本文主要是介绍Java 第19章 IO流 课堂练习+本章作业,希望对大家解决编程问题提供一定的参考价值,需要的开发者们随着小编来一起学习吧!
文章目录
- Buffered流拷贝二进制文件
- 创建文件写入文本
- 读取文本文件
- 存读Properties文件
Buffered流拷贝二进制文件
package com.hspedu.chapter19.outputStream;import java.io.*;public class BufferedCopy02 {public static void main(String[] args) {String srcFilePath = "c:\\bh.jpg";String destFilePath = "c:\\hsp.jpg";BufferedInputStream bis = null;BufferedOutputStream bos = null;try {bis = new BufferedInputStream(new FileInputStream(srcFilePath));bos = new BufferedOutputStream(new FileOutputStream(destFilePath));byte[] buff = new byte[1024];int readLen = 0;while ((readLen = bis.read(buff)) != -1) {bos.write(buff, 0, readLen);}System.out.println("Copied successfully..");} catch (IOException e) {throw new RuntimeException(e);} finally {try {bis.close();bos.close();} catch (IOException e) {throw new RuntimeException(e);}}}
}创建文件写入文本

import java.io.BufferedWriter;
import java.io.File;
import java.io.FileWriter;
import java.io.IOException;public class Homework01 {public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {String filePath = "c:\\mydir";File file = new File(filePath);if (!file.exists()) {if (file.mkdirs())System.out.println(filePath + " has been created successfully..");elseSystem.out.println(filePath + " was fail to be created..");} else {System.out.println(filePath + " has already existed..");}String destfile = filePath + "\\hello.txt";File file1 = new File(destfile);if (!file1.exists()) {if (file1.createNewFile()) {BufferedWriter bufferedWriter = new BufferedWriter(new FileWriter(file1));bufferedWriter.write("hello, world~~ 韩顺平教育");bufferedWriter.close();System.out.println(destfile + " has been created successfully..");} else {System.out.println(destfile + " has already existed..");}} else {System.out.println(destfile + " has already existed..");}}
}读取文本文件

public class Homework02 {public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {String filePath = "c:\\hello.txt";String line = "";int lineNum = 0;BufferedReader bufferedReader = new BufferedReader(new FileReader(filePath));while ((line = bufferedReader.readLine()) != null) {System.out.println(++lineNum + " " + line);}if (bufferedReader != null)bufferedReader.close();}
}

public class Homework02 {public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {String filePath = "c:\\hello.txt";// InputStreamReader指定编码方式InputStreamReader isr = new InputStreamReader(new FileInputStream(filePath), "gbk");String line = "";int lineNum = 0;BufferedReader bufferedReader = new BufferedReader(isr);while ((line = bufferedReader.readLine()) != null) {System.out.println(++lineNum + " " + line);}if (bufferedReader != null)bufferedReader.close();}
}
存读Properties文件
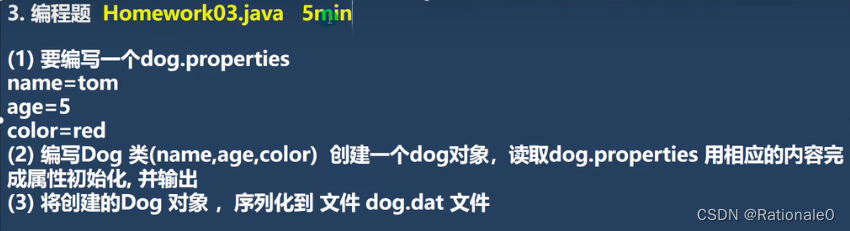
public class Homework03 {public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {String filePath = "src\\dog.properties";Properties properties = new Properties();properties.load(new FileReader(filePath));String name = properties.get("name") + ""; //Object -> Stringint age = Integer.parseInt(properties.get("age") + "");// Object -> intString color = properties.get("color") + "";//Object -> StringDog dog = new Dog(name, age, color);System.out.println("===dog对象信息====");System.out.println(dog);//将创建的Dog 对象 ,序列化到 文件 dog.dat 文件String serFilePath = "c:\\dog.dat";ObjectOutputStream oos = new ObjectOutputStream(new FileOutputStream(serFilePath));oos.writeObject(dog);//关闭流oos.close();System.out.println("dog对象,序列化完成...");}//在编写一个方法,反序列化dog@Testpublic void m1() throws IOException, ClassNotFoundException {String serFilePath = "e:\\dog.dat";ObjectInputStream ois = new ObjectInputStream(new FileInputStream(serFilePath));Dog dog = (Dog)ois.readObject();System.out.println("===反序列化后 dog====");System.out.println(dog);ois.close();}
}class Dog implements Serializable{private String name;private int age;private String color;public Dog(String name, int age, String color) {this.name = name;this.age = age;this.color = color;}@Overridepublic String toString() {return "Dog{" +"name='" + name + '\'' +", age=" + age +", color='" + color + '\'' +'}';}
}
这篇关于Java 第19章 IO流 课堂练习+本章作业的文章就介绍到这儿,希望我们推荐的文章对编程师们有所帮助!





