本文主要是介绍CF1033A King Escape 题解 思维,希望对大家解决编程问题提供一定的参考价值,需要的开发者们随着小编来一起学习吧!
King Escape
传送门
Alice and Bob are playing chess on a huge chessboard with dimensions n × n n \times n n×n. Alice has a single piece left — a queen, located at ( a x , a y ) (a_x, a_y) (ax,ay), while Bob has only the king standing at ( b x , b y ) (b_x, b_y) (bx,by). Alice thinks that as her queen is dominating the chessboard, victory is hers.
But Bob has made a devious plan to seize the victory for himself — he needs to march his king to ( c x , c y ) (c_x, c_y) (cx,cy) in order to claim the victory for himself. As Alice is distracted by her sense of superiority, she no longer moves any pieces around, and it is only Bob who makes any turns.
Bob will win if he can move his king from ( b x , b y ) (b_x, b_y) (bx,by) to ( c x , c y ) (c_x, c_y) (cx,cy) without ever getting in check. Remember that a king can move to any of the 8 8 8 adjacent squares. A king is in check if it is on the same rank (i.e. row), file (i.e. column), or diagonal as the enemy queen.
Find whether Bob can win or not.
Input
The first line contains a single integer n n n ( 3 ≤ n ≤ 1000 3 \leq n \leq 1000 3≤n≤1000) — the dimensions of the chessboard.
The second line contains two integers a x a_x ax and a y a_y ay ( 1 ≤ a x , a y ≤ n 1 \leq a_x, a_y \leq n 1≤ax,ay≤n) — the coordinates of Alice’s queen.
The third line contains two integers b x b_x bx and b y b_y by ( 1 ≤ b x , b y ≤ n 1 \leq b_x, b_y \leq n 1≤bx,by≤n) — the coordinates of Bob’s king.
The fourth line contains two integers c x c_x cx and c y c_y cy ( 1 ≤ c x , c y ≤ n 1 \leq c_x, c_y \leq n 1≤cx,cy≤n) — the coordinates of the location that Bob wants to get to.
It is guaranteed that Bob’s king is currently not in check and the target location is not in check either.
Furthermore, the king is not located on the same square as the queen (i.e. a x ≠ b x a_x \neq b_x ax=bx or a y ≠ b y a_y \neq b_y ay=by), and the target does coincide neither with the queen’s position (i.e. c x ≠ a x c_x \neq a_x cx=ax or c y ≠ a y c_y \neq a_y cy=ay) nor with the king’s position (i.e. c x ≠ b x c_x \neq b_x cx=bx or c y ≠ b y c_y \neq b_y cy=by).
Output
Print “YES” (without quotes) if Bob can get from ( b x , b y ) (b_x, b_y) (bx,by) to ( c x , c y ) (c_x, c_y) (cx,cy) without ever getting in check, otherwise print “NO”.
You can print each letter in any case (upper or lower).
Examples
input #1
8
4 4
1 3
3 1
output #1
YES
input #2
8
4 4
2 3
1 6
output #2
NO
input #3
8
3 5
1 2
6 1
output #3
NO
Note
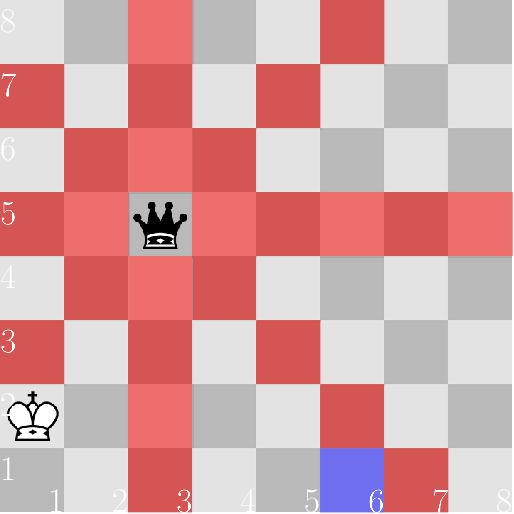
In the diagrams below, the squares controlled by the black queen are marked red, and the target square is marked blue.
In the first case, the king can move, for instance, via the squares ( 2 , 3 ) (2, 3) (2,3) and ( 3 , 2 ) (3, 2) (3,2). Note that the direct route through ( 2 , 2 ) (2, 2) (2,2) goes through check.
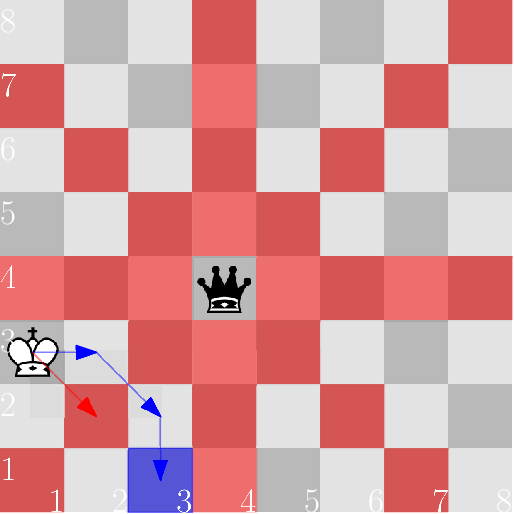
In the second case, the queen watches the fourth rank, and the king has no means of crossing it.
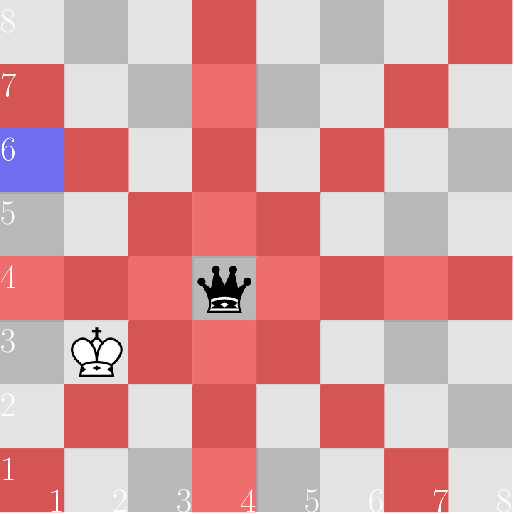
In the third case, the queen watches the third file.

题目TM翻译
爱丽丝和鲍勃正在一个尺寸为 n × n n \times n n×n 的巨大棋盘上下棋。爱丽丝只剩下一个棋子–位于 ( a x , a y ) (a_x, a_y) (ax,ay) 的皇后,而鲍勃只有位于 ( b x , b y ) (b_x, b_y) (bx,by) 的国王。爱丽丝认为她的皇后在棋盘上占据优势,胜利属于她。
但鲍勃却制定了一个狡猾的计划来为自己夺取胜利–他需要将国王行进到 ( c x , c y ) (c_x, c_y) (cx,cy) 处,以便为自己赢得胜利。由于爱丽丝被自己的优越感分散了注意力,她不再移动任何棋子,只有鲍勃在行动。
如果鲍勃能将国王从 ( b x , b y ) (b_x, b_y) (bx,by) 移动到 ( c x , c y ) (c_x, c_y) (cx,cy) ,那么他就赢了。鲍勃如果能将王从 ( b x , b y ) (b_x, b_y) (bx,by) 移动到 ( c x , c y ) (c_x, c_y) (cx,cy) ,而不被牵制,他就赢了。记住,国王可以移动到 8 8 8 个相邻位置中的任何一个。如果国王与敌方王后位于同一等级(即行)、文件(即列)或对角线上,国王就会被牵制。
找出鲍勃能否获胜。
输入格式
第一行包含一个整数 n n n ( 3 ≤ n ≤ 1000 3 \leq n \leq 1000 3≤n≤1000 ) - 棋盘的尺寸。
第二行包含两个整数 a x a_x ax 和 a y a_y ay ( 1 ≤ a x , a y ≤ n 1 \leq a_x, a_y \leq n 1≤ax,ay≤n )–爱丽丝皇后的坐标。
第三行包含两个整数 b x b_x bx 和 b y b_y by ( 1 ≤ b x , b y ≤ n 1 \leq b_x, b_y \leq n 1≤bx,by≤n ) --鲍勃的国王坐标。
第四行包含两个整数 c x c_x cx 和 c y c_y cy --鲍勃的国王坐标。( 1 ≤ c x , c y ≤ n 1 \leq c_x, c_y \leq n 1≤cx,cy≤n ) --鲍勃想要到达的位置的坐标。
**保证鲍勃的王目前没有被吃掉,目标位置也没有被吃掉。
此外,国王与王后不在同一位置(即 a x ≠ b x a_x \neq b_x ax=bx 或 a y ≠ b y a_y \neq b_y ay=by ),而目标位置既不与王后的位置(即 c x ≠ a x c_x \neq a_x cx=ax 或 c y ≠ a y c_y \neq a_y cy=ay )重合,也不与国王的位置(即 c x ≠ b x c_x \neq b_x cx=bx 或 c y ≠ b y c_y \neq b_y cy=by )重合。
输出格式
如果鲍勃能从 ( b x , b y ) (b_x, b_y) (bx,by) 到达 ( c x , c y ) (c_x, c_y) (cx,cy) 而不被检查到,则打印 “是”(不带引号),否则打印 “否”。
您可以用任何大小写(大写或小写)打印每个字母。
提示
在下图中,由黑色皇后控制的方格标记为红色,目标方格标记为蓝色。
例如,在第一种情况下,国王可以通过 ( 2 , 3 ) (2, 3) (2,3) 和 ( 3 , 2 ) (3, 2) (3,2) 这两个位置移动。请注意,通过 ( 2 , 2 ) (2, 2) (2,2) 的直接路线要经过格。
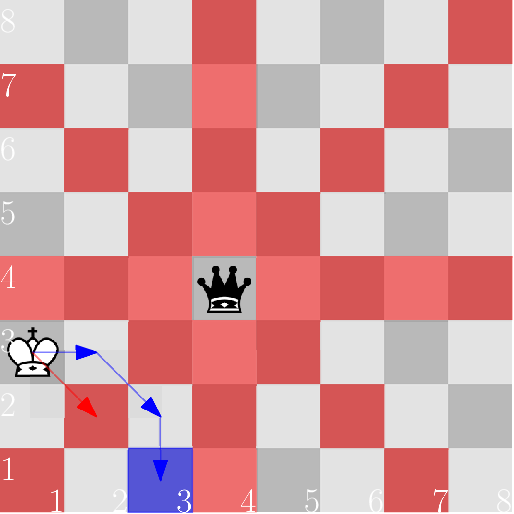
在第二种情况下,王后监视着第四位,国王没有办法越过它。
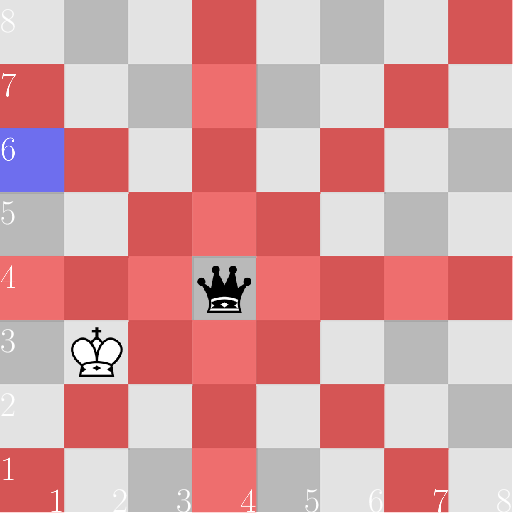
在第三种情况下,王后监视第三列。
以上来自 C o d e F o r c e s ,翻译: D e e p L 以上来自CodeForces,翻译:DeepL 以上来自CodeForces,翻译:DeepL
解题思路
前言
你英语好吗?好吗?好吗?好吗?好吗?好吗?好吗?好吗?好吗?好吗?好吗?好吗?好吗?好吗?好吗?好吗?好吗?好吗?好吗?好吗?好吗?好吗?好吗?好吗?好吗?好吗?好吗?好吗?好吗?好吗?好吗?好吗?好吗?好吗?好吗?好吗?好吗?好吗?好吗?好吗?好吗?好吗?好吗?好吗?好吗?好吗?好吗?好吗?好吗?好吗?好吗?好吗?好吗?好吗?好吗?好吗?好吗?好吗?好吗?好吗?好吗?好吗?好吗?好吗?好吗?好吗?好吗?好吗?好吗?好吗?好吗?好吗?好吗?好吗?好吗?好吗?好吗?好吗?好吗?好吗?好吗?好吗?好吗?好吗?好吗?好吗?好吗?好吗?好吗?好吗?好吗?好吗?好吗?好吗?好吗?好吗?好吗?好吗?好吗?好吗?好吗?好吗?好吗?好吗?好吗?好吗?好吗?好吗?好吗?好吗?好吗?好吗?好吗?
正文
想象一个二维平面,原点位于黑皇后的位置。我们注意到皇后将棋盘分割为多达四个连通分量,其中每个象限都是一个分量。因此,当且仅当原国王位置和目标位置位于同一个象限时,答案为“YES”。只要使用特判即可。
什么?你 dfs \operatorname{dfs} dfs 写过了?那你看什么题解。
AC Code
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
#define int long long
#define EX exit(0);
int n, ax, ay, bx, by, cx, cy;
inline bool check(int ax, int ay, int bx, int by, int cx, int cy);
inline void work() {cin >> n >> ax >> ay >> bx >> by >> cx >> cy;if (check(ax, ay, bx, by, cx, cy))puts("YES"), EXputs("NO");
}
signed main() {ios::sync_with_stdio(false);cin.tie(0);cout.tie(0);work();return 0;
}
inline bool check(int ax, int ay, int bx, int by, int cx, int cy) {return (bx < ax && by < ay && cx < ax && cy < ay) || (bx > ax && by < ay && cx > ax && cy < ay) || (bx < ax && by > ay && cx < ax && cy > ay) || (bx > ax && by > ay && cx > ax && cy > ay);
}
这篇关于CF1033A King Escape 题解 思维的文章就介绍到这儿,希望我们推荐的文章对编程师们有所帮助!





![P2858 [USACO06FEB] Treats for the Cows G/S 题解](/front/images/it_default.jpg)

