本文主要是介绍Linux系统编程P8,希望对大家解决编程问题提供一定的参考价值,需要的开发者们随着小编来一起学习吧!
文件与I/O(四)
文件描述符0:标准输入,一般为阻塞状态
文件描述符1:标准输出
代码示例:
#include<stdio.h>
#include<stdlib.h>
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <sys/stat.h>
#include <fcntl.h>
#include<errno.h>
#include<string.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#define ERROR_EXIT(m) (perror(m),exit(EXIT_FAILURE))
#define MAJOR(a) (int)((unsigned short)a>>8)
#define MINOR(a) (int)((unsigned short)a & 0xFF)
int filetype(struct stat * buf);
int main(int argc, char* argv[])
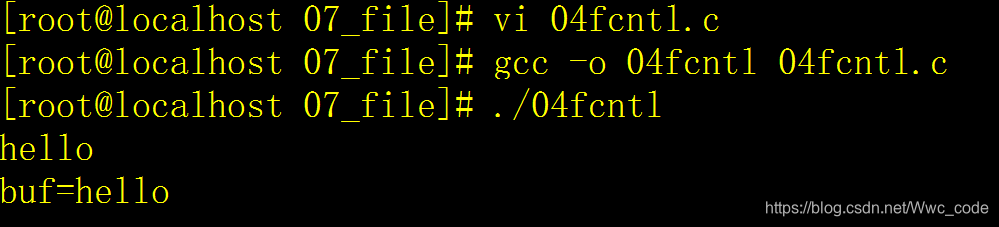
{char buf[1024]={0};int flag;int ret;//获取状态信息,0文件描述符表示输入一般为阻塞状态flag=fcntl(0,F_GETFL,0);if(flag==-1)ERROR_EXIT("get state error");//设置文件描述符状态信息,为非阻塞状态ret=fcntl(0,F_SETFL,O_NONBLOCK);if(ret==-1)ERROR_EXIT("set state error");ret=read(0,buf,1024);if(ret==-1)ERROR_EXIT("read error");printf("buf=%s\n",buf);
}

错误原因:
man 2 read:

#include<stdio.h>
#include<stdlib.h>
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <sys/stat.h>
#include <fcntl.h>
#include<errno.h>
#include<string.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#define ERROR_EXIT(m) (perror(m),exit(EXIT_FAILURE))
#define MAJOR(a) (int)((unsigned short)a>>8)
#define MINOR(a) (int)((unsigned short)a & 0xFF)
int filetype(struct stat * buf);
void set_flags(int fd,int flags);
void clr_flags(int fd,int flags);
int main(int argc, char* argv[])
{char buf[1024]={0};int flag;int ret;
"04fcntl.c" 55L, 1452C
void set_flags(int fd,int flags){int val;val=fcntl(fd,F_GETFL,0);if(val==-1)ERROR_EXIT("get error");val |= flags;if(fcntl(fd,F_SETFL,val)<0)ERROR_EXIT("set error");}
void clr_flags(int fd,int flags){int val;val=fcntl(fd,F_GETFL,0);if(val==-1)ERROR_EXIT("get error");val &= ~flags;if(fcntl(fd,F_SETFL,val)<0)ERROR_EXIT("set error");}
锁的用法代码示例(struct flock):

#include<stdio.h>
#include<stdlib.h>
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <sys/stat.h>
#include <fcntl.h>
#include<errno.h>
#include<string.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#define ERROR_EXIT(m) (perror(m),exit(EXIT_FAILURE))
#define MAJOR(a) (int)((unsigned short)a>>8)
#define MINOR(a) (int)((unsigned short)a & 0xFF)
int filetype(struct stat * buf);
int main(int argc, char* argv[])
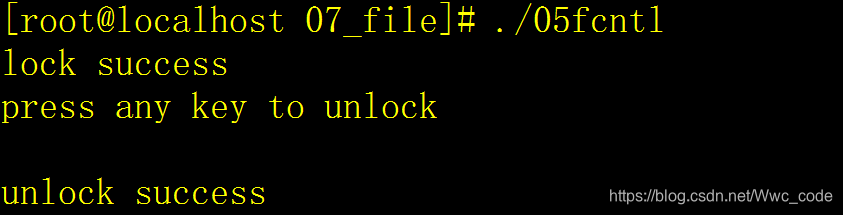
{//设置锁int fd=open("test5.c",O_CREAT | O_RDWR | O_TRUNC,0644);if(fd==-1)ERROR_EXIT("open error");struct flock lock;memset(&lock,0,sizeof(lock));lock.l_type=F_WRLCK;lock.l_whence=SEEK_SET;lock.l_start=0;lock.l_len=0;//对文件加锁,如果成功,另一个进程无法加锁if(fcntl(fd,F_SETLK,&lock)==0){printf("lock success\n");printf("press any key to unlock\n");getchar();lock.l_type=F_UNLCK;if(fcntl(fd,F_SETLK,&lock)==0){printf("unlock success\n");}else{ERROR_EXIT("unlock fail");}}else{ERROR_EXIT("lock fail");}return 0;
}
fcntl

fcntl常用操作

文件锁结构体

这篇关于Linux系统编程P8的文章就介绍到这儿,希望我们推荐的文章对编程师们有所帮助!





