本文主要是介绍yolov2原理到代码,希望对大家解决编程问题提供一定的参考价值,需要的开发者们随着小编来一起学习吧!
yolov2原理到代码
- yolov2较yolov1改进的地方
- 对图片真实框的处理
- 真实框与anchor box的IOU计算方法
- yolov2流程
yolov2较yolov1改进的地方
从输入图片角度:
- 用高分辨率图片对识别网络进行了微调
- 采用多尺度训练
从网络设计角度:
- 增加了Batchnorm层
- 设计了新的网络(Darknet19)
- 增加了细粒度分类
从损失函数角度:
- 采用anchors box
- 利用维度聚类得出anchors box的宽高和最佳个数(5个)
- 采用直接坐标预测法进行预测
对图片真实框的处理
- yolov1:计算出目标在 S ∗ S S*S S∗S 网格中的位置,将该网格对应的B个bounding box 均设为有目标,且具体目标信息(包括置信度、box坐标、类别概率)均一致,不涉及到IOU的计算。
- yolov2:分别计算一张图片中每个目标在 S ∗ S S*S S∗S 网格中的位置,再计算目标与每个anchor box的IOU,选择IOU最大的anchor box,将该位置设置为有目标,其他位置均设置为无目标。若最大的IOU为零,则所有anchor box位置均为无目标。
tips:其实不会出现完全没有交集,即IOU=0的情况。可根据计算iou的过程得出结论。
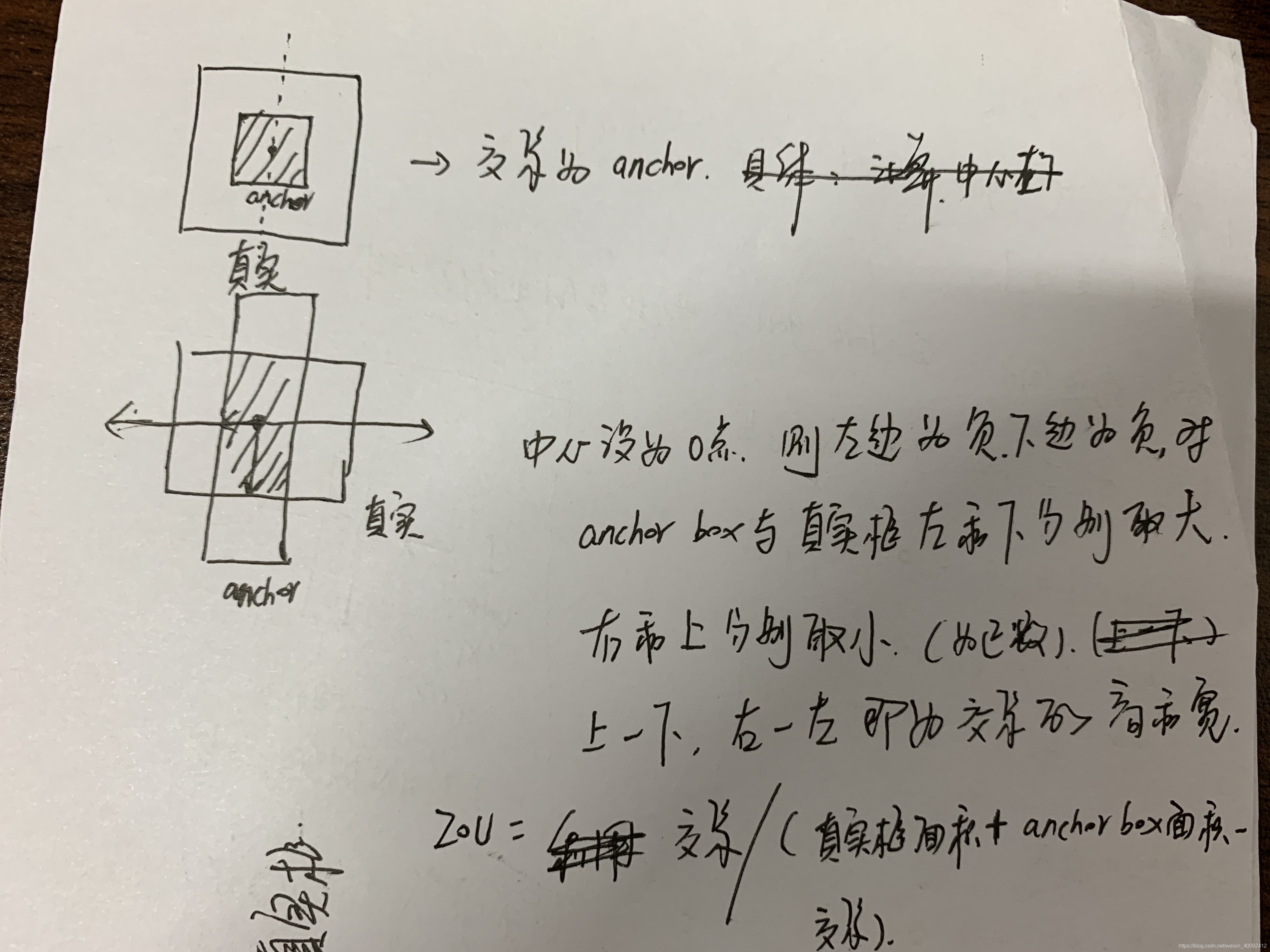
真实框与anchor box的IOU计算方法
由于anchor box提供的是宽和高,计算IOU时假定anchor box的中心与目标所在中心位置一致,因此计算IOU其实用不到目标中心坐标,只利用anchor box和真实框的宽和高就可算出。具体如下:
yolov2流程
-
对于输入图片image,设宽和高分别为 ( w i d t h , h e i g h t ) (width, height) (width,height),将true boxes的坐上坐标和右下坐标转化为中心坐标和宽高 ( x , y , w , h ) (x,y,w,h) (x,y,w,h),再 ( x , y , w , h ) / ( w i d t h , h e i g h t , w i t h , h e i g h t ) (x,y,w,h)/(width,height,with,height) (x,y,w,h)/(width,height,with,height)将true boxes归一化到 ( 0 , 1 ) (0,1) (0,1) 区间内。
-
根据处理后的true boxes、anchors以及resize的图片大小,将true boxes转化为 ( 13 ? , 13 ? , n u m a n c h o r s , 5 ) (13?,13?,num_{anchors},5) (13?,13?,numanchors,5)的形式,再输出一个 ( 13 ? , 13 ? , n u m a n c h o r s , 1 ) (13?,13?,num_{anchors},1) (13?,13?,numanchors,1)的向量,表示某个anchors与其中一个true box最匹配,匹配位置记为1,其他位置记为0。具体:
x , y , w , h x,y,w,h x,y,w,h乘上输出特征图大小(例如 13 ∗ 13 13*13 13∗13)对每个true box都做该处理,然后与anchor box进行匹配,计算出最匹配的anchor box,最终输出的 x , y x,y x,y为 ( x , y ) ∗ ( 13 , 13 ) − f l o o r ( ( x , y ) ∗ ( 13 , 13 ) ) (x,y)*(13,13)-floor((x,y)*(13,13)) (x,y)∗(13,13)−floor((x,y)∗(13,13)),输出的 w , h w,h w,h为 l o g ( ( ( w , h ) ∗ ( 13 , 13 ) ) / a n c h o r s [ b e s t a n c h o r ] ) log(((w,h)*(13,13))/anchors[best_{anchor}]) log(((w,h)∗(13,13))/anchors[bestanchor]),最后一个是类别。 -
构建模型
-
构建损失函数
损失函数计算:
1)首先将网络出书输出转化为与true boxes相同的格式:
网络输出为 ( 13 ? , 13 ? , n u m a n c h o r s , 5 + n u m c l a s s e s ) (13?,13?,num_{anchors},5+num_{classes}) (13?,13?,numanchors,5+numclasses), 5 + n u m c l a s s e s 5+num_{classes} 5+numclasses中的前两个分别为中心坐标 x , y x,y x,y,接下来两个人分别为宽高 w , h w,h w,h,再接下来一个是置信度,最后 n u m c l a s s e s num_{classes} numclasses个为类别概率。
将 x , y , c o n f i d e n c e x,y,confidence x,y,confidence分别用 s i g m o i d sigmoid sigmoid函数激活, w , h w,h w,h取指数,类别概率用 s o f t m a x softmax softmax函数激活。
将 x , y x,y x,y分别转化为相对于 13 ∗ 13 13*13 13∗13大小的图片的位置,范围还是 ( 0 , 1 ) (0,1) (0,1),将 w , h w,h w,h分别转化为相对于anchor box与 13 ∗ 13 13*13 13∗13的相对位置
对应代码段如下
box_xy = (box_xy + conv_index) / conv_dims
box_wh = box_wh * anchors_tensor / conv_dims
2)将pred box与true box的坐标形式 ( x , y , w , h ) (x,y,w,h) (x,y,w,h) 均转化为 ( x 1 , y 1 , x 2 , y 2 ) (x_1,y_1,x_2,y_2) (x1,y1,x2,y2) 的形式,计算IOU,根据最大的IOU是否超过设定阈值,判断该anchor box是否有目标,再计算损失函数(损失函数用的true box是根据第二项计算的 ( x , y , w , h ) (x,y,w,h) (x,y,w,h)算,用的pred box是根据下面的方式计算:
直接对输出 ( 13 ? , 13 ? , n u m a n c h o r s , 5 + n u m c l a s s e s ) (13?,13?,num_{anchors},5+num_{classes}) (13?,13?,numanchors,5+numclasses)中 5 + n u m c l a s s e s 5+num{classes} 5+numclasses 的前两个
取sigmoid作为中心坐标,后两个直接作为宽高,将这个作为pred box,与true box对应位置相减计算定位损失,对于分类损失和置信度损失用的是第1)步计算出的置信度和类别概率) -
预测时,输出的前四个为相对于anchors的 ( x , y , w , h ) (x,y,w,h) (x,y,w,h),先转化为相对于整张图片的 ( x , y , w , h ) (x,y,w,h) (x,y,w,h),再将其转化为 ( x 1 , y 1 , x 2 , y 2 ) (x_1,y_1,x_2,y_2) (x1,y1,x2,y2),计算得分,选择超过门限的anchors box,最后做非极大值抑制。
乘以原始图片的 ( w i d t h , h e i g h t , w i d t h , h e i g h t ) (width,height,width,height) (width,height,width,height)得出真实的坐标位置。
这篇关于yolov2原理到代码的文章就介绍到这儿,希望我们推荐的文章对编程师们有所帮助!


