本文主要是介绍使用MinGW 与 MSYS 编译 ffmpeg 的问题说明,希望对大家解决编程问题提供一定的参考价值,需要的开发者们随着小编来一起学习吧!
本文的目的是记录一下,Windows上搭建MinGW与MSYS开发环境并且编译ffmpeg并进行简单测试的过程中遇见的奇怪问题。
从MinGW官网http://www.mingw.org,下载并安装mingw
安装项:
- Basic Setup
- mingw-developer-toolkit Version:2013072300
- mingw32-base Version:2013072200
- msys-base Version:2013072300
特意记录一下unistd.h所在的包:
- mingw-mingwrt dev3.21
将MSYS/etc/fstab.sample 复制一份叫fstab,并且fstab内c:mingw改为自己的mingw安装目录
打开MSYS,进入ffmpeg所在目录,并且进行configure --disable-all
然后make
出错: 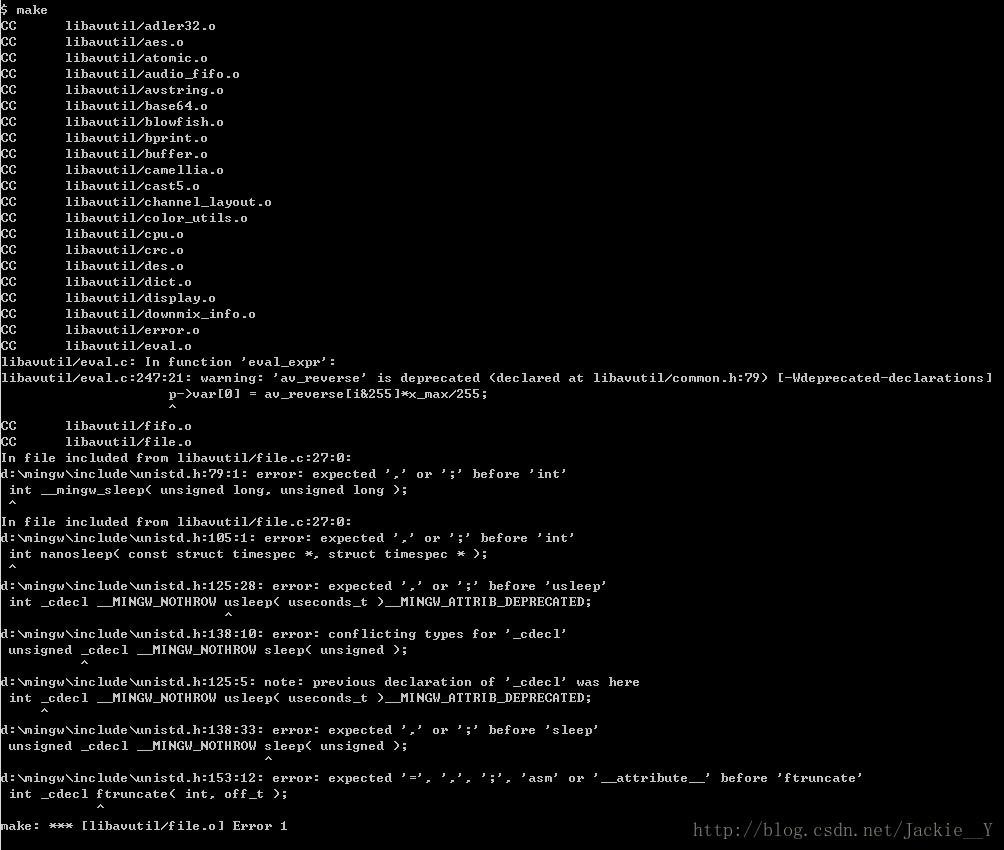

分析了一下出错的地方,发现是_cdecl这个宏的问题,搜索了一下MinGW的所有代码,发现这个宏是在windef.h中定义的,而且只在几处地方有引用,
应该是因为什么特殊原因需要避免使用__cdecl,才引入这个宏.
原始unistd.h
#ifndef _UNISTD_H
/** unistd.h** Standard header file declaring MinGW's POSIX compatibility features.** $Id$** Written by Rob Savoye <rob@cygnus.com>* Modified by Earnie Boyd <earnie@users.sourceforge.net>* Danny Smith <dannysmith@users.sourceforge.net>* Ramiro Polla <ramiro@lisha.ufsc.br>* Gregory McGarry <gregorymcgarry@users.sourceforge.net>* Keith Marshall <keithmarshall@users.sourceforge.net>* Copyright (C) 1997, 1999, 2002-2004, 2007-2009, 2014, MinGW.org Project.*** Permission is hereby granted, free of charge, to any person obtaining a* copy of this software and associated documentation files (the "Software"),* to deal in the Software without restriction, including without limitation* the rights to use, copy, modify, merge, publish, distribute, sublicense,* and/or sell copies of the Software, and to permit persons to whom the* Software is furnished to do so, subject to the following conditions:** The above copyright notice, this permission notice, and the following* disclaimer shall be included in all copies or substantial portions of* the Software.** THE SOFTWARE IS PROVIDED "AS IS", WITHOUT WARRANTY OF ANY KIND, EXPRESS* OR IMPLIED, INCLUDING BUT NOT LIMITED TO THE WARRANTIES OF MERCHANTABILITY,* FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE AND NONINFRINGEMENT. IN NO EVENT SHALL* THE AUTHORS OR COPYRIGHT HOLDERS BE LIABLE FOR ANY CLAIM, DAMAGES OR OTHER* LIABILITY, WHETHER IN AN ACTION OF CONTRACT, TORT OR OTHERWISE, ARISING* FROM, OUT OF OR IN CONNECTION WITH THE SOFTWARE OR THE USE OF OR OTHER* DEALINGS IN THE SOFTWARE.**/
#define _UNISTD_H 1
#pragma GCC system_header/* All MinGW headers MUST include _mingw.h before anything else,* to ensure proper initialization of feature test macros.*/
#include <_mingw.h>/* unistd.h maps (roughly) to io.h* Other headers included by unistd.h may be selectively processed;* __UNISTD_H_SOURCED__ enables such selective processing.*/
#define __UNISTD_H_SOURCED__ 1#include <io.h>
#include <process.h>
#include <getopt.h>/* These are defined in stdio.h. POSIX also requires that they* are to be consistently defined here; don't guard against prior* definitions, as this might conceal inconsistencies.*/
#define SEEK_SET 0
#define SEEK_CUR 1
#define SEEK_END 2#if _POSIX_C_SOURCE
/** POSIX process/thread suspension functions; all are supported by a* common MinGW API in libmingwex.a, providing for suspension periods* ranging from mean values of ~7.5 milliseconds, (see comments below),* extending up to a maximum of ~136 years.** Note that, whereas POSIX supports early wake-up of any suspended* process/thread, in response to a signal, this implementation makes* no attempt to emulate this signalling behaviour, (since signals are* not well supported by Windows); thus, unless impeded by an invalid* argument, this implementation always returns an indication as if* the sleeping period ran to completion.*/
_EXTERN_C _cdecl __MINGW_NOTHROW
int __mingw_sleep( unsigned long, unsigned long );/* Structure timespec is mandated by POSIX, for specification of* intervals with the greatest precision supported by the OS kernel.* Although this allows for specification to nanosecond precision, do* not be deluded into any false expectation that such short intervals* can be realized on Windows; on Win9x derivatives, the metronome used* by the process scheduler has a period of ~55 milliseconds, while for* WinNT derivatives, the corresponding period is ~15 milliseconds; thus,* the shortest intervals which can be realistically timed will range* from 0..55 milliseconds on Win9x hosts, and from 0..15 ms on WinNT,* with period values normally distributed around means of ~27.5 ms* and ~7.5 ms, for the two system types respectively.*/
#define _FAKE_TIME_H_SOURCED 1
#define __need_struct_timespec 1
#include <parts/time.h>_BEGIN_C_DECLS/* The nanosleep() function provides the most general purpose API for* process/thread suspension; it provides for specification of periods* ranging from ~7.5 ms mean, (on WinNT derivatives; ~27.5 ms on Win9x),* extending up to ~136 years, (effectively eternity).*/
_cdecl __MINGW_NOTHROW
int nanosleep( const struct timespec *, struct timespec * );#ifndef __NO_INLINE__
__CRT_INLINE __LIBIMPL__(( FUNCTION = nanosleep ))
int nanosleep( const struct timespec *period, struct timespec *residual )
{if( residual != (void *)(0) )residual->tv_sec = (long long)(residual->tv_nsec = 0);return __mingw_sleep((unsigned)(period->tv_sec), (period->tv_sec < 0LL)? (unsigned)(-1) : (unsigned)(period->tv_nsec));
}
#endif/* The usleep() function, and its associated useconds_t type specifier* were made obsolete in POSIX.1-2008; declared here, only for backward* compatibility, its continued use is not recommended. (It is limited* to specification of suspension periods ranging from ~7.5 ms mean up* to a maximum of 999,999 microseconds only).*/
typedef unsigned long useconds_t __MINGW_ATTRIB_DEPRECATED;
int _cdecl __MINGW_NOTHROW usleep( useconds_t )__MINGW_ATTRIB_DEPRECATED;#ifndef __NO_INLINE__
__CRT_INLINE __LIBIMPL__(( FUNCTION = usleep ))
int usleep( useconds_t period ){ return __mingw_sleep( 0, 1000 * period ); }
#endif/* The sleep() function is, perhaps, the most commonly used of all the* process/thread suspension APIs; it provides support for specification* of suspension periods ranging from 1 second to ~136 years. (However,* POSIX recommends limiting the maximum period to 65535 seconds, to* maintain portability to platforms with only 16-bit ints).*/
unsigned _cdecl __MINGW_NOTHROW sleep( unsigned );#ifndef __NO_INLINE__
__CRT_INLINE __LIBIMPL__(( FUNCTION = sleep ))
unsigned sleep( unsigned period ){ return __mingw_sleep( period, 0 ); }
#endif/* POSIX ftruncate() function.** Microsoft's _chsize() function is incorrectly described, on MSDN,* as a preferred replacement for the POSIX chsize() function. There* never was any such POSIX function; the actual POSIX equivalent is* the ftruncate() function.*/
int _cdecl ftruncate( int, off_t );#ifndef __NO_INLINE__
__CRT_INLINE __JMPSTUB__(( FUNCTION = ftruncate, REMAPPED = _chsize ))
int ftruncate( int __fd, off_t __length ){ return _chsize( __fd, __length ); }
#endif_END_C_DECLS#endif /* _POSIX_C_SOURCE */#undef __UNISTD_H_SOURCED__
#endif /* ! _UNISTD_H: $RCSfile$: end of file */#ifndef _UNISTD_H
/** unistd.h** Standard header file declaring MinGW's POSIX compatibility features.** $Id$** Written by Rob Savoye <rob@cygnus.com>* Modified by Earnie Boyd <earnie@users.sourceforge.net>* Danny Smith <dannysmith@users.sourceforge.net>* Ramiro Polla <ramiro@lisha.ufsc.br>* Gregory McGarry <gregorymcgarry@users.sourceforge.net>* Keith Marshall <keithmarshall@users.sourceforge.net>* Copyright (C) 1997, 1999, 2002-2004, 2007-2009, 2014, MinGW.org Project.*** Permission is hereby granted, free of charge, to any person obtaining a* copy of this software and associated documentation files (the "Software"),* to deal in the Software without restriction, including without limitation* the rights to use, copy, modify, merge, publish, distribute, sublicense,* and/or sell copies of the Software, and to permit persons to whom the* Software is furnished to do so, subject to the following conditions:** The above copyright notice, this permission notice, and the following* disclaimer shall be included in all copies or substantial portions of* the Software.** THE SOFTWARE IS PROVIDED "AS IS", WITHOUT WARRANTY OF ANY KIND, EXPRESS* OR IMPLIED, INCLUDING BUT NOT LIMITED TO THE WARRANTIES OF MERCHANTABILITY,* FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE AND NONINFRINGEMENT. IN NO EVENT SHALL* THE AUTHORS OR COPYRIGHT HOLDERS BE LIABLE FOR ANY CLAIM, DAMAGES OR OTHER* LIABILITY, WHETHER IN AN ACTION OF CONTRACT, TORT OR OTHERWISE, ARISING* FROM, OUT OF OR IN CONNECTION WITH THE SOFTWARE OR THE USE OF OR OTHER* DEALINGS IN THE SOFTWARE.**/
#define _UNISTD_H 1
#pragma GCC system_header/* All MinGW headers MUST include _mingw.h before anything else,* to ensure proper initialization of feature test macros.*/
#include <_mingw.h>/* unistd.h maps (roughly) to io.h* Other headers included by unistd.h may be selectively processed;* __UNISTD_H_SOURCED__ enables such selective processing.*/
#define __UNISTD_H_SOURCED__ 1#include <io.h>
#include <process.h>
#include <getopt.h>/* These are defined in stdio.h. POSIX also requires that they* are to be consistently defined here; don't guard against prior* definitions, as this might conceal inconsistencies.*/
#define SEEK_SET 0
#define SEEK_CUR 1
#define SEEK_END 2#if _POSIX_C_SOURCE
#ifdef __GNUC__
#ifndef _cdecl
#define _cdecl __attribute__((cdecl))
#endif
#else
#define _cdecl
#endif
/** POSIX process/thread suspension functions; all are supported by a* common MinGW API in libmingwex.a, providing for suspension periods* ranging from mean values of ~7.5 milliseconds, (see comments below),* extending up to a maximum of ~136 years.** Note that, whereas POSIX supports early wake-up of any suspended* process/thread, in response to a signal, this implementation makes* no attempt to emulate this signalling behaviour, (since signals are* not well supported by Windows); thus, unless impeded by an invalid* argument, this implementation always returns an indication as if* the sleeping period ran to completion.*/
_EXTERN_C _cdecl __MINGW_NOTHROW
int __mingw_sleep( unsigned long, unsigned long );/* Structure timespec is mandated by POSIX, for specification of* intervals with the greatest precision supported by the OS kernel.* Although this allows for specification to nanosecond precision, do* not be deluded into any false expectation that such short intervals* can be realized on Windows; on Win9x derivatives, the metronome used* by the process scheduler has a period of ~55 milliseconds, while for* WinNT derivatives, the corresponding period is ~15 milliseconds; thus,* the shortest intervals which can be realistically timed will range* from 0..55 milliseconds on Win9x hosts, and from 0..15 ms on WinNT,* with period values normally distributed around means of ~27.5 ms* and ~7.5 ms, for the two system types respectively.*/
#define _FAKE_TIME_H_SOURCED 1
#define __need_struct_timespec 1
#include <parts/time.h>_BEGIN_C_DECLS/* The nanosleep() function provides the most general purpose API for* process/thread suspension; it provides for specification of periods* ranging from ~7.5 ms mean, (on WinNT derivatives; ~27.5 ms on Win9x),* extending up to ~136 years, (effectively eternity).*/
_cdecl __MINGW_NOTHROW
int nanosleep( const struct timespec *, struct timespec * );#ifndef __NO_INLINE__
__CRT_INLINE __LIBIMPL__(( FUNCTION = nanosleep ))
int nanosleep( const struct timespec *period, struct timespec *residual )
{if( residual != (void *)(0) )residual->tv_sec = (long long)(residual->tv_nsec = 0);return __mingw_sleep((unsigned)(period->tv_sec), (period->tv_sec < 0LL)? (unsigned)(-1) : (unsigned)(period->tv_nsec));
}
#endif/* The usleep() function, and its associated useconds_t type specifier* were made obsolete in POSIX.1-2008; declared here, only for backward* compatibility, its continued use is not recommended. (It is limited* to specification of suspension periods ranging from ~7.5 ms mean up* to a maximum of 999,999 microseconds only).*/
typedef unsigned long useconds_t __MINGW_ATTRIB_DEPRECATED;
int _cdecl __MINGW_NOTHROW usleep( useconds_t )__MINGW_ATTRIB_DEPRECATED;#ifndef __NO_INLINE__
__CRT_INLINE __LIBIMPL__(( FUNCTION = usleep ))
int usleep( useconds_t period ){ return __mingw_sleep( 0, 1000 * period ); }
#endif/* The sleep() function is, perhaps, the most commonly used of all the* process/thread suspension APIs; it provides support for specification* of suspension periods ranging from 1 second to ~136 years. (However,* POSIX recommends limiting the maximum period to 65535 seconds, to* maintain portability to platforms with only 16-bit ints).*/
unsigned _cdecl __MINGW_NOTHROW sleep( unsigned );#ifndef __NO_INLINE__
__CRT_INLINE __LIBIMPL__(( FUNCTION = sleep ))
unsigned sleep( unsigned period ){ return __mingw_sleep( period, 0 ); }
#endif/* POSIX ftruncate() function.** Microsoft's _chsize() function is incorrectly described, on MSDN,* as a preferred replacement for the POSIX chsize() function. There* never was any such POSIX function; the actual POSIX equivalent is* the ftruncate() function.*/
int _cdecl ftruncate( int, off_t );#ifndef __NO_INLINE__
__CRT_INLINE __JMPSTUB__(( FUNCTION = ftruncate, REMAPPED = _chsize ))
int ftruncate( int __fd, off_t __length ){ return _chsize( __fd, __length ); }
#endif_END_C_DECLS#endif /* _POSIX_C_SOURCE */#undef __UNISTD_H_SOURCED__
#endif /* ! _UNISTD_H: $RCSfile$: end of file */再进行make,通过了
通过以后,思考了一下原因,
将两个头文件使用gcc -E进行预编译以后,发现结果除了文件名以外完全一致;
使用原始头文件单独对出错的file.c进行编译:
gcc -I.. -c file.c -o file.o
发现编译,竟然成功了。
因此这个错误一定就是与make有关系了,但是其中流程不清楚,等到以后有时间了再深究吧。
这篇关于使用MinGW 与 MSYS 编译 ffmpeg 的问题说明的文章就介绍到这儿,希望我们推荐的文章对编程师们有所帮助!




