本文主要是介绍uboot代码解析2:环境变量、调试信息、uboot升级、命令交互、C冷门知识,希望对大家解决编程问题提供一定的参考价值,需要的开发者们随着小编来一起学习吧!
https://ke.qq.com/course/4032547?flowToken=1042705
本文档的内容imx6ull中测试。
目录
https://ke.qq.com/course/4032547?flowToken=1042705
一 环境变量
env_init
getenv和setenv函数系列函数
int getenv_f(const char *name, char *buf, unsigned len)
调试信息相关
初始化波特率
串口输出调试信息
1 使用uboot自带的debug宏
2 使用自定义的宏
UBOOT版本信息
修改版本号
tftp下载并在内存中运行uboot
tftp升级uboot
从分区1,直接升级uboot。
将uboot.bin下载到SD卡中
命令交互
int run_command(const char *cmd, int flag)
二 结构体:typedef struct bd_info
bi_arch_number
bi_boot_params
冷门知识
typedef :函数类型和函数指针类型的用法
自定义类型func变量函数类型
自定义类型pfunc变量函数指针类型
.内嵌汇编
.typeof关键字
一 环境变量
env_init
不同的启动介质对应不同的环境变量初始化函数。所以这个含函数有很多不同的定义,都在common/env_xxx.c中定义,例如我的板子是emmc启动,那就是env_emmc中定义的env_init执行。
我的emmc的env_init的函数如下:
int env_init(void)
{/* use default */gd->env_addr = (ulong)&default_environment[0];gd->env_valid = 1;return 0;
}default_environment是定义如下
static char default_environment[]该变量在include/env_default.h文件中被定义,可以在该文件定义和修改环境变量默认值
getenv和setenv函数系列函数
有很多的getenv和setenv函数定义cmd/nvedit.c文件中。
int getenv_f(const char *name, char *buf, unsigned len)
调试信息相关
有两类初始化函数_r结尾的和_f结尾的,_r结尾的表示第二阶段的初始化,_f表示第一阶段的初始化函数,他们对应两个数据
初始化波特率
static int init_baud_rate(void)
{gd->baudrate = getenv_ulong("baudrate", 10, CONFIG_BAUDRATE);return 0;
}这里调用了函数getenv_ulong,它的返回值是整数,该函数定义在cmd/nvedit.c文件中。
也对应的也有setenv_ulong函数
如果设置波特率,那就是
setenv_ulong("baudrate",115200);这代码的含义就是设置环境变量中波特率的值是115200。
串口输出调试信息
1 使用uboot自带的debug宏
printf函数最终调用的输出函数puts在common/console.c文件中,这里就不解析了。
common/console.c个文件也有和输入相关的函数,命令交互的时候,会调用这些输入函数。
想在哪里输出调试信息的话,在该源文件开头添加如下代码
#ifdef DEBUG
#undef DEBUG
#define debug(fmt,args...) printf(fmt ,##args)
2 使用自定义的宏
//#define __DEBUG_INFO__
#ifdef __DEBUG_INFO__
#define DEBUG_INFO(format,...) printf("%s,%s,line=%d:"format"\n",__FILE__,__func__,__LINE__,##__VA_ARGS__)
#else
#define DEBUG_INFO(format,...)
#endif//#define __DEBUG_CORE__
#ifdef __DEBUG_CORE__
#define DEBUG_CORE(format,...) printf("%s,%s,line=%d:"format"\n",__FILE__,__func__,__LINE__,##__VA_ARGS__)
#else
#define DEBUG_CORE(format,...)
#endif//#define __DEBUG_PRINT__
#ifdef __DEBUG_PRINT__
#define DEBUG_PRINT(format,...) printf(format,##__VA_ARGS__)
#else
#define DEBUG_PRINT(format,...)
#endifUBOOT版本信息
修改版本号
U_BOOT_VERSION 定义在文件Version_autogenerated.h 中,如下所示,Version_autogenerated.h它是编译的时候自动生成的,它是在Makefile文件中生成的。
#define PLAIN_VERSION "2016.03"
#define U_BOOT_VERSION "U-Boot " PLAIN_VERSION
#define CC_VERSION_STRING "arm-linux-gnueabihf-gcc (Linaro GCC 4.9-2017.01) 4.9.4"
#define LD_VERSION_STRING "GNU ld (Linaro_Binutils-2017.01) 2.24.0.20141017 Linaro 2014_11-3-git"
在include/version.h文件中
#ifndef CONFIG_IDENT_STRING
#define CONFIG_IDENT_STRING ""
#endif#define U_BOOT_VERSION_STRING U_BOOT_VERSION " (" U_BOOT_DATE " - " \U_BOOT_TIME " " U_BOOT_TZ ")" CONFIG_IDENT_STRINGU_BOOT_VERSION_STRING 它就是uboot启动时输出的版本信息的宏,如下所示
U-Boot 2016.03 (Jun 02 2022 - 21:05:03 +0800)
测试一下
tftp下载并在内存中运行uboot
修改宏如下所示
#ifdef CONFIG_IDENT_STRING
#undef CONFIG_IDENT_STRING#ifndef CONFIG_IDENT_STRING
#define CONFIG_IDENT_STRING " for lkmao"
#endif通过uboot升级uboot,这个操作仅限于我自己的板子,别的板子可能不一样,思路还是可以参考的。
编译并下载
第一步,先将uboot下载到内存80800000地址处
=> tftp 80800000 u-boot.imx
FEC0 Waiting for PHY auto negotiation to complete.... done
Using FEC0 device
TFTP from server 192.168.0.11; our IP address is 192.168.0.3
Filename 'u-boot.imx'.
Load address: 0x80800000
Loading: ######################2.6 MiB/s
done
Bytes transferred = 314368 (4cc00 hex)
第二步 直接在80800000处运行uboot
=> go 80800000
## Starting application at 0x80800000 ...
好吧,这是个错误的尝试
看了文档,人家测的时候用8780 0000这个地址,重新下载
=> tftp 87800000 u-boot.bin
FEC0 Waiting for PHY auto negotiation to complete.... done
Using FEC0 device
TFTP from server 192.168.0.11; our IP address is 192.168.0.3
Filename 'u-boot.bin'.
Load address: 0x87800000
Loading: #####################2.1 MiB/s
done
Bytes transferred = 307920 (4b2d0 hex)
=> go 87800000
然后运行
go 87800000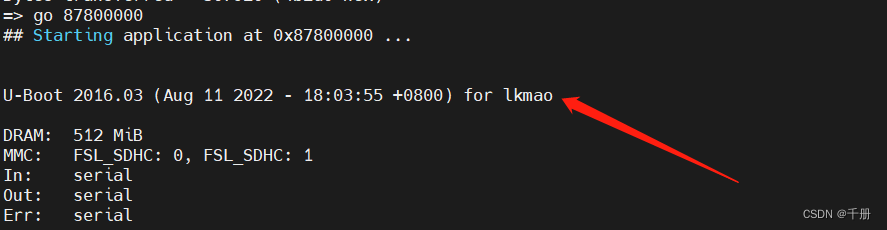
由上图可以,我刚刚修改的内容生效了,是不是有一点点欣慰啊。注意这个uboot只下载到了内存中,没有下载到flash中,重启后它就消失了。
如何下载到板卡中呢?
再测试一下:
tftp升级uboot
以下操作都是按照别人提供的资料操作的,自己可不敢在这个地方搞创新,特别是新手
最好还是再修改点东西,要不然,也不知道有没有成功升级。在版本号中添加"hello world",
这个宏是在include/version.h文件中。
#ifdef CONFIG_IDENT_STRING
#undef CONFIG_IDENT_STRING#ifndef CONFIG_IDENT_STRING
#define CONFIG_IDENT_STRING " hello world"
#endif重新编译,找到u-boot.imx文件。
第一步,上前面不同,这次是将u-boot.imx下载到内存中
=> tftp 87800000 u-boot.imx
FEC0 Waiting for PHY auto negotiation to complete.... done
Using FEC0 device
TFTP from server 192.168.0.11; our IP address is 192.168.0.3
Filename 'u-boot.imx'.
Load address: 0x87800000
Loading: ######################2.8 MiB/s
done
Bytes transferred = 314368 (4cc00 hex)
第二步,计算
314368/512 = 614(266) :314368是从第一步下载最后一行得到的文件大小信息,266就是扇区数。
第三步,开始下载
切换分区
=> mmc dev 1 0
switch to partitions #0, OK
mmc1(part 0) is current device
=>写分区
=> mmc write 87800000 2 266MMC write: dev # 1, block # 2, count 614 ... 614 blocks written: OK
=>配置分区
=> mmc partconf 1 1 0 0
=>
重启验证
重启命令是reset。由下图可知,u-boot.imx已经成功升级了。
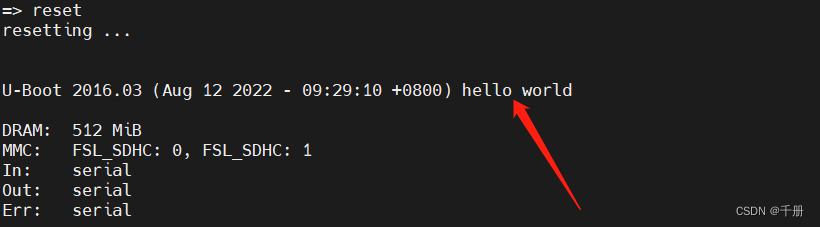
从分区1,直接升级uboot。
以下代码不具备可移植性,仅供参考。这一步可扩展为从文件系统升级。
这个首先将u-boot.imx通过文件系统下载到mmcblk1p1分区,然后到uboot中操作
fatload mmc 1:1 80800000 u-boot.imx
=> fatload mmc 1:1 80800000 u-boot.imx
reading u-boot.imx
379904 bytes read in 34 ms (10.7 MiB/s)
379904 /512 = 742(2e6)
mmc dev 1 0
mmc write 80800000 2 32E //烧写 u-boot.imx 到 EMMC 中
mmc partconf 1 1 0 0 //分区配置, EMMC 需要这一步!将uboot.bin下载到SD卡中
首先,将SD卡插到ubuntu中,如何知道知道SD卡的设备号呢,简单,插完卡后马上dmesg,如下所示看到sdb1 sdb2
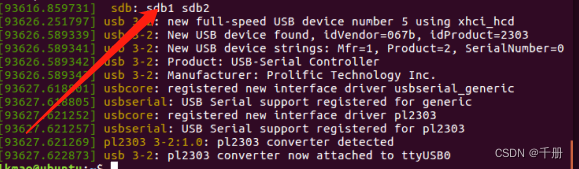
说明SD卡的设备就是/dev/sdb
下载
$ ./imxdownload u-boot.bin /dev/sdb
I.MX6ULL bin download software
Edit by:zuozhongkai
Date:2019/6/10
Version:V1.1
log:V1.0 initial version,just support 512MB DDR3V1.1 and support 256MB DDR3
file u-boot.bin size = 307920Bytes
Board DDR SIZE: 512MB
Delete Old load.imx
Create New load.imx
Download load.imx to /dev/sdb ......
[sudo] lkmao 的密码:
记录了607+1 的读入
记录了607+1 的写出
310992 bytes (311 kB, 304 KiB) copied, 0.95695 s, 325 kB/s
lkmao@ubuntu:~/imx/uboot/uboot_ws/uboot_ws_lkmao$
SD卡暂时无法测试,等能测试了,再把测试结果加进来
命令交互
int run_command(const char *cmd, int flag)
/** Run a command using the selected parser.** @param cmd Command to run* @param flag Execution flags (CMD_FLAG_...)* @return 0 on success, or != 0 on error.*/
int run_command(const char *cmd, int flag)
{
#ifndef CONFIG_SYS_HUSH_PARSER/** cli_run_command can return 0 or 1 for success, so clean up* its result.*/if (cli_simple_run_command(cmd, flag) == -1)return 1;return 0;
#elseint hush_flags = FLAG_PARSE_SEMICOLON | FLAG_EXIT_FROM_LOOP;if (flag & CMD_FLAG_ENV)hush_flags |= FLAG_CONT_ON_NEWLINE;return parse_string_outer(cmd, hush_flags);
#endif
}
二 结构体:typedef struct bd_info
bi_arch_number
ulong bi_arch_number;/* unique id for this board */这货是一个机器码,用来和内核匹配的,可不是UUID编号。属于板级的。
bi_boot_params
ulong bi_boot_params; /* where this board expects params */bootargs存放的地址,uboot把它传递给内核,内核启动后在设备树中能看到这个值
在目录/proc/device-tree/chosen
# ls -ls
total 00 -r--r--r-- 1 root root 9 Jan 1 00:00 UUID_ID00 -r--r--r-- 1 root root 9 Jan 1 00:00 UUID_ID10 -r--r--r-- 1 root root 84 Jan 1 00:00 bootargs0 -r--r--r-- 1 root root 18 Jan 1 00:00 ethaddr0 -r--r--r-- 1 root root 7 Jan 1 00:00 name0 -r--r--r-- 1 root root 57 Jan 1 00:00 stdout-path
# cat bootargs
console=ttymxc0,115200 root=/dev/ram0 rootfstype=ramfs rdinit=/linuxrc rootwait rw#
冷门知识
typedef :函数类型和函数指针类型的用法
typedef int (func)(int a,int b);
typedef int (*pfunc)(int a,int b);
写个代码测试一下
typedef int (func)(int a,int b);typedef int (*pfunc)(int a,int b);
int add(int a,int b)
{return a + b;
}
自定义类型func变量函数类型
int a = 5,b = 10;
func *f1 = add;
printf("%d\n",f1(a , b));自定义类型pfunc变量函数指针类型
int a = 5,b = 10;
pfunc f2 = add;
printf("%d\n",f2(a , b));.内嵌汇编
被定义成了宏mb() 和dmb()
#define mb() asm volatile("dsb sy" : : : "memory")
#define dmb() __asm__ __volatile__ ("" : : : "memory")据说这个主要是为了防止gcc的优化造成乱序执行错误。
下面是它被调用的地方
#define __iormb() dmb()
#define __iowmb() dmb()#define writeb(v,c) ({ u8 __v = v; __iowmb(); __arch_putb(__v,c); __v; })
#define writew(v,c) ({ u16 __v = v; __iowmb(); __arch_putw(__v,c); __v; })
#define writel(v,c) ({ u32 __v = v; __iowmb(); __arch_putl(__v,c); __v; })
#define writeq(v,c) ({ u64 __v = v; __iowmb(); __arch_putq(__v,c); __v; })#define readb(c) ({ u8 __v = __arch_getb(c); __iormb(); __v; })
#define readw(c) ({ u16 __v = __arch_getw(c); __iormb(); __v; })
#define readl(c) ({ u32 __v = __arch_getl(c); __iormb(); __v; })
#define readq(c) ({ u64 __v = __arch_getq(c); __iormb(); __v; })如果写过linux驱动是不是很熟悉,可以拿来读写IO口读写内存。
.typeof关键字
众所周知typeof可以获取变量或者表达式的类型,先看三行代码
int a = 10;
typeof (a++) b = 15;
printf("a = %d\n",a);变量b被定义了以后,a的值是10还是11呢,小伙伴也验证一下
a = 10为什么要验证这个呢,我因为看达到一段比较大小的代码,如下所示:
#define maxint(a,b) \({\typeof (a) __max1 = (a);\typeof (b) __max2 = (b);\(void)( &__max1 == &__max2);\__max1 > __max2?__max1:__max2;})这是个比较大小的代码,只有当typeof (a++)被执行的时候,a的值没有改变,这个代码才是有效的,实际上也确实如此。
在看两行代码
int a = 10;
typeof (a++ + a++) b = 15;
printf("a = %d\n",a);这个执行完以后a的值还是10
再看两行代码
int a = 10;
typeof (&a) c;
printf("c = %d\n",c);
printf("d =%d\n",d);warning: format ‘%d’ expects argument of type ‘int’, but argument 2 has type ‘int *’ [-Wformat=]printf("c = %d\n",c);
她说c是一个int类型的指针。
就是说typeof计算了取地址表达式&,没有计算加法运算。
typeof (*c) d = 10;这个说明啥呢,typeof计算了解引用吗,暂时也这样理解吧,这个也可能是编译器干的好事。再次写一个函数验证一下
最后看一个奇怪的
#include <stdio.h>
void hello()
{printf("hello world");
}
int main(int argc,char *argv[])
{int a = 10;typeof (a+=10,printf("a = %d\n",++a),hello(),a) b = 15;printf("b = %d\n",b);return 0;
}输出结果
$ ./a.out
b = 15
好了,不分析了,适可而止吧,继续分析没啥意义了。
这篇关于uboot代码解析2:环境变量、调试信息、uboot升级、命令交互、C冷门知识的文章就介绍到这儿,希望我们推荐的文章对编程师们有所帮助!



