本文主要是介绍ByteBuffer之equals和compareTo比较,希望对大家解决编程问题提供一定的参考价值,需要的开发者们随着小编来一起学习吧!
ByteBuffer介绍
ByteBuffer是Java NIO的重要组成部分。如何比较2个ByteBuffer是否相等可以使用equals()、compareTo()两个方法。
equals()
源码分析
public boolean equals(Object ob) {if (this == ob)return true;if (!(ob instanceof ByteBuffer))return false;ByteBuffer that = (ByteBuffer)ob;if (this.remaining() != that.remaining())return false;int p = this.position();for (int i = this.limit() - 1, j = that.limit() - 1; i >= p; i--, j--)if (!equals(this.get(i), that.get(j)))return false;return true;
}
判断的逻辑是:
1、如果是自身,true。
2、如果不是ByteBuffer,false
3、remaining()是否一样,如果不一样,返回false。remaining = limit - position。
4、两个ByteBuffer的position~limit的数据是否一样,一样true,不一样返回false。
Buffer的重要指标:position、limit参与了比较。但是mark、capacity却没有参与比较。
测试
@Test
public void test1(){ByteBuffer b1 = ByteBuffer.wrap(new byte[]{1,2,3,4,5});ByteBuffer b2 = ByteBuffer.wrap(new byte[]{1,2,3,4,5,1,2,3,4,5});BufferUtil.print(b1);BufferUtil.print(b2);System.out.println(b1.equals(b2)); //falseb2.position(5);BufferUtil.print(b2);System.out.println(b1.equals(b2)); //true
}

compareTo()
源码分析
public int compareTo(ByteBuffer that) {int n = this.position() + Math.min(this.remaining(), that.remaining());for (int i = this.position(), j = that.position(); i < n; i++, j++) {int cmp = compare(this.get(i), that.get(j));if (cmp != 0)return cmp;}return this.remaining() - that.remaining();
}private static int compare(byte x, byte y) {return Byte.compare(x, y);
}
大概意思是:
1、从2个ByteBuffer的当前位置position开始比较每个字节,如果出结果了就return。
2、否则就比较2个ByteBuffer的剩余元素个数。
测试
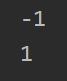
@Test
public void test2(){ByteBuffer b1 = ByteBuffer.wrap(new byte[]{1,2,3,4,5});ByteBuffer b2 = ByteBuffer.wrap(new byte[]{0,1,2,3,4,5,6});b2.position(1);System.out.println(b1.compareTo(b2)); //-1b1.clear();b2.clear();System.out.println(b1.compareTo(b2)); //1
}
这篇关于ByteBuffer之equals和compareTo比较的文章就介绍到这儿,希望我们推荐的文章对编程师们有所帮助!




