本文主要是介绍Codeforces Round #442 (Div. 2) ABCDE,希望对大家解决编程问题提供一定的参考价值,需要的开发者们随着小编来一起学习吧!
升紫了,开心~
水题。
然而还WA了一发
#include <cstdio>
#include <iostream>
#include <string.h>
#include <string>
#include <map>
#include <queue>
#include <deque>
#include <vector>
#include <set>
#include <algorithm>
#include <math.h>
#include <cmath>
#include <stack>
#include <iomanip>
#define mem0(a) memset(a,0,sizeof(a))
#define meminf(a) memset(a,0x3f,sizeof(a))
using namespace std;
typedef long long ll;
typedef long double ld;
typedef double db;
const int maxn=100005,inf=0x3f3f3f3f;
const ll llinf=0x3f3f3f3f3f3f3f3f;
const ld pi=acos(-1.0L);
string s[15];int main() {int n,k;s[1]="Danil";s[2]="Olya";s[3]="Slava";s[4]="Ann";s[5]="Nikita";string t;cin >> t;int sum=0;for (int i=1;i<=5;i++) {string a=t;k=0;int l=t.length();for (int j=0;j+s[i].length()-1<l;j++) {if (t.substr(j,s[i].length())==s[i]) k++;}if (k==1) sum++; else if (k>1) sum+=2;}if (sum==1) printf("YES"); else printf("NO");return 0;
}
简单DP
#include <cstdio>
#include <iostream>
#include <string.h>
#include <string>
#include <map>
#include <queue>
#include <deque>
#include <vector>
#include <set>
#include <algorithm>
#include <math.h>
#include <cmath>
#include <stack>
#include <iomanip>
#define mem0(a) memset(a,0,sizeof(a))
#define meminf(a) memset(a,0x3f,sizeof(a))
using namespace std;
typedef long long ll;
typedef long double ld;
typedef double db;
const int maxn=5005,inf=0x3f3f3f3f;
const ll llinf=0x3f3f3f3f3f3f3f3f;
const ld pi=acos(-1.0L);
int dp[maxn][3];
char s[maxn];int main() {scanf("%s",s+1);int i,j,len,ans=0;len=strlen(s+1);mem0(dp);for (i=1;i<=len;i++) {if (s[i]=='a') dp[i][0]=dp[i-1][0]+1; else dp[i][0]=dp[i-1][0];ans=max(ans,dp[i][0]);}for (i=1;i<=len;i++) {if (s[i]=='b') dp[i][1]=max(dp[i-1][1],dp[i-1][0])+1; else dp[i][1]=max(dp[i][0],dp[i-1][1]);ans=max(ans,dp[i][1]);}for (i=1;i<=len;i++) {if (s[i]=='a') dp[i][2]=max(dp[i-1][1],dp[i-1][2])+1; else dp[i][2]=max(dp[i][1],dp[i-1][2]);ans=max(ans,dp[i][2]);}printf("%d\n",ans);return 0;
}Slava plays his favorite game "Peace Lightning". Now he is flying a bomber on a very specific map.
Formally, map is a checkered field of size 1�6�5�6�5n, the cells of which are numbered from 1 to n, in each cell there can be one or several tanks. Slava doesn't know the number of tanks and their positions, because he flies very high, but he can drop a bomb in any cell. All tanks in this cell will be damaged.
If a tank takes damage for the first time, it instantly moves to one of the neighboring cells (a tank in the cell n can only move to the cell n�6�5-�6�51, a tank in the cell 1 can only move to the cell 2). If a tank takes damage for the second time, it's counted as destroyed and never moves again. The tanks move only when they are damaged for the first time, they do not move by themselves.
Help Slava to destroy all tanks using as few bombs as possible.
The first line contains a single integer n (2�6�5≤�6�5n�6�5≤�6�5100�6�5000) — the size of the map.
In the first line print m — the minimum number of bombs Slava needs to destroy all tanks.
In the second line print m integers k1,�6�5k2,�6�5...,�6�5km. The number ki means that the i-th bomb should be dropped at the cell ki.
If there are multiple answers, you can print any of them.
2
3 2 1 2
3
4 2 1 3 2
有一排n个格子,假设每个格子都有很多坦克,每个坦克第一次被击中会走向相邻的格子,第二次会被摧毁。问最少多少次可以在最坏情况下摧毁所有坦克。
有趣的构造题。
先选偶数的格子,再选奇数,再选偶数,即可。
#include <cstdio>
#include <iostream>
#include <string.h>
#include <string>
#include <map>
#include <queue>
#include <deque>
#include <vector>
#include <set>
#include <algorithm>
#include <math.h>
#include <cmath>
#include <stack>
#include <iomanip>
#define mem0(a) memset(a,0,sizeof(a))
#define meminf(a) memset(a,0x3f,sizeof(a))
using namespace std;
typedef long long ll;
typedef long double ld;
typedef double db;
const int maxn=100005,inf=0x3f3f3f3f;
const ll llinf=0x3f3f3f3f3f3f3f3f;
const ld pi=acos(-1.0L);
vector<int> v;int main() {int n,i,m,l,r;scanf("%d",&n);if (n==2) {printf("3\n2 1 2\n");return 0;}for (i=2;i<=n;i+=2) v.push_back(i);for (i=1;i<=n;i+=2) v.push_back(i);for (i=2;i<=n;i+=2) v.push_back(i);m=v.size();printf("%d\n",m);for (i=0;i<m;i++) printf("%d ",v[i]);return 0;
}
Olya loves energy drinks. She loves them so much that her room is full of empty cans from energy drinks.
Formally, her room can be represented as a field of n × m cells, each cell of which is empty or littered with cans.
Olya drank a lot of energy drink, so now she can run k meters per second. Each second she chooses one of the four directions (up, down, left or right) and runs from 1 to k meters in this direction. Of course, she can only run through empty cells.
Now Olya needs to get from cell (x1, y1) to cell (x2, y2). How many seconds will it take her if she moves optimally?
It's guaranteed that cells (x1, y1) and (x2, y2) are empty. These cells can coincide.
The first line contains three integers n, m and k (1 ≤ n, m, k ≤ 1000) — the sizes of the room and Olya's speed.
Then n lines follow containing m characters each, the i-th of them contains on j-th position "#", if the cell (i, j) is littered with cans, and "." otherwise.
The last line contains four integers x1, y1, x2, y2 (1 ≤ x1, x2 ≤ n, 1 ≤ y1, y2 ≤ m) — the coordinates of the first and the last cells.
Print a single integer — the minimum time it will take Olya to get from (x1, y1) to (x2, y2).
If it's impossible to get from (x1, y1) to (x2, y2), print -1.
3 4 4 .... ###. .... 1 1 3 1
3
3 4 1 .... ###. .... 1 1 3 1
8
2 2 1 .# #. 1 1 2 2
-1
In the first sample Olya should run 3 meters to the right in the first second, 2 meters down in the second second and 3 meters to the left in the third second.
In second sample Olya should run to the right for 3 seconds, then down for 2 seconds and then to the left for 3 seconds.
Olya does not recommend drinking energy drinks and generally believes that this is bad.
一个n*m矩阵,每步可以朝上下左右走1-k格,问起点到终点最少走多少步。
简单bfs一下,加一个剪枝(每个格子仅入队一次)即可。
#include <cstdio>
#include <iostream>
#include <string.h>
#include <string>
#include <map>
#include <queue>
#include <deque>
#include <vector>
#include <set>
#include <algorithm>
#include <math.h>
#include <cmath>
#include <stack>
#include <iomanip>
#define mem0(a) memset(a,0,sizeof(a))
#define meminf(a) memset(a,0x3f,sizeof(a))
using namespace std;
typedef long long ll;
typedef long double ld;
typedef double db;
const int maxn=1005,inf=0x3f3f3f3f;
const ll llinf=0x3f3f3f3f3f3f3f3f;
const ld pi=acos(-1.0L);
int dp[maxn][maxn];
char s[maxn][maxn];
bool inque[maxn][maxn];
int n,m;struct node{int x,y,k;node(int x,int y,int k): x(x),y(y),k(k) {}
};bool judge(int x,int y) {return x>0&&x<=n&&y>0&&y<=m;
}int main() {int k,i,j,sx,sy,tx,ty;scanf("%d%d%d",&n,&m,&k);for (i=1;i<=n;i++) {scanf("%s",s[i]+1); }scanf("%d%d%d%d",&sx,&sy,&tx,&ty);if (sx==tx&&sy==ty) {printf("0");return 0;}mem0(inque);queue<node> q;meminf(dp);dp[sx][sy]=0;if (s[sx][sy]!='#') q.push(node(sx,sy,0));int ans=-1,flag=0;while (!q.empty()) {node now=q.front();q.pop();
// cout << now.x << ' ' << now.y << ' ' << now.k << endl; for (i=1;i<=k;i++) {if (!judge(now.x+i,now.y)) break;if (dp[now.x+i][now.y]<now.k+1||s[now.x+i][now.y]=='#') break;if (now.x+i==tx&&now.y==ty) {ans=now.k+1;flag=1;break;} else if (!inque[now.x+i][now.y]) {inque[now.x+i][now.y]=1;q.push(node(now.x+i,now.y,now.k+1)),dp[now.x+i][now.y]=now.k+1;}}if (flag) break;for (i=1;i<=k;i++) {if (!judge(now.x-i,now.y)) break;if (dp[now.x-i][now.y]<now.k+1||s[now.x-i][now.y]=='#') break;if (now.x-i==tx&&now.y==ty) {ans=now.k+1;flag=1;break;} else if (!inque[now.x-i][now.y]) {inque[now.x-i][now.y]=1;q.push(node(now.x-i,now.y,now.k+1)),dp[now.x-i][now.y]=now.k+1;}}if (flag) break;for (i=1;i<=k;i++) {if (!judge(now.x,now.y+i)) break;if (dp[now.x][now.y+i]<now.k+1||s[now.x][now.y+i]=='#') break;if (now.x==tx&&now.y+i==ty) {ans=now.k+1;flag=1;break;} else if (!inque[now.x][now.y+i]) {inque[now.x][now.y+i]=1;q.push(node(now.x,now.y+i,now.k+1)),dp[now.x][now.y+i]=now.k+1;}}if (flag) break;for (i=1;i<=k;i++) {if (!judge(now.x,now.y-i)) break;if (dp[now.x][now.y-i]<now.k+1||s[now.x][now.y-i]=='#') break;if (now.x==tx&&now.y-i==ty) {ans=now.k+1;flag=1;break;} else if (!inque[now.x][now.y-i]) {inque[now.x][now.y-i]=1;q.push(node(now.x,now.y-i,now.k+1)),dp[now.x][now.y-i]=now.k+1;}}if (flag) break;}printf("%d\n",ans);return 0;
}
/*
5 5 3
..#..
.....
.....
.....
.....
3 3 1 2
*/Danil decided to earn some money, so he had found a part-time job. The interview have went well, so now he is a light switcher.
Danil works in a rooted tree (undirected connected acyclic graph) with n vertices, vertex 1 is the root of the tree. There is a room in each vertex, light can be switched on or off in each room. Danil's duties include switching light in all rooms of the subtree of the vertex. It means that if light is switched on in some room of the subtree, he should switch it off. Otherwise, he should switch it on.
Unfortunately (or fortunately), Danil is very lazy. He knows that his boss is not going to personally check the work. Instead, he will send Danil tasks using Workforces personal messages.
There are two types of tasks:
- pow v describes a task to switch lights in the subtree of vertex v.
- get v describes a task to count the number of rooms in the subtree of v, in which the light is turned on. Danil should send the answer to his boss using Workforces messages.
A subtree of vertex v is a set of vertices for which the shortest path from them to the root passes through v. In particular, the vertex v is in the subtree of v.
Danil is not going to perform his duties. He asks you to write a program, which answers the boss instead of him.
The first line contains a single integer n (1 ≤ n ≤ 200 000) — the number of vertices in the tree.
The second line contains n - 1 space-separated integers p2, p3, ..., pn (1 ≤ pi < i), where pi is the ancestor of vertex i.
The third line contains n space-separated integers t1, t2, ..., tn (0 ≤ ti ≤ 1), where ti is 1, if the light is turned on in vertex i and 0 otherwise.
The fourth line contains a single integer q (1 ≤ q ≤ 200 000) — the number of tasks.
The next q lines are get v or pow v (1 ≤ v ≤ n) — the tasks described above.
For each task get v print the number of rooms in the subtree of v, in which the light is turned on.
4 1 1 1 1 0 0 1 9 get 1 get 2 get 3 get 4 pow 1 get 1 get 2 get 3 get 4
2 0 0 1 2 1 1 0
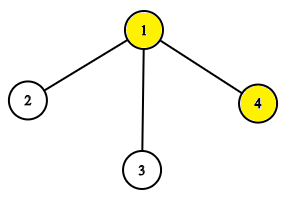 The tree before the task pow 1.
The tree before the task pow 1. 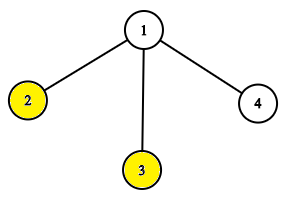 The tree after the task pow 1.
The tree after the task pow 1.
一棵树,每个点的点权是0或1.现在要求完成两种操作:对某节点及其子树取反、查询某节点及其子树权值和。
dfs序+线段树模板题,靠着线段树模板20分钟打完,终于上紫了。
#include <cstdio>
#include <iostream>
#include <string.h>
#include <string>
#include <map>
#include <queue>
#include <deque>
#include <vector>
#include <set>
#include <algorithm>
#include <math.h>
#include <cmath>
#include <stack>
#include <iomanip>
#define mem0(a) memset(a,0,sizeof(a))
#define meminf(a) memset(a,0x3f,sizeof(a))
using namespace std;
typedef long long ll;
typedef long double ld;
typedef double db;
const int maxn=200005,inf=0x3f3f3f3f;
const ll llinf=0x3f3f3f3f3f3f3f3f;
const ld pi=acos(-1.0L);
int head[maxn],in[maxn],out[maxn],a[maxn],s[maxn];
bool visit[maxn];
int num,dfn;struct Edge {int from, to, pre;
};
Edge edge[maxn * 2];void addedge(int from, int to) {edge[num] = (Edge){from, to, head[from]};head[from] = num++;
}struct Tree {int lc,rc,l,r,sum,tag;
};
Tree tree[4*maxn];void build(int now,int l,int r) {tree[now].l=l;tree[now].r=r;tree[now].sum=tree[now].tag=0;if (l!=r) {num++;tree[now].lc=num;build(num,l,(l+r)/2);num++;tree[now].rc=num;build(num,(l+r)/2+1,r);tree[now].sum=tree[tree[now].lc].sum+tree[tree[now].rc].sum;} else tree[now].sum=s[tree[now].l];
// cout << now << ' ' << tree[now].l << ' ' << tree[now].r << endl;
}void pushdown(int now) {if (tree[now].tag==0) return;int l=tree[now].lc,r=tree[now].rc;tree[l].tag^=tree[now].tag;tree[r].tag^=tree[now].tag;tree[l].sum=tree[l].r-tree[l].l+1-tree[l].sum;tree[r].sum=tree[r].r-tree[r].l+1-tree[r].sum;tree[now].tag=0;
}void update (int now,int l,int r) {if (tree[now].l>=l&&tree[now].r<=r) {tree[now].tag^=1;tree[now].sum=tree[now].r-tree[now].l+1-tree[now].sum;} else {pushdown(now);if (l<=(tree[now].l+tree[now].r)/2) update(tree[now].lc,l,r);if (r>(tree[now].l+tree[now].r)/2)update(tree[now].rc,l,r);tree[now].sum=tree[tree[now].lc].sum+tree[tree[now].rc].sum;}
}int findsum(int now,int l,int r) {
// cout << now << ' ' << tree[now].l << ' ' << tree[now].r << ' ' << tree[now].tag << endl;if (tree[now].l>=l&&tree[now].r<=r) {return tree[now].sum;} else {pushdown(now);int f=0;if (l<=(tree[now].l+tree[now].r)/2) f=findsum(tree[now].lc,l,r);if (r>(tree[now].l+tree[now].r)/2)f+=findsum(tree[now].rc,l,r);return f;}
}void dfs(int now) {s[++dfn]=a[now];in[now]=dfn;for (int i=head[now];i!=-1;i=edge[i].pre) { int to=edge[i].to; if (!visit[to]) { dfs(to);} } out[now]=dfn;
}int main() {int n,i,x,j,m;char t[15];num=dfn=0;memset(head,-1,sizeof(head));scanf("%d",&n);for (i=2;i<=n;i++) {scanf("%d",&x);addedge(x,i);}for (i=1;i<=n;i++) {scanf("%d",&a[i]);}dfs(1);num=1;build(1,1,n);scanf("%d",&m);for (i=1;i<=m;i++) {scanf("%s",t);if (t[0]=='g') {scanf("%d",&x);int ans=findsum(1,in[x],out[x]);printf("%d\n",ans);} else {scanf("%d",&x);update(1,in[x],out[x]);}}return 0;
}F等秦皇岛站比赛之后补
CF的题目变水了。。。还不如自己找以前的Div 1比赛来打
这篇关于Codeforces Round #442 (Div. 2) ABCDE的文章就介绍到这儿,希望我们推荐的文章对编程师们有所帮助!





