本文主要是介绍LDD学习笔记 -- Linux字符设备驱动,希望对大家解决编程问题提供一定的参考价值,需要的开发者们随着小编来一起学习吧!
LDD学习笔记 -- Linux字符设备驱动
- 虚拟文件系统 VFS
- 设备号
- 相关Kernel APIs
- 动态申请设备号
- 动态创建设备文件
- 内核空间和用户空间的数据交换
- 系统调用方法
- read
- write
- lseek
- 写一个伪字符设备驱动
- 在主机上测试pcd(HOST)
- 在目标板上测试pcd(TARGET)
字符驱动程序用于与Linux内核中的设备进行交互;
字符设备指的是像内存区域这样的硬件组件,通常称为伪设备;
用户空间应用程序通常使用open read write等系统调用与这些设备通信;
虚拟文件系统 VFS
把用户空间的系统调用连接到设备驱动的系统调用实现方法上。
内核的虚拟文件系统 virtual file system,在内核空间
设备驱动需要使用内核的API向虚拟文件系统注册
设备号
Major numbers(指示特定的驱动) + Minor numbers(表示指定的设备文件)
设备创建时候在VFS注册设备号,虚拟文件系统,将设备文件的设备号与驱动程序列表进行比较,选择正确的驱动程序,并将用户请求连接到对应驱动程序的文件操作方法。
相关Kernel APIs
| kernel functions and data structures(Creation) | (Deletion) | kernel header file |
|---|---|---|
alloc_chrdev_region() | unregister_chrdev_region() | include/linux/fs.h |
cdev_init() cdev_add() | cdev_del() | include/linux/cdev.h |
device_creat() class_creat() | device_destory() class_destory | include/linux/device.h |
copy_to_user() copy_from_user() | include/linux/uaccess.h | |
VFS structure definitions | include/linux/cdev.h |
动态申请设备号
alloc_chrdev_region() 可以动态申请主设备号,保证唯一性,传输设备号(dev_t [u32])地址和次设备号起始(一般0)和个数。
dev_t device_number; //32bit
int minor_no = MINOR(device_number); //后20bit `kdev_t.h`
int major_no = MAJOR(device_number); //前12bitMKDEV(int major, int minor);
动态创建设备文件
当收到uevent,udev根据uevent内存储的细节在dev目录下创建设备文件。
class_create :在sysf中创建一个目录/sys/Class/<your_class_name>
device_create:在上面目录下使用设备名创建一个子目录/sys/Class/<your_class_name>/<your_device_name> /dev 这里的dev文件存储设备名主副设备号等
udev:用户空间的应用,动态创建设备文件/sys/Class/<your_class_name>/<your_device_name> /dev --> dev/your_device_name
内核空间和用户空间的数据交换
用户空间的指针不是完全可信的,用户地址空间有时可能无效,虚拟内存管理器可以交换出这些内存位置。
内核级代码不能直接引用用户级内存指针;
使用内核数据复制工具copy_to_user copy_from_user。工具会检查用户空间指针是否有效
系统调用方法
read
用户级进程执行read系统调用从文件中读取。文件可以是普通文件,也可以是一个设备文件(处理具体设备)。
例如前面的伪字符设备,有一块内存数组(设备内存buffer)。当用户程序在该设备文件上发出read系统调用时,应该将数据从设备buffer传到用户buffer。该数据拷贝发生在内核端到用户端。
write
将数据从用户空间复制到内核空间,
用户程序想把一些数据写入设备内存buffer。
lseek
改变f_pos(struct file)变量的位置,将文件位置指针向前/向后移动。
写一个伪字符设备驱动
- 动态申请设备号
- 创建
cdev结构体变量和file_operiations结构体变量 - 使用fops初始化字符设备结构体变量
- 向内核VFS注册设备
- 实现
file operiation的方法 - 初始化
file operiation变量 - 创建设备文件
class_create()device_create() - 驱动清理函数功能实现
#include <linux/module.h>
#include <linux/fs.h>
#include <linux/cdev.h>
#include <linux/device.h>
#include <linux/kdev_t.h>
#include <linux/uaccess.h>
#include <uapi/asm-generic/errno-base.h>#define DEV_MEM_SIZE 512/* pseudo device's memory */
char device_buffer[DEV_MEM_SIZE];/* This hold the device number */
dev_t device_number;/* Cdev variable */
struct cdev pcd_cdev;loff_t pcd_llseek(struct file *filp, loff_t offset, int whence)
{pr_info("%s\n", __func__);loff_t temp;switch (whence){case SEEK_SET:if ((offset > DEV_MEM_SIZE) || (offset < 0))return -EINVAL;filp->f_pos = offset;break;case SEEK_CUR:temp = filp->f_pos + offset;if ((temp > DEV_MEM_SIZE) || (offset < 0))return -EINVAL;filp->f_pos = temp;break;case SEEK_END:temp = DEV_MEM_SIZE + offset;if ((temp > DEV_MEM_SIZE) || (offset < 0))return -EINVAL;filp->f_pos = temp;break;default:return -EINVAL;}pr_info("New value of the file position = %lld\n", filp->f_pos);return filp->f_pos;// return 0;}ssize_t pcd_read(struct file *filp, char __user *buff, size_t count, loff_t *f_pos)
{pr_info("%s :Read requested for %zu bytes\n", __func__, count);if((*f_pos + count) > DEV_MEM_SIZE)count = DEV_MEM_SIZE - *f_pos;if(copy_to_user(buff, &device_buffer[*f_pos], count)){return -EFAULT;}*f_pos += count;pr_info("Number of bytes successful read = %zu\n", count);pr_info("Update file position = %lld\n", *f_pos);return count;
}
ssize_t pcd_write(struct file *filp, const char __user *buff, size_t count, loff_t *f_pos)
{pr_info("%s :Write requested for %zu bytes, current file position = %lld\n", __func__, count, *f_pos);if((*f_pos + count) > DEV_MEM_SIZE)count = DEV_MEM_SIZE - *f_pos;if(!count)return -ENOMEM;if(copy_from_user(&device_buffer[*f_pos], buff, count)){return -EFAULT;}*f_pos += count;pr_info("Number of bytes successful writtens = %zu\n", count);pr_info("Update file position = %lld\n", *f_pos);return count;
}
int pcd_open(struct inode *inode, struct file *filp)
{pr_info("%s\n", __func__);return 0;
}
int pcd_release(struct inode *inode, struct file *filp)
{pr_info("%s\n", __func__);return 0;
}/* file operations variable */
struct file_operations pcd_fops = {.open = pcd_open,.write = pcd_write,.read = pcd_read,.llseek = pcd_llseek,.release = pcd_release,.owner = THIS_MODULE
};struct class *class_pcd;
struct device *device_pcd;static int __init pcd_driver_init(void)
{pr_info("pcd_driver_init\n");/* 1. Dynamically allocate a device number */alloc_chrdev_region(&device_number, 0, 1, "pcd");pr_info("Device number <major>:<minor> = %d:%d\n", MAJOR(device_number), MINOR(device_number));/* 2. Initialize the cdev structure with fops */cdev_init(&pcd_cdev, &pcd_fops);/* 3. Register a device(cdev structure) with VFS */pcd_cdev.owner = THIS_MODULE;cdev_add(&pcd_cdev, device_number, 1);/* creat device class under /sys/class / */class_pcd = class_create(THIS_MODULE, "pcd_class");/* populate the sysfs with device information */device_pcd = device_create(class_pcd, NULL, device_number, NULL, "pcd");pr_info("Module init was successful\n");return 0;
}/* This is module clean-up entry point */
static void __exit pcd_driver_exit(void)
{pr_info("my hello module exit\n");device_destroy(class_pcd, device_number);class_destroy(class_pcd);cdev_del(&pcd_cdev);unregister_chrdev_region(device_number, 1);pr_info("module unloaded\n");
}/* registration */
module_init(pcd_driver_init);
module_exit(pcd_driver_exit);/* This is description information about the module */
MODULE_LICENSE("GPL");
MODULE_AUTHOR("NAME");
MODULE_DESCRIPTION("A pseudo device driver");
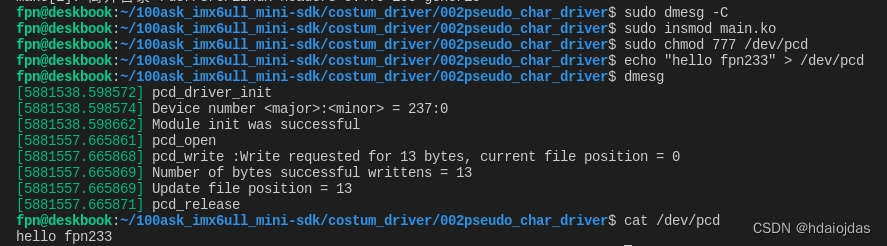
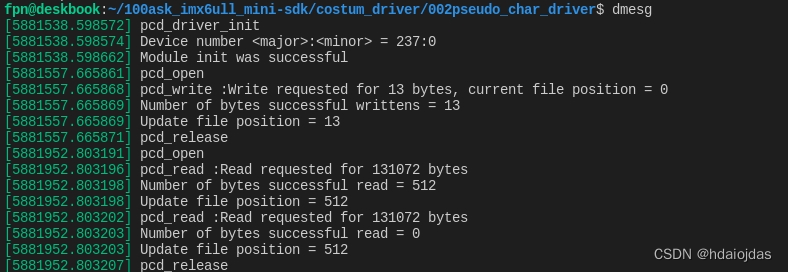
在主机上测试pcd(HOST)
使用echo 命令测试向PCD写数据
使用cat命令测试从PCD读数据
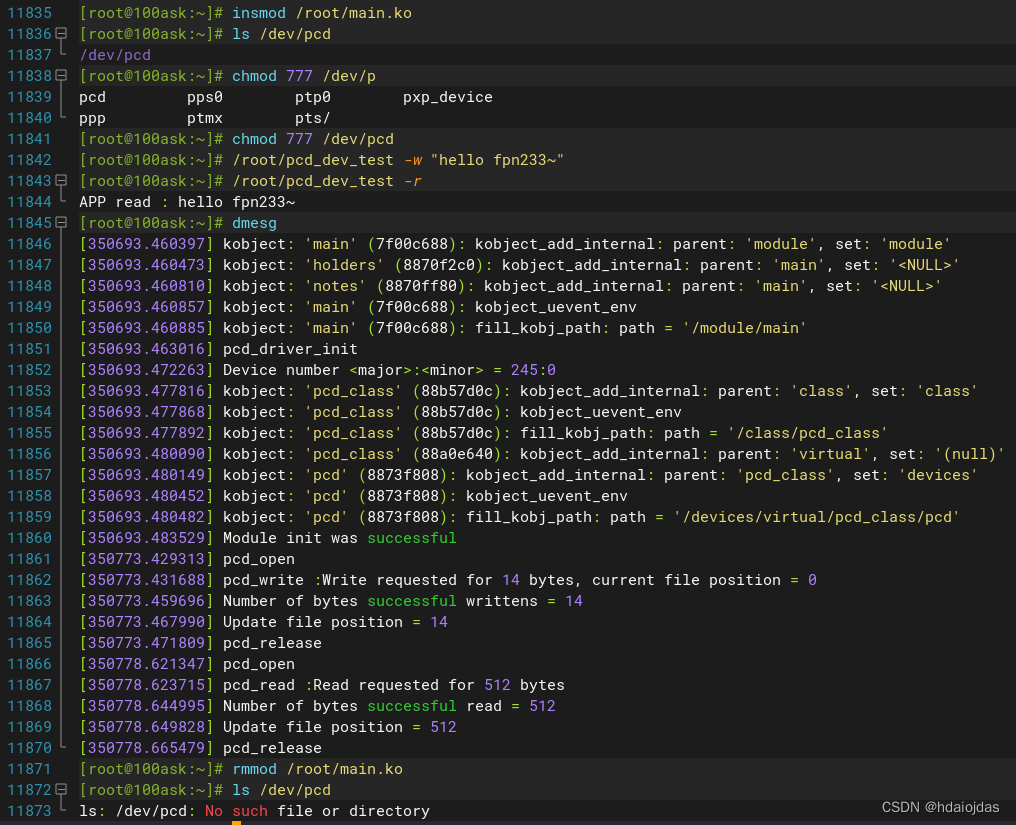
在目标板上测试pcd(TARGET)
需要在用户空间写一个应用程序(测试应用)来测试字符设备驱动程序。使用对应目标板的编译工具链编译.c文件成目标板上的可执行文件,有没有.exe后缀都可,自己知道就行。
arm-buildroot-linux-gnueabihf-gcc ./pcd_drv_test.c -o pcd_dev_test
将上面设备驱动编译出的目标板的.ko文件和我们的测试应用文件都放到目标板上。
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <sys/stat.h>
#include <fcntl.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <stdio.h>
#include <string.h>/** ./pcd_drv_test -w hello fpn233~* ./pcd_drv_test -r*/
int main(int argc, char **argv)
{int fd;char buf[512];int len;/* 1. 判断参数 */if (argc < 2) {printf("Usage: %s -w <string>\n", argv[0]);printf(" %s -r\n", argv[0]);return -1;}/* 2. 打开文件 */fd = open("/dev/pcd", O_RDWR);if (fd == -1){printf("can not open file /dev/pcd\n");return -1;}/* 3. 写文件或读文件 */if ((0 == strcmp(argv[1], "-w")) && (argc == 3)){len = strlen(argv[2]) + 1;len = len < 512 ? len : 512;write(fd, argv[2], len);}else{len = read(fd, buf, 512); buf[1023] = '\0';printf("APP read : %s\n", buf);}close(fd);return 0;
}
这篇关于LDD学习笔记 -- Linux字符设备驱动的文章就介绍到这儿,希望我们推荐的文章对编程师们有所帮助!









