本文主要是介绍Django3.0.8生产环境部署nginx、uwsgi、daphne、supervisor、gunicorn、celery,希望对大家解决编程问题提供一定的参考价值,需要的开发者们随着小编来一起学习吧!
目录
- 前言
- 环境配置
- 技术方法
- 实现过程
- 安装Python3.8.3
- 安装Nginx
- 安装MySQL
- 安装Redis
- 安装虚拟环境 virtualenv
- 创建虚拟环境
- python中的virtualenv命令集
- 在虚拟环境中安装pip包
- 将项目文件上传到服务器规划的目录
- 拉取所有需要的static file到同一目录
- 配置nginx作为反向代理服务器
- 编辑uwsgi文件
- 使用supervisor管理daphne和uwsgi进程
- 使用gunicorn + gevent替代uwsgi, 并发性能会好一点
- 使用logrotate + crontabs切割日志
- settings.py 中LOGGING的配置
- 最后
- 部署中遇到的错误和解决办法
- 1. 启动supervisor时报错:
- 2. Nginx Permission Denie问题:
- 3. Nginx启动时报错:
- 4. MySQL报错
- 原因分析:
- 解决方案
前言
因为项目中用到了channels做websocket消息推送,所以以前那种nginx+uwsgi的模式行不通了~,channels推荐的是daphne服务器,所以Google了一下,都说是用nginx+uwsgi+daphne+supervisor这一套组合来部署。看了下网上的教程,七零八落的,好不容易才拼凑起来,所以才有自己总结一下的想法。
环境配置
服务器:CentOS8.2 64位
开发平台: Python3.8.3
Web框架: Django3.0.8
数据库: MySQL 8.0
缓存数据库: Redis
技术方法
使用Nginx代理,将http部分请求发送给uwsgi或者gunicorn进行处理,将websocket部分请求发送给daphne进行处理。uwsgi和daphhe均使用supervisord进行控制。
需要注意的是,由于Nginx无法识别http请求和websocket请求,需要通过路由来区分是哪种协议。我使用的方法是规定所有的websocket的路由均以/ws开头(如: ws://www.example/ws/table/table_id/),这样就可以让Nginx将所有以/ws开头的请求全部转发给daphne进行处理。
当然,这一切都是在服务器的一个虚拟环境中。
实现过程
安装Python3.8.3
安装方法在我另一篇博客中: 如何在 CentOS 8 上安装 Python 3.8
如果嫌pip安装太慢,可以参考这篇文章:更换pip源到国内镜像
安装Nginx
- 安装 Nginx
yum install nginx -y
- 启动软件并设置开机启动
systemctl enable nginx
systemctl start nginx
- 查看命令行检测安装完成。
[root@www.mf8.biz ~]# nginx -V
nginx version: nginx/1.14.1
built by gcc 8.2.1 20180905 (Red Hat 8.2.1-3) (GCC)
built with OpenSSL 1.1.1 FIPS 11 Sep 2018
TLS SNI support enabled
configure arguments: --prefix=/usr/share/nginx --sbin-path=/usr/sbin/nginx --modules-path=/usr/lib64/nginx/modules --conf-path=/etc/nginx/nginx.conf --error-log-path=/var/log/nginx/error.log --http-log-path=/var/log/nginx/access.log --http-client-body-temp-path=/var/lib/nginx/tmp/client_body --http-proxy-temp-path=/var/lib/nginx/tmp/proxy --http-fastcgi-temp-path=/var/lib/nginx/tmp/fastcgi --http-uwsgi-temp-path=/var/lib/nginx/tmp/uwsgi --http-scgi-temp-path=/var/lib/nginx/tmp/scgi --pid-path=/run/nginx.pid --lock-path=/run/lock/subsys/nginx --user=nginx --group=nginx --with-file-aio --with-ipv6 --with-http_ssl_module --with-http_v2_module --with-http_realip_module --with-http_addition_module --with-http_xslt_module=dynamic --with-http_image_filter_module=dynamic --with-http_sub_module --with-http_dav_module --with-http_flv_module --with-http_mp4_module --with-http_gunzip_module --with-http_gzip_static_module --with-http_random_index_module --with-http_secure_link_module --with-http_degradation_module --with-http_slice_module --with-http_stub_status_module --with-http_perl_module=dynamic --with-http_auth_request_module --with-mail=dynamic --with-mail_ssl_module --with-pcre --with-pcre-jit --with-stream=dynamic --with-stream_ssl_module --with-debug --with-cc-opt='-O2 -g -pipe -Wall -Werror=format-security -Wp,-D_FORTIFY_SOURCE=2 -Wp,-D_GLIBCXX_ASSERTIONS -fexceptions -fstack-protector-strong -grecord-gcc-switches -specs=/usr/lib/rpm/redhat/redhat-hardened-cc1 -specs=/usr/lib/rpm/redhat/redhat-annobin-cc1 -m64 -mtune=generic -fasynchronous-unwind-tables -fstack-clash-protection -fcf-protection' --with-ld-opt='-Wl,-z,relro -Wl,-z,now -specs=/usr/lib/rpm/redhat/redhat-hardened-ld -Wl,-E'
- 设置防火墙规则
firewall-cmd --permanent --zone=public --add-service=http
firewall-cmd --permanent --zone=public --add-service=https
firewall-cmd --reload
- 访问IP即可
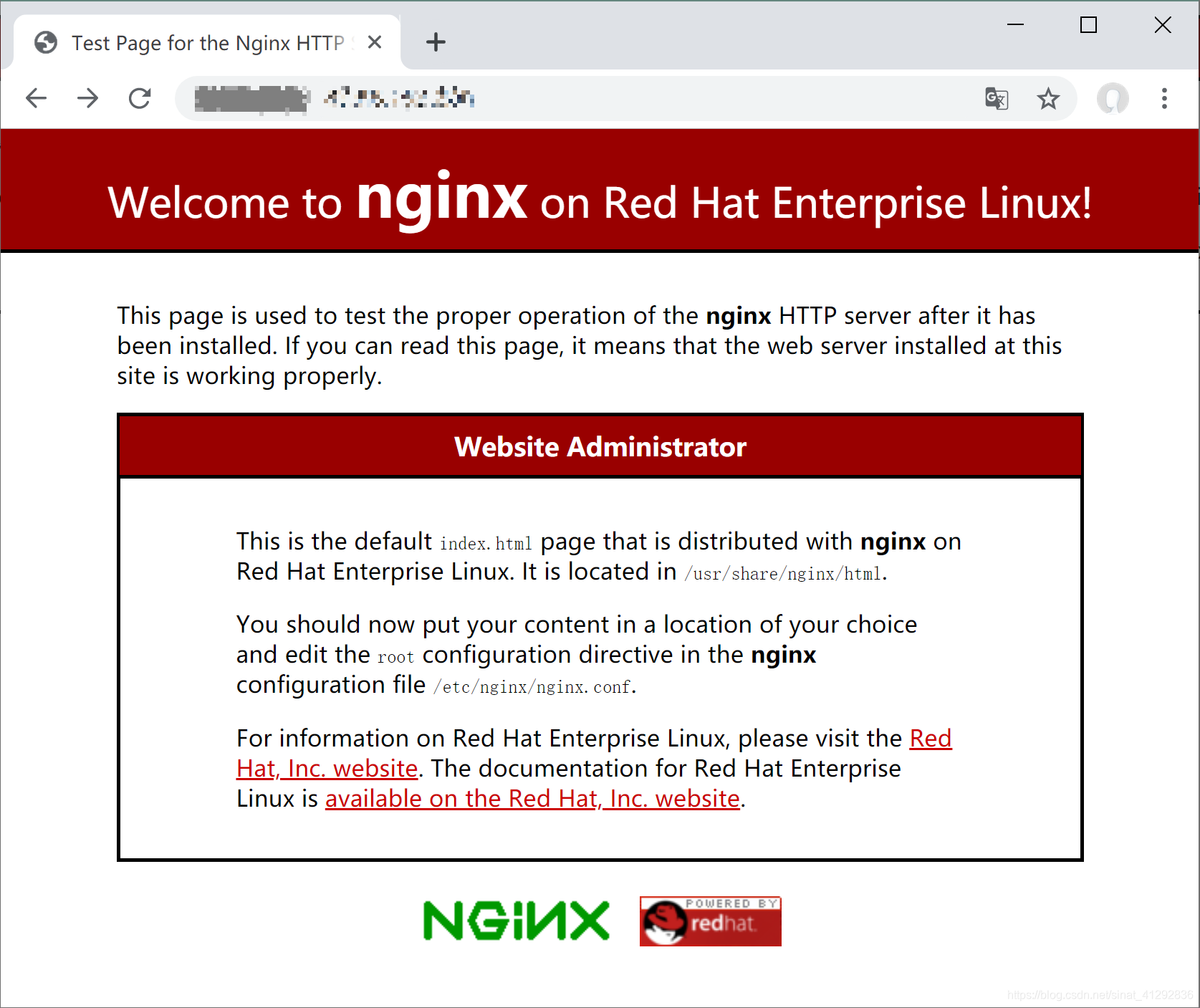
配置文件目录
主配置文件:/etc/nginx/nginx.conf默认文件目录:/usr/share/nginx/html错误日志:/var/log/nginx/error.log访问日志:/var/log/nginx/access.log
安装MySQL
参考我的这篇文章: CentOS 8 安装MySQL 8.0
安装Redis
参考我的这篇文章:CentOS 8安装Redis的两种方式
安装虚拟环境 virtualenv
pip install virtualenvwrapper
接下来编辑.bashrc文件,这是重点
[root@ITCMDB ~]# vi ~/.bashrc添加下面j几行
VIRTUALENVWRAPPER_PYTHON=/usr/bin/python # 指定virtualenvwrapper执行的python版本
export WORKON_HOME=$HOME/.virtualenvs # 指定虚拟环境存放目录,.virtualenvs目录名可自拟
VIRTUALENVWRAPPER_VIRTUALENV_ARGS='' # 添加virtualenvwrapper的参数,生成干净隔绝的环境source /usr/local/bin/virtualenvwrapper.sh # virtualenvwrapper.sh所在目录
保存后,重载./bashrc文件
source ~/.bashrc
创建虚拟环境
执行命令
mkvirtualenv kzitcmdb(虚拟环境名称)
就创建好了, 当然,还有许多命令选项,我这里就不多说了
python中的virtualenv命令集
irtualenv
# 安装
$ pip install virtualenv
# 激活虚拟环境
$ source my_project/bin/activate
# 退出虚拟环境
$ deactivate
# 输出当前依赖包
$ pip freeze > requirements.txt
# 安装依赖包
$ pip install -r requirements.txt
virtualenvwrapper
# 安装
$ pip install virtualenvwrapper
# 修改~/.zshrc
$ cat ~/.zshrc
if [ -f /usr/local/bin/virtualenvwrapper.sh ]; thenexport WORKON_HOME=$HOME/virtualenvssource /usr/local/bin/virtualenvwrapper.sh
fi
# 创建虚拟环境,创建成功后 $WORKON_HOME 下会多出一个文件夹
$ mkvirtualenv my_prj
# 使用虚拟环境
$ workon my_prj
# 退出虚拟环境
$ deactivate
# 删除
$ rmvirtualenv my_prj
# 列出所有环境
$ lsvirtualenv
# 进入到当前虚拟环境中
$ cdvirtualenv
# 进入到当前虚拟环境的 site-packages 中
$ cdsitepackages
.gitignore
*.py[cod] # 将匹配 .pyc、.pyo 和 .pyd文件
__pycache__/ # 排除整个文件夹
在虚拟环境中安装pip包
将准备的requirements.txt上传到服务器
然后执行下面命令
[root@ITCMDB /]# workon led_dev
(led_dev) [root@ITCMDB /]# pip install -r requirements.txt
等待安装完成即可
将项目文件上传到服务器规划的目录
/root/webapp
同时,将数据库上传到服务器
本例中,用navicat进行数据库的复制。
此时,可以通过python内置的服务器进行测试
(kzitcmdb) [root@ITCMDB wwwroot]# python manage.py runserver 0.0.0.0:9999
启动成功后,在浏览器进行测试。
拉取所有需要的static file到同一目录
在django的setting文件中,添加下面一行内容:
STATIC_URL = '/static/'STATICFILES_DIRS = [os.path.join(BASE_DIR, "static"),
]
并在项目根目录下运行命令:
python manage.py collectstatic
完成后,重启nginx
配置nginx作为反向代理服务器
我这里是把我的项目的nginx配置文件放在了项目文件夹中,便于管理
在这个目录下新建一个led.conf
[root@ITCMDB nginx]# pwd/root/webapp/LED/conf/nginx/
编辑led.conf
upstream led {server unix:///root/webapp/LED/conf/sock/server.sock fail_timeout=0;
}upstream websocket {server unix:///root/webapp/LED/conf/sock/websocket.sock fail_timeout=0;
}log_format access_exp '$remote_addr - $remote_user [$time_local] "$request" ''$status $body_bytes_sent "$http_referer" ''"$http_user_agent" "$http_x_forwarded_for"';server {listen 8000;server_name 192.168.12.156; # substitute your machine's IP address or FQDNcharset utf-8;client_max_body_size 1024M;location /media {alias /root/webapp/LED/media/;}location /static {alias /root/webapp/LED/static/;}access_log /root/webapp/LED/log/nginx/access.log access_exp;error_log /root/webapp/LED/log/nginx/error.log;open_log_file_cache max=10;location / {# gunicorn 配置# proxy_set_header X-Forwarded-For $proxy_add_x_forwarded_for;# proxy_set_header Host $http_host;# proxy_redirect off;# if (!-f $request_filename) {# proxy_pass http://led;# break;#}# uwsgi 配置uwsgi_pass led;include /root/webapp/LED/conf/uwsgi/uwsgi_params;}location /ftp {alias /root/webapp/LED/media/file/; #目录文件服务器根目录autoindex on; #允许nginx在浏览器以文件夹形式访问autoindex_exact_size off; #显示文件大小autoindex_localtime on; #显示文件时间charset utf-8; # 避免中文乱码}location /push {proxy_pass http://websocket;proxy_http_version 1.1;proxy_set_header Upgrade $http_upgrade;proxy_set_header Connection "upgrade";proxy_redirect off;proxy_set_header Host $host;proxy_set_header X-Real-IP $remote_addr;proxy_set_header X-Forwarded-For $proxy_add_x_forwarded_for;proxy_set_header X-Forwarded-Host $server_name;proxy_read_timeout 36000s;proxy_send_timeout 36000s;}
}然后需要将led.conf软链接到/etc/nginx/conf.d/文件夹下,这样nginx才能加载到你的配置文件
ln -s /root/webapp/LED/conf/nginx/led.conf /etc/nginx/conf.d/
在Nginx和daphne以及uwsgi进行通信时,有http socket和file socket两种通信方式,推荐使用后一种file socket的方式, 也就是我用的这种。
编辑uwsgi文件
我这里是把我的项目uwsgi的ini文件也放在了项目文件夹中,便于管理
在这个目录下新建一个led.ini
[root@ITCMDB uwsgi]# pwd/root/webapp/LED/conf/uwsgi/
编辑led.ini
[uwsgi]
#使用nginx连接时使用
socket=/root/webapp/LED/conf/sock/server.sock#直接做web服务器使用 python manage.py runserver ip:port
#http=0.0.0.0:8000#项目目录
chdir=/root/webapp/LED#项目中wsgi.py文件的目录,相对于项目目录
wsgi-file=LED/wsgi.py#指定启动的工作进程数
processes=2#指定工作进程中的线程数
threads=2#指定在这些进程里有一个主进程
master=True#保存启动之后主进程的pid
pidfile=/root/webapp/LED/conf/uwsgi/uwsgi.pid#设置uwsgi后台运行,uwsgi.log保存日志信息
daemonize=/root/webapp/LED/log/uwsgi.log#设置日志文件最大字节数
log-maxsize = 100000#设置每个进程最大请求数
max-requests = 1000#设置虚拟环境的路径
virtualenv=/root/.virtualenvs/led_dev重点:nginx的配置文件中有一个uwsgi_params文件,在/etc/nginx/文件夹内,拷贝到这个文件夹
使用supervisor管理daphne和uwsgi进程
安装教程:CentOS安装Supervisor
使用教程: supervised使用教程
我的daphne和uwsgi都是用supervisor管理的
编辑/etc/supervisord.conf 解除注释并修改(文件末尾)
[include]
files = /root/webapp/LED/conf/supervisor/*.conf在/root/webapp/LED/conf/supervisor/文件夹新建 daphne.conf、uwsgi.conf、celery_worker.conf文件,因为我还用了celery,所以多一个celery的配置。
daphne.conf
[program:led.daphne]
command=/root/.virtualenvs/led_dev/bin/daphne -u /root/webapp/LED/conf/sock/websocket.sock LED.asgi:application
directory=/root/webapp/LED
user=root
autostart=true ; 随着supervisord的启动而启动
autorestart=true ; 自动重启。。当然要选上了
startretries=10 ; 启动失败时的最多重试次数
exitcodes=0 ; 正常退出代码
stopsignal=KILL ; 用来杀死进程的信号
stopwaitsecs=10 ; 发送SIGKILL前的等待时间
redirect_stderr=true ; 重定向stderr到stdout
stdout_logfile_maxbytes=20MB
stdout_logfile_backups=20
redirect_stderr=true
stdout_logfile=/root/webapp/LED/log/supervisor/daphne.log
; 给每个进程命名,便于管理
process_name=daphne_led
; 默认为 false,如果设置为 true,当进程收到 stop 信号时,会自动将该信号发给该进$
stopasgroup=true ; send stop signal to the UNIX process
; 默认为 false,如果设置为 true,当进程收到 kill 信号时,会自动将该信号发给该进$
killasgroup=true ; SIGKILL the UNIX process group (def false)uwsgi.conf
;[program:led.uwsgi]
;command=/root/.virtualenvs/led_dev/bin/uwsgi --ini /root/webapp/LED/conf/uwsgi/led.ini
;directory=/root/webapp/LED
;user=root
;autostart=true ; 随着supervisord的启动而启动
;autorestart=true ; 自动重启。。当然要选上了
;startretries=10 ; 启动失败时的最多重试次数
;exitcodes=0 ; 正常退出代码
;stopsignal=KILL ; 用来杀死进程的信号
;stopwaitsecs=10 ; 发送SIGKILL前的等待时间
;redirect_stderr=true ; 重定向stderr到stdout
;stdout_logfile_maxbytes=20MB
;stdout_logfile_backups=20
;stdout_logfile=/root/webapp/LED/log/supervisor/uwsgi.log
; 默认为 false,如果设置为 true,当进程收到 stop 信号时,会自动将该信号发给该进$
;stopasgroup=true ; send stop signal to the UNIX process
; 默认为 false,如果设置为 true,当进程收到 kill 信号时,会自动将该信号发给该进$
;killasgroup=true ; SIGKILL the UNIX process group (def false)
celery_worker.conf
[program:led.celery.worker]
command=/root/.virtualenvs/led_dev/bin/celery -A LED worker -B -l info ; 被监控的进程路径
directory=/root/webapp/LED
user=root
numprocs=1
autostart=true ; 随着supervisord的启动而启动
autorestart=true ; 自动重启。。当然要选上了
startretries=3 ; 启动失败时的最多重试次数
exitcodes=0 ; 正常退出代码
stopsignal=KILL ; 用来杀死进程的信号
stopwaitsecs=10 ; 发送SIGKILL前的等待时间
redirect_stderr=true ; 重定向stderr到stdout
stdout_logfile_maxbytes=20MB
stdout_logfile_backups=20
stdout_logfile=/root/webapp/LED/log/supervisor/celery.log
; 给每个进程命名,便于管理
process_name=celery_led
; 默认为 false,如果设置为 true,当进程收到 stop 信号时,会自动将该信号发给该进$
stopasgroup=true ; send stop signal to the UNIX process
; 默认为 false,如果设置为 true,当进程收到 kill 信号时,会自动将该信号发给该进$
killasgroup=true ; SIGKILL the UNIX process group (def false)
启动supervisor
supervisord -c /etc/supervisord.conf
使用gunicorn + gevent替代uwsgi, 并发性能会好一点
gunicorn使用教程:
python之gunicorn的配置
gunicorn 使用教程
gunicorn + nginx:通过套接字或代理服务器
- 安装gunicorn
pip install gunicorn
pip install gevent # 因为我使用的是gevent方式启动gunicorn
- 配置gunicorn
在/root/webapp/LED/conf/gunicorn/ 文件夹内新建gunicorn.conf.py
import multiprocessing
import os
import sysBASE_DIR = '/root/webapp/LED/'sys.path.append(BASE_DIR)LOG_DIR = os.path.join(BASE_DIR, 'log/gunicorn/')
if not os.path.exists(LOG_DIR):os.makedirs(LOG_DIR)# 监听地址和端口
# bind = "127.0.0.1:8001"# 使用套接字
bind = "unix:/root/webapp/LED/conf/sock/server.sock"# 以守护进程的形式后台运行
daemon = True# 服务器中在pending状态的最大连接数,即client处于waiting的数目。超过这个数目, client连接会得到一个error。
# 建议值64-2048。
backlog = 512# 超时
timeout = 30# 调试状态
debug = False# gunicorn要切换到的目的工作目录
chdir = BASE_DIR# 工作进程类型(默认的是 sync 模式,还包括 eventlet, gevent, or tornado, gthread, gaiohttp)
worker_class = 'gevent'# 工作进程数
workers = (multiprocessing.cpu_count()) + 1# 客户端最大同时连接数。只适用于eventlet, gevent工作方式。
worker_connections = ((multiprocessing.cpu_count()) + 1) * 1000# 指定每个工作进程开启的线程数
# threads = multiprocessing.cpu_count() * 2# 日志
# 日志级别,这个日志级别指的是错误日志的级别(debug、info、warning、error、critical),而访问日志的级别无法设置
loglevel = 'info'# 其每个选项的含义如下:
'''
h remote address
l '-'
u currently '-', may be user name in future releases
t date of the request
r status line (e.g. ``GET / HTTP/1.1``)
s status
b response length or '-'
f referer
a user agent
T request time in seconds
D request time in microseconds
L request time in decimal seconds
p process ID
'''# 访问日志文件
accesslog = os.path.join(LOG_DIR, 'gunicorn.access.log')# 错误日志文件
errorlog = os.path.join(LOG_DIR, 'gunicorn.error.log')# pid 文件
pidfile = os.path.join(BASE_DIR, 'conf/gunicorn/led_gunicorn.pid')# 进程名
proc_name = 'led.pid'# 指定worker进程的运行用户名。
user = 'root'# 更多配置请执行:gunicorn -h 进行查看在/root/webapp/LED/conf/supervisor/文件夹新建 gunicorn.conf,注意: gunicorn.conf 和 uwsgi.conf部署的时候二选一就行了。到时候可以把另一个注释掉。
gunicorn.conf
[program:led.gunicorn]
command=/root/.virtualenvs/led_dev/bin/gunicorn LED.wsgi:application -c /root/webapp/LED/conf/gunicorn/gunicorn.conf.py --log-level=info
directory=/root/webapp/LED
user=root
autostart=true ; 随着supervisord的启动而启动
autorestart=true ; 自动重启。。当然要选上了
startretries=10 ; 启动失败时的最多重试次数
exitcodes=0 ; 正常退出代码
stopsignal=KILL ; 用来杀死进程的信号
stopwaitsecs=10 ; 发送SIGKILL前的等待时间
redirect_stderr=true ; 重定向stderr到stdout
stdout_logfile_maxbytes=20MB
stdout_logfile_backups=20
stdout_logfile=/root/webapp/LED/log/supervisor/gunicorn.log
; 给每个进程命名,便于管理
process_name=gunicorn_led
; 默认为 false,如果设置为 true,当进程收到 stop 信号时,会自动将该信号发给该进$
stopasgroup=true ; send stop signal to the UNIX process
; 默认为 false,如果设置为 true,当进程收到 kill 信号时,会自动将该信号发给该进$
killasgroup=true ; SIGKILL the UNIX process group (def false)
使用gunicorn的nginx配置:
led.conf
upstream led {server unix:///root/webapp/LED/conf/sock/server.sock fail_timeout=0;
}upstream websocket {server unix:///root/webapp/LED/conf/sock/websocket.sock fail_timeout=0;
}log_format access_exp '$remote_addr - $remote_user [$time_local] "$request" ''$status $body_bytes_sent "$http_referer" ''"$http_user_agent" "$http_x_forwarded_for"';server {listen 8000;server_name 192.168.12.156; # substitute your machine's IP address or FQDNcharset utf-8;client_max_body_size 1024M;location /media {alias /root/webapp/LED/media/;}location /static {alias /root/webapp/LED/static/;}access_log /root/webapp/LED/log/nginx/access.log access_exp;error_log /root/webapp/LED/log/nginx/error.log;open_log_file_cache max=10;location / {# gunicorn 配置proxy_set_header X-Forwarded-For $proxy_add_x_forwarded_for;proxy_set_header Host $http_host;proxy_redirect off;if (!-f $request_filename) {proxy_pass http://led;break;}# uwsgi 配置# uwsgi_pass led;# include /root/webapp/LED/conf/uwsgi/uwsgi_params;}location /ftp {alias /root/webapp/LED/media/file/; #目录文件服务器根目录autoindex on; #允许nginx在浏览器以文件夹形式访问autoindex_exact_size off; #显示文件大小autoindex_localtime on; #显示文件时间charset utf-8; # 避免中文乱码}location /push {proxy_pass http://websocket;proxy_http_version 1.1;proxy_set_header Upgrade $http_upgrade;proxy_set_header Connection "upgrade";proxy_redirect off;proxy_set_header Host $host;proxy_set_header X-Real-IP $remote_addr;proxy_set_header X-Forwarded-For $proxy_add_x_forwarded_for;proxy_set_header X-Forwarded-Host $server_name;proxy_read_timeout 36000s;proxy_send_timeout 36000s;}
}启动supervisor
supervisord -c /etc/supervisord.conf
启动nginx
systemctl start nginx.service
没报错的话就是可以了~
使用logrotate + crontabs切割日志
安装:
yum -y install logrotate crontabs
配置:
- 先配置logrotate
gunicorn-log-rotate和nginx-log-rotate文件:
/root/webapp/LED/log/gunicorn/*.log {su root rootnocompressdailycopytruncatecreatenotifemptyrotate 7olddir /root/webapp/LED/log/gunicornmissingokdateextpostrotate[ -e /root/webapp/LED/conf/gunicorn/led_gunicorn.pid ] && kill -USR1 $(cat /root/webapp/LED/conf/gunicorn/led_gunicorn.pid)endscript
}
/root/webapp/LED/log/nginx/*.log {su root rootnocompressdailycopytruncatecreatenotifemptyrotate 7olddir /root/webapp/LED/log/nginxmissingokdateextpostrotate[ -e /var/run/nginx.pid ] && kill -USR1 `cat /var/run/nginx.pid`endscript
}
- 配置crontabs, 每天0点定时切割日志
运行:
sudo crontab -e
然后编辑:
# rotate nginx log erery day0 0 * * * /usr/sbin/logrotate -f /root/webapp/LED/conf/logrotate/nginx-log-rotate0 0 * * * /usr/sbin/logrotate -f /root/webapp/LED/conf/logrotate/gunicorn-log-rotatesettings.py 中LOGGING的配置
LOGGING = {'version': 1,'disable_existing_loggers': False,'filters': {'require_debug_false': {'()': 'django.utils.log.RequireDebugFalse'},'skip_static_requests': {'()': 'django.utils.log.CallbackFilter','callback': skip_static_requests},},'formatters': {'verbose': {'format': '%(levelname)s %(asctime)s %(process)d %(thread)d %(name)s:%(lineno)s %(funcName)s() %(message)s'},'verbose_sql': {'format': '%(levelname)s %(asctime)s %(process)d %(thread)d %(name)s:%(lineno)s %(funcName)s() %(sql)s\n%(params)s\n%(duration)ss'},},'handlers': {'console': {'level': 'DEBUG','filters': ['skip_static_requests'],'class': 'logging.StreamHandler','formatter': 'verbose',},'console_error': {'level': 'ERROR','filters': ['skip_static_requests'],'class': 'logging.StreamHandler','formatter': 'verbose',},'console_sql': {'level': 'WARNING','filters': ['skip_static_requests'],'class': 'logging.StreamHandler','formatter': 'verbose_sql',},},'loggers': {'django': {'handlers': ['console'],'level': 'INFO','propagate': True,},'django.request': {'handlers': ['console_error'],'level': 'ERROR','propagate': False,},'django.db.backends': {'handlers': ['console_sql'],'level': 'WARNING','propagate': False,},'django.security': {'handlers': ['console_error'],'level': 'ERROR','propagate': False,},'daphne': {'handlers': ['console',],'level': 'INFO'},},
}
def skip_static_requests(record):if isinstance(record.args, dict):if record.args.get('path', None):if record.args.get('path').startswith('/static/'):return Falseif record.args.get('path').startswith('/media/'):return Falseif record.args.get('path').startswith('/captcha/image/'):return Falsereturn True最后
按上面步骤一步步来的话,基本就可以部署成功了,记得部署之前要把项目的settings配置文件配置好。
部署中遇到的错误和解决办法
1. 启动supervisor时报错:
Error: Another program is already listening on a port that one of our HTTP servers is configured to use. Shut this program down first before starting supervisord.
解决办法:
运行命令
unlink /tmp/supervisor.sock
2. Nginx Permission Denie问题:
open() "/etc/nginx/conf.d/led.conf" failed (13: Permission denied) in /etc/nginx/nginx.conf
或者是nginx静态资源文件无法访问,403 forbidden错误:
解决方法:
- CentOS8 下 解决Nginx Permission Denied问题(推荐)
- 解决Nginx出现403 forbidden (13: Permission denied)报错的四种方法
3. Nginx启动时报错:
nginx: [error] invalid PID number "" in "/run/nginx.pid"
解决办法
需要先执行
nginx -c /etc/nginx/nginx.conf
nginx.conf文件的路径可以从nginx -t的返回中找到。
nginx -t
nginx -s reload
4. MySQL报错
ERROR 2002 (HY000): Can't connect to local MySQL server through socket '/var/lib/mysql/mysql.sock' (2)
原因分析:
我们在连接mysql的时候,如果host是localhost, 就会使用Unix Domain Socket来连接, MySql默认的sock文件路径是/tmp/mysql.sock, 一些mysql 安装方法 将 mysql .sock放在/var/lib/mysql .sock或者其他的什么地方,你可以通过修改/etc/my.cnf文件来修正它(8.0的配置文件好像是在/etc/my.cnf.d/mysql-server.cnf),打开文件,可以看到如下的东东:
[mysqld]
datadir=/var/lib/mysql
socket=/var/lib/mysql/mysql.sock
log-error=/var/log/mysql/mysqld.log
pid-file=/run/mysqld/mysqld.pid解决方案
1. 修改HOST
打开settings.py文件,找到DATABASES的HOST字段。
有两种修改方案:
- 把localhost改成127.0.0.1, 使用内网连接
- 把localhost改成/var/lib/mysql/mysql.sock
DATABASES = {'default': { 'ENGINE': 'django.db.backends.mysql','NAME': 'xxx','USER': 'root','PASSWORD': 'passwd','HOST':'127.0.0.1', # 或者 `/tmp/mysql.sock`'PORT':'3306',}}
2. 修改mysql的sock文件路径
vi etc/my.cnf # 或者 /etc/my.cnf.d/mysql-server.cnf
将sock路径变更为/var/lib/mysql/mysql.sock
socket = /tmp/mysql.sock
重启MySql服务。
Centos机器上
systemctl restart mysqld.service
在这里我用的是软链接的方式,因为我不想修改这些默认的配置,毕竟小白一个…
mysql.sock 一般不是在 /tmp/mysql.sock 就是在 /var/lib/mysql/mysql.sock 这里,没有的话就用
ln -s /var/lib/mysql/mysql.sock /tmp/mysql.sock
或者是
ln -s /tmp/mysql.sock /var/lib/mysql/mysql.sock
3. 数据库连接指定sock路径
DATABASES = {'default': {'ENGINE': 'django.db.backends.mysql','NAME': 'xxx','USER': 'root','PASSWORD': 'passwd','OPTIONS': {"unix_socket": "/tmp/mysql.sock",},}
}
这篇关于Django3.0.8生产环境部署nginx、uwsgi、daphne、supervisor、gunicorn、celery的文章就介绍到这儿,希望我们推荐的文章对编程师们有所帮助!







