本文主要是介绍FFmpeg之AVFilter,希望对大家解决编程问题提供一定的参考价值,需要的开发者们随着小编来一起学习吧!
文章目录
- 一、概述
- 二、重要结构体
- 2.1、AVFilterGraph
- 2.2、AVFilter
- 2.3、AVFilterContext
- 三、流程梳理
- 3.1、FFmpeg AVFilter 使用整体流程
- 3.2、过滤器构建流程
- 3.2.1、分配AVFilterGraph
- 3.2.2、创建过滤器源
- 3.2.3、创建接收过滤器
- 3.2.4、生成源和接收过滤器的输入输出
- 3.2.5、通过解析过滤器字符串添加过滤器
- 3.2.6、检查过滤器的完整性
- 3.3、数据加工
- 3.3.1、向源过滤器加入AVFrame
- 3.3.2、从buffersink接收处理后的AVFrame
- 3.4、资源释放
- 四、实例
团队博客: 汽车电子社区
filter,可以翻译为过滤器,滤镜。在FFmpeg中有多种多样的滤镜,你可以把他们当成一个个小工具,专门用于处理视频和音频数据,以便实现一定的目的。如overlay这个滤镜,可以将一个图画覆盖到另一个图画上transport这个滤镜可以将图画做旋转等等。
一、概述
FFMPEG 除了具有强大的封装/解封装,编/解码功能之外,还包含了一个非常强大的组件,滤镜avfilter。 avfilter 组件常用于多媒体处理与编辑,ffmpeg 包含多种滤镜,比如旋转,加水印,多宫格等等。
一个filter的输出可以作为另一个filter的输入,因此多个filter可以组织成为一个网状的filter graph,从而实现更加复杂或者综合的任务。
关于 filter 的概念和用法可以去查找 FFmpeg 的其他资料,这里不再赘述。
libavfilter 库实现了 filter 相关的功能,使得我们可以利用 FFmpeg 提供的诸多 filter 来实现自己所需的功能。具体的使用方法见官方示例:filter_audio.c,filtering_audio.c,filtering_video.c。
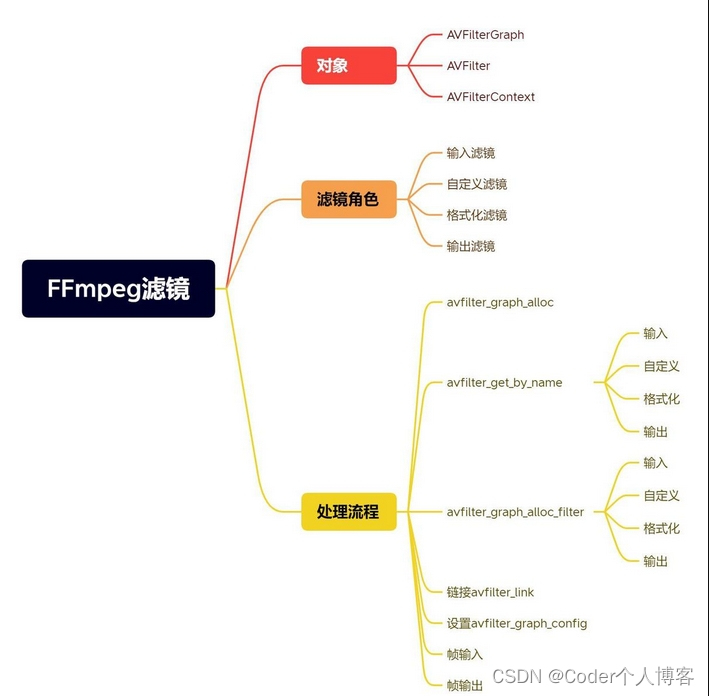
二、重要结构体
在使用FFmpeg开发时,使用AVFilter的流程较为复杂,涉及到的数据结构和函数也比较多,那么使用FFmpeg AVFilter的整体流程是什么样,在其执行过程中都有哪些步骤,需要注意哪些细节?这些都是需要我们整理和总结的。
首先,我们需要引入三个概念结构体:AVFilterGraph 、AVFilterContext、AVFilter。
2.1、AVFilterGraph
AVFilterGraph表示一个filter graph,当然它也包含了filter chain的概念,对filters系统的整体管理。
graph 包含了诸多 filter context实例,并负责它们之间的link,graph会负责创建、保存、释放 这些相关的 filter context和link,一般不需要用户进行管理。除此之外,它还有线程特性和最大线程数量的字段和filter context类似。
graph的操作有:分配一个graph,往graph中添加一个filter context,添加一个 filter graph,对 filter 进行 link 操作,检查内部的link和format是否有效,释放graph等。
typedef struct AVFilterGraph {const AVClass *av_class;AVFilterContext **filters;unsigned nb_filters;char *scale_sws_opts; ///< sws options to use for the auto-inserted scale filters/*** Type of multithreading allowed for filters in this graph. A combination* of AVFILTER_THREAD_* flags.** May be set by the caller at any point, the setting will apply to all* filters initialized after that. The default is allowing everything.** When a filter in this graph is initialized, this field is combined using* bit AND with AVFilterContext.thread_type to get the final mask used for* determining allowed threading types. I.e. a threading type needs to be* set in both to be allowed.*/int thread_type;/*** Maximum number of threads used by filters in this graph. May be set by* the caller before adding any filters to the filtergraph. Zero (the* default) means that the number of threads is determined automatically.*/int nb_threads;/*** Opaque object for libavfilter internal use.*/AVFilterGraphInternal *internal;/*** Opaque user data. May be set by the caller to an arbitrary value, e.g. to* be used from callbacks like @ref AVFilterGraph.execute.* Libavfilter will not touch this field in any way.*/void *opaque;/*** This callback may be set by the caller immediately after allocating the* graph and before adding any filters to it, to provide a custom* multithreading implementation.** If set, filters with slice threading capability will call this callback* to execute multiple jobs in parallel.** If this field is left unset, libavfilter will use its internal* implementation, which may or may not be multithreaded depending on the* platform and build options.*/avfilter_execute_func *execute;char *aresample_swr_opts; ///< swr options to use for the auto-inserted aresample filters, Access ONLY through AVOptions/*** Private fields** The following fields are for internal use only.* Their type, offset, number and semantic can change without notice.*/AVFilterLink **sink_links;int sink_links_count;unsigned disable_auto_convert;
} AVFilterGraph;
我们简单点看,我们在调用的时候我们真正能触及到的一般主要是const AVClass av_class;AVFilterContext ** filters; 这两个对象
av_class在初始化AVFilterGraph 的时候就已经一起初始化了,它就是存储滤镜一些相关配置的,在初始化时就已经有一些默认的配置被赋值。
filters需要后续滤镜生成后再进行赋值绑定的,它是滤镜上下文指针类型的指针。
2.2、AVFilter
滤镜结构体,是用来存储具体滤镜信息和一些函数指针,函数指针能让我们外部的进行重写逻辑,作为回调等等。但对于我们实现基本滤镜来说我们根本不需要了解,我们只要关注一些基本信息,例如滤镜名字,滤镜参数等。
typedef struct AVFilter {/*** Filter name. Must be non-NULL and unique among filters.*/const char *name;/*** A description of the filter. May be NULL.** You should use the NULL_IF_CONFIG_SMALL() macro to define it.*/const char *description;/*** List of static inputs.** NULL if there are no (static) inputs. Instances of filters with* AVFILTER_FLAG_DYNAMIC_INPUTS set may have more inputs than present in* this list.*/const AVFilterPad *inputs;/*** List of static outputs.** NULL if there are no (static) outputs. Instances of filters with* AVFILTER_FLAG_DYNAMIC_OUTPUTS set may have more outputs than present in* this list.*/const AVFilterPad *outputs;/*** A class for the private data, used to declare filter private AVOptions.* This field is NULL for filters that do not declare any options.** If this field is non-NULL, the first member of the filter private data* must be a pointer to AVClass, which will be set by libavfilter generic* code to this class.*/const AVClass *priv_class;/*** A combination of AVFILTER_FLAG_**/int flags;/****************************************************************** All fields below this line are not part of the public API. They* may not be used outside of libavfilter and can be changed and* removed at will.* New public fields should be added right above.******************************************************************//*** The number of entries in the list of inputs.*/uint8_t nb_inputs;/*** The number of entries in the list of outputs.*/uint8_t nb_outputs;/*** This field determines the state of the formats union.* It is an enum FilterFormatsState value.*/uint8_t formats_state;/*** Filter pre-initialization function** This callback will be called immediately after the filter context is* allocated, to allow allocating and initing sub-objects.** If this callback is not NULL, the uninit callback will be called on* allocation failure.** @return 0 on success,* AVERROR code on failure (but the code will be* dropped and treated as ENOMEM by the calling code)*/int (*preinit)(AVFilterContext *ctx);/*** Filter initialization function.** This callback will be called only once during the filter lifetime, after* all the options have been set, but before links between filters are* established and format negotiation is done.** Basic filter initialization should be done here. Filters with dynamic* inputs and/or outputs should create those inputs/outputs here based on* provided options. No more changes to this filter's inputs/outputs can be* done after this callback.** This callback must not assume that the filter links exist or frame* parameters are known.** @ref AVFilter.uninit "uninit" is guaranteed to be called even if* initialization fails, so this callback does not have to clean up on* failure.** @return 0 on success, a negative AVERROR on failure*/int (*init)(AVFilterContext *ctx);/*** Filter uninitialization function.** Called only once right before the filter is freed. Should deallocate any* memory held by the filter, release any buffer references, etc. It does* not need to deallocate the AVFilterContext.priv memory itself.** This callback may be called even if @ref AVFilter.init "init" was not* called or failed, so it must be prepared to handle such a situation.*/void (*uninit)(AVFilterContext *ctx);/*** The state of the following union is determined by formats_state.* See the documentation of enum FilterFormatsState in internal.h.*/union {/*** Query formats supported by the filter on its inputs and outputs.** This callback is called after the filter is initialized (so the inputs* and outputs are fixed), shortly before the format negotiation. This* callback may be called more than once.** This callback must set ::AVFilterLink's* @ref AVFilterFormatsConfig.formats "outcfg.formats"* on every input link and* @ref AVFilterFormatsConfig.formats "incfg.formats"* on every output link to a list of pixel/sample formats that the filter* supports on that link.* For audio links, this filter must also set* @ref AVFilterFormatsConfig.samplerates "incfg.samplerates"* /* @ref AVFilterFormatsConfig.samplerates "outcfg.samplerates"* and @ref AVFilterFormatsConfig.channel_layouts "incfg.channel_layouts"* /* @ref AVFilterFormatsConfig.channel_layouts "outcfg.channel_layouts"* analogously.** This callback must never be NULL if the union is in this state.** @return zero on success, a negative value corresponding to an* AVERROR code otherwise*/int (*query_func)(AVFilterContext *);/*** A pointer to an array of admissible pixel formats delimited* by AV_PIX_FMT_NONE. The generic code will use this list* to indicate that this filter supports each of these pixel formats,* provided that all inputs and outputs use the same pixel format.** This list must never be NULL if the union is in this state.* The type of all inputs and outputs of filters using this must* be AVMEDIA_TYPE_VIDEO.*/const enum AVPixelFormat *pixels_list;/*** Analogous to pixels, but delimited by AV_SAMPLE_FMT_NONE* and restricted to filters that only have AVMEDIA_TYPE_AUDIO* inputs and outputs.** In addition to that the generic code will mark all inputs* and all outputs as supporting all sample rates and every* channel count and channel layout, as long as all inputs* and outputs use the same sample rate and channel count/layout.*/const enum AVSampleFormat *samples_list;/*** Equivalent to { pix_fmt, AV_PIX_FMT_NONE } as pixels_list.*/enum AVPixelFormat pix_fmt;/*** Equivalent to { sample_fmt, AV_SAMPLE_FMT_NONE } as samples_list.*/enum AVSampleFormat sample_fmt;} formats;int priv_size; ///< size of private data to allocate for the filterint flags_internal; ///< Additional flags for avfilter internal use only./*** Make the filter instance process a command.** @param cmd the command to process, for handling simplicity all commands must be alphanumeric only* @param arg the argument for the command* @param res a buffer with size res_size where the filter(s) can return a response. This must not change when the command is not supported.* @param flags if AVFILTER_CMD_FLAG_FAST is set and the command would be* time consuming then a filter should treat it like an unsupported command** @returns >=0 on success otherwise an error code.* AVERROR(ENOSYS) on unsupported commands*/int (*process_command)(AVFilterContext *, const char *cmd, const char *arg, char *res, int res_len, int flags);/*** Filter activation function.** Called when any processing is needed from the filter, instead of any* filter_frame and request_frame on pads.** The function must examine inlinks and outlinks and perform a single* step of processing. If there is nothing to do, the function must do* nothing and not return an error. If more steps are or may be* possible, it must use ff_filter_set_ready() to schedule another* activation.*/int (*activate)(AVFilterContext *ctx);
} AVFilter;
AVFilter表示一个被注册的filter类型,如果仅是为了使用它,我们只需知道它的部分特性就可以了。
1、AVFilter.name 和 AVFilter.description:filter 的名称和描述。
2. AVFilter.inputs 和 AVFilter.outputs:AVFilterPad 的数组,描述了filter的输入和输出。
3. AVFilter.flags:filter的特性。
首先,针对 filter 的输入和输出数组,有以下三个帮助函数:
/*** 获取 AVFilterPad 数组的数量,该数组以NULL结尾,一般传入AVFilter.inputs和AVFilter.outputs*/
unsigned avfilter_filter_pad_count(const AVFilter *filter, int is_output)
{return is_output ? filter->nb_outputs : filter->nb_inputs;
}/*** Get the name of an AVFilterPad.** @param pads an array of AVFilterPads* @param pad_idx index of the pad in the array; it is the caller's* responsibility to ensure the index is valid** @return name of the pad_idx'th pad in pads*/
const char *avfilter_pad_get_name(const AVFilterPad *pads, int pad_idx)
{return pads[pad_idx].name;
}/*** Get the type of an AVFilterPad.** @param pads an array of AVFilterPads* @param pad_idx index of the pad in the array; it is the caller's* responsibility to ensure the index is valid** @return type of the pad_idx'th pad in pads*/
// 获取数组中指向下标的 pad 所需的数据类型,调用者应确保传入的下标有效
enum AVMediaType avfilter_pad_get_type(const AVFilterPad *pads, int pad_idx);
然后,就是 AVFilter 的 flag,其可取值如下:
/*** The number of the filter inputs is not determined just by AVFilter.inputs.* The filter might add additional inputs during initialization depending on the* options supplied to it.*/
#define AVFILTER_FLAG_DYNAMIC_INPUTS (1 << 0)
/*** The number of the filter outputs is not determined just by AVFilter.outputs.* The filter might add additional outputs during initialization depending on* the options supplied to it.*/
#define AVFILTER_FLAG_DYNAMIC_OUTPUTS (1 << 1)
/*** The filter supports multithreading by splitting frames into multiple parts* and processing them concurrently.*/
#define AVFILTER_FLAG_SLICE_THREADS (1 << 2)
/*** The filter is a "metadata" filter - it does not modify the frame data in any* way. It may only affect the metadata (i.e. those fields copied by* av_frame_copy_props()).** More precisely, this means:* - video: the data of any frame output by the filter must be exactly equal to* some frame that is received on one of its inputs. Furthermore, all frames* produced on a given output must correspond to frames received on the same* input and their order must be unchanged. Note that the filter may still* drop or duplicate the frames.* - audio: the data produced by the filter on any of its outputs (viewed e.g.* as an array of interleaved samples) must be exactly equal to the data* received by the filter on one of its inputs.*/
#define AVFILTER_FLAG_METADATA_ONLY (1 << 3)/*** The filter can create hardware frames using AVFilterContext.hw_device_ctx.*/
#define AVFILTER_FLAG_HWDEVICE (1 << 4)
/*** Some filters support a generic "enable" expression option that can be used* to enable or disable a filter in the timeline. Filters supporting this* option have this flag set. When the enable expression is false, the default* no-op filter_frame() function is called in place of the filter_frame()* callback defined on each input pad, thus the frame is passed unchanged to* the next filters.*/
#define AVFILTER_FLAG_SUPPORT_TIMELINE_GENERIC (1 << 16)
/*** Same as AVFILTER_FLAG_SUPPORT_TIMELINE_GENERIC, except that the filter will* have its filter_frame() callback(s) called as usual even when the enable* expression is false. The filter will disable filtering within the* filter_frame() callback(s) itself, for example executing code depending on* the AVFilterContext->is_disabled value.*/
#define AVFILTER_FLAG_SUPPORT_TIMELINE_INTERNAL (1 << 17)
/*** Handy mask to test whether the filter supports or no the timeline feature* (internally or generically).*/
#define AVFILTER_FLAG_SUPPORT_TIMELINE (AVFILTER_FLAG_SUPPORT_TIMELINE_GENERIC | AVFILTER_FLAG_SUPPORT_TIMELINE_INTERNAL)
2.3、AVFilterContext
AVFilterContext表示一个AVFilter的实例,我们在实际使用filter时,就是使用这个类型。
AVFilterContext在被使用前,它必须是ready状态的,也就是被初始化的。说白了,就是需要对filter进行一些选项上的设置,然后通过初始化告诉FFmpeg我们已经做了相关的配置。
/** An instance of a filter */
struct AVFilterContext {const AVClass *av_class; ///< needed for av_log() and filters common optionsconst AVFilter *filter; ///< the AVFilter of which this is an instancechar *name; ///< name of this filter instanceAVFilterPad *input_pads; ///< array of input padsAVFilterLink **inputs; ///< array of pointers to input linksunsigned nb_inputs; ///< number of input padsAVFilterPad *output_pads; ///< array of output padsAVFilterLink **outputs; ///< array of pointers to output linksunsigned nb_outputs; ///< number of output padsvoid *priv; ///< private data for use by the filterstruct AVFilterGraph *graph; ///< filtergraph this filter belongs to/*** Type of multithreading being allowed/used. A combination of* AVFILTER_THREAD_* flags.** May be set by the caller before initializing the filter to forbid some* or all kinds of multithreading for this filter. The default is allowing* everything.** When the filter is initialized, this field is combined using bit AND with* AVFilterGraph.thread_type to get the final mask used for determining* allowed threading types. I.e. a threading type needs to be set in both* to be allowed.** After the filter is initialized, libavfilter sets this field to the* threading type that is actually used (0 for no multithreading).*/int thread_type;/*** An opaque struct for libavfilter internal use.*/AVFilterInternal *internal;struct AVFilterCommand *command_queue;char *enable_str; ///< enable expression stringvoid *enable; ///< parsed expression (AVExpr*)double *var_values; ///< variable values for the enable expressionint is_disabled; ///< the enabled state from the last expression evaluation/*** For filters which will create hardware frames, sets the device the* filter should create them in. All other filters will ignore this field:* in particular, a filter which consumes or processes hardware frames will* instead use the hw_frames_ctx field in AVFilterLink to carry the* hardware context information.** May be set by the caller on filters flagged with AVFILTER_FLAG_HWDEVICE* before initializing the filter with avfilter_init_str() or* avfilter_init_dict().*/AVBufferRef *hw_device_ctx;/*** Max number of threads allowed in this filter instance.* If <= 0, its value is ignored.* Overrides global number of threads set per filter graph.*/int nb_threads;/*** Ready status of the filter.* A non-0 value means that the filter needs activating;* a higher value suggests a more urgent activation.*/unsigned ready;/*** Sets the number of extra hardware frames which the filter will* allocate on its output links for use in following filters or by* the caller.** Some hardware filters require all frames that they will use for* output to be defined in advance before filtering starts. For such* filters, any hardware frame pools used for output must therefore be* of fixed size. The extra frames set here are on top of any number* that the filter needs internally in order to operate normally.** This field must be set before the graph containing this filter is* configured.*/int extra_hw_frames;
};
AVFilterContext 表示 AVFilter 的一个实例。其重要字段如下:
1. AVFilterContext .filter:这个 filter context 是那种 filter 的实例。
2. AVFilterContext .name:这个 filter context 的名称。
3. AVFilterContext.graph:这个 filter context 属于哪个 graph。
4. AVFilterContext .input_pads,AVFilterContext.inputs ,AVFilterContext.nb_inputs:分别描述了input pads数组,input links数组,以及input 数量。
5. AVFilterContext .output_pads,AVFilterContext.outputs ,AVFilterContext.nb_outputs:分别描述了output pads数组,output links数组,以及 output 数量。
6. AVFilterContext.thread_type,AVFilterContext.nb_threads:线程特性和可开启的最大线程数量。
7. AVFilterContext.is_disabled:filter 关于 timeline 特征的开启标志。
8. AVFilterContext.ready:表示 filter 是否被初始化,非 0 值表示 filter 需要被初始化,且值越大表示越急切。
filter context初始化的方法有三种:avfilter_init_str()和avfilter_init_dict(),以及通过AVOption API直接操作filter context。
注意初始化的 avfilter_init_str() 和 avfilter_init_dict() 在行为上的差别:当传入的 options 中有不被 filter 所支持的参数时,这两个函数的行为是不同,avfilter_init_str() 调用会失败,而 avfilter_init_dict() 函数则不会失败,它会将不能应用于指定 filter 的 option 通过参数返回,然后继续执行任务。
/** 使用提供的参数初始化 filter。** 参数args:表示用于初始化 filter 的 options。该字符串必须使用 ":" 来分割各个键值对,* 而键值对的形式为 'key=value'。如果不需要设置选项,args为空。** 除了这种方式设置选项之外,还可以利用 AVOptions API 直接对 filter 设置选项。** 返回值:成功返回0,失败返回一个负的错误值
*/
int avfilter_init_str(AVFilterContext *ctx, const char *args);/** 使用提供的参数初始化filter。** 参数 options:以 dict 形式提供的 options。** 返回值:成功返回0,失败返回一个负的错误值* * 注意:这个函数和 avfilter_init_str 函数的功能是一样的,只不过传递的参数形式不同。* 但是当传入的 options 中有不被 filter 所支持的参数时,这两个函数的行为是不同:* avfilter_init_str 调用会失败,而这个函数则不会失败,它会将不能应用于指定 filter 的 option 通过参数 options 返回,然后继续执行任务。
*/
int avfilter_init_dict(AVFilterContext *ctx, AVDictionary **options);/** 释放 filter context。
*/
void avfilter_free(AVFilterContext *filter);
三、流程梳理
3.1、FFmpeg AVFilter 使用整体流程
下图就是FFmpeg AVFilter在使用过程中的流程图:
![[图片]](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/direct/09010b6cdf6c44849789068ee4c3c8f6.png)
我们对上图先做下说明,理解下图中每个步骤的关系,然后,才从代码的角度来给出其使用的步骤。
1. 最顶端的AVFilterGraph,这个结构前面介绍过,主要管理加入的过滤器,其中加入的过滤器就是通过函数avfilter_graph_create_filter来创建并加入,这个函数返回是AVFilterContext(其封装了AVFilter的详细参数信息)。
2. buffer和buffersink这两个过滤器是FFMpeg为我们实现好的,buffer表示源,用来向后面的过滤器提供数据输入(其实就是原始的AVFrame);buffersink过滤器是最终输出的(经过过滤器链处理后的数据AVFrame),其它的诸如filter 1 等过滤器是由avfilter_graph_parse_ptr函数解析外部传入的过滤器描述字符串自动生成的,内部也是通过avfilter_graph_create_filter来创建过滤器的。
3. 上面的buffer、filter 1、filter 2、filter n、buffersink之间是通过avfilter_link函数来进行关联的(通过AVFilterLink结构),这样子过滤器和过滤器之间就通过AVFilterLink进行关联上了,前一个过滤器的输出就是下一个过滤器的输入,注意,除了源和接收过滤器之外,其它的过滤器至少有一个输入和输出,这很好理解,中间的过滤器处理完AVFrame后,得到新的处理后的AVFrame数据,然后把新的AVFrame数据作为下一个过滤器的输入。
4. 过滤器建立完成后,首先我们通过av_buffersrc_add_frame把最原始的AVFrame(没有经过任何过滤器处理的)加入到buffer过滤器的fifo队列。
5. 然后调用buffersink过滤器的av_buffersink_get_frame_flags来获取处理完后的数据帧(这个最终放入buffersink过滤器的AVFrame是通过之前创建的一系列过滤器处理后的数据)。
6. 使用流程图就介绍到这里,下面结合上面的使用流程图详细说下FFMpeg中使用过滤器的步骤,这个过程我们分为三个部分:过滤器构建、数据加工、资源释放。
初始的流程大概可以总结为,创建filtergraph, 创建source filter 和sink filter, 将 filter连接起来添加到filtergraph, 配置filtergraph,可参考下图:
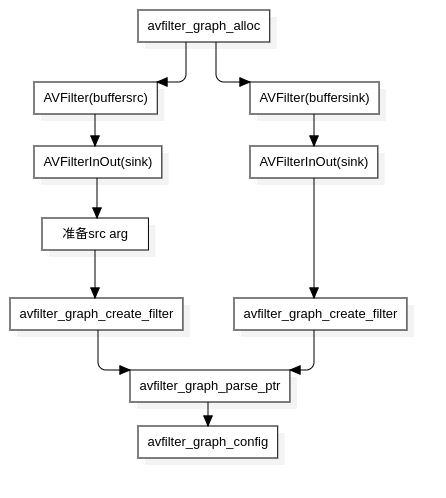
3.2、过滤器构建流程
3.2.1、分配AVFilterGraph
AVFilterGraph* graph = avfilter_graph_alloc();
3.2.2、创建过滤器源
char srcArgs[256] = {0};
AVFilterContext *srcFilterCtx;
AVFilter* srcFilter = avfilter_get_by_name("buffer");
avfilter_graph_create_filter(&srcFilterCtx, srcFilter ,"out_buffer", srcArgs, NULL, graph);
3.2.3、创建接收过滤器
AVFilterContext *sinkFilterCtx;
AVFilter* sinkFilter = avfilter_get_by_name("buffersink");
avfilter_graph_create_filter(&sinkFilterCtx, sinkFilter,"in_buffersink", NULL, NULL, graph);
3.2.4、生成源和接收过滤器的输入输出
这里主要是把源和接收过滤器封装给AVFilterInOut结构,使用这个中间结构来把过滤器字符串解析并链接进graph,主要代码如下:
AVFilterInOut *inputs = avfilter_inout_alloc();
AVFilterInOut *outputs = avfilter_inout_alloc();
outputs->name = av_strdup("in");
outputs->filter_ctx = srcFilterCtx;
outputs->pad_idx = 0;
outputs->next = NULL;
inputs->name = av_strdup("out");
inputs->filter_ctx = sinkFilterCtx;
inputs->pad_idx = 0;
inputs->next = NULL;
这里源对应的AVFilterInOut的name最好定义为in,接收对应的name为out,因为FFMpeg源码里默认会通过这样个name来对默认的输出和输入进行查找。
3.2.5、通过解析过滤器字符串添加过滤器
const *char filtergraph = "[in1]过滤器名称=参数1:参数2[out1]";
int ret = avfilter_graph_parse_ptr(graph, filtergraph, &inputs, &outputs, NULL);
3.2.6、检查过滤器的完整性
avfilter_graph_config(graph, NULL);
3.3、数据加工
3.3.1、向源过滤器加入AVFrame
AVFrame* frame; // 这是解码后获取的数据帧
int ret = av_buffersrc_add_frame(srcFilterCtx, frame);
3.3.2、从buffersink接收处理后的AVFrame
int ret = av_buffersink_get_frame_flags(sinkFilterCtx, frame, 0);
现在我们就可以使用处理后的AVFrame,比如显示或播放出来。
3.4、资源释放
使用结束后,调用avfilter_graph_free(&graph);释放掉AVFilterGraph类型的graph。
四、实例
extern "C" {#include <libavcodec/avcodec.h>#include <libavformat/avformat.h>#include <libavfilter/avfiltergraph.h>#include <libavfilter/buffersink.h>#include <libavfilter/buffersrc.h>#include <libavutil/opt.h>#include <libavutil/imgutils.h>
}int main(int argc, char* argv)
{int ret = 0;// input yuvFILE* inFile = NULL;const char* inFileName = "sintel_480x272_yuv420p.yuv";fopen_s(&inFile, inFileName, "rb+");if (!inFile) {printf("Fail to open file\n");return -1;}int in_width = 480;int in_height = 272;// output yuvFILE* outFile = NULL;const char* outFileName = "out_crop_vfilter.yuv";fopen_s(&outFile, outFileName, "wb");if (!outFile) {printf("Fail to create file for output\n");return -1;}avfilter_register_all();AVFilterGraph* filter_graph = avfilter_graph_alloc();if (!filter_graph) {printf("Fail to create filter graph!\n");return -1;}// source filterchar args[512];_snprintf_s(args, sizeof(args),"video_size=%dx%d:pix_fmt=%d:time_base=%d/%d:pixel_aspect=%d/%d",in_width, in_height, AV_PIX_FMT_YUV420P,1, 25, 1, 1);AVFilter* bufferSrc = avfilter_get_by_name("buffer");AVFilterContext* bufferSrc_ctx;ret = avfilter_graph_create_filter(&bufferSrc_ctx, bufferSrc, "in", args, NULL, filter_graph);if (ret < 0) {printf("Fail to create filter bufferSrc\n");return -1;}// sink filterAVBufferSinkParams *bufferSink_params;AVFilterContext* bufferSink_ctx;AVFilter* bufferSink = avfilter_get_by_name("buffersink");enum AVPixelFormat pix_fmts[] = { AV_PIX_FMT_YUV420P, AV_PIX_FMT_NONE };bufferSink_params = av_buffersink_params_alloc();bufferSink_params->pixel_fmts = pix_fmts;ret = avfilter_graph_create_filter(&bufferSink_ctx, bufferSink, "out", NULL, bufferSink_params, filter_graph);if (ret < 0) {printf("Fail to create filter sink filter\n");return -1;}// split filterAVFilter *splitFilter = avfilter_get_by_name("split");AVFilterContext *splitFilter_ctx;ret = avfilter_graph_create_filter(&splitFilter_ctx, splitFilter, "split", "outputs=2", NULL, filter_graph);if (ret < 0) {printf("Fail to create split filter\n");return -1;}// crop filterAVFilter *cropFilter = avfilter_get_by_name("crop");AVFilterContext *cropFilter_ctx;ret = avfilter_graph_create_filter(&cropFilter_ctx, cropFilter, "crop", "out_w=iw:out_h=ih/2:x=0:y=0", NULL, filter_graph);if (ret < 0) {printf("Fail to create crop filter\n");return -1;}// vflip filterAVFilter *vflipFilter = avfilter_get_by_name("vflip");AVFilterContext *vflipFilter_ctx;ret = avfilter_graph_create_filter(&vflipFilter_ctx, vflipFilter, "vflip", NULL, NULL, filter_graph);if (ret < 0) {printf("Fail to create vflip filter\n");return -1;}// overlay filterAVFilter *overlayFilter = avfilter_get_by_name("overlay");AVFilterContext *overlayFilter_ctx;ret = avfilter_graph_create_filter(&overlayFilter_ctx, overlayFilter, "overlay", "y=0:H/2", NULL, filter_graph);if (ret < 0) {printf("Fail to create overlay filter\n");return -1;}// src filter to split filterret = avfilter_link(bufferSrc_ctx, 0, splitFilter_ctx, 0);if (ret != 0) {printf("Fail to link src filter and split filter\n");return -1;}// split filter's first pad to overlay filter's main padret = avfilter_link(splitFilter_ctx, 0, overlayFilter_ctx, 0);if (ret != 0) {printf("Fail to link split filter and overlay filter main pad\n");return -1;}// split filter's second pad to crop filterret = avfilter_link(splitFilter_ctx, 1, cropFilter_ctx, 0);if (ret != 0) {printf("Fail to link split filter's second pad and crop filter\n");return -1;}// crop filter to vflip filterret = avfilter_link(cropFilter_ctx, 0, vflipFilter_ctx, 0);if (ret != 0) {printf("Fail to link crop filter and vflip filter\n");return -1;}// vflip filter to overlay filter's second padret = avfilter_link(vflipFilter_ctx, 0, overlayFilter_ctx, 1);if (ret != 0) {printf("Fail to link vflip filter and overlay filter's second pad\n");return -1;}// overlay filter to sink filterret = avfilter_link(overlayFilter_ctx, 0, bufferSink_ctx, 0);if (ret != 0) {printf("Fail to link overlay filter and sink filter\n");return -1;}// check filter graphret = avfilter_graph_config(filter_graph, NULL);if (ret < 0) {printf("Fail in filter graph\n");return -1;}char *graph_str = avfilter_graph_dump(filter_graph, NULL);FILE* graphFile = NULL;fopen_s(&graphFile, "graphFile.txt", "w");fprintf(graphFile, "%s", graph_str);av_free(graph_str);AVFrame *frame_in = av_frame_alloc();unsigned char *frame_buffer_in = (unsigned char *)av_malloc(av_image_get_buffer_size(AV_PIX_FMT_YUV420P, in_width, in_height, 1));av_image_fill_arrays(frame_in->data, frame_in->linesize, frame_buffer_in,AV_PIX_FMT_YUV420P, in_width, in_height, 1);AVFrame *frame_out = av_frame_alloc();unsigned char *frame_buffer_out = (unsigned char *)av_malloc(av_image_get_buffer_size(AV_PIX_FMT_YUV420P, in_width, in_height, 1));av_image_fill_arrays(frame_out->data, frame_out->linesize, frame_buffer_out,AV_PIX_FMT_YUV420P, in_width, in_height, 1);frame_in->width = in_width;frame_in->height = in_height;frame_in->format = AV_PIX_FMT_YUV420P;while (1) {if (fread(frame_buffer_in, 1, in_width*in_height * 3 / 2, inFile) != in_width*in_height * 3 / 2) {break;}//input Y,U,Vframe_in->data[0] = frame_buffer_in;frame_in->data[1] = frame_buffer_in + in_width*in_height;frame_in->data[2] = frame_buffer_in + in_width*in_height * 5 / 4;if (av_buffersrc_add_frame(bufferSrc_ctx, frame_in) < 0) {printf("Error while add frame.\n");break;}/* pull filtered pictures from the filtergraph */ret = av_buffersink_get_frame(bufferSink_ctx, frame_out);if (ret < 0)break;//output Y,U,Vif (frame_out->format == AV_PIX_FMT_YUV420P) {for (int i = 0; i < frame_out->height; i++) {fwrite(frame_out->data[0] + frame_out->linesize[0] * i, 1, frame_out->width, outFile);}for (int i = 0; i < frame_out->height / 2; i++) {fwrite(frame_out->data[1] + frame_out->linesize[1] * i, 1, frame_out->width / 2, outFile);}for (int i = 0; i < frame_out->height / 2; i++) {fwrite(frame_out->data[2] + frame_out->linesize[2] * i, 1, frame_out->width / 2, outFile);}}printf("Process 1 frame!\n");av_frame_unref(frame_out);}fclose(inFile);fclose(outFile);av_frame_free(&frame_in);av_frame_free(&frame_out);avfilter_graph_free(&filter_graph);return 0;
}
这篇关于FFmpeg之AVFilter的文章就介绍到这儿,希望我们推荐的文章对编程师们有所帮助!







