本文主要是介绍Linux的热拔插UDEV机制和守护进程,希望对大家解决编程问题提供一定的参考价值,需要的开发者们随着小编来一起学习吧!
linux的热拔插UDEV机制
1.udev是设备管理工具,udev以守护进程的形式运行。
2.通过侦听内核发出的uevent管理dev下的设备文件。
3.udev在用户空间运行,而不在内核空间运行。
4.能够态动态更新设备文件,创建,删除等。
系统框架图
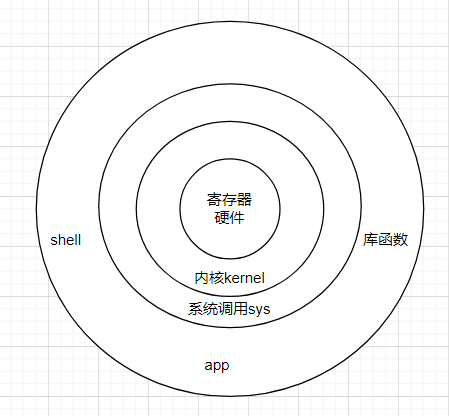
守护进程
1.运行在后台的进程。
2.独立于终端且周期性地执行
3.每次运行不需手动拉起。
4.守护进程的名称通常以d结尾
5.常见守护进程:syslogd,httpd,sendmail和mysqld等。
守护进程特点
1.生存周期长,随操作系统启动,关闭。
2.守护进程和终端无关联,控制终端退出,守护任然运行
3.守护进程是在后台运行,不会占着终端,终端可以执行其他命令
4.守护进程的父进程是init进程,真父进程fork出子进程后先于子进程退出 ,是一个由init继承的孤
儿进程
5.[]叫内核守护进程,不带[]为普通守护进程
6.init:是系统守护进程,很多进程的PPID是init,负责收养孤儿进程
守护进程API
#include <unistd.h>int daemon(int nochdir, int noclose);当nochdir为0时,daemon将更改进程工作目录为根目录。当noclose为0是,daemon将进程的STDIN, STDOUT, STDERR都重定向到/dev/null。时间相关API
struct tm { int tm_sec; 秒,范围从 0 到 59 int tm_min; 分,范围从 0 到 59 int tm_hour; 小时,范围从 0 到 23 int tm_mday; 一月中的第几天,范围从 1 到 31 int tm_mon; 月份,范围从 0 到 11 int tm_year; 自 1900 起的年数 int tm_wday; 一周中的第几天,范围从 0 到 6 int tm_yday; 一年中的第几天,范围从 0 到 365 int tm_isdst; 夏令时 };char* asctime(struct tm * ptr)功能:将结构struct tm * ptr所表示的时间以字符串表示,返回的时间字符串格式为:星期,月,日,小时:分:秒,年参数:ptr通过函数localtime()或gmtime()得到struct tm *localtime(const time_t *timer)使用timer()函数的值来填充tm结构。timer的值被分解为tm结构,并用本地时区表示struct tm *gmtime(time_t *timer)使用timer()函数的值来填充tm结构。timer的值被分解为tm结构,并用格林威治标准时间表示time_t time(time_t *timer)timer=NULL时得到当前日历时间(从1970-01-01 00:00:00到现在的秒数)timer=时间数值时,用于设置日历时间,time_t是一个unsigned long类型如果timer不为空,则返回值也存储在变量 timer中,返回当前日历时间或者设置日历时间demo1:
利用API创建守护进程,每隔5s将当前时间写入文件
代码示例:
#include <unistd.h>
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <sys/stat.h>
#include <fcntl.h>
#include <signal.h>
#include <time.h>
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <stdbool.h>
#include <pthread.h>bool flag = true;void signal_handler(int signal_num,siginfo_t *info,void *context)
{flag = false;
}void *func1()
{struct sigaction act;act.sa_sigaction = signal_handler;act.sa_flags = SA_SIGINFO;while(1){sigaction(SIGINT,&act,NULL);}pthread_exit(NULL);
}void *func2()
{int fd;time_t t;char *buf = NULL;while(flag){umask(0);fd = open("/root/pro/date.log",O_CREAT|O_RDWR|O_APPEND,0666);if(fd == -1){printf("open/create file fail\n");perror("error");exit(-1);}t = time(NULL);buf = asctime(localtime(&t));write(fd,buf,64);sleep(5);}pthread_exit(NULL);
}int main()
{int ret;pthread_t sig;pthread_t wri;ret = daemon(0,0);if(ret == -1){printf("create daemon fail\n");perror("error");exit(-1);}pthread_create(&sig,NULL,func1,NULL);pthread_create(&wri,NULL,func2,NULL);pthread_join(sig,NULL);pthread_join(wri,NULL);return 0;
}代码结果示例:
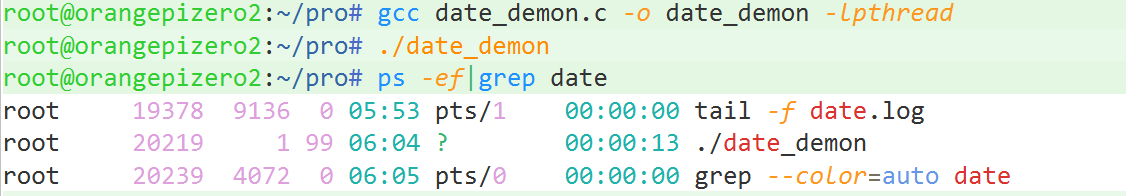
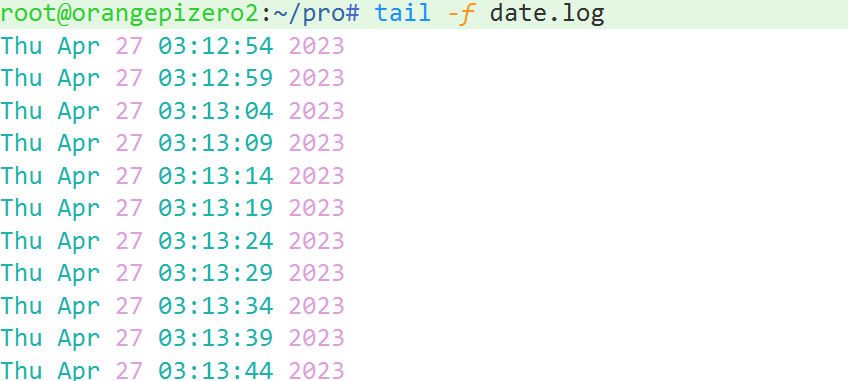
demo2:
自定义daemonAPI,实现demo1
代码示例:
#include <unistd.h>
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <sys/stat.h>
#include <fcntl.h>
#include <signal.h>
#include <time.h>
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <stdbool.h>
#include <pthread.h>bool flag = true;void sighandler_t(int signal_num)
{flag = false;
}void *func1()
{while(1){signal(SIGINT,sighandler_t);}pthread_exit(NULL);
}void *func2()
{int fd;time_t t;char *buf = NULL;while(flag){umask(0);fd = open("/root/pro/date.log",O_CREAT|O_RDWR|O_APPEND,0666);if(fd == -1){printf("open/create file fail\n");perror("error");exit(-1);}t = time(NULL);buf = asctime(localtime(&t));write(fd,buf,64);sleep(5);}pthread_exit(NULL);
}void mydaemon()
{pid_t pid = fork();if( pid == -1) {perror("fork");exit(1);}else if(pid) {exit(0);}//创建新会话,子进程为会话和进程的组长。if(setsid() == -1) {perror("setsid");exit(1);}//关掉从父进程继承的文件描述符。int max_fd = sysconf(_SC_OPEN_MAX);for(int i = 0; i < max_fd; ++i) {close(i);}umask(0);chdir("/");
}int main()
{int ret;pthread_t sig;pthread_t wri;mydaemon();pthread_create(&sig,NULL,func1,NULL);pthread_create(&wri,NULL,func2,NULL);pthread_join(sig,NULL);pthread_join(wri,NULL);return 0;
}代码结果示例:
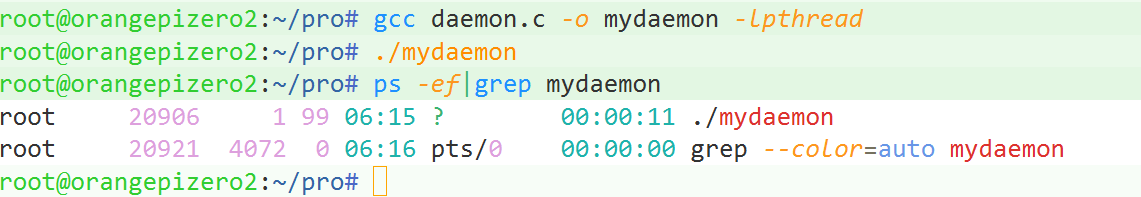
这篇关于Linux的热拔插UDEV机制和守护进程的文章就介绍到这儿,希望我们推荐的文章对编程师们有所帮助!




