本文主要是介绍DBFace: 源码阅读(三),希望对大家解决编程问题提供一定的参考价值,需要的开发者们随着小编来一起学习吧!
7 推断部分
推断部分主要是在test.py中
主要函数其实很短,如下,代码其实被我改了一部分,和原始的github上可能有点区别
mean = [0.408, 0.447, 0.47]
std = [0.289, 0.274, 0.278]# trial_name = "small-H-dense-wide64-UCBA-keep12-noext-ignoresmall2"trial_name = "mv2-320x320-without-wf_20200811"jobdir = f"jobs/{trial_name}"image = common.imread("imgs/selfie.jpg")
model = DBFace(has_landmark=True, wide=64, has_ext=True, upmode="DeCBA")
model.load(f"{jobdir}/models/74.pth")
model.eval()
model.cuda()outs = eval_tool.detect_image(model, image, mean, std, 0.2)
outs = nms(outs, 0.2)
print("objs = %d" % len(outs))
for obj in outs:common.drawbbox(image, obj)common.imwrite(f"{jobdir}/result.jpg", image)
print("ok")model.load()下载对应的模型,推断最主要的函数是
outs = eval_tool.detect_image(model, image, mean, std, 0.2)
我们来看下detect_image函数:
def detect_image(model, image, mean, std, threshold=0.4):
# pad主要是因为网络推断中stride=32,所以为了保证可以上采样回去,需要进行pad操作image = common.pad(image)#预处理操作image = ((image / 255 - mean) / std).astype(np.float32)image = image.transpose(2, 0, 1)image = torch.from_numpy(image).unsqueeze(0).cuda()# 推断center, box, landmark = model(image)
#得到结果回归框中心点的heatmap,通过sigmoid来得到0-1center = center.sigmoid()box = torch.exp(box)# debug# center = F.max_pool2d(center, kernel_size=3, padding=1, stride=1)return detect_images_giou_with_netout(center, box, landmark, threshold)我们再来看下detect_images_giou_with_netout这个函数:
def detect_images_giou_with_netout(output_hm, output_tlrb, output_landmark, threshold=0.4, ibatch=0):stride = 4_, num_classes, hm_height, hm_width = output_hm.shapehm = output_hm[ibatch].reshape(1, num_classes, hm_height, hm_width)tlrb = output_tlrb[ibatch].cpu().data.numpy().reshape(1, num_classes * 4, hm_height, hm_width)# landmark = output_landmark[ibatch].cpu().data.numpy().reshape(1, num_classes * 10, hm_height, hm_width)landmark = output_landmark[ibatch].cpu().data.numpy().reshape(1, num_classes * 50, hm_height, hm_width)# 使用最大池化来筛选值nmskey = _nms(hm, 3)# 选出top值2000,人脸较多的情况下值可以大一些,但是如果人脸比较少,或者图像比较小,建议还是小一些kscore, kinds, kcls, kys, kxs = _topk(nmskey, 2000)kys = kys.cpu().data.numpy().astype(np.int)kxs = kxs.cpu().data.numpy().astype(np.int)kcls = kcls.cpu().data.numpy().astype(np.int)key = [[], [], [], []]for ind in range(kscore.shape[1]):score = kscore[0, ind]if score > threshold:key[0].append(kys[0, ind])key[1].append(kxs[0, ind])key[2].append(score)key[3].append(kcls[0, ind])imboxs = []if key[0] is not None and len(key[0]) > 0:ky, kx = key[0], key[1]classes = key[3]scores = key[2]for i in range(len(kx)):class_ = classes[i]cx, cy = kx[i], ky[i]x1, y1, x2, y2 = tlrb[0, class_ * 4:(class_ + 1) * 4, cy, cx]x1, y1, x2, y2 = (np.array([cx, cy, cx, cy]) + np.array([-x1, -y1, x2, y2])) * stride# 根据关键点个数进行修改# x5y5 = landmark[0, 0:10, cy, cx]# x5y5 = np.array(common.exp(x5y5 * 4))# x5y5 = (x5y5 + np.array([cx] * 5 + [cy] * 5)) * stride# boxlandmark = list(zip(x5y5[:5], x5y5[5:]))x5y5 = landmark[0, 0:50, cy, cx]#注意这个exp()x5y5 = np.array(common.exp(x5y5 * 4))x5y5 = (x5y5 + np.array([cx] * 25 + [cy] * 25)) * strideboxlandmark = list(zip(x5y5[:25], x5y5[25:]))imboxs.append(common.BBox(label=str(class_), xyrb=common.floatv([x1, y1, x2, y2]), score=scores[i].item(),landmark=boxlandmark))return imboxs
最后将返回得到的候选框和关键点坐标在通过nms进行处理
def nms(objs, iou=0.5):if objs is None or len(objs) <= 1:return objsobjs = sorted(objs, key=lambda obj: obj.score, reverse=True)keep = []flags = [0] * len(objs)for index, obj in enumerate(objs):if flags[index] != 0:continuekeep.append(obj)for j in range(index + 1, len(objs)):if flags[j] == 0 and obj.iou(objs[j]) > iou:flags[j] = 1return keep
使用NMS来去除冗余的框,得到最后的结果
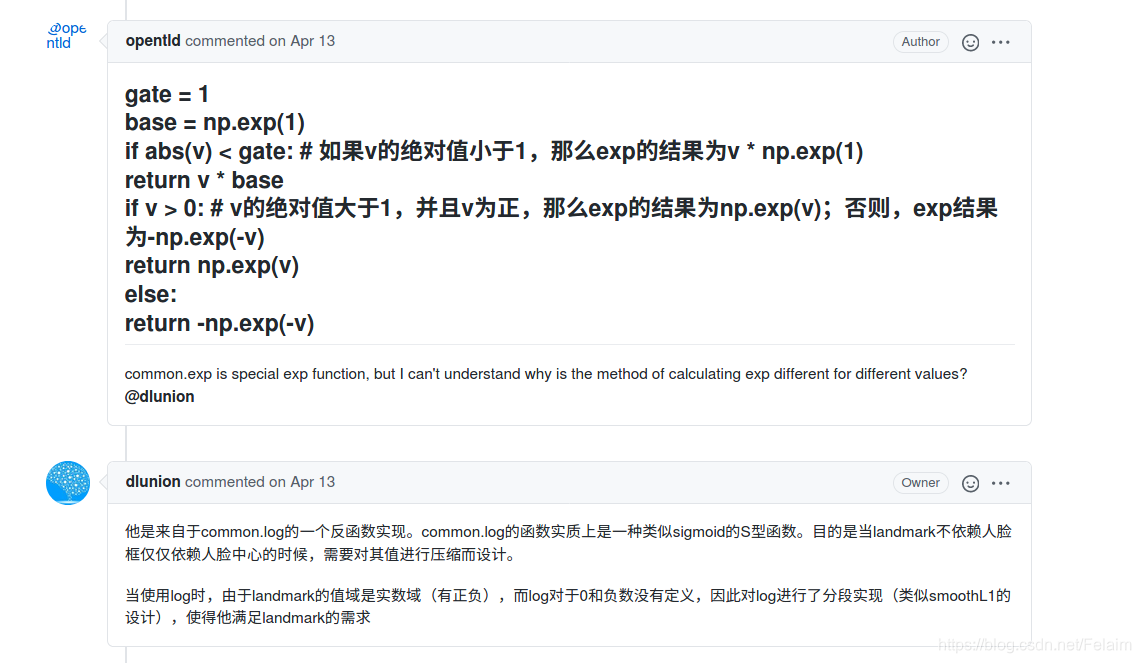
当中,其实有些细节,例如关键点的后处理要进行exp():
def exp(v):if isinstance(v, tuple) or isinstance(v, list):return [exp(item) for item in v]elif isinstance(v, np.ndarray):return np.array([exp(item) for item in v], v.dtype)gate = 1base = np.exp(1)if abs(v) < gate:return v * baseif v > 0:return np.exp(v)else:return -np.exp(-v)为什么呢?我们来看下作者是怎么解释的?
第三篇还是有些细节是需要注意的,后面一篇写下转caffemodel?还是其他呢。。。
这篇关于DBFace: 源码阅读(三)的文章就介绍到这儿,希望我们推荐的文章对编程师们有所帮助!