本文主要是介绍第十一站:运算符重载operate(+-*/),希望对大家解决编程问题提供一定的参考价值,需要的开发者们随着小编来一起学习吧!
目录
使用成员函数重载运算符
使用非成员函数重载运算符
使用重载函数运算整数
禁区:
赋值重载运算符=
bug:
关系重载运算符><
下标运算符重载
bug
输入输出运算符重载<<,>>
使用成员函数
使用友元函数 (更方便)
普通类型==>类类型
类类型==>普通类型
类类型转换成类类型(拷贝)
operate(+,-,*,/,=,->,<<,>>)支持使用友元函数
(),=,->,[]不支持使用友元函数
局限:C/C++的运算符,支持的数据类型,仅限于基本数据类型
使用成员函数重载运算符
//一只牛+一只羊
Pig operator+(const Goat& goat);//一个参数是本类,一个是goat类,返回值是pig类
//一只牛+一只牛
Pig operator+(const Cow& cow);//相当于将值返回给猪,牛.operate+(羊)
Pig Cow::operator+(const Goat& goat){
int tmp = this->weight * 2 + goat.getWeight() * 3;
return Pig(tmp);
}
Pig Cow::operator+(const Cow& cow) {
int tmp = (this->weight + cow.weight) * 2;
return Pig(tmp);
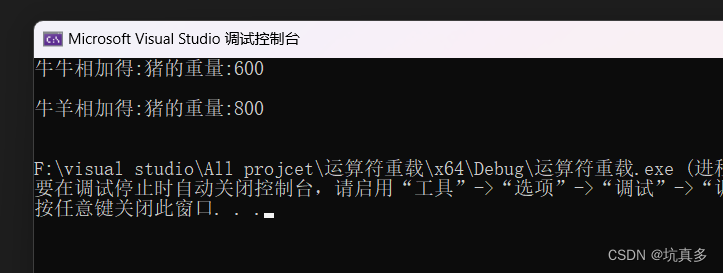
}cout << "牛牛相加得:";
Cow h1(100);
Cow h2(200);
Pig p1 = h1+h2;cout << p1.describe() << endl;
使用非成员函数重载运算符

friend Pig operator+(const Cow& cow, const Goat& goat);
friend Pig operator+(const Cow& cow, const Cow& cow1);Pig operator+(const Cow& cow, const Goat& goat) {
int tmp = cow.weight * 2 + goat.getWeight()*3;
return tmp;
}Pig operator+(const Cow& cow , const Cow& cow1) {
int tmp = cow.weight * 2 + cow1.weight * 2;
return tmp;
}cout << "牛牛相加得:";
Cow h1(100);
Cow h2(200);
Pig p1 = operator+(h1,h2);
cout << p1.describe() << endl;
使用重载函数运算整数
Pig operator+(int n);//一个参数是本身,一个是整数n,,返回值是pig类
禁区:
不能对标准运算符进行重载:1+1=2
不能改变原运算符的语法规则,单目运算符不能变为双目运算符
不能改变运算符的优先级
不能创造新的运算符(错:operator**)
(),=,->,[]不支持使用友元函数
赋值重载运算符=

.h
#pragma once
#include <string>
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
class Boy{
public:Boy(const char* name=NULL, int age=0, int salary=0, int darkHorse=0);Boy& operator=(const Boy& boy);~Boy();string decribe();
private:char* name;int age;int salary;int darkHorse;unsigned int id;static int LAST_ID;
};.cpp
#include "Boy.h"
#include <string>
#include <sstream>
int Boy::LAST_ID = 0;//编号初始化为0Boy::Boy(const char* name, int age, int salary, int darkHorse){if (!name){name = "未知";}this->name = new char[strlen(name) + 1];strcpy_s(this->name, strlen(name) + 1, name);this->age = age;this->salary = salary;this->darkHorse = darkHorse;this->id = ++LAST_ID;
}Boy& Boy::operator=(const Boy& boy){if (!name){delete name;}this->name = new char[strlen(name) + 1];strcpy_s(this->name, strlen(name) + 1, boy.name);this->age = boy.age;this->salary = boy.salary;this->darkHorse = boy.darkHorse;return *this;
}Boy::~Boy()
{if (!name){delete name;}
}string Boy::decribe(){stringstream ret;ret << "编号:" << id << "\t姓名:" << name << "\t年龄:" << age<< "\t薪资:" << salary << "\t黑马值:" << darkHorse << endl;return ret.str();
}
bug:

使用指针是无法达到赋值运算符的重载的,这时候使用赋值运算重载,是编译器默认的合成赋值重载------->以下代码纯粹无效
Boy& operator=(const Boy* boy);
//h2 = h1
//h2.operator(h1)//Boy boy = h1//这里会调用合成的拷贝构造函数,严重出错
有两个影响:
1) 浪费性能
2) 如果没有自定义的拷贝构造函数,而且这个类又有指针成员时,就会调用自动生成的拷贝构
造函数,导致浅拷贝
如果析构函数中,对这个指针指向的内存做了释放,那就导致数据损坏或崩溃Boy& Boy::operator=(const Boy boy);
Boy& Boy::operator=(const Boy& boy);//正确
Boy& Boy::operator=(const Boy* boy){
if (!name){
delete name;
}
this->name = new char[strlen(boy->name) + 1];
strcpy_s(this->name, strlen(boy->name) + 1, boy->name);
this->age = boy->age;
this->salary = boy->salary;
this->darkHorse = boy->darkHorse;
this->id = ++LAST_ID;//id有问题
return *this;
}
主函数.cpp
#include "Boy.h"
#include <iostream>using namespace std;int main(void) {Boy h1("Rock", 23, 42000, 10);Boy h2, h3;h3 = h2 = h1;cout << h1.decribe() << endl;cout << h2.decribe() << endl;cout << h3.decribe() << endl;return 0;
}关系重载运算符><

bool operator<(const Boy& boy);
bool operator>(const Boy& boy);int power() const;
bool Boy::operator>(const Boy& boy) {
if (this->power() > boy.power()) {
return true;
}
else {
return false;
}
}
int Boy::power() const{
薪资* 黑马系数 + (100 - 年龄) * 1000
int power = salary * darkHorse + (100 - age) * 1000;
return power;
}
cout << "比较的结果" << endl;
if (h1<h2) {
cout << h2.decribe() << endl;
}else{
cout << h1.decribe() << endl;
}
下标运算符重载

#pragma once
#include <string>
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;#define NAME_key "name"
#define AGE_key "age"
#define SALARY_key "salary"
#define DARKH_key "darkHorse"
#define Power_key "power"enum MyEnum
{AGE, //"age"SALARY, //"salary"DARKH, //"darkHorse"Power //"power"
};
class Boy{
public:Boy(const char* name=NULL, int age=0, int salary=0, int darkHorse=0);Boy& operator=(const Boy& boy);~Boy();/*bool operator<(const Boy& boy);bool operator>(const Boy& boy);*/int operator[](string name);int operator[](int index);int power() const;string decribe();
private:char* name;int age;int salary;int darkHorse;unsigned int id;static int LAST_ID;
};.cppint Boy::operator[](string name){if (name == AGE_key){return age;}else if (name == SALARY_key) {return salary;}else if (name == DARKH_key) {return darkHorse;}else if (name == Power_key) {return power();}else {return -1;}
}int Boy::operator[](int index) {if (index == 0) {return age;}else if (index == 1) {return salary;}else if (index == 2) {return darkHorse;}else if (index == 3) {return power();}else {return -1;}
}Boy h1("Rock", 23, 42000, 10);
Boy h2("Jack", 30, 40000, 5);cout << "年龄:" << h1[AGE_key] << "\t\t薪资:" << h1[SALARY_key] << "\t\t黑马值:" << h1[DARKH_key] << "\t\t综合能力值:" << h1[Power_key] << endl;cout << "年龄:" << h1[AGE]<< "\t\t薪资:" << h1[SALARY]<< "\t\t黑马值:" << h1[DARKH]<< "\t\t综合能力值:" << h1[Power] << endl;bug
下标运算符重载使用const时,要注意
int operator[](string name)const;
int operator[](int index);const Boy h1;
cout<<h1[1];//这种的话他是不会调用参数为整数的下标重载运算符的
因为const只能调用const方法
输入输出运算符重载<<,>>
使用成员函数
ostream& operator<<(ostream& os) const;
ostream& Boy::operator<<(ostream& os) const
{
os << "编号:" << id << "\t姓名:" << name << "\t年龄:" << age
<< "\t薪资:" << salary << "\t黑马值:" << darkHorse;
return os;
}h1<<cout;
使用友元函数 (更方便)
friend ostream& operator<<(ostream& os, const Boy& boy);
ostream& operator<<(ostream &os,const Boy &boy) {
os << "编号:" << boy.id << "\t姓名:" << boy.name << "\t年龄:" << boy.age
<< "\t薪资:" << boy.salary << "\t黑马值:" << boy.darkHorse;
return os;
}istream& operator>>(istream& is, Boy& boy) {
string name1;
is >> name1 >> boy.age >> boy.salary >> boy.darkHorse;
boy.name = new char[sizeof(name1)];
strcpy_s(boy.name, sizeof(name1), name1.c_str());
return is;
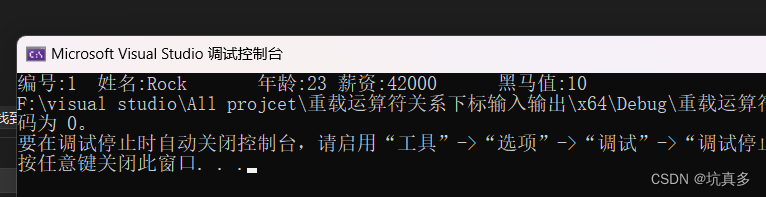
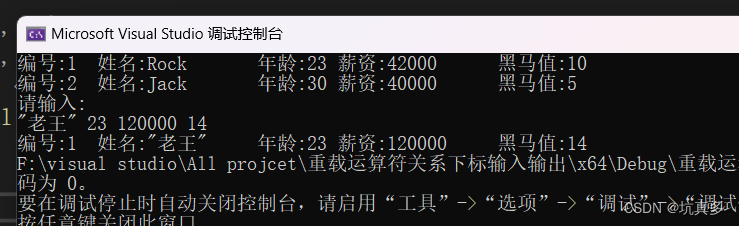
}Boy h1("Rock", 23, 42000, 10);
Boy h2("Jack", 30, 40000, 5);
cout << h1 << endl << h2 << endl;
cout << "请输入:" << endl;
cin >> h1;
h1 << cout;
普通类型==>类类型
boy.h
//普通类型转类类型,使用构造函数
Boy(int salary);
Boy(const char* name);BOY.cpp
Boy::Boy(int salary){const char* name1 = "未命名的";name = new char[strlen(name1) + 1];strcpy_s(this->name, strlen(name1) + 1, name1);this->age = 0;this->salary = salary;this->darkHorse = 0;this->id = ++LAST_ID;
}
Boy::Boy(const char* name) {this->name = new char[strlen(name) + 1];strcpy_s(this->name, strlen(name) + 1, name);this->age = 0;this->salary = 0;this->darkHorse = 0;this->id = ++LAST_ID;
}
main.cpp
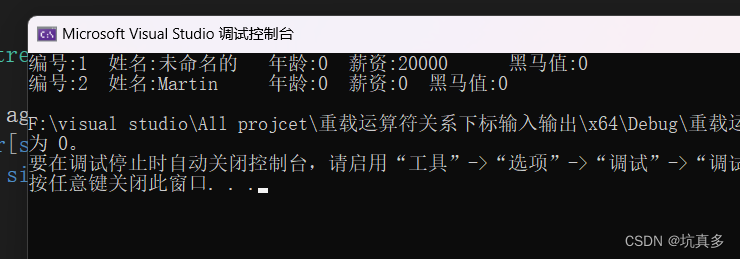
Boy h1("Rock", 23, 42000, 10);
Boy h2("Jack", 30, 40000, 5);
//普通类型转类类型(构造函数)
h1 = 20000; // h1(2000);
cout << h1 << endl;h2 = "Martin";//h2("Martin");
cout << h2 << endl;
类类型==>普通类型

boy.h
//将类类型转换成普通类型
operator int()const;
operator char* ()const;boy.cpp
Boy::operator int() const{return salary;
}
Boy::operator char* ()const {return this->name;
}
main.cpp
Boy h1("Rock", 23, 42000, 10);
Boy h2("Jack", 30, 40000, 5);
//将类型转成普通类型(operator 数据类型())
int salary = h1;
cout << "薪资:" << salary << endl;;
char *name = h2;
cout <<"姓名"<< name;类类型转换成类类型
Boy.hfriend class MAN;MAN.h
#pragma once
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
class Boy;class MAN{
public:MAN(const char* name, int age, int salary);~MAN();MAN(const Boy& boy1);private:char* name;int age;int salary;static int id;friend ostream& operator<<(ostream& os, const MAN& man);
};
ostream& operator<<(ostream& os, const MAN& man);MAN.cpp#include "MAN.h"
#include "Boy.h"
int MAN::id = 0;
MAN::MAN(const char* name, int age, int salary)
{this->name = new char(strlen(name) + 1);strcpy_s(this->name, strlen(name) + 1, name);this->age = age;this->salary = salary;this->id = ++id;
}MAN::~MAN(){delete name;
}MAN ::MAN(const Boy& boy1){/*this->name = new char(strlen(boy1.name) + 1);strcpy_s(this->name, strlen(name) + 1, boy1.name);*/int len = strlen(boy1) + 1;this->name = new char[(char)len];strcpy_s(name, (char)len, (char*)boy1);/*int operator[](string name)const;int operator[](int index) const;*///这里使用下标调用是需要注意,引用的Boy为const类型//所有对应下标运算符重载也要为const类型//this->age = boy1[AGE];//this->salary = boy1[SALARY];this->age = boy1.age;this->salary = boy1.salary;this->id = boy1.id;
}ostream& operator<<(ostream& os, const MAN& man)
{os << "编号:" << man.id << "\t姓名:" << man.name << "\t年龄:"<< man.age << "\t薪资:" << man.salary << endl;return os;
}
main.cppMAN man = h1;
cout << h1 << endl;
cout << man << endl;这篇关于第十一站:运算符重载operate(+-*/)的文章就介绍到这儿,希望我们推荐的文章对编程师们有所帮助!








