本文主要是介绍Spring Boot3整合Redis,希望对大家解决编程问题提供一定的参考价值,需要的开发者们随着小编来一起学习吧!

⛰️个人主页: 蒾酒
🔥系列专栏:《spring boot实战》
🌊山高路远,行路漫漫,终有归途。
目录
前置条件
1.导依赖
2.配置连接信息以及连接池参数
3.配置序列化方式
4.编写测试
前置条件
已经初始化好一个spring boot项目且版本为3X,项目可正常启动。
作者版本为3.2.2
初始化教程:
新版idea(2023)创建spring boot3项目-CSDN博客![]() https://blog.csdn.net/qq_62262918/article/details/135785412?spm=1001.2014.3001.5501
https://blog.csdn.net/qq_62262918/article/details/135785412?spm=1001.2014.3001.5501
1.导依赖
pom.xml:
<dependency><groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId><artifactId>spring-boot-starter-data-redis</artifactId>
</dependency>如果还没安装redis可以参照这篇:
阿里云ECS使用docke搭建redis服务-CSDN博客![]() https://blog.csdn.net/qq_62262918/article/details/135707725?spm=1001.2014.3001.5502
https://blog.csdn.net/qq_62262918/article/details/135707725?spm=1001.2014.3001.5502
2.配置连接信息以及连接池参数
application.yml:

server:port: 8080
spring:data:redis: # Redis连接配置host: localhost # Redis主机地址port: 6379 # Redis端口号password: 123456 # 访问Redis所需密码database: 0 # 使用的数据库编号lettuce: #Lettuce客户端配置pool: # 连接池配置max-active: 8 # 最大活跃连接数max-wait: -1 # 最大等待时间(-1表示无限等待)max-idle: 8 # 最大空闲连接数min-idle: 0 # 最小空闲连接数修改为你的连接信息即可。
这里要说的是:
Lettuce和Jedis两者都是Java连接Redis的客户端
选择使用Lettuce而不是Jedis的原因如下:
线程安全性:
- Lettuce 是基于 Netty 构建的,它使用异步和事件驱动的方式处理连接。因此,它可以在多个线程之间共享一个连接而不需要额外的同步,因此在高并发环境下更高效。
- Jedis 是基于阻塞 I/O 的,并且不是线程安全的,如果在多个线程中共享同一个 Jedis 实例,需要使用连接池进行同步管理,这可能引入额外的复杂性。
连接方式:
- Lettuce 支持基于 Reactive Streams 的响应式编程模型,能够更好地与 Spring Reactor、Project Reactor 等框架集成,提供异步和非阻塞的操作。
- Jedis 是同步的,并且在执行某些操作时会阻塞线程,这可能会影响应用程序的性能和响应性。
性能和扩展性:
- Lettuce 的设计目标是高性能和扩展性,它可以更好地利用 Redis 4.0 中引入的一些新特性(如 Redis Sentinel 和 Redis Cluster)。
- Jedis 的设计目标更偏向于简单易用,对于一些特殊的 Redis 集群模式可能支持不够完善。
维护和更新:
- Lettuce 是一个活跃的项目,并且持续地得到更新和改进。
- Jedis 在某些方面已经相对稳定,并且在一段时间内没有大的更新。
3.配置序列化方式
config目录下新建redis配置类

配置类代码如下:
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
import org.springframework.data.redis.connection.RedisConnectionFactory;
import org.springframework.data.redis.core.RedisTemplate;
import org.springframework.data.redis.serializer.JdkSerializationRedisSerializer;
import org.springframework.data.redis.serializer.StringRedisSerializer;/*** @author mijiupro*/
@Configuration
public class RedisConfig {@Beanpublic RedisTemplate<String, Object> redisTemplate(RedisConnectionFactory connectionFactory) {RedisTemplate<String, Object> redisTemplate = new RedisTemplate<>();redisTemplate.setConnectionFactory(connectionFactory);// 设置key和value的序列化方式redisTemplate.setKeySerializer(new StringRedisSerializer()); // 设置key的序列化器为StringRedisSerializerredisTemplate.setValueSerializer(new JdkSerializationRedisSerializer()); // 设置value的序列化器为JdkSerializationRedisSerializerredisTemplate.setHashKeySerializer(new StringRedisSerializer()); // 设置hash key的序列化器为StringRedisSerializerredisTemplate.setHashValueSerializer(new JdkSerializationRedisSerializer()); // 设置hash value的序列化器为JdkSerializationRedisSerializerredisTemplate.afterPropertiesSet(); // 初始化RedisTemplatereturn redisTemplate; // 返回配置好的RedisTemplate}
}4.编写测试

import org.junit.jupiter.api.Test;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.boot.test.context.SpringBootTest;
import org.springframework.data.redis.core.StringRedisTemplate;import java.util.concurrent.TimeUnit;@SpringBootTest
public class RedisTest {@Autowiredprivate StringRedisTemplate stringRedisTemplate;@Test//测试redisvoid contextLoads2() {//添加缓存键值对name:mijiu并设置过期时间为1小时stringRedisTemplate.opsForValue().set("name","mijiu",10, TimeUnit.SECONDS);System.out.println(stringRedisTemplate.opsForValue().get("name"));}
}运行测试
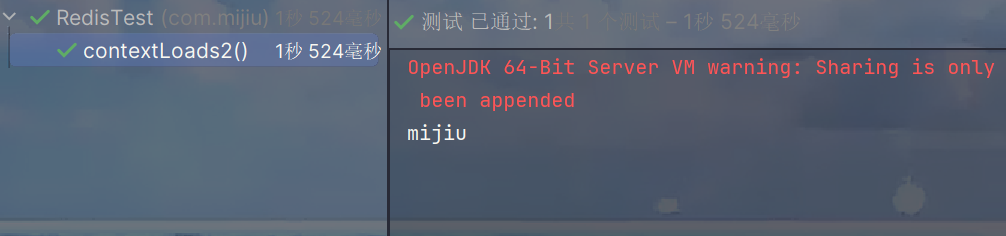
测试成功,整合完毕!
这篇关于Spring Boot3整合Redis的文章就介绍到这儿,希望我们推荐的文章对编程师们有所帮助!






