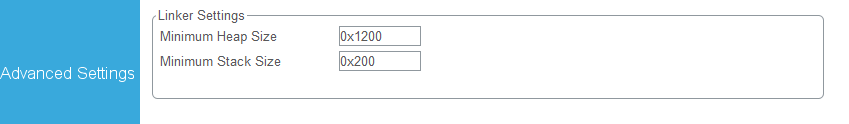
heap大小:比我们设置的USB pack大512字节就够了。
代码
spi flash 驱动以前文章有写。
user_diskio.c
DSTATUS USER_initialize (BYTE pdrv /* Physical drive nmuber to identify the drive */
)
{Stat = BSP_W25Q256_Init();return Stat;
}DSTATUS USER_status (BYTE pdrv /* Physical drive number to identify the drive */
)
{return Stat;
}DRESULT USER_read (BYTE pdrv, /* Physical drive nmuber to identify the drive */BYTE *buff, /* Data buffer to store read data */DWORD sector, /* Sector address in LBA */UINT count /* Number of sectors to read */
)
{if(BSP_W25Q256_Read(buff, sector << 12, count << 12) != W25Q256_OK)return RES_ERROR;}DRESULT USER_write (BYTE pdrv, /* Physical drive nmuber to identify the drive */const BYTE *buff, /* Data to be written */DWORD sector, /* Sector address in LBA */UINT count /* Number of sectors to write */
)
{if(BSP_W25Q256_Erase_Sector(sector << 12) != W25Q256_OK)return RES_ERROR;if(BSP_W25Q256_Write((uint8_t*)buff, sector << 12, count << 12) != W25Q256_OK)return RES_ERROR;return RES_OK;
}DRESULT USER_ioctl (BYTE pdrv, /* Physical drive nmuber (0..) */BYTE cmd, /* Control code */void *buff /* Buffer to send/receive control data */
)
{DRESULT res = RES_ERROR;if(pdrv != 0) return RES_PARERR;switch(cmd){case CTRL_SYNC:res = RES_OK;break;case GET_SECTOR_COUNT:*(DWORD*)buff = (W25Q256FV_FLASH_SIZE / W25Q256FV_SECTOR_SIZE);res = RES_OK;break;case GET_SECTOR_SIZE:*(WORD*)buff = W25Q256FV_SECTOR_SIZE;res = RES_OK;break;case GET_BLOCK_SIZE:*(DWORD*)buff = 1;res = RES_OK;break;default:res = RES_PARERR;break;}return res;
}usbd_storage_if.c
#define MYSTORAGE_LUN_NBR 1
#define MYSTORAGE_BLK_NBR (W25Q256FV_FLASH_SIZE / W25Q256FV_SECTOR_SIZE);
#define MYSTORAGE_BLK_SIZ W25Q256FV_SECTOR_SIZEint8_t STORAGE_Init_FS(uint8_t lun)
{return (USBD_OK);
}int8_t STORAGE_GetCapacity_FS(uint8_t lun, uint32_t *block_num, uint16_t *block_size)
{*block_num = MYSTORAGE_BLK_NBR;*block_size = MYSTORAGE_BLK_SIZ;return (USBD_OK);
}int8_t STORAGE_IsReady_FS(uint8_t lun)
{return (USBD_OK);
}int8_t STORAGE_IsWriteProtected_FS(uint8_t lun)
{return (USBD_OK);
}int8_t STORAGE_Read_FS(uint8_t lun, uint8_t *buf, uint32_t blk_addr, uint16_t blk_len)
{if(BSP_W25Q256_Read(buf, blk_addr << 12, blk_len << 12) != W25Q256_OK)return USBD_FAIL;return (USBD_OK);
}int8_t STORAGE_Write_FS(uint8_t lun, uint8_t *buf, uint32_t blk_addr, uint16_t blk_len)
{if(BSP_W25Q256_Erase_Sector(blk_addr << 12) != W25Q256_OK)return USBD_FAIL;if(BSP_W25Q256_Write(buf, blk_addr << 12, blk_len << 12) != W25Q256_OK)return USBD_FAIL;return (USBD_OK);
}int8_t STORAGE_GetMaxLun_FS(void)
{return (MYSTORAGE_LUN_NBR - 1);
}
main.c
#include <stdio.h>
#include "w25q256.h"FIL fil;
FATFS spi_fs;
unsigned char work[4096] = {0};
unsigned char read_buf[50] = {0};
unsigned char write_buf[4096] = "hello sudaroot\r\n";static void USB_GPIO_Init(void);int main(void)
{/* USER CODE BEGIN 1 */unsigned int res = 0;unsigned int count = 0;/* USER CODE END 1 *//* MCU Configuration--------------------------------------------------------*//* Reset of all peripherals, Initializes the Flash interface and the Systick. */HAL_Init();/* USER CODE BEGIN Init *//* USER CODE END Init *//* Configure the system clock */SystemClock_Config();/* USER CODE BEGIN SysInit */USB_GPIO_Init();/* USER CODE END SysInit *//* Initialize all configured peripherals */MX_GPIO_Init();MX_USART1_UART_Init();MX_USB_DEVICE_Init();MX_SPI5_Init();MX_FATFS_Init();/* USER CODE BEGIN 2 */printf("sudaroot usb and fatfs msc\r\n");res = f_mount(&spi_fs, "0:", 1);if(res != FR_OK){printf("文件系统挂载失败,f_mount = %d\r\n", res);res = f_mkfs("0:", FM_ANY, 0, (void*)&work, 4096);if(res != FR_OK){printf("文件系统格式化失败,f_mkfs = %d\r\n", res);}else{printf("重新挂载文件系统\r\n");res = f_mount(&spi_fs, "0:", 1);if(res != FR_OK){printf("文件系统挂载失败,f_mount = %d\r\n", res);}else{printf("文件系统挂载成功\r\n");}}}else printf("文件系统挂载成功\r\n");/*----------------------- 文件系统测试:写测试 -----------------------------*/printf("\r\n****** 即将进行文件写入测试... ******\r\n");res = f_open(&fil, "0:sudaroot.txt", FA_OPEN_APPEND | FA_WRITE);if(res == FR_OK){res = f_write(&fil, write_buf, 4096, &count);if(res != FR_OK){printf("f_write 发生错误,err = %d, count = %d\r\n", res, count);printf("关闭打开的sudaroot.txt文件\r\n");count = 0;f_close(&fil);}else{if(count == 0){printf("没有空间写入数据了\r\n");}count = 0;f_close(&fil);}}else{printf("打开/创建sudaroot.txt文件失败,err = %d\r\n", res);}printf("\r\n****** 结束进行文件写入测试... ******\r\n");/*------------------- 文件系统测试:读测试 ------------------------------------*/printf("****** 即将进行文件读取测试... ******\r\n");res = f_open(&fil, "0:sudaroot.txt", FA_OPEN_EXISTING | FA_READ);if(res == FR_OK){printf("打开sudaroot.txt文件成功\r\n");res = f_read(&fil, read_buf, sizeof(read_buf), &count);if(res != FR_OK){printf("f_read 发生错误,err = %d\r\n", res);printf("关闭打开的sudaroot.txt文件\r\n");f_close(&fil);}else{printf("文件读取成功,读取字节数据:%d\n", count);printf("向文件读取的数据为:\r\n%s\r\n", read_buf);printf("关闭打开的sudaroot.txt文件\r\n");f_close(&fil);}}else printf("打开sudaroot.txt文件失败,err = %d\r\n", res);/*------------------- 不再使用文件系统,取消挂载文件系统 ------------------------------------*/printf("不再使用文件系统,取消挂载文件系统\r\n");res = f_mount(NULL, "0:", 1);if(res == FR_OK) printf("取消挂载文件系统成功\r\n");else printf("取消挂载文件系统失败,err = %d\r\n", res);printf("文件系统测试结束\r\n");printf("csize = 0x%X = %d\r\n", spi_fs.csize, spi_fs.csize);printf("ssize = 0x%X = %d\r\n", spi_fs.ssize, spi_fs.ssize);printf("n_fatent = 0x%lX = %lu\r\n", spi_fs.n_fatent, spi_fs.n_fatent);printf("database = 0x%lX = %lu\r\n", spi_fs.database, spi_fs.database);printf("fsize = 0x%lX = %lu\r\n", spi_fs.fsize, spi_fs.fsize);printf("last_clst = 0x%lX = %lu\r\n", spi_fs.last_clst, spi_fs.last_clst);printf("free_clst = 0x%lX = %lu\r\n", spi_fs.free_clst, spi_fs.free_clst);/* USER CODE END 2 *//* Infinite loop *//* USER CODE BEGIN WHILE */while (1){/* USER CODE END WHILE *//* USER CODE BEGIN 3 */HAL_GPIO_TogglePin(RUN_LED_GPIO_Port, RUN_LED_Pin);HAL_Delay(500);}/* USER CODE END 3 */
}int fputc(int ch, FILE *FILE)
{HAL_UART_Transmit(&huart1, (unsigned char *)&ch, 1, HAL_MAX_DELAY);return ch;
}static void USB_GPIO_Init(void)
{GPIO_InitTypeDef GPIO_InitStruct = {0};/* GPIO Ports Clock Enable */__HAL_RCC_GPIOA_CLK_ENABLE();/*Configure GPIO pin Output Level */HAL_GPIO_WritePin(GPIOA, GPIO_PIN_11 | GPIO_PIN_12, GPIO_PIN_RESET);/*Configure GPIO pin : W25Q256_CS_Pin */GPIO_InitStruct.Pin = GPIO_PIN_11 | GPIO_PIN_12;GPIO_InitStruct.Mode = GPIO_MODE_OUTPUT_PP;GPIO_InitStruct.Pull = GPIO_PULLDOWN;GPIO_InitStruct.Speed = GPIO_SPEED_FREQ_VERY_HIGH;HAL_GPIO_Init(GPIOA, &GPIO_InitStruct);HAL_Delay(2);
}效果:

扩容:
先算一下1GB转换成4KB一个扇区的话一共有几个扇区。
1GB = 1024MB =1024 * 1024KB
总扇区数 = 1024 * 1024KB / 4 KB = 262144
修改 user_diskio.c
DRESULT USER_ioctl (BYTE pdrv, /* Physical drive nmuber (0..) */BYTE cmd, /* Control code */void *buff /* Buffer to send/receive control data */
)
{
...case GET_SECTOR_COUNT:*(DWORD*)buff = 262144;res = RES_OK;break;
...
}修改usbd_storage_if.c
#define MYSTORAGE_BLK_NBR 262144int8_t STORAGE_Write_FS(uint8_t lun, uint8_t *buf, uint32_t blk_addr, uint16_t blk_len)
{
// if(BSP_W25Q256_Erase_Sector(blk_addr << 12) != W25Q256_OK)
// return USBD_FAIL;// if(BSP_W25Q256_Write(buf, blk_addr << 12, blk_len << 12) != W25Q256_OK)
// return USBD_FAIL;return (USBD_OK);
}main.c
#include <stdio.h>
#include "w25q256.h"FIL fil;
FATFS spi_fs;
unsigned char work[4096] = {0};
unsigned char read_buf[50] = {0};
unsigned char write_buf[4096] = "hello sudaroot\r\n";static void USB_GPIO_Init(void);int main(void)
{/* USER CODE BEGIN 1 */unsigned int res = 0;unsigned int count = 0;/* USER CODE END 1 *//* MCU Configuration--------------------------------------------------------*//* Reset of all peripherals, Initializes the Flash interface and the Systick. */HAL_Init();/* USER CODE BEGIN Init *//* USER CODE END Init *//* Configure the system clock */SystemClock_Config();/* USER CODE BEGIN SysInit */USB_GPIO_Init();/* USER CODE END SysInit *//* Initialize all configured peripherals */MX_GPIO_Init();MX_USART1_UART_Init();MX_USB_DEVICE_Init();MX_SPI5_Init();MX_FATFS_Init();/* USER CODE BEGIN 2 */printf("sudaroot usb and fatfs msc\r\n");res = f_mount(&spi_fs, "0:", 1);if(res != FR_OK){printf("文件系统挂载失败,f_mount = %d\r\n", res);res = f_mkfs("0:", FM_ANY, 0, (void*)&work, 4096);if(res != FR_OK){printf("文件系统格式化失败,f_mkfs = %d\r\n", res);}else{printf("重新挂载文件系统\r\n");res = f_mount(&spi_fs, "0:", 1);if(res != FR_OK){printf("文件系统挂载失败,f_mount = %d\r\n", res);}else{printf("文件系统挂载成功\r\n");}}}else printf("文件系统挂载成功\r\n");printf("csize = 0x%X = %d\r\n", spi_fs.csize, spi_fs.csize);printf("ssize = 0x%X = %d\r\n", spi_fs.ssize, spi_fs.ssize);printf("n_fatent = 0x%lX = %lu\r\n", spi_fs.n_fatent, spi_fs.n_fatent);printf("database = 0x%lX = %lu\r\n", spi_fs.database, spi_fs.database);printf("fsize = 0x%lX = %lu\r\n", spi_fs.fsize, spi_fs.fsize);printf("last_clst = 0x%lX = %lu\r\n", spi_fs.last_clst, spi_fs.last_clst);printf("free_clst = 0x%lX = %lu\r\n", spi_fs.free_clst, spi_fs.free_clst);/* USER CODE END 2 *//* Infinite loop *//* USER CODE BEGIN WHILE */while (1){/* USER CODE END WHILE *//* USER CODE BEGIN 3 */HAL_GPIO_TogglePin(RUN_LED_GPIO_Port, RUN_LED_Pin);HAL_Delay(500);}/* USER CODE END 3 */
}int fputc(int ch, FILE *FILE)
{HAL_UART_Transmit(&huart1, (unsigned char *)&ch, 1, HAL_MAX_DELAY);return ch;
}static void USB_GPIO_Init(void)
{GPIO_InitTypeDef GPIO_InitStruct = {0};/* GPIO Ports Clock Enable */__HAL_RCC_GPIOA_CLK_ENABLE();/*Configure GPIO pin Output Level */HAL_GPIO_WritePin(GPIOA, GPIO_PIN_11 | GPIO_PIN_12, GPIO_PIN_RESET);/*Configure GPIO pin : W25Q256_CS_Pin */GPIO_InitStruct.Pin = GPIO_PIN_11 | GPIO_PIN_12;GPIO_InitStruct.Mode = GPIO_MODE_OUTPUT_PP;GPIO_InitStruct.Pull = GPIO_PULLDOWN;GPIO_InitStruct.Speed = GPIO_SPEED_FREQ_VERY_HIGH;HAL_GPIO_Init(GPIOA, &GPIO_InitStruct);HAL_Delay(2);
}编译烧录重启连接USB到PC

一切正常。
分析:
先分析一下FATFS结构体和容量相关的参数,然再改。
/* File system object structure (FATFS) */typedef struct {
...
WORD csize; / *簇大小[扇区] * /
WORD ssize; / *扇区大小(512,1024,2048或4096)* /
DWORD last_clst; / *最后分配的簇* /
DWORD free_clst; / *没使用簇数量* /
DWORD n_fatent; / * FAT条目数(簇数+ 2)* /
DWORD fsize; / * FAT的大小[扇区] * /
DWORD volbase; / *卷起始扇区* /
DWORD fatbase; / * FAT起始扇区* /
DWORD dirbase; / *根目录基本扇区* /
DWORD database; / *数据起始扇区* /
...
} FATFS;簇是文件系统的最小单位,spi_flash的最小擦除单位是扇区。
变量csize表示一个簇由几个扇区组成,ssize表示一个扇区大小。n_fatent表示可用于存数据簇的总数。
还有就是一般小于4GB的文件系统都会格式化成FAT12或者FAT16,这种方式扩容不支持FAT32。
由上面串口打印的信息我们可以看出
簇大小 = csize * ssize = 8 * 4KB = 32KB
那么1GB可以分成几个32KB的簇
簇总数 = 1GB / 32KB = 1024 * 1024KB / 32KB = 32768 = 0X8000
文件表和保留扇区用几个簇 = 簇总数 - n_fatent = 32768 - 32759 = 9
本来是32MB的flash = 8192 * 4KB = 1024 * 32KB
所以我们使用更改n_fatent = 1024 - 9 = 1015
还要注意的是n_fatent会在实际可用簇的基础上+2。
但是直接更改n_fatent是不行的,因为n_fatent会写入分区表,这样子会破坏分区表。
所以换一种方法,看哪里用n_fatent分配空间,在那里把n_fatent修改成常量。
下面这个函数是分配新的簇函数
/*-----------------------------------------------------------------------*/
/* FAT handling - Stretch a chain or Create a new chain */
/*-----------------------------------------------------------------------*/
static
DWORD create_chain ( /* 0:No free cluster, 1:Internal error, 0xFFFFFFFF:Disk error, >=2:New cluster# */_FDID* obj, /* Corresponding object */DWORD clst /* Cluster# to stretch, 0:Create a new chain */
)
{DWORD cs, ncl, scl;FRESULT res;FATFS *fs = obj->fs;if (clst == 0) { /* Create a new chain */scl = fs->last_clst; /* Get suggested cluster to start from */if (scl == 0 || scl >= fs->n_fatent) scl = 1;}else { /* Stretch current chain */cs = get_fat(obj, clst); /* Check the cluster status */if (cs < 2) return 1; /* Invalid FAT value */if (cs == 0xFFFFFFFF) return cs; /* A disk error occurred */if (cs < fs->n_fatent) return cs; /* It is already followed by next cluster */scl = clst;}#if _FS_EXFATif (fs->fs_type == FS_EXFAT) { /* On the exFAT volume */ncl = find_bitmap(fs, scl, 1); /* Find a free cluster */if (ncl == 0 || ncl == 0xFFFFFFFF) return ncl; /* No free cluster or hard error? */res = change_bitmap(fs, ncl, 1, 1); /* Mark the cluster 'in use' */if (res == FR_INT_ERR) return 1;if (res == FR_DISK_ERR) return 0xFFFFFFFF;if (clst == 0) { /* Is it a new chain? */obj->stat = 2; /* Set status 'contiguous' */} else { /* It is a stretched chain */if (obj->stat == 2 && ncl != scl + 1) { /* Is the chain got fragmented? */obj->n_cont = scl - obj->sclust; /* Set size of the contiguous part */obj->stat = 3; /* Change status 'just fragmented' */}}if (obj->stat != 2) { /* Is the file non-contiguous? */if (ncl == clst + 1) { /* Is the cluster next to previous one? */obj->n_frag = obj->n_frag ? obj->n_frag + 1 : 2; /* Increment size of last framgent */} else { /* New fragment */if (obj->n_frag == 0) obj->n_frag = 1;res = fill_last_frag(obj, clst, ncl); /* Fill last fragment on the FAT and link it to new one */if (res == FR_OK) obj->n_frag = 1;}}} else
#endif{ /* On the FAT12/16/32 volume */ncl = scl; /* Start cluster */for (;;) {ncl++; /* Next cluster */if (ncl >= fs->n_fatent) { /* Check wrap-around */ncl = 2;if (ncl > scl) return 0; /* No free cluster */}cs = get_fat(obj, ncl); /* Get the cluster status */if (cs == 0) break; /* Found a free cluster */if (cs == 1 || cs == 0xFFFFFFFF) return cs; /* An error occurred */if (ncl == scl) return 0; /* No free cluster */}res = put_fat(fs, ncl, 0xFFFFFFFF); /* Mark the new cluster 'EOC' */if (res == FR_OK && clst != 0) {res = put_fat(fs, clst, ncl); /* Link it from the previous one if needed */}}if (res == FR_OK) { /* Update FSINFO if function succeeded. */fs->last_clst = ncl;if (fs->free_clst <= fs->n_fatent - 2) fs->free_clst--;fs->fsi_flag |= 1;} else {ncl = (res == FR_DISK_ERR) ? 0xFFFFFFFF : 1; /* Failed. Generate error status */}return ncl; /* Return new cluster number or error status */
}#endif /* !_FS_READONLY */
修改一下
static
DWORD create_chain ( /* 0:No free cluster, 1:Internal error, 0xFFFFFFFF:Disk error, >=2:New cluster# */_FDID* obj, /* Corresponding object */DWORD clst /* Cluster# to stretch, 0:Create a new chain */
)
{...if (clst == 0) { /* Create a new chain */scl = fs->last_clst; /* Get suggested cluster to start from *///if (scl == 0 || scl >= fs->n_fatent) scl = 1;if (scl == 0 || scl >= 1015) scl = 1;}
...//if (ncl >= fs->n_fatent) { /* Check wrap-around */if (ncl >= 1015) { /* Check wrap-around */ncl = 2;if (ncl > scl) return 0; /* No free cluster */}
....
}把注释的两行的fs->n_fatent 换成我们算出来的 1015;
测试程序:
每次调用f_write()往缓存区写入4096个字节数据,统计能写多少次。
f_write(&fil, write_buf, 4096, &count); 函数返回值不等于FR_OK一般是配置出错,或者硬件出错。
而count写入字节统计为0的话才是没用多余的空间写入。
FIL fil;
FATFS spi_fs;
unsigned char read_buf[50] = {0};
unsigned char work[4096] = {0};
unsigned char write_buf[4096] = "\r\nhello sudaroot\r\n";/*** @brief The application entry point.* @retval int*/
int main(void)
{/* USER CODE BEGIN 1 */unsigned int res = 0;unsigned int count = 0;unsigned int sum = 0;/* USER CODE END 1 *//* MCU Configuration--------------------------------------------------------*//* Reset of all peripherals, Initializes the Flash interface and the Systick. */HAL_Init();/* USER CODE BEGIN Init *//* USER CODE END Init *//* Configure the system clock */SystemClock_Config();/* USER CODE BEGIN SysInit */USB_GPIO_Init();/* USER CODE END SysInit *//* Initialize all configured peripherals */MX_GPIO_Init();MX_USART1_UART_Init();MX_USB_DEVICE_Init();MX_SPI5_Init();MX_FATFS_Init();/* USER CODE BEGIN 2 */HAL_Delay(1000);BSP_W25Q256_Erase_Sector(0);HAL_Delay(100);printf("sudaroot usb and fatfs msc\r\n");res = f_mount(&spi_fs, "0:", 1);if(res != FR_OK){printf("文件系统挂载失败,f_mount = %d\r\n", res);res = f_mkfs("0:", FM_ANY, 0, (void*)&work, 4096);if(res != FR_OK){printf("文件系统格式化失败,f_mkfs = %d\r\n", res);}else{printf("重新挂载文件系统\r\n");res = f_mount(&spi_fs, "0:", 1);if(res != FR_OK){printf("文件系统挂载失败,f_mount = %d\r\n", res);}else{printf("文件系统挂载成功\r\n");}}}else printf("文件系统挂载成功\r\n");printf("csize = 0x%X = %d\r\n", spi_fs.csize, spi_fs.csize);printf("ssize = 0x%X = %d\r\n", spi_fs.ssize, spi_fs.ssize);printf("n_fatent = 0x%lX = %lu\r\n", spi_fs.n_fatent, spi_fs.n_fatent);printf("database = 0x%lX = %lu\r\n", spi_fs.database, spi_fs.database);printf("fsize = 0x%lX = %lu\r\n", spi_fs.fsize, spi_fs.fsize);printf("last_clst = 0x%lX = %lu\r\n", spi_fs.last_clst, spi_fs.last_clst);printf("free_clst = 0x%lX = %lu\r\n", spi_fs.free_clst, spi_fs.free_clst);/*----------------------- 文件系统测试:写测试 -----------------------------*/printf("\r\n****** 即将进行文件写入测试... ******\r\n");while(1){res = f_open(&fil, "0:sudaroot.txt", FA_OPEN_APPEND | FA_WRITE);if(res == FR_OK){res = f_write(&fil, write_buf, 4096, &count);if(res != FR_OK){printf("f_write 发生错误,err = %d, count = %d\r\n", res, count);printf("关闭打开的sudaroot.txt文件\r\n");count = 0;f_close(&fil);break;}else{if(count == 0){printf("没有空间写入数据了\r\n");break;}sum++;count = 0;f_close(&fil);}}else{printf("打开/创建sudaroot.txt文件失败,err = %d\r\n", res);break;}HAL_GPIO_TogglePin(RUN_LED_GPIO_Port, RUN_LED_Pin);HAL_Delay(1);}printf("总计:sum = %u\r\n", sum);/* USER CODE END 2 *//* Infinite loop *//* USER CODE BEGIN WHILE */while (1){/* USER CODE END WHILE *//* USER CODE BEGIN 3 */HAL_GPIO_TogglePin(RUN_LED_GPIO_Port, RUN_LED_Pin);HAL_Delay(500);}/* USER CODE END 3 */
}效果:

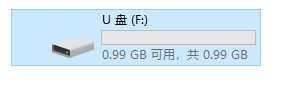
电脑也能读取。

上图等值写入了8104次数据。每次写4KB字节。那么共写入了 8104 * 4KB = 32,416KB数据。
计算一下,和上面数据对比。
我们上面计算出n_fatent = 1015;但是n_fatent会多加比实际可用簇多加2个簇。
![]()
故实际的簇是n_fatent - 2 = 1015 - 2 = 1013;
因为一簇 = 32KB;
故32MB实际可用 = 1013 * 32KB = 32416KB;
对比发现,和计算结果和测试效果一致。
扩容成功。
全篇完。
本人是一个嵌入式未入门小白,博客仅仅代表我个人主观见解,记录成长笔记。
笔记是以最简单的方式,只展示最核心的原理。
若有与 大神大大 见解有歧义,我绝对坚信 大神大大 见解是对的,我的是错的。
若无积分等无法下载源码,可加入QQ群657407920下载交流经验。感谢~!

这篇关于STM32CbueMX之SPI_FLASH + FATFS + USB MSC + 虚拟扩容的文章就介绍到这儿,希望我们推荐的文章对编程师们有所帮助!







