本文主要是介绍20160716 面向对象,希望对大家解决编程问题提供一定的参考价值,需要的开发者们随着小编来一起学习吧!
/*面向对象:一.程序需求:把大象装进冰箱面向过程:1.打开冰箱;2.把大象塞进去;3.把冰箱门关上. 三个步骤都是自己在完成,注重过程面向对象:1.调用冰箱开门(具体冰箱怎么开门不需要我们关心);2.让大象塞到冰箱里面去(指挥某个对象,有可能是大象自己);3.调用冰箱自己关门.二.程序需求:旅游;拍电影(后期处理);游戏(外挂);飞行器(飞控)面向过程:面向对象:java是一个面向对象的语言,需求,首先我应该考虑是否已有现有对象能帮我完成需求?如果有,调用就可以了;如果没有?自己写,封装对象去完成.特性:1.更符合人类行为思考方式2.将复杂的事情简单化3.将我们变成了程序的指挥者(让专业的人去做专业的事,节能-->高效率,重复代码使用,节约内存开销)*/
//人类
class Person
{String name="li chen";int age=22;public void say(){System.out.println("说话");}public void eat(){System.out.println("吃饭");}public void sleep(){System.out.println("睡觉");}}class Demon1
{public static void main(String[]args){Person p=new Person();System.out.println(p.name); //li chenSystem.out.println(p.age); //22p.sleep(); //睡觉}
}
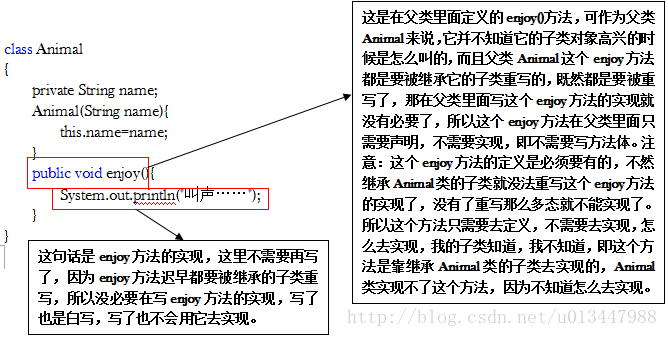
/*开发的过程:其实就是不断的创建对象,使用对象,指挥对象做事情设计的过程:其实就是在管理和维护对象之间的关系面向对象的特征:封装(encapsulation)继承(inheritance)多态(polymorphism)
*//* 第二大点:---
类与对象: class Person 现实中有人类--足球运动员类(赵明剑)特征:场上位置(后卫)/所属俱乐部(山东鲁能泰山俱乐部)/年龄功能:踢球/兔子特征:长耳朵/红眼睛/短尾/三瓣嘴行为功能:草食/跑跳大象特征:大耳朵,长鼻子,粗腿行为功能:叫/攻击/驼人java类是描述现实事物的,特征--属性(用类的属性描述特征)行为功能--方法*/
******************************************************************************<pre name="code" class="java">/*成员变量和局部变量成员变量:定义在类中,在整个类中都可以被访问,随着对象的建立而建立,存于对象所在的堆内存中演示成员变量和局部变量的区别:1.成员变量有初始值;局部变量没有初始化值,而且必须手动初始化.2.成员变量所有方法都能访问,局部变量只限于变量内部访问.局部代码块中的变量只能在局部代码块中使用.3.存储位置:成员变量存储在堆内存中,和对象在一起局部变量存储在栈内存中
*/
class Student
{String name;//成员变量有初始值int age;public void say() //局部变量没有初始化值,而且必须手动初始化. 定义了必然是要用{int num=101; //执行后会消失 //不定义num .Demon2.java:22: 错误: 找不到符号/numSystem.out.println(name+"说我多大了:"+age+"学号是:"+num);}public void sleep(){//System.out.println(num+name);//错误的演示,找不到num变量.int num1=120; //加了{},就是局部代码块,只能在局部代码块中引用System.out.println(num1+name);}
}class Demon2
{public static void main(String[]args){Student s=new Student();System.out.println(s.name);System.out.println(s.age);s.say();s.sleep();}
}*********************************************************************************
<pre name="code" class="java">/*
电脑类特征:type,price,outTime行为功能:开发代码,玩游戏,看国足类在内存中如何对应多个对象对象和对象之间的属性是没有直接关系的
*/
class Computer
{String type;//类型 国产/进口int price; //价格String outTime;//出厂时间public void program(){System.out.println("开发代码");}public void playGame(){System.out.println("LOL");}public void lookChinaFootball(){System.out.println("看国足");}
}
class Demon3
{public static void main(String[]args){//创建电脑对象//对象一Computer c=new Computer();c.type="国产";System.out.println(c.type);//国产(已定义)System.out.println(c.price);//0(int)System.out.println(c.outTime);//null(String)c.program();//开发代码c.playGame();//LOLc.lookChinaFootball();//看国足//对象二Computer c1=new Computer();c1.type="进口";System.out.println(c1.type);}
}
************************************************************************************
<pre name="code" class="java">/*匿名对象,没有名称对象当我们只需要调用某个对象一次时,使用匿名对象来完成匿名对象还可用于参数传递需求:对比两个学生的年龄大小
*///定义学生类
class Student
{String name;int age;public void say(){System.out.println("说话");}
}class Demon4
{public static void main(String[] args) {//创建对象Student s=new Student();System.out.println(s.name);//nullSystem.out.println(s.age);//0s.say();//"说话"//匿名对象 如何调用对象?new Student().say();//说话//比较两个学生对象的年龄大小Student s1=new Student();s1.name="任航";s1.age=23;Student s2=new Student();s2.name="李学鹏";s2.age=22;boolean isSize=studentAgeEque(s1,s2);System.out.println(isSize);//匿名对象做参数传递 知道能这么去用就可以(目前)boolean isSize1=studentAgeEque(new Student(),new Student());//0 不大于 0,falseSystem.out.println(isSize1);//练习:使用美女老师类Teacher t1=new Teacher();t1.age=18;t1.tall=163;System.out.println("*************");Teacher t2=new Teacher();t2.age=20;t2.tall=165;System.out.println("*************");boolean isYoung=teacherAgeYoung(t1,t2);System.out.println(isYoung);System.out.println("*************");boolean isyoung1=teacherAgeYoung(new Teacher(18,163),new Teacher(20,165));System.out.println("*************");System.out.println(isYoung);}//(s1,s2) s1.age>s2.age;public static boolean studentAgeEque(Student s1,Student s2){return s1.age>s2.age;}//Teacherpublic static boolean teacherAgeYoung(Teacher t1,Teacher t2){return t1.age>t2.age;}}//定义美女老师类
class Teacher{Teacher(){System.out.println("临时");}Teacher(int aa,int bb){age=aa;tall=bb;System.out.println("暂时");}int age;int tall;}***************************************************************************
<pre name="code" class="java">/*封装:保证数据安全性,代码的复用性,提高开发效率.保证数据安全:1.属性 不能随便让外面的类访问 public private 默认 保护的2.向外提供一个公共的方法区设置age属性.3.向外提供一个访问该属性的公共方法.
*/
class Student
{String name;private int age;//私有化了 //1.属性 不能随便让外面的类访问 public private 默认 保护的public void setAge(int num)//2.向外提供一个公共的方法区设置age属性.{if(num>=0&&num<=200){age=num;}else{System.out.println("非法年龄,你是外星那个人吗?");}}public int getAge()//3.向外提供一个访问该属性的公共方法.{return age;}public void say()//方法区{System.out.println(name+"说其的年龄是:"+age);}public void setName(String nam){name=nam;}public String getName(){return name;}
}class Demon5
{public static void main(String[] args) {Student s1=new Student();s1.name="邓肯";//s1.age=39;//0--200 如何保证学生年龄的数字不是非法的(不符合现实逻辑)System.out.println(s1.name);//System.out.println(s1.age);//Demon5.java:40: 错误: age可以在Student中访问privates1.setAge(-1); //设置属性System.out.println(s1.getAge()); //访问属性s1.setName("加内特");System.out.println(s1.getName());s1.say();//邓肯说其的年龄是:18}
}
***********************************************************************************
/*
构造函数:
格式;权限修饰符(public 默认 保护的 private(私有的))
<span style="white-space:pre"> </span>
<span style="white-space:pre"> </span> 类名称(){构造函数体}
<span style="white-space:pre"> </span> 1.每个类中都会有一个默认的空参数构造函数Airplane(){},一旦我们自己写了空参数构造函数,就是重写的这个函数. 复写!!!
2.只要我们写出一个或多个构造函数,默认的空参数构造函数就没有了,如果我们需要保留空参数创建对象方式,那么我们必须手动写一个空参数的函数
<span style="white-space:pre"> </span>构造方法与普通方法有什么不同?
<span style="white-space:pre"> </span>1.构造方法在new对象的时候就被执行,而且只被执行一次
<span style="white-space:pre"> </span> 普通使用对象.方法() 这种方法去调用 我们手动写代码取调用
2.格式区别
<span style="white-space:pre"> </span>构造函数 没有返回值也不需要void关键字
<span style="white-space:pre"> </span>普通方法 有返回值必须执行返回值类型,如果没有必须使用void关键字描述
<span style="white-space:pre"> </span>3.函数名称
<span style="white-space:pre"> </span>构造函数的函数名称必须与类名保持一致
<span style="white-space:pre"> </span>普通方法名称可以随便取
*/
class Airplane
{
<span style="white-space:pre"> </span>//构造函数
<span style="white-space:pre"> </span>Airplane() //加public也可以
<span style="white-space:pre"> </span>{
System.out.println("构造函数");
<span style="white-space:pre"> </span> }
//调用有參构造函数
Airplane(String aa)
<span style="white-space:pre"> </span> {
<span style="white-space:pre"> </span> name=aa;
<span style="white-space:pre"> </span> System.out.println("调用有參构造函数");
}
Airplane(String aa,int bb)
<span style="white-space:pre"> </span> {
<span style="white-space:pre"> </span> name=aa;
<span style="white-space:pre"> </span> age=bb;
<span style="white-space:pre"> </span> System.out.println("调用多个有参构造函数1");
}
<span style="white-space:pre"> </span>
<span style="white-space:pre"> </span>
<span style="white-space:pre"> </span>String name;
<span style="white-space:pre"> </span>int age;
<span style="white-space:pre"> </span>public void attack()//权限修饰符不写也可以
<span style="white-space:pre"> </span>{
<span style="white-space:pre"> </span>System.out.println("攻击");
<span style="white-space:pre"> </span> }
}
class Demon6
{
<span style="white-space:pre"> </span>public static void main(String[] args)
<span style="white-space:pre"> </span>{
<span style="white-space:pre"> </span>//"说话"
<span style="white-space:pre"> </span>Airplane a=new Airplane();
a.attack();
<span style="white-space:pre"> </span>Airplane a1=new Airplane("p-51");
<span style="white-space:pre"> </span>Airplane a2=new Airplane("p-38",6);
<span style="white-space:pre"> </span>System.out.println(a2.name);
<span style="white-space:pre"> </span>System.out.println(a2.age);
<span style="white-space:pre"> </span>}
}
**********************************************************************************<pre name="code" class="java">/*this关键字(指当前对象)总结:1.当局部代码块要引用变量:a.局部代码块中去找有没有这个变量b.去类中找全局变量,如果全局变量没有找到--报错2.当局部变量和全局变量名称有一致的情况下,使用this关键字取描述哪个变量是全局的new Tank().name="J-9";全局变量||this.name ="J-9";*/class Tank
{Tank(String name,int weigh){this.name=name;//name=name 局部变量赋给局部变量,无用this.weigh=weigh;}String name;//全局变量int weigh;public void attack(){System.out.println(name+"坦克重:"+weigh+"吨");}
}
class Demon7
{public static void main(String[] args) {Tank t1=new Tank("J-9",21);Tank t2=new Tank("虎式",60);t1.attack();t2.attack();}
}
************************************************************************
<pre name="code" class="java">/*
使用好的方法来实现两个学生对象年龄对比*/
class Student
{Student(String name,int age){this.name=name;this.age=age;}String name;int age;public void say(){System.out.println(name+"告诉我们他多大了"+age);}//对比其他学生对象的年龄public boolean studentAgeEque(Student s){ return this.age>age;}
}class Demon8
{public static void main(String[] args) {//直接比较两个学生对象年龄,使用对象匿名方式boolean isSize=studentAgeEque(new Student("大鹏",35),new Student("杨颖",30));System.out.println(isSize);//boolean isSize1=new Student("Uzi",19).studentAgeEque(new Student("Acorn",26));//System.out.println(this.age);//Demon8.java:39: 错误: 无法从静态上下文中引用非静态 变量 thisSystem.out.println(isSize1);}//比对两个学生的年龄大小public static boolean studentAgeEque(Student s1,Student s2){return s1.age>s2.age;}
}
***********************************************************************
<pre name="code" class="java">/*使用代码描述人类特征:name,age,肤色行为:说话,睡觉,吃饭
*/
class Person
{String name;//名字int age; //年龄String skin;//肤色public void saying() //说话{System.out.println("说话");}public void sleep() //睡觉{System.out.println("睡觉");}public void eat() //吃饭{System.out.println("吃饭");}
}class PersonDemon1
{public static void main(String[] args) {Person p=new Person(); //新建一个Person(类 人)System.out.println(p.name);System.out.println(p.age);System.out.println(p.skin);p.saying();p.sleep();p.eat();System.out.println("************");Clothes c=new Clothes(); //新建一件Clothes(类 衣服)System.out.println(c.color);System.out.println(c.size);System.out.println(c.price);c.dress();}
}class Clothes //类 衣服
{String color="yellow"; //颜色char size='M'; //尺寸int price=49;public void dress() //功能{System.out.println("着衣"); }
}
这篇关于20160716 面向对象的文章就介绍到这儿,希望我们推荐的文章对编程师们有所帮助!