本文主要是介绍福建农林大学 html +css + JavaScript 期末复习 -- 保姆级,希望对大家解决编程问题提供一定的参考价值,需要的开发者们随着小编来一起学习吧!
html +css + JavaScript 期末复习(保姆级复盘)
考试题型
1、选择题 20题 30分
2、判断题 15题 15分
3、程序题 3 题 30分
4、综合题 2 题 25分
1、网页第一代文本标签(直接上代码,看保姆级注解)
<!-- doctype: document type -->
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head><!-- meta标签是元数据标签,告诉浏览器要做的任务 --><meta charset="UTF-8"><meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="IE=edge"><meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0"><title>Document</title>
</head>
<body><!-- h:heading 标题 --><h1>1.福建农林大学</h1><h2>1.1福建农林大学</h2><h3>1.1.1福建农林大学</h3><h4>1.1.1.1福建农林大学</h4><h5>1.1.1.1.1福建农林大学</h5><h6>1.1.1.1.1.1福建农林大学</h6><!-- horizontal ruler --><!-- 单标签 --><hr><p>meta标签是元数据标签,告诉浏览器要做的任务meta标签是元数据标签,告诉浏览器要做的任务meta标签是元数据标签</p><p>meta标签是元数据标签,告诉浏览器要做的任务meta标签是元数据标签,告诉浏览器要做的任务meta标签是元数据标签,告诉浏览器要做的任务</p><p>meta标签是元数据标签,告诉浏览器要做的任务meta标签是元数据标签,告诉浏览器要做的任务meta标签是元数据标签,告诉浏览器要做的任务</p><hr><!-- ul:unordered list 无序列表, li:list item 列表项--><!-- emmet语法 --><ul type="square"><li>星期一<ol> <!--ol:有序列表 li:列表项--><li>语文课</li><li>数学课</li><li>英语课</li><li>体育课</li></ol></li><li>星期二</li><li>星期三</li><li>星期四</li></ul><!-- 单属性 --><!--type:指定序号类型,start:开始的序号,reversed:指定成倒叙(默认是升序)--><ol type="1" start="50" reversed> <li>语文课</li><li>数学课</li><li>英语课</li><li>体育课</li></ol><hr><!-- dl:definition list 定义一个列表, dt: definition title 定义一个标题 , dd: definition description 定义一个标题的描述--><dl><dt>计算机</dt><dd>一种能自动计算的设备</dd><dt>javaEE</dt><dd>一种java web解决方案</dd></dl><hr><!-- i:italic 斜体 , b:bold 加粗 ,del:delect,删除, ins:insert下划线--><font size="30" color="red" face="verdana"><i>this</i> <b>is</b> <del>a</del> <ins>flower</ins>!</font><hr><!-- sub:下标, sup:上标 -->H<sub>2</sub>O, a<sup>2</sup>+b<sup>2</sup>=c<sup>2</sup><hr><!-- 表格是多个标签协同工作的结果 tr:table row, th: table header, td:table data--><table border="1" cellspacing="0" cellpadding="5px"><caption align="bottom">学生表</caption><!-- <thead> --><tr> <!--tr:table row :表格行,th:table head :表头--><th>学号</th><th>姓名</th><th>年龄</th></tr><!-- </thead> --><!-- <tbody> --><tr> <!--tr:table row :表格行,td:table data:表格数据--><td>s001</td><td>mary</td><td>12</td></tr><tr><td>s002</td><td>kate</td><td rowspan="2">11</td> <!--行合并--></tr><tr><td>s003</td><td>陈海</td></tr><tr><td>s004</td><!-- line,column --><td colspan="2">信息不详1</td> <!--列合并--></tr><!-- </tbody> --></table><hr><!-- 设置宽度或者高度,另外一侧是自动等比例缩放 --><img src="car.jpg" height="400" alt="这是一张宝马轿车图片"> ,<!--alt:在图片加载不出来的时候用来提示该区域是什么的作用--><!-- br:break and return --><br><br><br><br><br><br><br><br><br><br> <!--br 换行符-->
</body>
</html>实验一中的制作表格代码(亦可回顾https://blog.csdn.net/qq_52495761/article/details/134759245)
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head><meta charset="UTF-8"><meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0"><title>学生信息登记表</title><style>table {border-collapse: collapse;}th, td {border: 1px solid black;padding: 5px;text-align: left;min-width: 80px; /* 设置最小宽度,根据实际需要调整 */}th {text-align: center;}textarea {width: calc(100%);border: 0; /*隐藏 输入框的边框*/padding: 6px;box-sizing: border-box;height: 100%; /* Set the height to 100% to fill the entire cell */resize: vertical;}input[type="text"] {width: calc(100%); /* Adjust the input field width */border: 0;/*隐藏多行输入框的边框*/padding: 6px; /* Adjust the padding for better appearance */box-sizing: border-box; /* Include padding and border in the element's total width and height */}.vertical-text {writing-mode: vertical-rl; /* 设置垂直显示 */text-align: center;}</style>
</head>
<body><h3 style="text-align: center;">2013-2014年度第一学期国土资源学院学生信息登记表</h3><table style="margin: auto;height: 100vh;width: auto;"><tr><th>姓名</th><td><input type="text" name="name"></td><th>性别</th><td><input type="text" name="gender"></td><th>出生年月</th><td><input type="text" name="birthdate" ></td><td rowspan="4" style="width: 180px;"></td></tr><tr><th>年级班</th><td><input type="text" name="grade"></td><th>专业</th><td><input type="text" name="major"></td><th>学号</th><td><input type="text" name="studentId"></td></tr><tr><th>联系方式</th><td><input type="text" name="contact"></td><th>寝室号</th><td><input type="text" name="dormitory"></td><th>政治面貌</th><td><input type="text" name="politicalStatus"></td></tr><tr><th>身份证号</th><td colspan="5"><input type="text" name="idNumber"></td></tr><tr><th>家庭住址</th><td colspan="6"><input type="text" name="homeAddress"></td></tr><tr><th rowspan="2">家长电话</th><td colspan="6"><input type="text" name="parentContact1"></td></tr><tr><td colspan="6"><input type="text" name="parentContact2"></td></tr><tr><th>紧急联系人</th><td><input type="text" name="emergencyContactName"></td><th>联系方式</th><td><input type="text" name="emergencyContactNumber"></td><th>与本人关系</th><td colspan="2"><input type="text" name="emergencyContactRelationship"></td></tr><tr><th class="vertical-text" rowspan="5">上期情况</th><th>获奖情况</th><td colspan="5"><input type="text" name="award"></td></tr><tr><th>任职情况</th><td colspan="5"><input type="text" name="position"></td></tr><tr><th>过级情况</th><td colspan="5"><input type="text" name="promotion"></td></tr><tr><th>考证情况</th><td colspan="5"><input type="text" name="certification"></td></tr><tr><th>实践情况</th><td colspan="5"><input type="text" name="practice"></td></tr><tr><th class="vertical-text">本期目标</th><td colspan="6" rowspan="5"><textarea name="goals"></textarea></td></tr>
</table></body>
</html>
2、表单标签(直接上代码,看注解)
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head><meta charset="UTF-8"><meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="IE=edge"><meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0"><title>Document</title>
</head>
<body><h3>新生登记表</h3><!--action 是定义的是一个当点击submit的时候所需要跳转的页面的路径 method定义的是表单的提交方式 两种提交的方式区别以及各自的优缺点:1. get提交,数据被放在网址后头,也就是url后头提交模式是:url?key1=value1&key2=value2&......&keyn=valuenprocess.html?seccode=AESH1&stuno=s00001&schoolId=03025&stuname=mike&stupwd=123456&gender=m&birth=2023-09-21&favourcolor=%235977f0&photo=chrome_elf.dll&hobby=cm&hobby=rn&hobby=rd&stuorigin=qz&stumemo=good缺点:1)url允许的长度有限,无法提交大数据2)安全性不够3)不适合传英文之外的语言符号优点:成本很低url?id=102. post提交, 系统先预先在内存中构建了一个容器,然后把数据保存到容器中,偷偷发送给服务器,网址上看不见优点:1)可以传大数据,几个GB都没问题2)安全保密性高3)可以传中文缺点:成本高表单提交一般都是使用post打包传送--><form action="process.html" method="post"> <!--这是表单中的一个隐藏输入字段,用于存储对用户不可见的数据。它存储了一个名为 seccode,值为 "AESH1" 的安全码。--><input type="hidden" name="seccode" value="AESH1"> <div><label>学生学号:</label><input type="text" name="stuno" maxlength="6" size="30" placeholder="请输入6位学号"><!--placeholder:在输入字段中显示占位符文本--></div><div><label>学校编码:</label><input type="text" name="schoolId" value="03025" size="10" readonly><!--readonly:只读--></div><div><label>学生姓名:</label><input type="text" name="stuname"></div><div><label>学生密码:</label><input type="password" name="stupwd" maxlength="6" size="10"></div><div><labe>学生性别</label><!-- name设置为一致,形成互斥组 -- 从而实现多个radio是只能选中其中的一个,默认选中通过checked--><input type="radio" name="gender" value="f" checked>女<input type="radio" name="gender" value="m">男<input type="radio" name="gender" value="s">保密</div><div><label>学生生日</label><input type="date" name="birth"></div><div><label>最爱色彩</label><input type="color" name="favourcolor"></div><div><label>学生照片</label><input type="file" name="photo"></div><div><label>学生爱好</label><!-- 同样的名字,hobby,会形成一个数组, 其就是数组的名字 ,默认选中通过checked--><input type="checkbox" name="hobby" value="cm" checked>爬山<input type="checkbox" name="hobby" value="rn">跑步<input type="checkbox" name="hobby" value="rd" checked>阅读<input type="checkbox" name="hobby" value="sw">游泳</div><div><label>学生籍贯</label><select name="stuorigin"><!--下拉选择框,通过selected实现默认选中--><option value="">--请选择--</option><option value="fz">福州</option><option value="xm" selected>厦门</option><option value="qz">泉州</option><option value="np">南平</option></select></div><div><label>学生备注</label><textarea name="stumemo" cols="60" rows="4">请留言</textarea><!--多行输入框--></div><div><input type="submit" value="确认登记"><input type="reset" value="取消"></div></form></body>
</html>
3、why-css(样式表的优势)
<!--使用在标签上进行渲染-->
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head><meta charset="UTF-8"><meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0"><title>Document</title>
</head>
<body><div><font size="16" color="red">福州大学</font></div><div><font size="16" color="red">福建农林大学</font></div>
</body>
</html><!--通过css样式进行渲染-->
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head><meta charset="UTF-8"><meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0"><title>Document</title><link rel="stylesheet" href="style.css">
</head>
<body><div>龙岩学院</div><div>福建工程学院</div>
</body>
</html>
div{color:red;font-size: 16px;
}
上述的两种形式都可以实现对div中方文字进行渲染
使用标签做外观渲染的缺点:
1)一眼看过去,看到的都是做外观的标签,不容易阅读到正文
2)内容和外观相混合,无法做到合理分工
3)渲染成本高,使用标签,要额外占用内存空间。
4)使用标签做外观,网页比较冗长,网络带宽占用大
那么怎么解决这个问题?引入css,在css中单独进行定义样式(装修)
使用css样式的优点:(优缺点的的对比就是为什么需要css的原因)
1.容易阅读正文,内容和显示效果相分离,有利于分工协作
2.提高了渲染速度,减少了标签的数量
3.实现了类似函数的效果,可以一处修改,处处修改。同时可以通过外部样式表的形式,控制多个页面的外观
4. 减少了网页的体积,提高了网站负载,降低了运营成本
5. 样式表渲染效果更好,选项更多
selector 的优先级( id选择器 > 类选择器 > 标签选择器 )
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head><meta charset="UTF-8"><meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0"><title>Document</title><style>div{color:red;font-size: 20px;}/* 类选择器(class selector) 1) 类选择器优先级高于标签选择器,如果有属性设置冲突,则类选择器优先2) 类选择器可以跨标签,无论什么标签,只要设置好class属性即可被选中3) 可以用多个类来同时修饰一个标签, 后定义的类的优先级高于先定义的类id选择器优先级高于类选择器*/.u211{color:blue;background-color: yellow;}.u985{font-size: 30px;color:pink;text-decoration: underline;}#host{font-size: 40px;text-shadow: 3px 3px 3px #666;}</style>
</head>
<body><div class="u211">福州大学</div><div>福建农林大学</div><div>江夏学院</div><!-- 内联样式的优先级比id还高 --><div class="u211 u985" id="host" style="font-size: 50px;">厦门大学</div><div>福建师范大学</div><div class="u211 u985">清华大学</div><span class="u211">高校会议组委会</span>
</body>
</html><!-- 样式的混合运算:font-size: 20px;color:blue;background-color: yellow;-->
4、盒子定位
1、静态定位(默认情况就是静态定位)
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head><meta charset="UTF-8"><meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0"><title>Document</title><style>/*每个网页元素都是盒子,称为盒子模型(box model)盒子在页面中的排列,默认定位是静态定位(static position)*/*{margin: 0px;padding: 0px;}span{/* position: static; */border: 2px solid blue;display: inline-block;width: 100px;height: 30px;text-align: center;/*水平居中*/line-height: 30px;}</style>
</head>
<body><span>星期一</span><span>星期二</span><span>星期三</span><span>星期四</span><span>星期五</span>
</body>
</html>
效果图

2、相对定位(相对定位是根据静态定位的某一个顶点进行偏移,偏移后的位置空着 )
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head><meta charset="UTF-8"><meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0"><title>Document</title><style>*{margin: 0px;padding: 0px;}/* body{padding: 100px;} */span{border: 2px solid blue;display: inline-block;width: 100px;height: 30px;text-align: center;/*水平居中*/line-height: 30px;/*垂直居中*/}/* 相对定位是根据静态定位的某一个顶点进行偏移,偏移后的位置空着 */.myspan{position: relative;/* left: 50px;top: 50px; */right: -50px;bottom: -50px;}</style>
</head>
<body><span>星期一</span><span class="myspan">星期二</span><span>星期三</span><span>星期四</span><span>星期五</span>
</body>
</html>
效果图(偏移解释)

相对于静态的某一点进行相对定位的偏移(原来的位置还在)

3、绝对定位
1、绝对定位-1
<!--效果图1 -->
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head><meta charset="UTF-8"><meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0"><title>Document</title><style>*{margin: 0px;padding: 0px;}span{border: 2px solid blue;display: inline-block;width: 100px;height: 30px;text-align: center;/*水平居中*/line-height: 30px;/*垂直居中*/}/* 绝对于父容器进行偏移,原来位置消失 */.myspan{position: absolute;left: 100px;top: 100px;}/* span的父容器是body 最后一个元素绝对与body进行偏离 */span:last-child{position: absolute;right: 100px;bottom: 100px;}/* 测试时需将myspan关上才能生效,span的父容器是body ,倒数第四个元素绝对与body进行偏离 *//* span:nth-last-child(4){position: absolute;left: 100px;bottom: 100px;} */</style>
</head>
<body><span>星期一</span><span class="myspan">星期二</span><span>星期三</span><span>星期四</span><span>星期五</span>
</body>
</html>
效果图 1
2、绝对定位–2

<!--效果图 2 -- 3 -->
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head><meta charset="UTF-8"><meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0"><title>Document</title><style>*{margin: 0px;padding: 0px;}/* id选择器,选中id=mydiv的元素 */#mydiv{width: 500px;height: 400px;border: 3px solid red;/* 测试这个的有无,即可体现不一样 */position: relative; }/* 绝对定位的元素要寻找最接近的被定位过的祖先(非静态定位)作为定位参照物,如果没有,就以body作为参照物 */#mydiv>span{display: inline-block;width: 100px;height: 30px;text-align: center;line-height: 30px;border: 3px solid blue;position: absolute;right: 50px;bottom: 50px;}</style>
</head>
<body><div id="mydiv"><span>surperstar</span></div>
</body>
</html>
效果图 2(无position) – 3(有position)


3、绝对定位-3
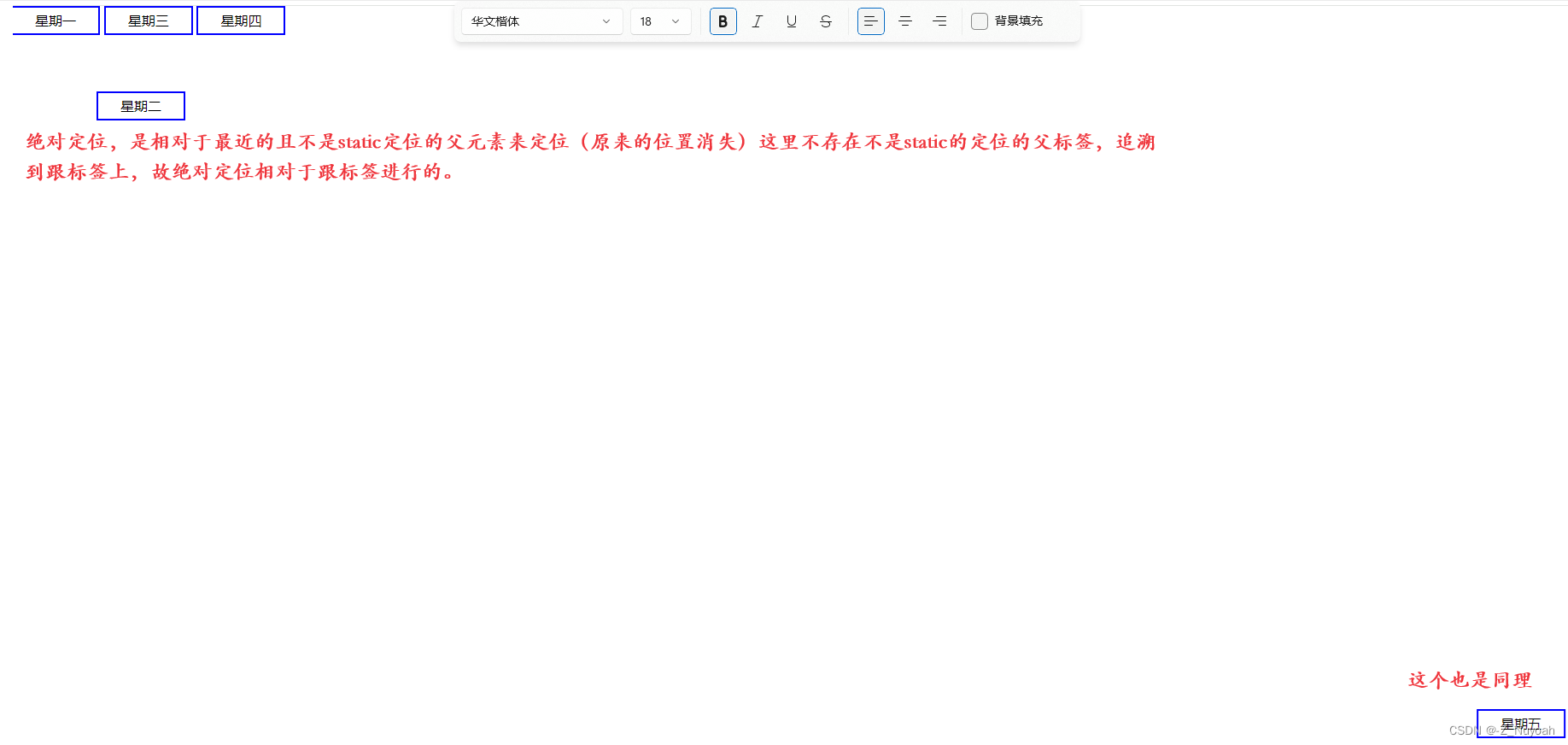
在定位过程中,如果有元素重合,可以使用
z-index进行堆叠顺序,数值大的在上面 。
如果没有设置z-index,发生重合时,后面的定义的在前面的上面。
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head><meta charset="UTF-8"><meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0"><title>Document</title><style>*{margin: 0px;padding: 0px;}#mydiv{width: 300px;height: 300px;background-color: red;position: absolute;left: 150px;top: 150px;z-index: 2;}#mydiv2{width: 300px;height: 300px;background-color: blue;position: absolute;left: 250px;top: 250px;z-index: 1;/* 在定位过程中,如果有元素重合,可以使用z-index进行堆叠顺序,数值大的在上面 */}</style>
</head>
<body><!-- 如果没有设置z-index,发生重合时,后面的定义的在前面的上面 --><div id="mydiv"></div><div id="mydiv2"></div>
</body>
</html>
效果图 4
补充扩展内容(考虑一下绝对和相对的区别)
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
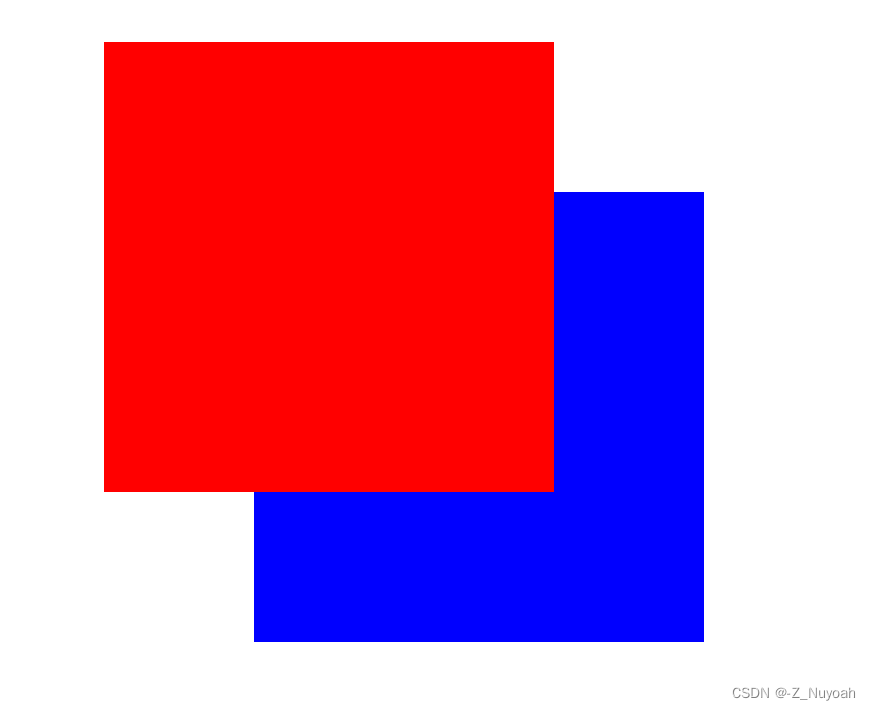
<head><meta charset="UTF-8"><meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0"><title>Document</title><style>.div1{background-color: red;padding: 10px;margin: 5px;color: white;font-weight: bold;}.div2{background-color: green;padding: 10px;margin: 5px;color: white;font-weight: bold;}.div3{background-color: blue;padding: 10px;margin: 5px;color: white;font-weight: bold;}.div4{background-color: greenyellow;padding: 10px;margin: 5px;color: white;font-weight: bold;}</style>
</head>
<body><div class="div1">div1</div><div class="div2">div2</div><div class="div3">div3</div><div class="div4">div4</div>
</body></html>
初始效果图
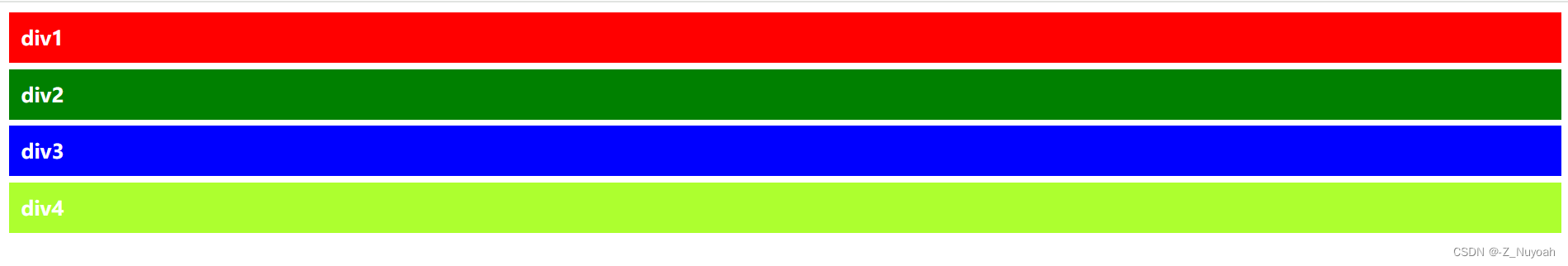
1、给第二个div设置absolute:
<style>.div2{background-color: red;padding: 10px;margin: 5px;color: white;font-weight: bold;/*添加一下部分*/position: absolute;top: 50px;left: 50px;}</style>
效果图一
解释:第二个div设置了absolute,则该div的宽度就由文本决定,
且下面的div会上移占据之前第二个div的位置,top和left是相对于离它最近且不是static定位的父元素来定位的,在此div1因为没有父元素,所以第二个div相对于根元素body来定位。
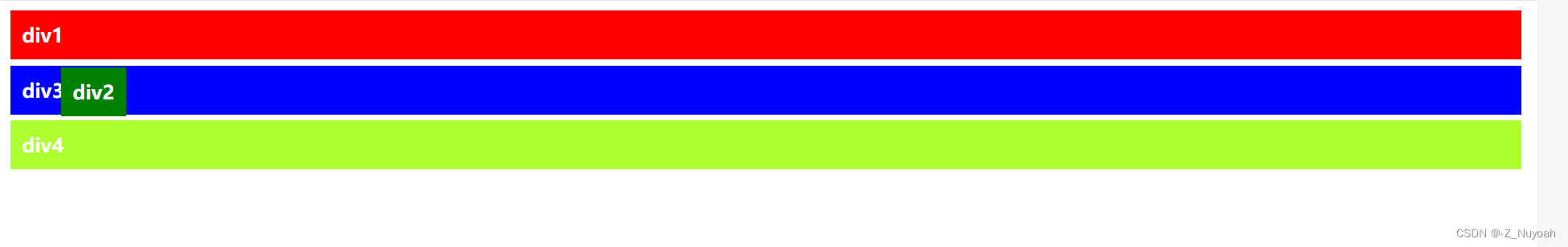
2、将div1的position设置成relative
<style>.div2{background-color: red;padding: 10px;margin: 5px;color: white;font-weight: bold;/*添加一下部分*/position: relative;top: 50px;left: 50px;}</style>
效果图二
偏移解释:设置relative的div
不会影响其他div的位置,且top和left是相对于它原本自身的位置来定位,并且原来的位置还在不会覆盖住。
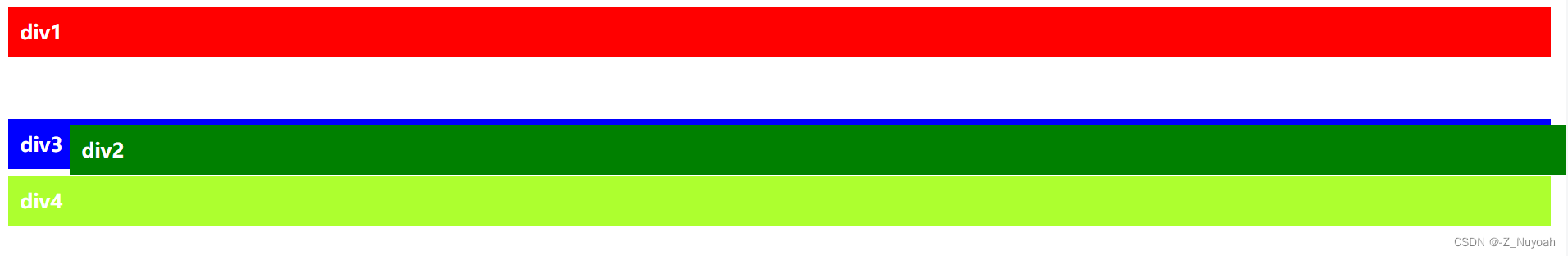
3、给第二个div添加一个父div:
<style>.div2{background-color: red;padding: 10px;margin: 5px;color: white;font-weight: bold;/*添加一下部分*/position: absolute;top: 50px;left: 50px;}.container1{position: absolute;height: 200px;background-color: aqua; }</style><div class="container1">第二个div的父容器<div class="div2">div2</div></div>效果图三
效果图解释:div2的父div设置为absolute,下面的div3,div4会上移,div2也设置为absolute,div2就会相对于父div来定位。
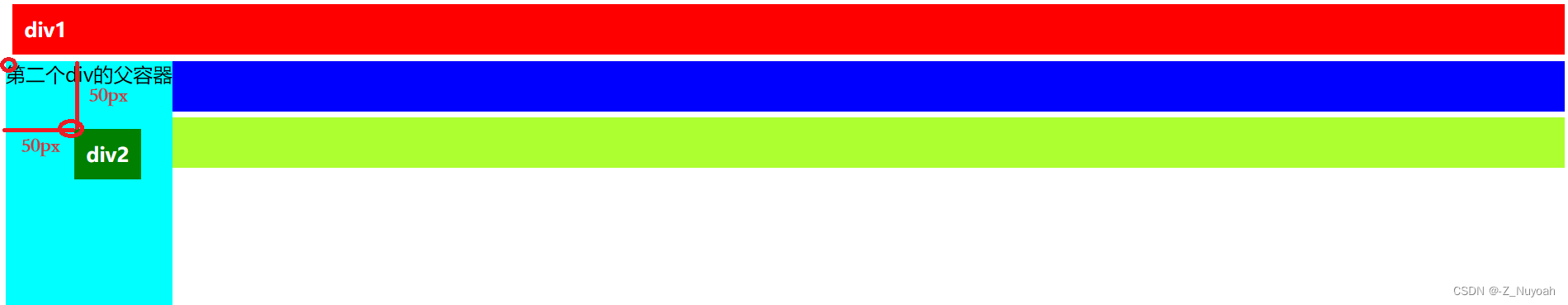
4、若只将第二个div的absolute改为relative
<style>.div2{background-color: red;padding: 10px;margin: 5px;color: white;font-weight: bold;/*添加一下部分*/position: relative;top: 50px;left: 50px;}</style>
效果图四
解释:这是时的定位应是文字下的点作为参照点,进行偏移。
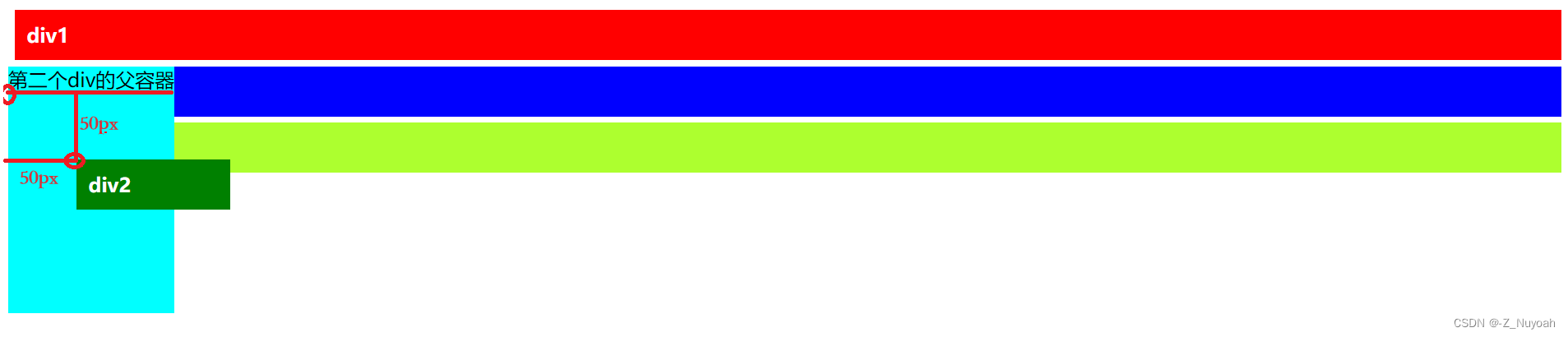
注意:上面两个图的第二个div与父div的上边距是不同的,第一个是相对父div来定位,第二个是相对原来本身的位置来定位。可能此时你会注意到两个图的第二个div的宽度不同,在没有给div设置宽度的情况下,第一个是设为absolute,所以宽度为文本宽度,第二个是relative,所以宽度与父元素宽度相同。
5、若在3,4的基础上只改变div2的宽度,观察absolute 和relative的区别
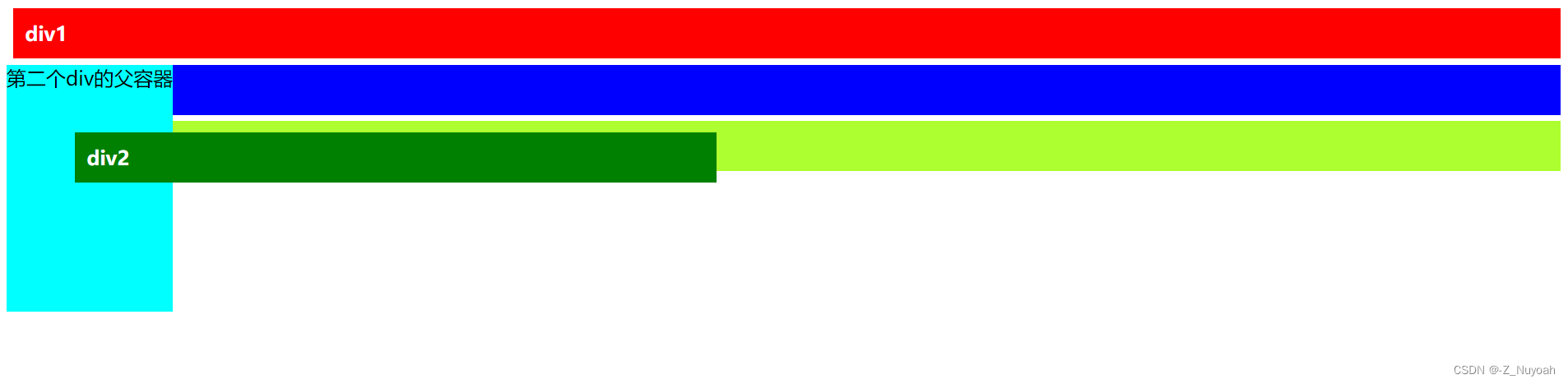
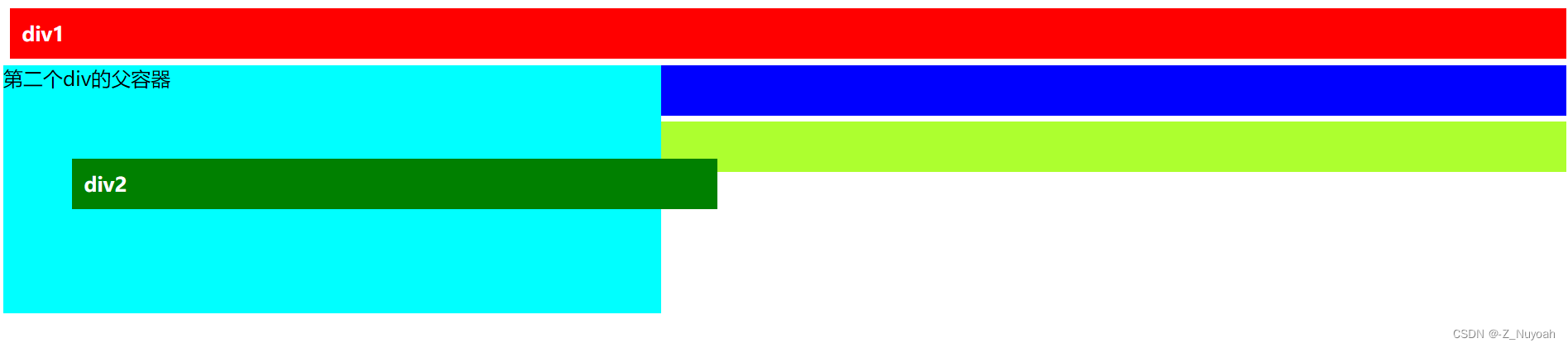
由上图可以知道,absolute定位的子元素宽度不会影响父元素的宽,而relative定位的子元素会撑大父元素。
4、固定定位
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head><meta charset="UTF-8"><meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0"><title>Document</title><style>*{margin: 0px;padding: 0px;}#notice{width: 300px;height: 60px;text-align: center;line-height: 60px;font-size: 16px;font-weight:bold ;font-family: "微软雅黑";border: 3px solid blue;position: fixed;right: 0px;bottom: 0px;}</style>
</head>
<body><div id="notice">你已欠费,请缴费</div><h2>测试</h2><h2>测试</h2><h2>测试</h2><h2>测试</h2><h2>测试</h2><h2>测试</h2><h2>测试</h2><h2>测试</h2><h2>测试</h2><h2>测试</h2><h2>测试</h2><h2>测试</h2><h2>测试</h2><h2>测试</h2><h2>测试</h2><h2>测试</h2><h2>测试</h2><h2>测试</h2><h2>测试</h2><h2>测试</h2><h2>测试</h2><h2>测试</h2><h2>测试</h2><h2>测试</h2><h2>测试</h2><h2>测试</h2><h2>测试</h2><h2>测试</h2><h2>测试</h2><h2>测试</h2><h2>测试</h2><h2>测试</h2><h2>测试</h2><h2>测试</h2><h2>测试</h2><h2>测试</h2><h2>测试</h2><h2>测试</h2><h2>测试</h2><h2>测试</h2><h2>测试</h2><h2>测试</h2><h2>测试</h2><h2>测试</h2><h2>测试</h2><h2>测试</h2><h2>测试</h2><h2>测试</h2><h2>测试</h2><h2>测试</h2><h2>测试</h2><h2>测试</h2><h2>测试</h2><h2>测试</h2><h2>测试</h2><h2>测试</h2><h2>测试</h2><h2>测试</h2><h2>测试</h2><h2>测试</h2><h2>测试</h2><h2>测试</h2><h2>测试</h2><h2>测试</h2><h2>测试</h2><h2>测试</h2><h2>测试</h2><h2>测试</h2><h2>测试</h2><h2>测试</h2><h2>测试</h2><h2>测试</h2><h2>测试</h2><h2>测试</h2><h2>测试</h2><h2>测试</h2><h2>测试</h2><h2>测试</h2><h2>测试</h2><h2>测试</h2><h2>测试</h2><h2>测试</h2><h2>测试</h2><h2>测试</h2><h2>测试</h2><h2>测试</h2><h2>测试</h2><h2>测试</h2><h2>测试</h2><h2>测试</h2><h2>测试</h2><h2>测试</h2><h2>测试</h2><h2>测试</h2><h2>测试</h2><h2>测试</h2><h2>测试</h2><h2>测试</h2><h2>测试</h2><h2>测试</h2>
</body>
</html>
效果图(某个模块钉在某个位置不移动)

5、浮动定位
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head><meta charset="UTF-8"><meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0"><title>Document</title><style>*{margin: 0px;padding: 0px;}/* 网页上的主页选项卡就属于浮动定位 */span{border: 2px solid blue;display: inline-block;width: 300px;height: 30px;text-align: center;/*水平居中*/line-height: 30px;/*垂直居中*/float: left;}</style>
</head>
<body><span>星期一</span><span>星期二</span><!--clear: both; 表示该元素不允许左侧或右侧存在浮动元素。它会导致元素出现在前面的所有浮动元素的下方,而不允许浮动元素出现在该元素的左侧或右侧。--><span style="clear: both;">星期三</span> <span>星期四</span><span>星期五</span>
</body>
</html>
效果图

5、盒子模型
W3C盒子模型由内容(content)、填充(padding)、边框(border)、边界(margin)组成
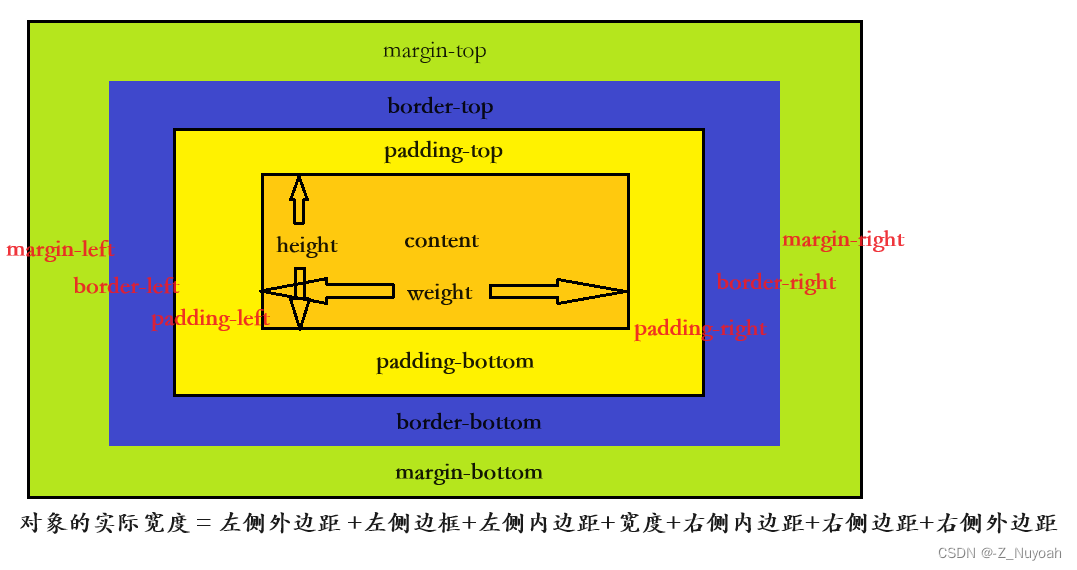
border边框
border属性设置一个元素的边框,它有三个要素:宽、样式、颜色,统称“边框三要素”。
border:宽度 样式 颜色
border: 1px solid red;
border-style设置边框的样式,有五种常用样式可选
1、点状dotted
2、实线solid
3、双线double ( 需要最起码设置为3像素,不然显示不下)
4、虚线dashed
5、无边框none
border的三要素可以统一写在”border”属性中,也可以单独设置。
统一的写法:border: 1px solid red;
单独设置的写法:
// 不写width会有默认3像素的值。
// 不写颜色会默认为黑色。
border-width:;
border-style:; //在style属性为空的情况下,整个边框是不会出现的。
border-color:;
外边距
围绕在元素边框周围的空白区域
会在元素外创建额外的空白区域
外边距是透明的
margin-top/right/bottom/left: value;
// value可取值为像素,%,auto,负值
margin:value(四个方向相同) ;
margin: value(上下) value(左右);
margin: value(上) value(左右) value(下);
margin: value(上) value(右) value(下) value(左);
内边距
内容区域和边框之间的空间
会扩大元素边框所占用的区域
语法:padding:value;
padding-top/right/bottom/left:value;
// value可取值为像素,百分比,但不能为负数padding:value(四个方向相同) ;padding: value(上下) value(左右);padding: value(上) value(左右) value(下);padding: value(上) value(右) value(下) value(左);
怪异盒子模型
盒子模型分两种,一种是符合W3C规范的标准例子模型,另一种是IE的盒子模型,IE的盒子模型也被叫怪异盒子。
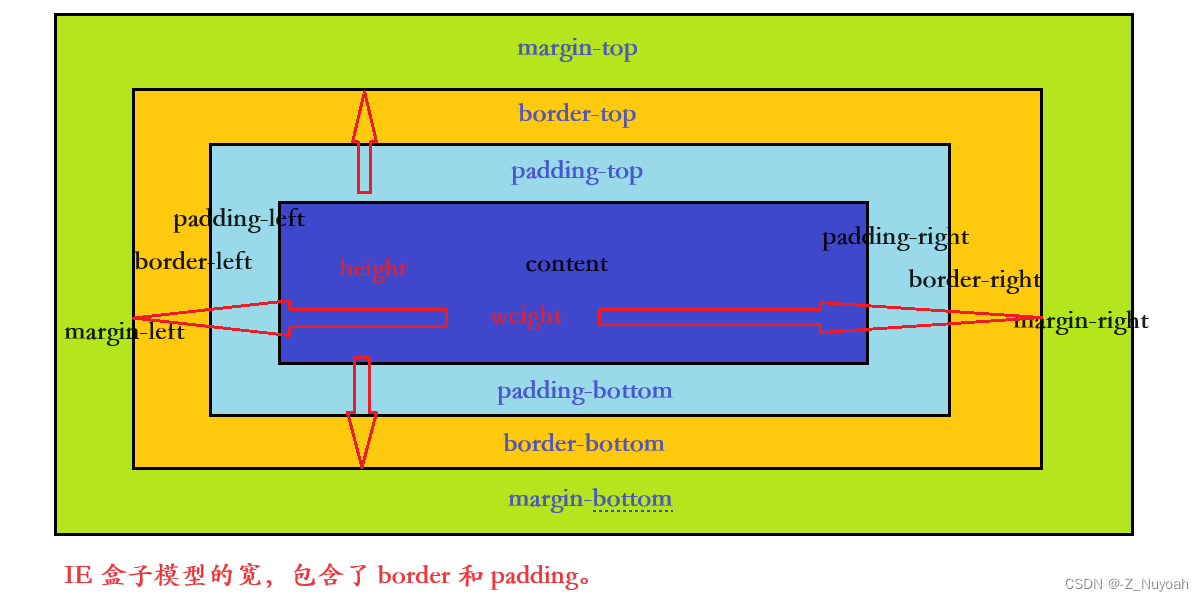
box-sizing – 指定盒子类型
box-sizing属性允许你以“W3C的盒模型”或“IE盒模型”来定义元素,以适应区域。换句话说,当前元素使用哪种盒模型,可以由box-sizing属性来指定
box-sizing 的两个值
1、content-box(标准)
padding和border不被包含在width和height内,元素的实际大小为宽高+border+padding,此为标准模式下的盒模型。
2、border-box(怪异)
padding和border被包含在定义的width和height中,元素实际的大小为你定义了多宽就是多宽。此属性为怪异模式下的盒模型。
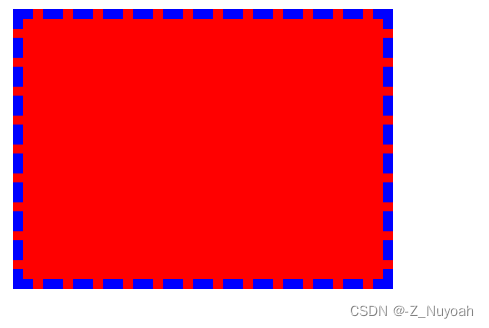
6、背景处理
1、背景颜色绘制区域
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head><meta charset="UTF-8"><meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0"><title>Document</title><style>#mydiv{width: 300px;height: 200px;padding: 30px;margin: 10px;border: 10px dashed blue;background-color: red;/* background-clip: padding-box; 从padding开始绘制颜色*//* background-clip: content-box; 从content开始绘制颜色*/background-clip: border-box; /*从border开始绘制颜色*/}</style>
</head>
<body><div id="mydiv"></div>
</body>
</html>
三种绘制的效果图
border-box
padding-box
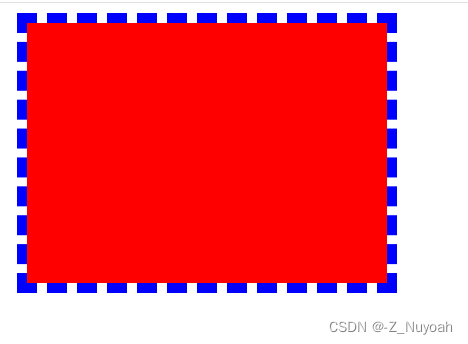
content-box

2、背景图 (背景图和背景颜色同时存在时,背景图在背景颜色上面(背景图优先))
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head><meta charset="UTF-8"><meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0"><title>Document</title><style>#mydiv{width: 600px;height: 590px;padding: 30px;margin: 10px;border: 10px dashed blue;background-color: red;/* background-clip: padding-box; *//* background-clip: content-box; *//* 背景图和背景颜色同时存在时,背景图在背景颜色上面(背景图优先) */background-clip: border-box;background-image: url(./bg125.jpg);/*背景图的设置*/background-size: 35%,45%;/* background-repeat: no-repeat;background-repeat: repeat-x;background-repeat: repeat-y; */background-repeat: repeat;/*图片是否需要重复以及重复的方向*/}</style>
</head>
<body><div id="mydiv"></div>
</body>
</html>
四种background-repeat的效果图
background-repeat: no-repeat 不重复

background-repeat: repeat-x 横向重复
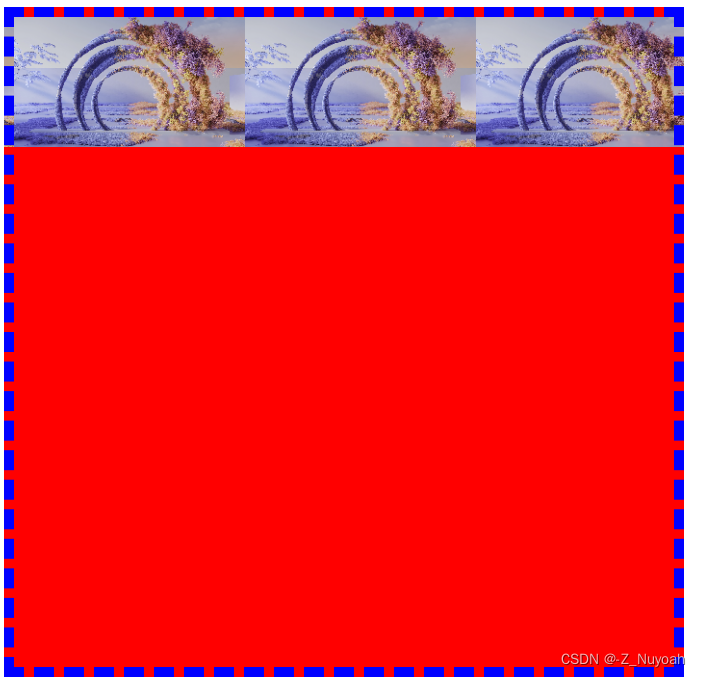
background-repeat: repeat-y 纵向重复
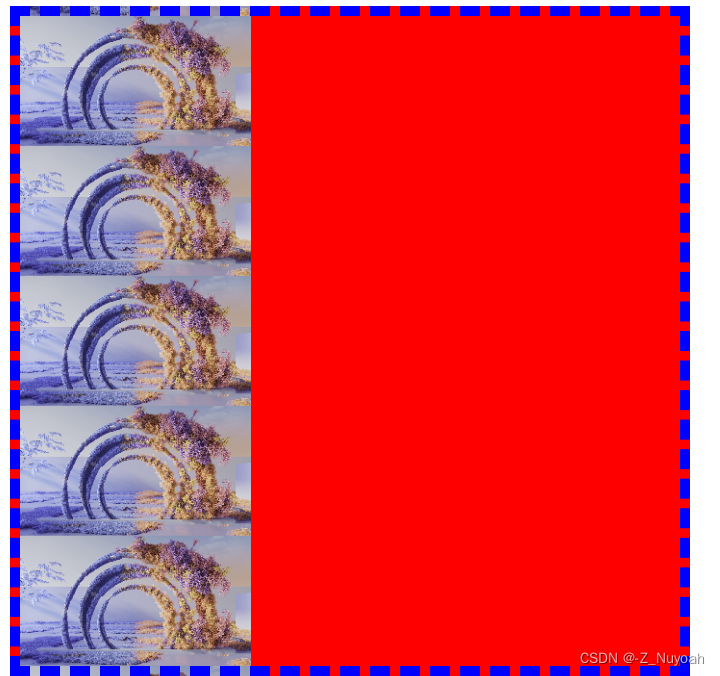
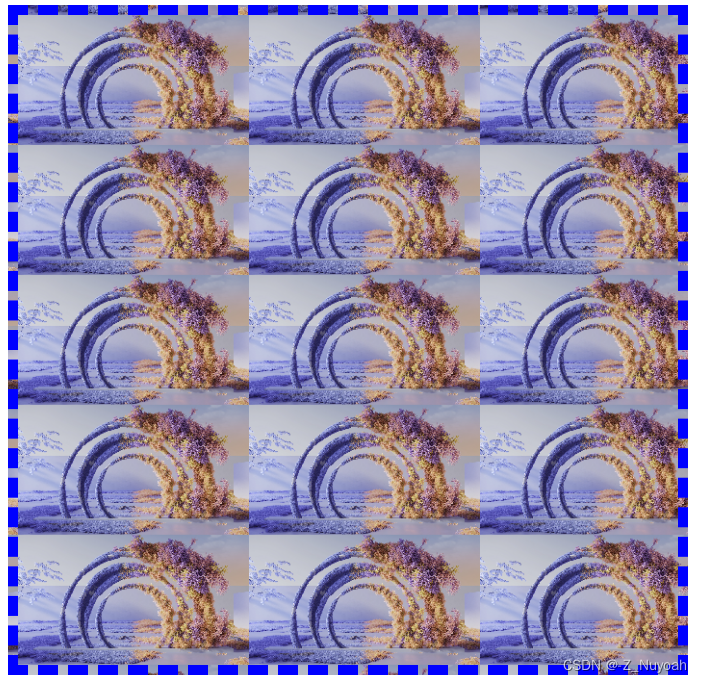
background-repeat: repeat 横纵向都重复

3、背景图的cover和contain
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head><meta charset="UTF-8"><meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0"><title>Document</title><style>#mydiv{width: 600px;height: 590px;padding: 30px;margin: 10px;border: 10px dashed blue;background-color: red;/* background-clip: padding-box; *//* background-clip: content-box; *//* 背景图和背景颜色同时存在时,背景图在背景颜色上面(背景图优先) */background-clip: border-box;background-image: url(./bg125.jpg);background-size: contain; /* 让这张图片全部显示出来,不能切割 *//* background-size: cover;覆盖界面,图片会被切割 */background-repeat: no-repeat;}</style>
</head>
<body><div id="mydiv"></div>
</body>
</html>
两种方式的效果图
background-size: contain; -- 让这张图片全部显示出来,不能切割

background-size: cover; -- 覆盖界面,图片会被切割
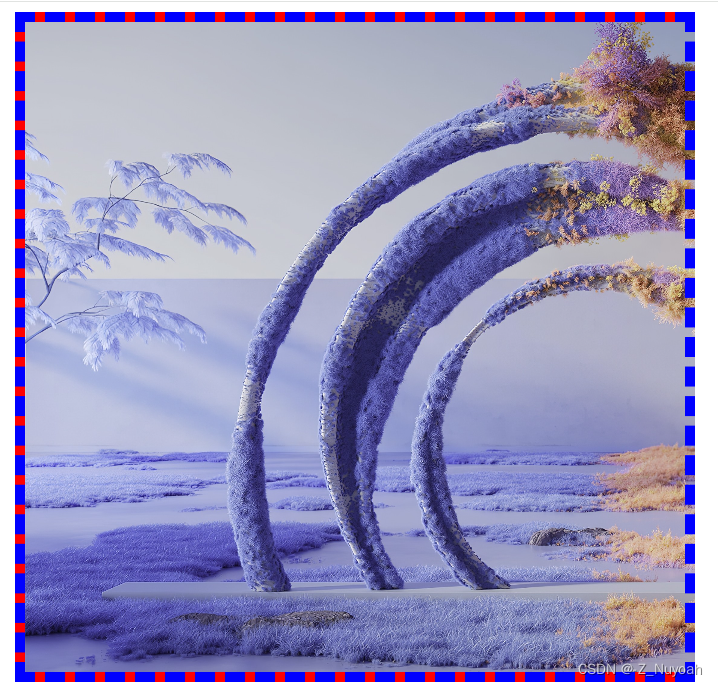

4、背景图position
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head><meta charset="UTF-8"><meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0"><title>Document</title><style>#mydiv{width: 600px;height: 590px;padding: 30px;margin: 10px;border: 10px dashed blue;background-color: red;background-clip: border-box;background-image: url(./bg125.jpg);background-size: 400px,200px;background-position: 50%,50%;/*right,top*/background-repeat: no-repeat;}</style>
</head>
<body><div id="mydiv"></div>
</body>
</html>
效果图

5、背景图 origin – 三种填充
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head><meta charset="UTF-8"><meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0"><title>Document</title><style>#mydiv{width: 600px;height: 590px;padding: 30px;margin: 10px;border: 10px dashed blue;background-image: url(./bg125.jpg);background-size: 400px,200px;background-repeat: no-repeat;background-color: red;/* background-origin: content-box; 从content开始填充*//* background-origin: padding-box; 从padding开始填充*/background-origin: border-box; /*从border开始填充*/}</style>
</head>
<body><div id="mydiv"></div>
</body>
</html>
三种效果图
background-origin: border-box; /*从border开始填充*/

background-origin: padding-box; 从padding开始填充

background-origin: content-box; 从content开始填充

6、背景图 attachment – 黏贴在某个位置
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head><meta charset="UTF-8"><meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0"><title>Document</title><style>#mydiv{background-image: url(./bg125.jpg);background-size: 400px,190px;background-repeat: no-repeat;/* background-attachment: scroll; *//* attachment是设置图片是否钉在某个位置 */background-attachment: fixed;}</style>
</head>
<body><div id="mydiv"><h2>你好</h2><h2>你好</h2><h2>你好</h2><h2>你好</h2><h2>你好</h2><h2>你好</h2><h2>你好</h2><h2>你好</h2><h2>你好</h2><h2>你好</h2><h2>你好</h2><h2>你好</h2><h2>你好</h2><h2>你好</h2><h2>你好</h2><h2>你好</h2><h2>你好</h2><h2>你好</h2><h2>你好</h2><h2>你好</h2><h2>你好</h2><h2>你好</h2><h2>你好</h2><h2>你好</h2><h2>你好</h2><h2>你好</h2><h2>你好</h2><h2>你好</h2><h2>你好</h2><h2>你好</h2><h2>你好</h2><h2>你好</h2><h2>你好</h2><h2>你好</h2><h2>你好</h2><h2>你好</h2><h2>你好</h2><h2>你好</h2><h2>你好</h2><h2>你好</h2><h2>你好</h2><h2>你好</h2><h2>你好</h2><h2>你好</h2><h2>你好</h2><h2>你好</h2><h2>你好</h2><h2>你好</h2><h2>你好</h2><h2>你好</h2><h2>你好</h2><h2>你好</h2><h2>你好</h2><h2>你好</h2><h2>你好</h2><h2>你好</h2><h2>你好</h2><h2>你好</h2><h2>你好</h2><h2>你好</h2><h2>你好</h2><h2>你好</h2><h2>你好</h2><h2>你好</h2><h2>你好</h2><h2>你好</h2><h2>你好</h2><h2>你好</h2><h2>你好</h2><h2>你好</h2><h2>你好</h2><h2>你好</h2><h2>你好</h2><h2>你好</h2><h2>你好</h2><h2>你好</h2><h2>你好</h2><h2>你好</h2><h2>你好</h2><h2>你好</h2><h2>你好</h2><h2>你好</h2><h2>你好</h2><h2>你好</h2><h2>你好</h2><h2>你好</h2><h2>你好</h2><h2>你好</h2><h2>你好</h2><h2>你好</h2><h2>你好</h2><h2>你好</h2><h2>你好</h2><h2>你好</h2><h2>你好</h2><h2>你好</h2><h2>你好</h2><h2>你好</h2><h2>你好</h2><h2>你好</h2></div></body>
</html>
效果

7、两个关键字 initial 和 inherit

1、initial设置默认值

<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<style>
div {color: red;
}
</style>
</head>
<body><h1>使用 JavaScript 设置初始值 initial</h1><div><h1 id="bc">Hello World</h1><ul><li id="a">Item one</li><li id="b">Item two</li><li id="c">Item three</li></ul>
</div><p>单击“试一试”按钮,将第二个列表项的颜色属性值设置为"initial":</p><button onclick="myFunction()">试一试</button><script>
function myFunction() {document.getElementById("b").style.color = "initial";
}
</script><p><b>注意:</b>“initial”关键字在 Internet Explorer 11 及更早版本中不受支持。</p></body>
</html>效果

2、inherit 继承父元素的值

<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<style>
span {color: blue;border:1px solid black;
}
</style>
</head>
<body><h1>使用 JavaScript 设置继承</h1><div>这是<span>一个 span 元素</span> 在一个没有设置颜色属性的元素中。<div style="color:green">这是 <span id="mySpan">一个 span 元素</span> 在一个颜色为 color:green 的元素中。</div><div style="color:red">这是 <span>一个 span 元素</span> 在一个颜色为 color:red 元素中。</div>
</div><p>单击“试一试”按钮,将第二个 SPAN 元素的颜色属性值设置为继承"inherit":</p>
<button onclick="myFunction()">试一试</button><script>
function myFunction() {document.getElementById("mySpan").style.color = "inherit";
}
</script></body>
</html>
效果

7、css原型信封 – 应用以上知识实战
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head><meta charset="UTF-8"><meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="IE=edge"><meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0"><title>Document</title><style>body,div,span{margin: 0px;padding: 0px;box-sizing: border-box;font-family: "微软雅黑";}#letter{width: 800px;height: 380px;border:5px solid blue;margin: 140px auto;box-shadow: 10px 10px 5px #666;;position: relative;}#recevier-postcode{position: absolute;left: 5px;top: 5px;/* border:1px solid red; */}#sender-postcode{position: absolute;right: 5px;bottom: 5px;/* border:1px solid red; */}#recevier-postcode>span,#sender-postcode>span{display: inline-block;width: 45px;height: 42px;margin-left: 5px;border:3px solid black;text-align: center;line-height: 42px;font-size: 26px;}#address{position: absolute;left: 20px;top: 120px;width: 95%;}#address>span{display: block;/*分行的一种办法,将span设置成一个块,独占一行*/border-bottom:3px solid black;margin-top: 15px;padding-bottom: 5px;font-size:30px;font-weight: bold;}#address>span:first-child{padding-left: 50px;}#address>span:nth-child(2){text-align: right;padding-right: 50px;}#stamp{width: 100px;height: 120px;display: inline-block;/* border:1px solid red; */position: absolute;right: 5px;top: 5px;background-image: url(./stamp.jpg);background-size: contain;background-repeat: no-repeat;}</style>
</head>
<body><div id="letter"><div id="recevier-postcode"><span>3</span><span>5</span><span>0</span><span>0</span><span>0</span><span>9</span></div><div id="sender-postcode"><span>3</span><span>5</span><span>0</span><span>0</span><span>0</span><span>1</span></div><div id="address"><span>福建农林大学金山学院计算机系</span><span>王海涛(收)</span></div><span id="stamp"></span></div>
</body>
</html>
效果图

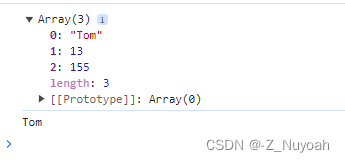
8、JavaScript - array(base and method)
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head><meta charset="UTF-8"><meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0"><title>Document</title><script>var arr1 = new Array(100,200,"福州",true);var info = new Array(new Array('Tom', 13, 155),new Array('Lucy', 11, 152));console.log(info[0]); // 输出结果:(3) ["Tom", 13, 155]console.log(info[0][0]); // 输出结果:Tom</script>
</head>
<body></body>
</html>
效果图
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
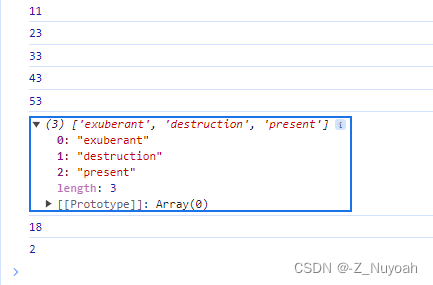
<head><meta charset="UTF-8"><meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0"><title>Document</title><script>var arr=[11,20,30,40,50];var arr1 = ['spray', 'elite', 'exuberant', 'destruction', 'present'];function work(a){console.log(a);}// arr.forEach(work);// arr.forEach(function(a){// console.log(a);// });arr.forEach(function(val,idx){ // foreachif(val%2==0)arr[idx]+=3;console.log(arr[idx]);})var arr1_change = arr1.filter((word)=>word.length>6); // fitterconsole.log(arr1_change);var ages = [3, 10, 18, 20];function checkAdult(age) {return age >= 18;}console.log(ages.find(checkAdult));console.log(ages.findIndex(checkAdult));</script>
</head>
<body></body>
</html>
效果图
9、函数 function (arguments 、callback)
1、function的基本实现
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
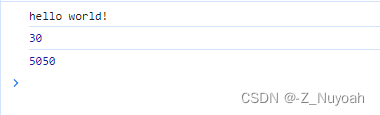
<head><meta charset="UTF-8"><meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0"><title>Document</title><script>function sayHello(){console.log("hello world!");}sayHello();function add(a,b){console.log(a+b);}add(10,20);function calcSum(a,b){let sum = 0;for(let i=a;i<=b;i++)sum += i;return sum;}console.log(calcSum(1,100));function work(a,b){console.log(a,b);}</script>
</head>
<body></body>
</html>
效果图
2、arguments 的传递
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
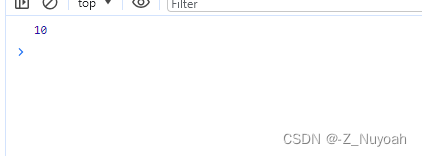
<head><meta charset="UTF-8"><meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0"><title>Document</title><script>function add(){//arguments是一个类似数组的对象,注意,其不是数组,但是支持数组的一些操作模式console.log(arguments.length);for(let i=0;i<arguments.length;i++)console.log(arguments[i]);}// add();// add(1);// add(1,2,3);function add2(a,b){ //实现多参数(大于两个参数的时候也能适用)的之和// a->arguments[0]// b->arguments[1]// 所谓形式参数,其实就是arguments对象成员的一种快捷访问方式let sum = a+b;if(arguments.length>2)for(let i=2;i<arguments.length;i++)sum += arguments[i];return sum;}console.log(add2(1,2,3,4));</script>
</head>
<body></body>
</html>
效果图
3、callback的实现
被作为实参传入另一函数,并在该外部函数内被调用,用以来完成某些任务的函数,称为回调函数。
调用过程:函数a的参数为函数b,当函数a执行完之后再去执行b
打个比方:
你去上学,妈妈送你去上学并叮嘱你要记得将缴费单交给老师。
此时,函数a为妈妈送你上学,函数b为你将缴费单交给老师。也就是你要做完函数a,才会去执行函数b。
问题:那么问题来了,为什么不直接把整个事情在函数a中写好,而是要通过一个参数进行回调呢?
答:如果你直接写进去,function a(){…;b();},那就直接写死了,
失去了变量的灵活性。当你要传入别的函数时,需要重新写一遍函数a。
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
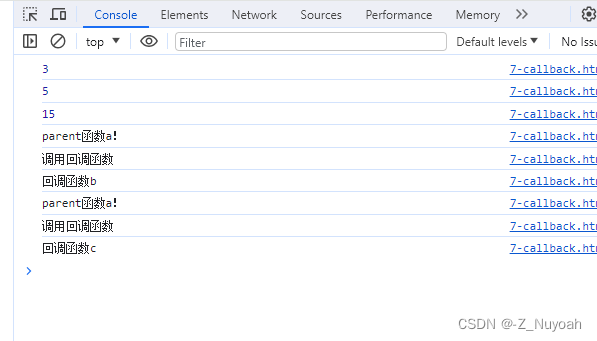
<head><meta charset="UTF-8"><meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0"><title>Document</title><script>//回调函数 callbackfunction calc(num1,num2,calcMethod){console.log(calcMethod(num1,num2));}function add(a,b){return a+b;}function sub(a,b){return a-b;}function multiply(a,b){return a*b;}calc(1,2,add);calc(10,5,sub);calc(3,5,multiply);function a(callback) { console.log("parent函数a!"); console.log("调用回调函数"); callback(); // 调用回调函数}function b(){ console.log("回调函数b"); } function c() { console.log("回调函数c"); } function test(){ a(b); a(c); }test();</script>
</head>
<body></body>
</html>
效果图
10、简单编程题
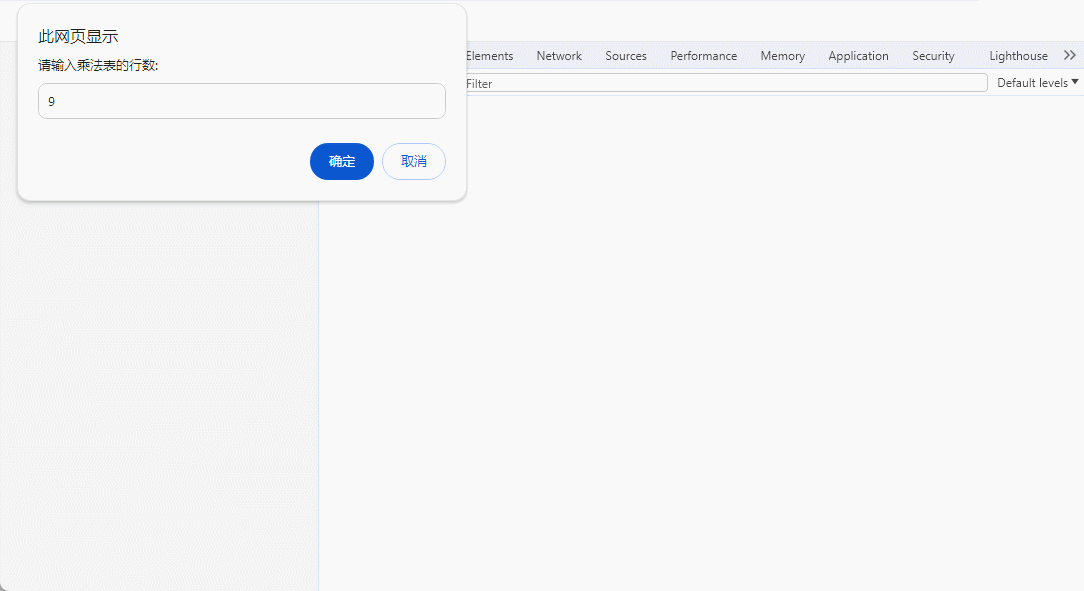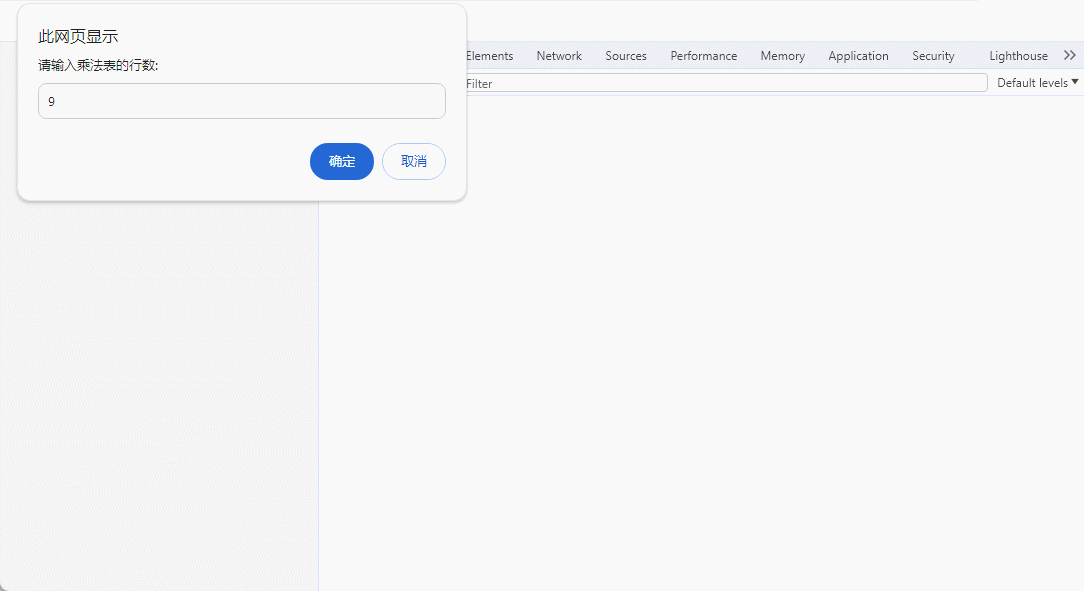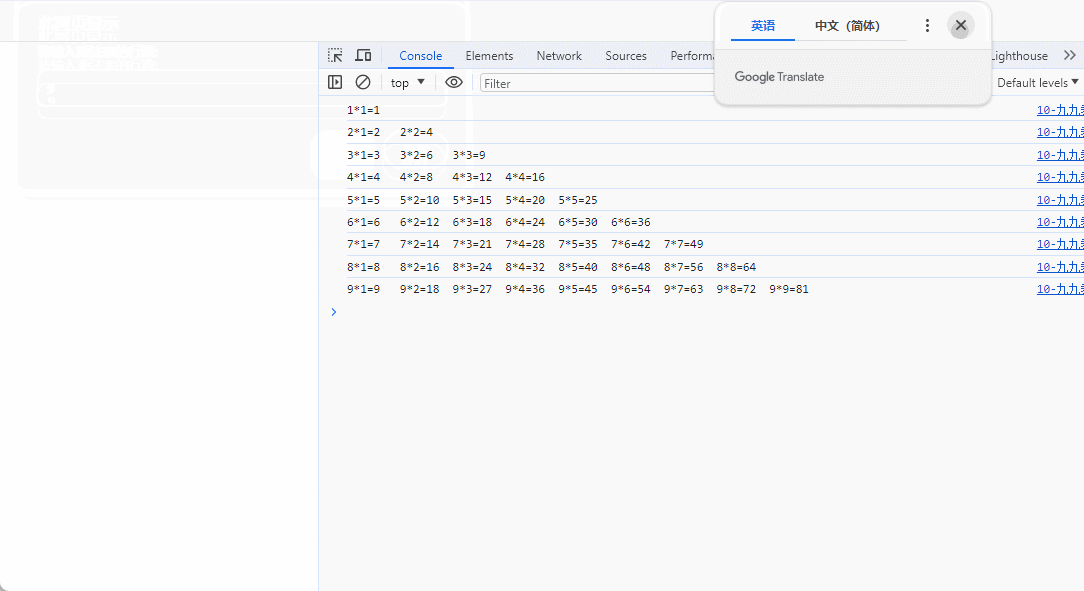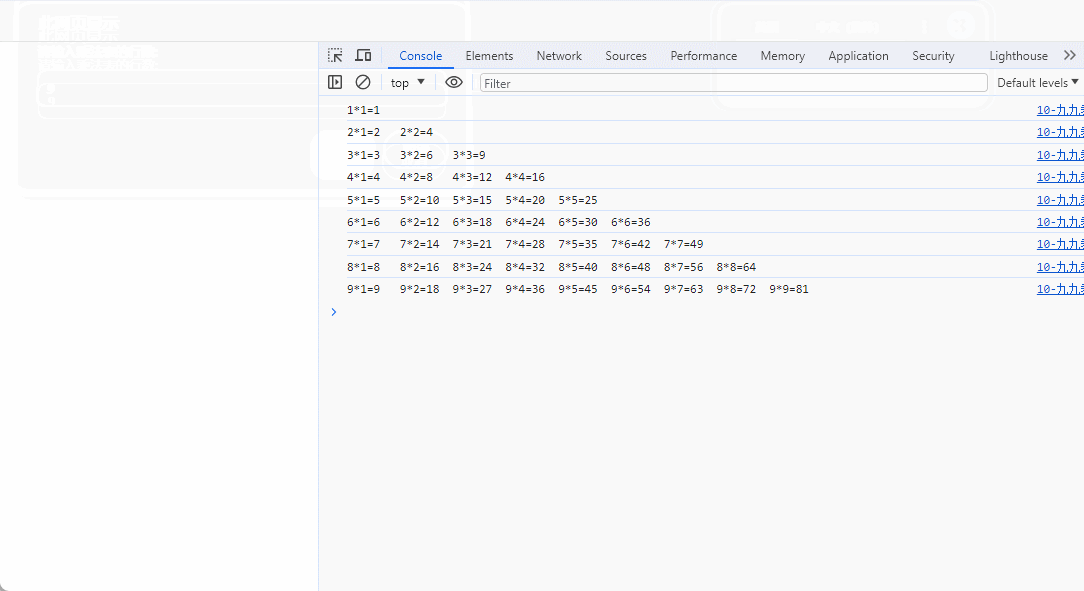
1、九九乘法表
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head><meta charset="UTF-8"><meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0"><title>Document</title><script>// n*n的乘法表// n的数量手动录入,范围1-9, 如果输入9, 就是九九乘法表/*1*1=12*1=2 2*2=43*1=3 3*2=6 3*3=9*/var lines = parseInt(prompt("请输入乘法表的行数:","9"));var lineContent;for(let i=1;i<=lines;i++){ //行的循环lineContent="";for(let j=1;j<=i;j++) //列的循环lineContent += `${i}*${j}=${i*j}\t`;console.log(lineContent);}</script>
</head>
<body>
</body>
</html>
**效果图 **
2、求某范围数字和
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
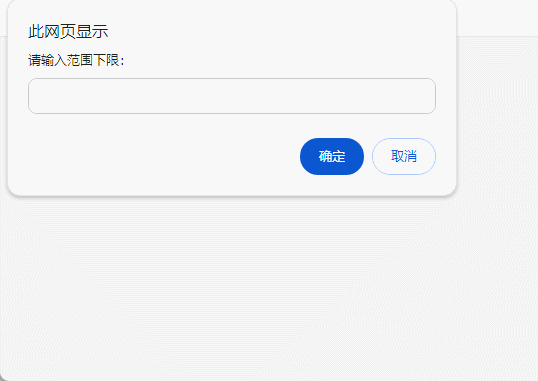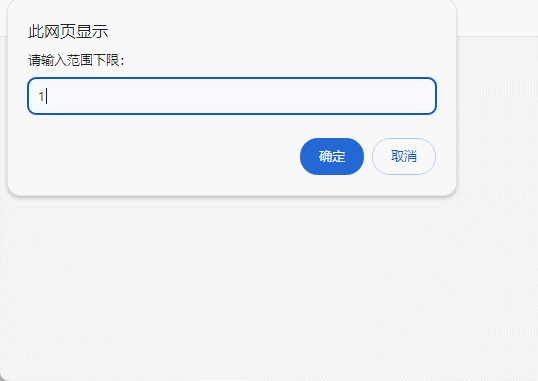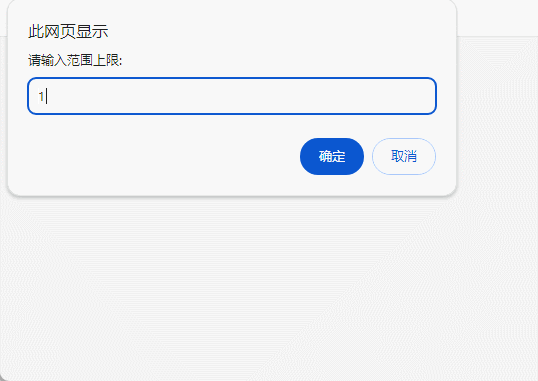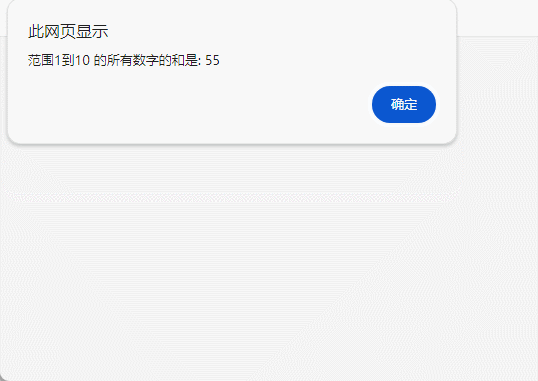
<head><meta charset="UTF-8"><meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0"><title>Document</title><script>//获取用户输入的范围下限var lowerLimit = prompt("请输入范围下限:")// 获取用户输入的范围上限var upperLimit = prompt("请输入范围上限:");// 将用户输入的字符串转换为数字lowerLimit = parseInt(lowerLimit);upperLimit = parseInt(upperLimit);// 检查输入是否为有效数字if (!isNaN(upperLimit)&&!isNaN(lowerLimit)) {// 初始化和的变量var sum = 0;// 计算范围内所有数字的和for (var i = lowerLimit; i <= upperLimit; i++) {sum += i;}// 输出结果alert("范围"+lowerLimit+"到" + upperLimit + " 的所有数字的和是: " + sum);} else {// 用户输入无效,弹出提示alert("请输入有效的数字。");}</script>
</head>
<body></body>
</html>
效果图
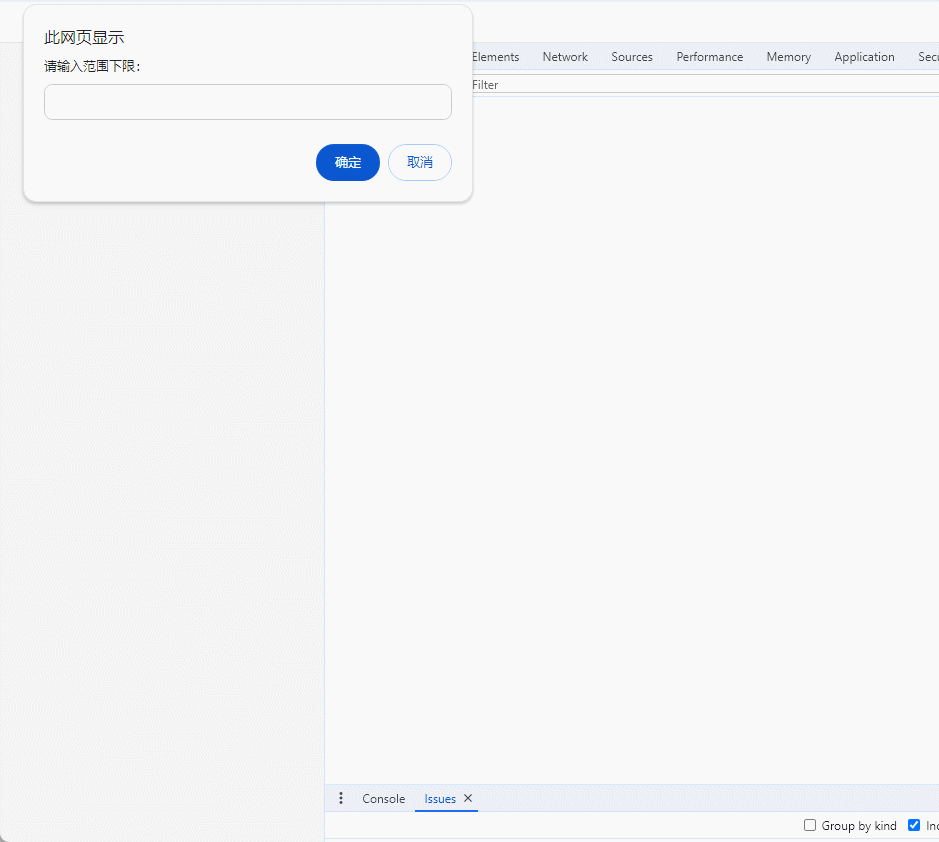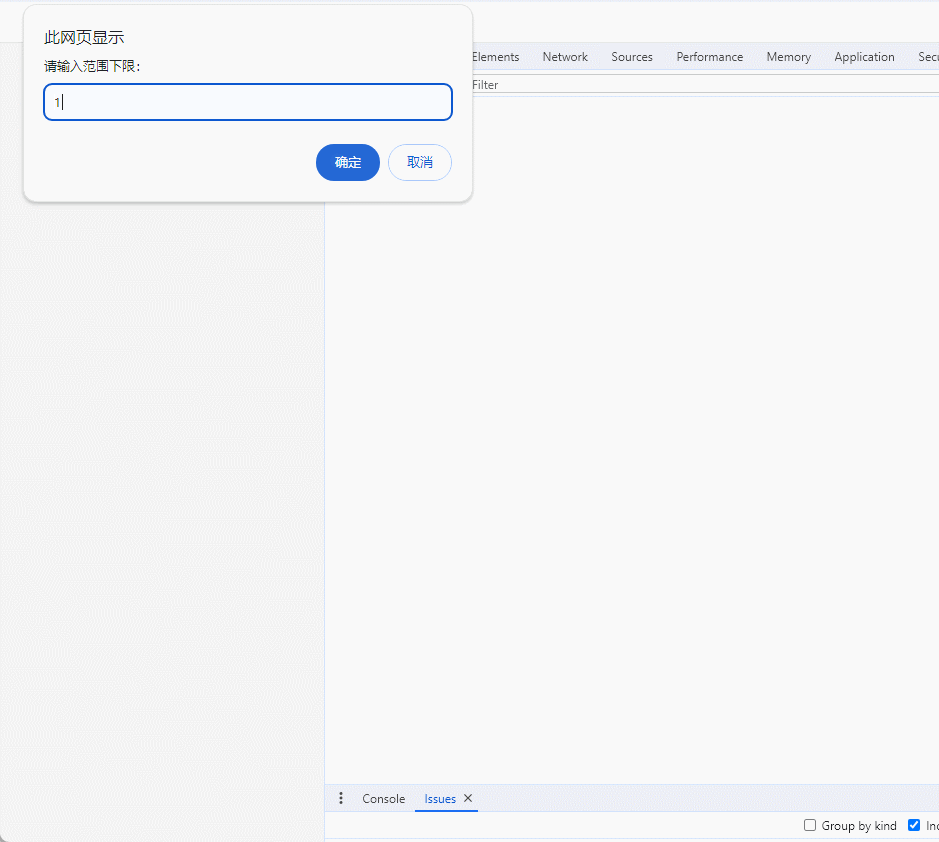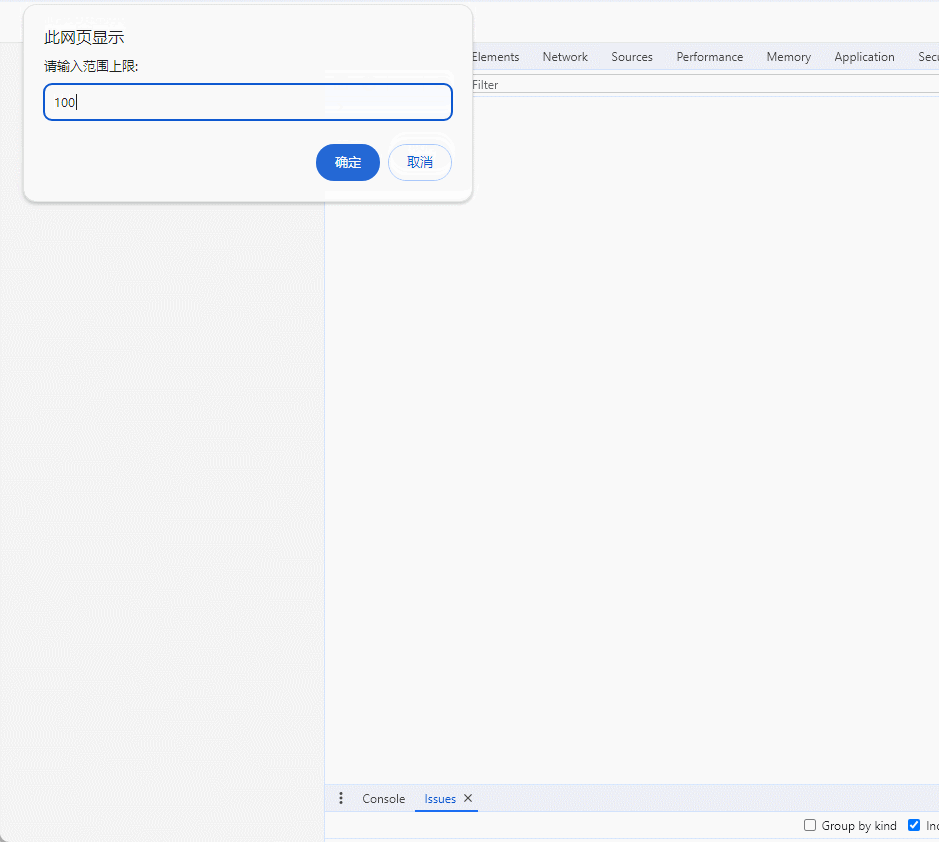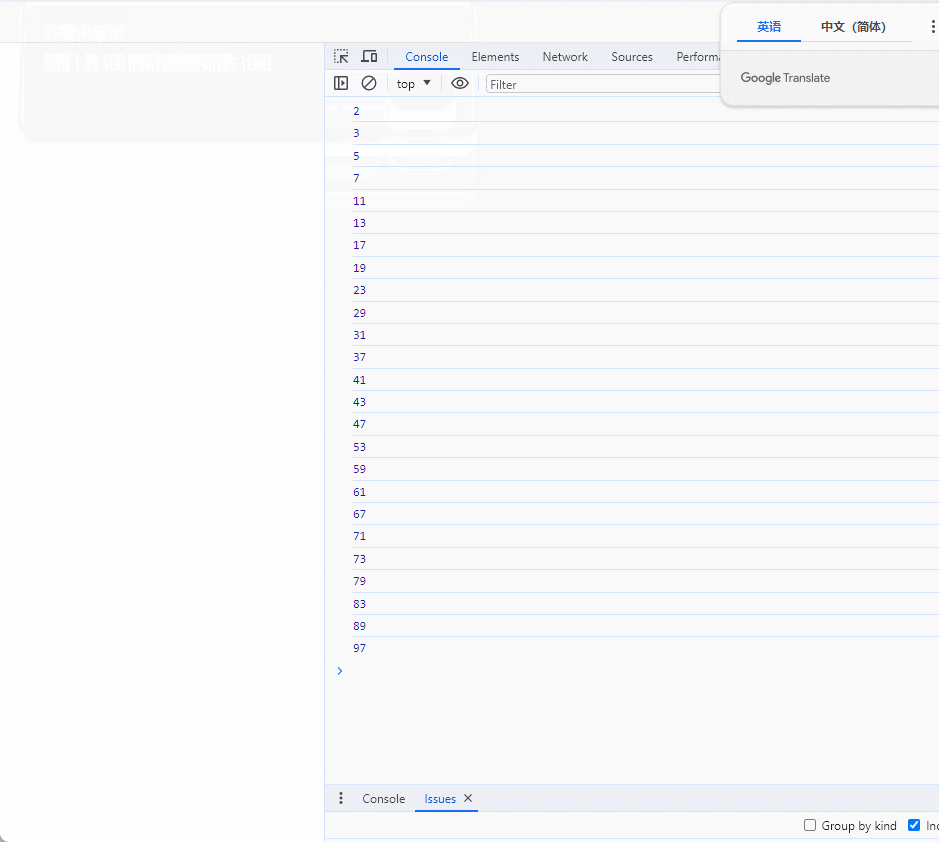
3、求某范围质数和
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head><meta charset="UTF-8"><meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0"><title>计算质数和</title><script>function isPrime(num) {if (num < 2) {return false;}for (var i = 2; i <= Math.sqrt(num); i++) {if (num % i === 0) {return false;}}return true;}// 获取用户输入的范围下限var lowerLimit = prompt("请输入范围下限:");// 获取用户输入的范围上限var upperLimit = prompt("请输入范围上限:");// 将用户输入的字符串转换为数字lowerLimit = parseInt(lowerLimit);upperLimit = parseInt(upperLimit);// 检查输入是否为有效数字if (!isNaN(upperLimit) && !isNaN(lowerLimit)) {// 初始化和的变量var sumOfPrimes = 0;// 计算范围内所有质数的和for (var i = lowerLimit; i <= upperLimit; i++) {if (isPrime(i)) {console.log(i);sumOfPrimes += i;}}// 输出结果alert("范围 " + lowerLimit + " 到 " + upperLimit + " 的所有质数的和是: " + sumOfPrimes);} else {// 用户输入无效,弹出提示alert("请输入有效的数字。");}</script>
</head>
<body>
</body>
</html>效果图
11、DOM
1、dom的基本概念
DOM:文档对象模型,是W3C组织推荐的处理可扩展标记语言的标准
编程接口。
2、获取元素
1、根据id获取元素
1|document.getElementById('id')
<!DOCTYPE html>
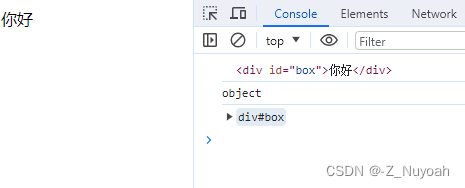
<html><head><meta charset="UTF-8"><title>Document</title></head><body><div id="box">你好</div><script>var Obox = document.getElementById('box');console.log(Obox); // 结果为:<div id="box">你好</div>console.log(typeof Obox); // 结果为:objectconsole.dir(Obox); // 结果为:div#box</script></body>
</html>
效果图
2、根据标签获取元素
1|document.getElementsByTagName("TagName")
<!DOCTYPE html>
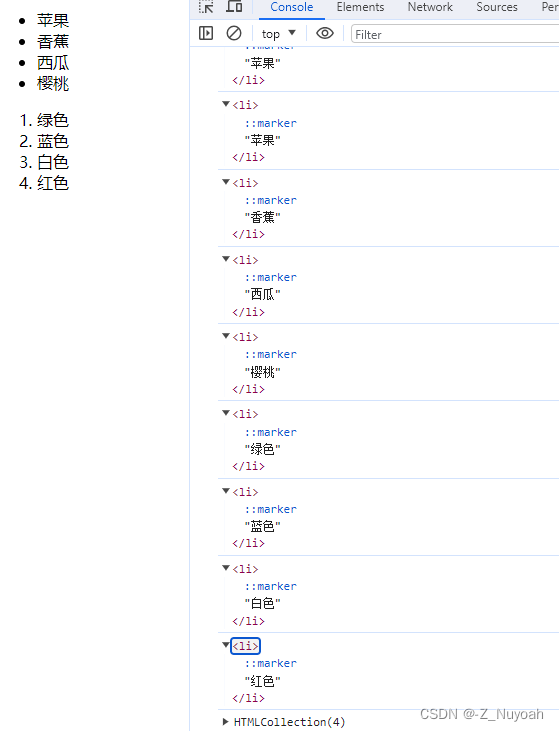
<html><head><meta charset="UTF-8"><title>Document</title></head><body><ul><li>苹果</li><li>香蕉</li><li>西瓜</li><li>樱桃</li></ul><ol id="ol"><li>绿色</li><li>蓝色</li><li>白色</li><li>红色</li></ol><script>var lis = document.getElementsByTagName('li');// 结果为:HTMLCollection(8) [li, li, li, li, li, li, li, li]console.log(lis);// 查看集合中的索引为0的元素,结果为:<li>苹果</li>console.log(lis[0]);// 遍历集合中的所有元素for (var i = 0; i < lis.length; i++) {console.log(lis[i]);}// 通过元素对象获取元素var ol = document.getElementById('ol');// 结果为:HTMLCollection(4) [li, li, li, li]console.log(ol.getElementsByTagName('li'));</script></body>
</html>
效果
3、根据name获取元素
1|document.getElementsByName('Name')
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html><head><meta charset="UTF-8"><title>Document</title></head><body><p>请选择你最喜欢的水果(多选)</p><label><input type="checkbox" name="fruit" value="苹果">苹果</label><label><input type="checkbox" name="fruit" value="香蕉">香蕉</label><label><input type="checkbox" name="fruit" value="西瓜">西瓜</label><script>var fruits = document.getElementsByName('fruit');fruits[0].checked = true;</script></body>
</html>
效果图

4、H5新增三种的获取方式
1、document.getElementsByClassName('');
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html><head><meta charset="UTF-8"><title>Document</title></head><body><span class="one">英语</span> <span class="two">数学</span><span class="one">语文</span> <span class="two">物理</span><script>var Ospan1 = document.getElementsByClassName('one');var Ospan2 = document.getElementsByClassName('two');Ospan1[0].style.fontWeight = 'bold';Ospan2[1].style.background = 'red';</script></body>
</html>
效果图

2、querySelector() 返回的是指定选择器的第一个元素对象
<!DOCTYPE html>
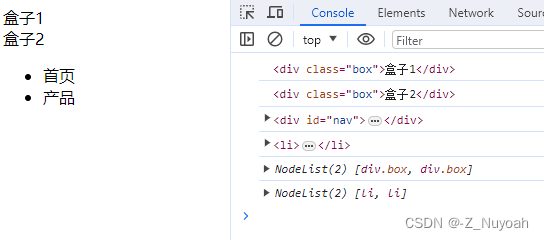
<html><head><meta charset="UTF-8"><title>Document</title></head><body><div class="box">盒子1</div><div class="box">盒子2</div><div id="nav"><ul><li>首页</li><li>产品</li></ul></div><script>var firstBox = document.querySelector('.box');console.log(firstBox); // 获取class为box的第1个divvar secondBox = document.querySelectorAll('.box')[1];console.log(secondBox);// 获取class为box的第2个divvar nav = document.querySelector('#nav');console.log(nav); // 获取id为nav的第1个div var li = document.querySelector('li');console.log(li); // 获取匹配到的第一个livar allBox = document.querySelectorAll('.box');console.log(allBox); // 获取class为box的所有divvar lis = document.querySelectorAll('li');console.log(lis); // 获取匹配到的所有li</script></body>
</html>
效果
3、document.querySelectorAll() 返回所有,若要返回除了第一个以外的元素对象,需要通过这个实现
<!DOCTYPE html>
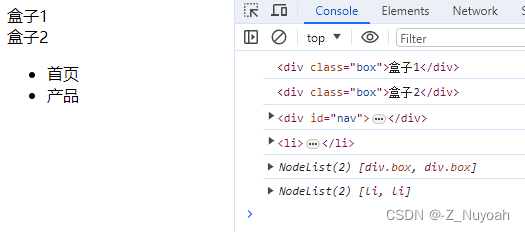
<html><head><meta charset="UTF-8"><title>Document</title></head><body><div class="box">盒子1</div><div class="box">盒子2</div><div id="nav"><ul><li>首页</li><li>产品</li></ul></div><script>var firstBox = document.querySelector('.box');console.log(firstBox); // 获取class为box的第1个divvar secondBox = document.querySelectorAll('.box')[1];console.log(secondBox);// 获取class为box的第2个divvar nav = document.querySelector('#nav');console.log(nav); // 获取id为nav的第1个div var li = document.querySelector('li');console.log(li); // 获取匹配到的第一个livar allBox = document.querySelectorAll('.box');console.log(allBox); // 获取class为box的所有divvar lis = document.querySelectorAll('li');console.log(lis); // 获取匹配到的所有li</script></body>
</html>
效果
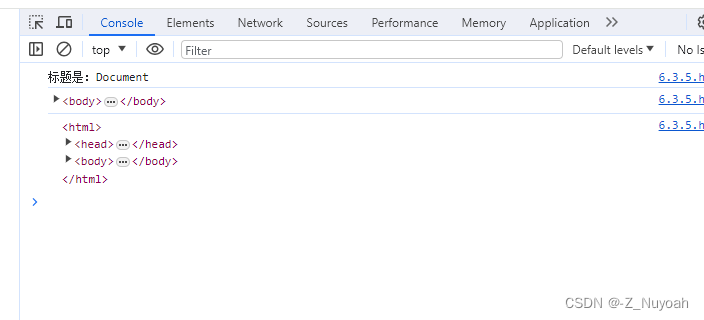
4、document对象的属性
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html><head><meta charset="UTF-8"><title>Document</title></head><body><script>var htmlTitle = document.title; // 返回标题console.log("标题是:"+htmlTitle);var bodyEle = document.body; // 返回bodyconsole.log("body是"+bodyEle);console.dir("dump详情"+bodyEle);// console.dir主要用来dump某些对象的详细信息var htmlEle = document.documentElement;// 返回htmlconsole.log(htmlEle);</script></body>
</html>
效果
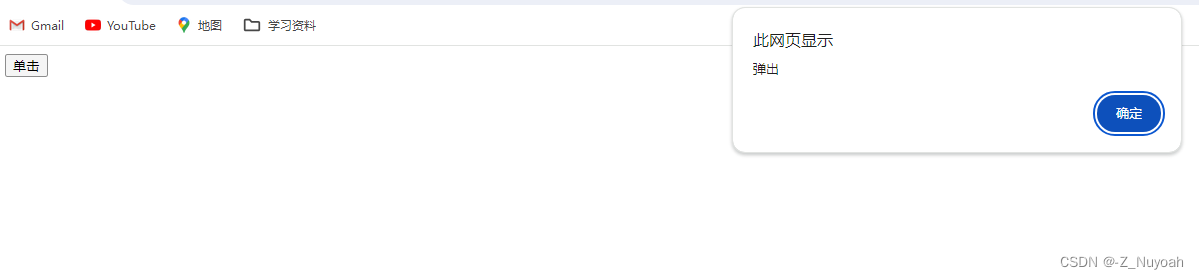
3、事件
事件是指可以被JavaScript侦测到的行为,
是一种‘触发-响应’的机制。
三要素
1、事件源 —谁触发了事件
2、事件类型 —触发了什么事件
3、事件处理程序 –触发事件以后要做什么
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html><head><meta charset="UTF-8"><title>Document</title></head><body><button id="btn">单击</button><script>var btn = document.getElementById('btn'); // 第1步:获取事件源// 第2步:注册事件btn.onclickbtn.onclick = function () { // 第3步:添加事件处理程序(采取函数赋值形式)alert('弹出');};</script></body>
</html>
效果
4、操作元素
1、操作元素内容

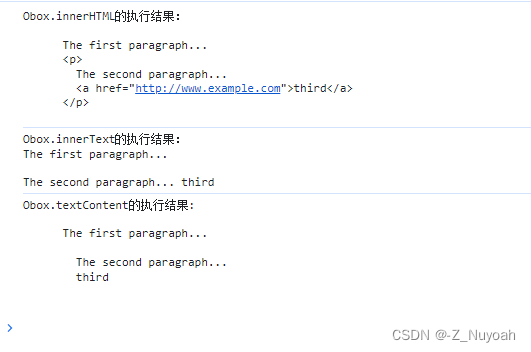
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html><head><meta charset="UTF-8"><title>Document</title></head><body><div id="box">The first paragraph...<p>The second paragraph...<a href="http://www.example.com">third</a></p></div><script>var Obox = document.getElementById('box')console.log("Obox.innerHTML的执行结果:\n"+Obox.innerHTML)console.log("Obox.innerText的执行结果:\n"+Obox.innerText)console.log("Obox.textContent的执行结果:\n"+Obox.textContent)</script></body>
</html>
2、操作元素属性 -- 重要 案例 --四叶草和鲜花的切换

<!DOCTYPE html>
<html><head><meta charset="UTF-8"><title>Document</title></head><body><button id="flower">鲜花</button><button id="grass">四叶草</button> <br><img src="images/grass.png" alt="" title="四叶草"><script>// 1. 获取元素var flower = document.getElementById('flower');var grass = document.getElementById('grass');var img = document.querySelector('img');// 2. 注册事件处理程序flower.onclick = function () {img.src = 'images/flower.png';img.title = '鲜花';};grass.onclick = function () {img.src = 'images/grass.png';img.title = '四叶草';};</script></body>
</html>
效果

3、dom对象 -- 全选,随机选择的按键
<!DOCTYPE html PUBLIC "-//W3C//DTD HTML 4.01 Transitional//EN" "http://www.w3.org/TR/html4/loose.dtd">
<html>
<head>
<meta http-equiv="Content-Type" content="text/html; charset=UTF-8">
<title>全选练习</title>
<script type="text/javascript">var items;window.onload = function(){//获取四个多选框itemsvar items = document.getElementsByName("items");//获取全选/全不选的多选框var checkedAllBox = document.getElementById("checkedAllBox");/** 全选按钮* - 点击按钮以后,四个多选框全都被选中*///1.#checkedAllBtn//为id为checkedAllBtn的按钮绑定一个单击响应函数var checkedAllBtn = document.getElementById("checkedAllBtn");checkedAllBtn.onclick = function(){//遍历itemsfor(var i=0 ; i<items.length ; i++){//通过多选框的checked属性可以来获取或设置多选框的选中状态//alert(items[i].checked);//设置四个多选框变成选中状态items[i].checked = true;}//将全选/全不选设置为选中checkedAllBox.checked = true;};/** 全不选按钮* - 点击按钮以后,四个多选框都变成没选中的状态*///2.#checkedNoBtn//为id为checkedNoBtn的按钮绑定一个单击响应函数var checkedNoBtn = document.getElementById("checkedNoBtn");checkedNoBtn.onclick = function(){for(var i=0; i<items.length ; i++){//将四个多选框设置为没选中的状态items[i].checked = false;}//将全选/全不选设置为不选中checkedAllBox.checked = false;};/** 反选按钮* - 点击按钮以后,选中的变成没选中,没选中的变成选中*///3.#checkedRevBtnvar checkedRevBtn = document.getElementById("checkedRevBtn");checkedRevBtn.onclick = function(){//将checkedAllBox设置为选中状态checkedAllBox.checked = true;for(var i=0; i<items.length ; i++){//判断多选框状态/*if(items[i].checked){//证明多选框已选中,则设置为没选中状态items[i].checked = false;}else{//证明多选框没选中,则设置为选中状态items[i].checked = true;}*/items[i].checked = !items[i].checked;//判断四个多选框是否全选//只要有一个没选中则就不是全选if(!items[i].checked){//一旦进入判断,则证明不是全选状态//将checkedAllBox设置为没选中状态checkedAllBox.checked = false;}}//在反选时也需要判断四个多选框是否全都选中};/** 提交按钮:* - 点击按钮以后,将所有选中的多选框的value属性值弹出*///4.#sendBtn//为sendBtn绑定单击响应函数var sendBtn = document.getElementById("sendBtn");sendBtn.onclick = function(){//遍历itemsfor(var i=0 ; i<items.length ; i++){//判断多选框是否选中if(items[i].checked){alert(items[i].value);}}};//5.#checkedAllBox/** 全选/全不选 多选框* - 当它选中时,其余的也选中,当它取消时其余的也取消* * 在事件的响应函数中,响应函数是给谁绑定的this就是谁*///为checkedAllBox绑定单击响应函数checkedAllBox.onclick = function(){//alert(this === checkedAllBox);//设置多选框的选中状态for(var i=0; i <items.length ; i++){items[i].checked = this.checked;}};//6.items/** 如果四个多选框全都选中,则checkedAllBox也应该选中* 如果四个多选框没都选中,则checkedAllBox也不应该选中*///为四个多选框分别绑定点击响应函数for(var i=0 ; i<items.length ; i++){items[i].onclick = function(){//将checkedAllBox设置为选中状态checkedAllBox.checked = true;for(var j=0 ; j<items.length ; j++){//判断四个多选框是否全选//只要有一个没选中则就不是全选if(!items[j].checked){//一旦进入判断,则证明不是全选状态//将checkedAllBox设置为没选中状态checkedAllBox.checked = false;//一旦进入判断,则已经得出结果,不用再继续执行循环break;} }};}//7.#randomBtn//为id为randomBtn的按钮绑定一个单击响应函数var randomBtn = document.getElementById("randomBtn");randomBtn.onclick = function(){//随机选择四个多选框的状态for(var i=0; i<items.length ; i++){//生成随机数,决定多选框的选中状态var randomState = Math.random() < 0.5; // 50% chance of being trueitems[i].checked = randomState;}//更新全选/全不选多选框的状态updateCheckedAllBoxState();}};</script>
</head>
<body><form method="post" action="">你爱好的运动是?<input type="checkbox" id="checkedAllBox" />全选/全不选 <br /><input type="checkbox" name="items" value="足球" />足球<input type="checkbox" name="items" value="篮球" />篮球<input type="checkbox" name="items" value="羽毛球" />羽毛球<input type="checkbox" name="items" value="乒乓球" />乒乓球<br /><input type="button" id="checkedAllBtn" value="全 选" /><input type="button" id="checkedNoBtn" value="全不选" /><input type="button" id="checkedRevBtn" value="反 选" /><input type="button" id="randomBtn" value="随机选择" /><input type="button" id="sendBtn" value="提 交" /></form>
</body>
</html>效果图

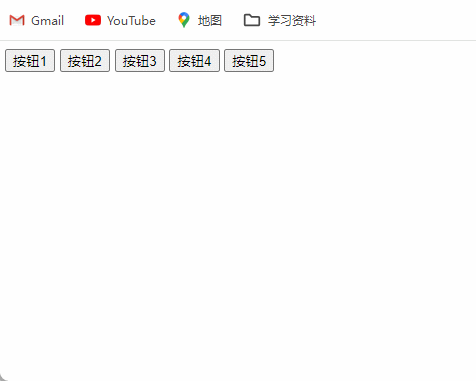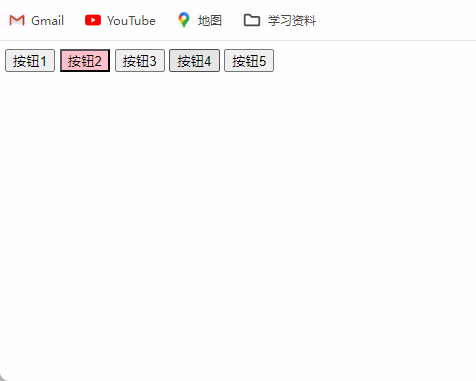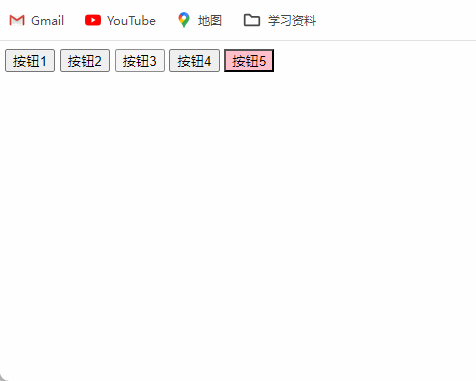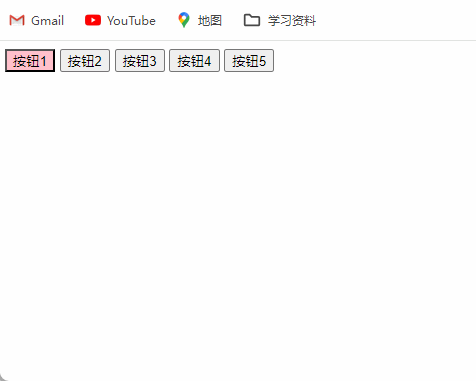
4、排他思维按键案例
排他思想:简单理解就是排除掉其他的(包括自己),然后再给自己设置想要实现的效果。总而言之,
排他思维的实现步骤就是所有元素全部清除与设置当前元素。
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html><head><meta charset="UTF-8"><title>Document</title></head><body><button>按钮1</button><button>按钮2</button><button>按钮3</button><button>按钮4</button><button>按钮5</button><script>// 获取所有按钮元素var btns = document.getElementsByTagName('button');// btns得到的是类数组对象,使用btns[i]访问数组里的每一个元素for (var i = 0; i < btns.length; i++) {btns[i].onclick = function () {// (1) 先把所有的按钮背景颜色去掉for (var i = 0; i < btns.length; i++) {btns[i].style.backgroundColor = '';}// (2) 然后设置当前的元素背景颜色this.style.backgroundColor = 'pink';}}</script></body>
</html>
效果图
5、鼠标指针经过时背景变色
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html><head><meta charset="UTF-8"><title>Document</title><style>table {width: 800px;margin: 100px auto;text-align: center;border-collapse: collapse;font-size: 14px;}thead tr {height: 30px;background-color: skyblue;}tbody tr {height: 30px;}tbody td {border-bottom: 1px solid #d7d7d7;font-size: 12px;color: blue;}.bg {background-color: pink;}</style></head><body><table><thead><tr><th>代码</th><th>名称</th><th>最新公布净值</th><th>累计净值</th><th>前单位净值</th><th>净值增长率</th></tr></thead><tbody><tr><td>0035**</td><td>3个月定期开放债券</td><td>1.075</td><td>1.079</td><td>1.074</td><td>+0.047%</td></tr><tr><td>0035**</td><td>3个月定期开放债券</td><td>1.075</td><td>1.079</td><td>1.074</td><td>+0.047%</td></tr><tr><td>0035**</td><td>3个月定期开放债券</td><td>1.075</td><td>1.079</td><td>1.074</td><td>+0.047%</td></tr><tr><td>0035**</td><td>3个月定期开放债券</td><td>1.075</td><td>1.079</td><td>1.074</td><td>+0.047%</td></tr></tbody></table><script>// 1. 获取元素var trs = document.querySelector('tbody').querySelectorAll('tr');// 2. 利用循环绑定注册事件for (var i = 0; i < trs.length; i++) {// 3. 鼠标经过事件 onmouseovertrs[i].onmouseover = function () {this.className = 'bg';};// 4. 鼠标离开事件 onmouseouttrs[i].onmouseout = function () {this.className = '';};}</script></body>
</html>
效果
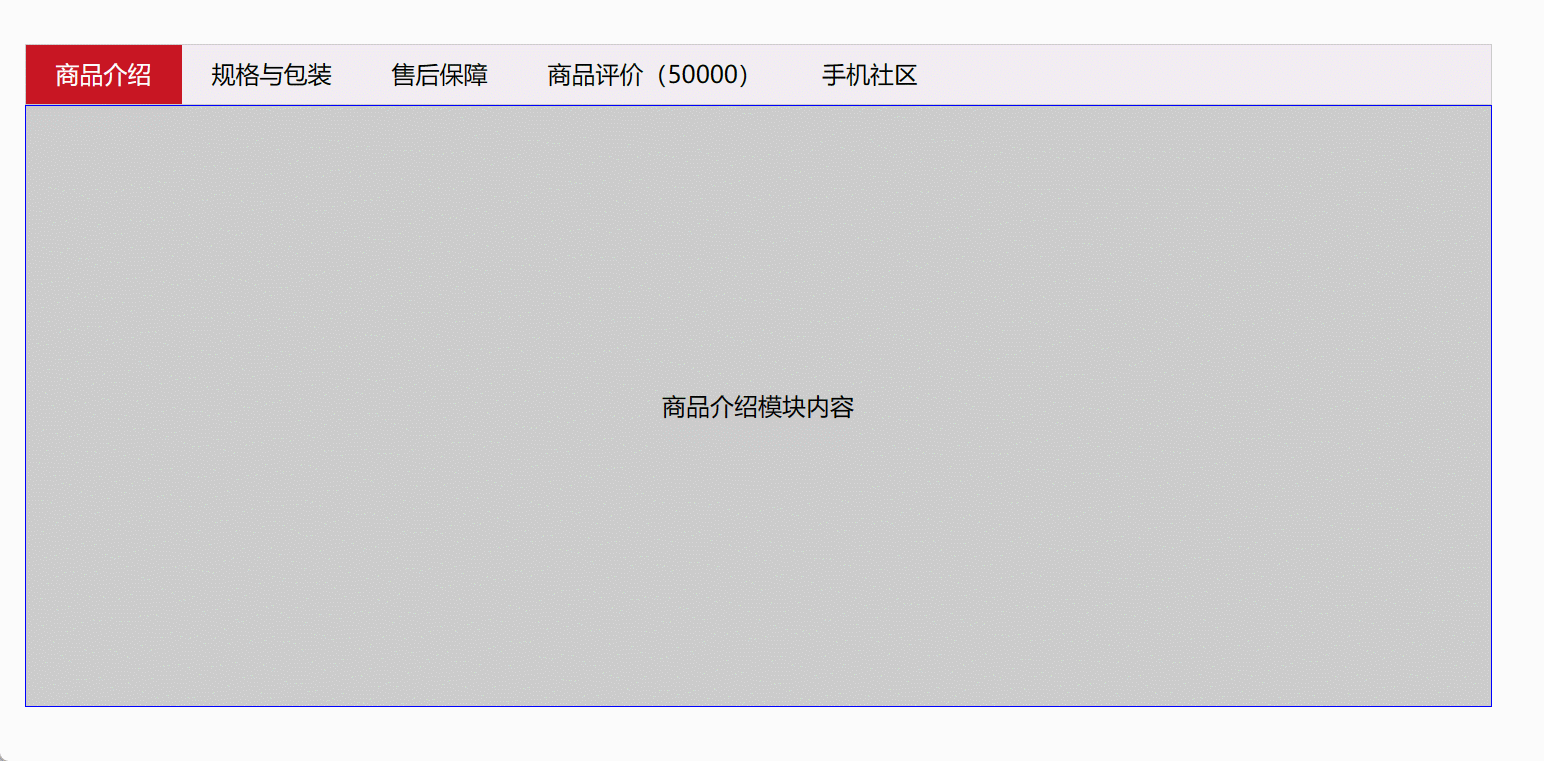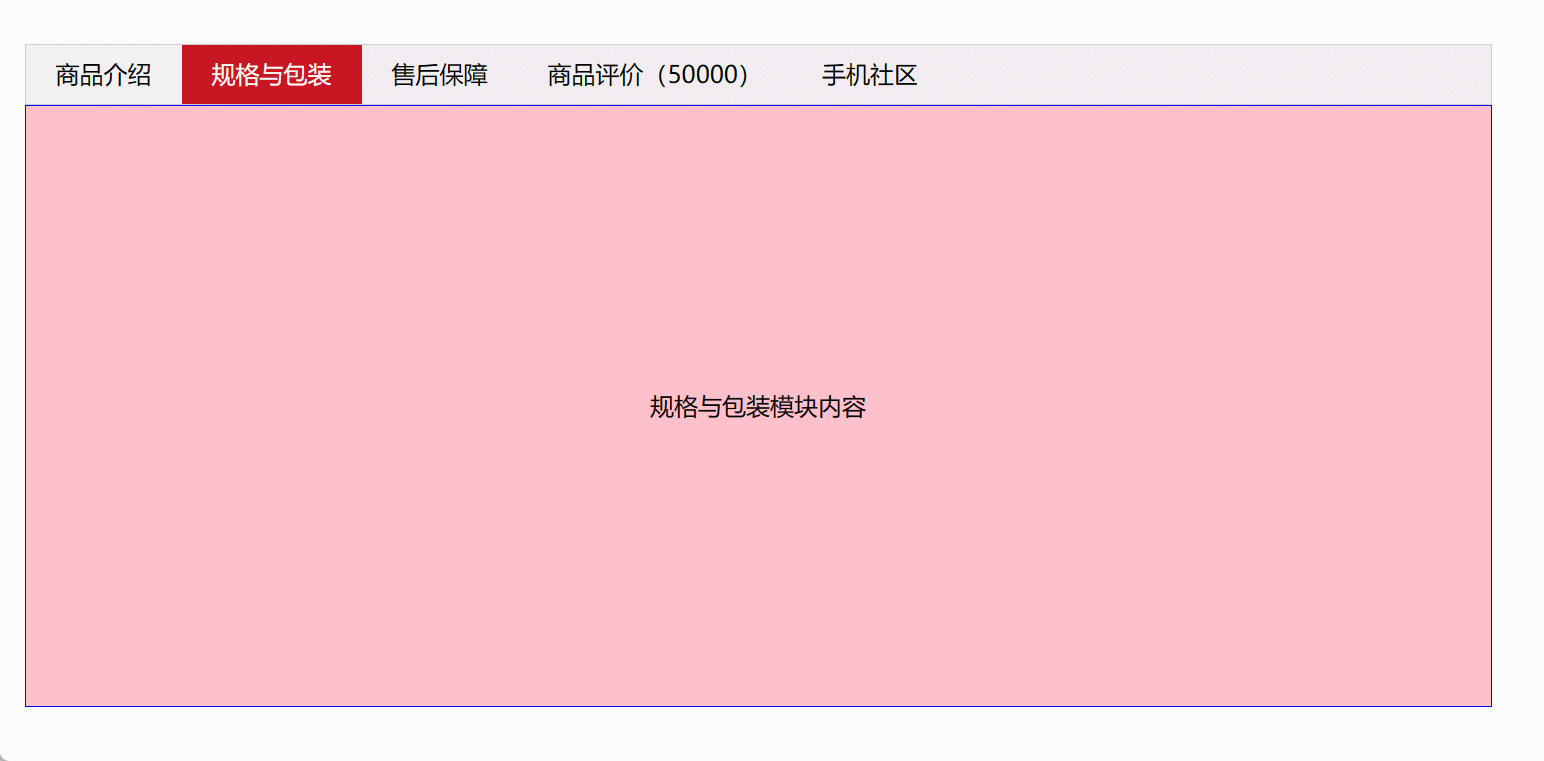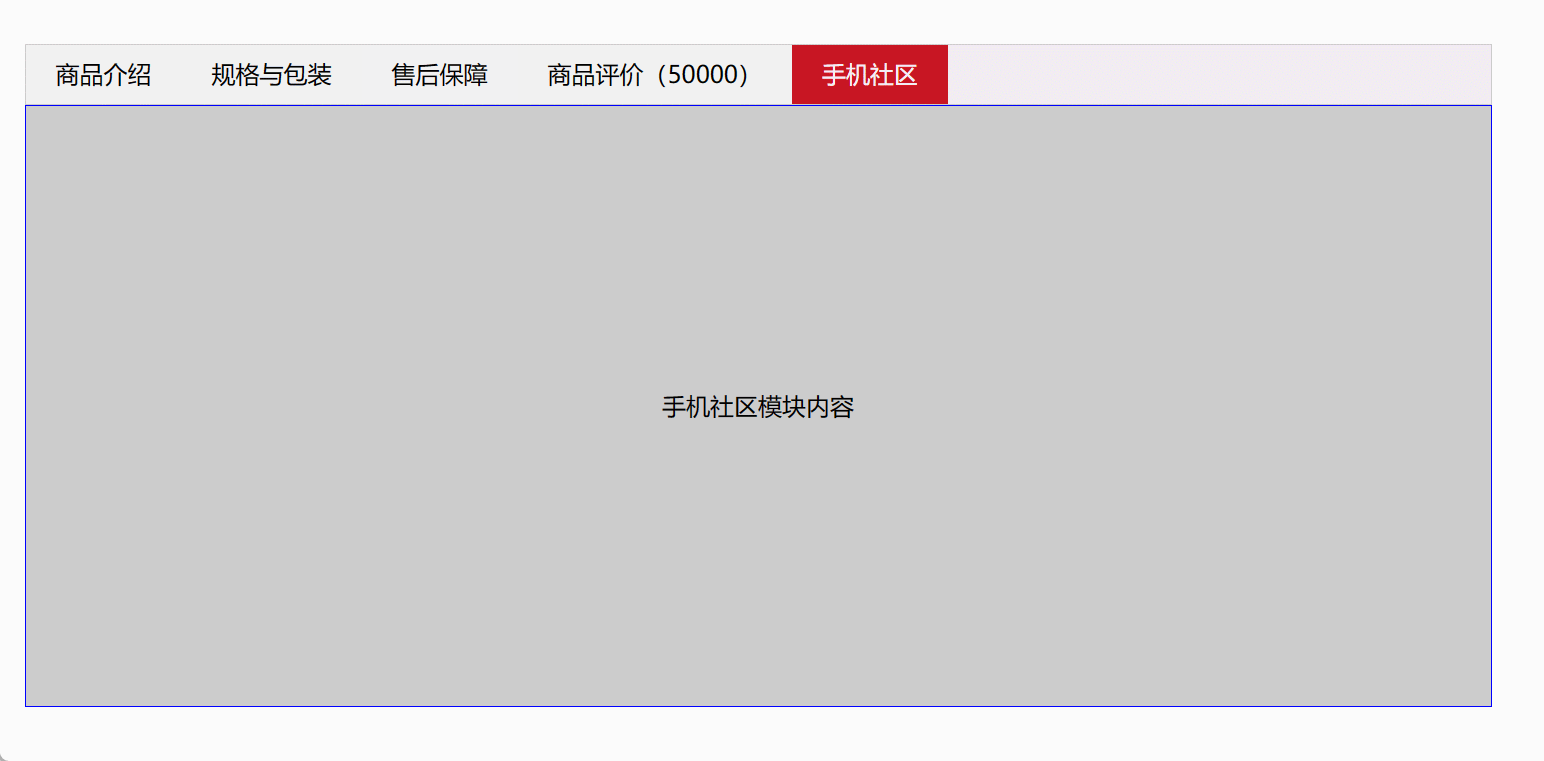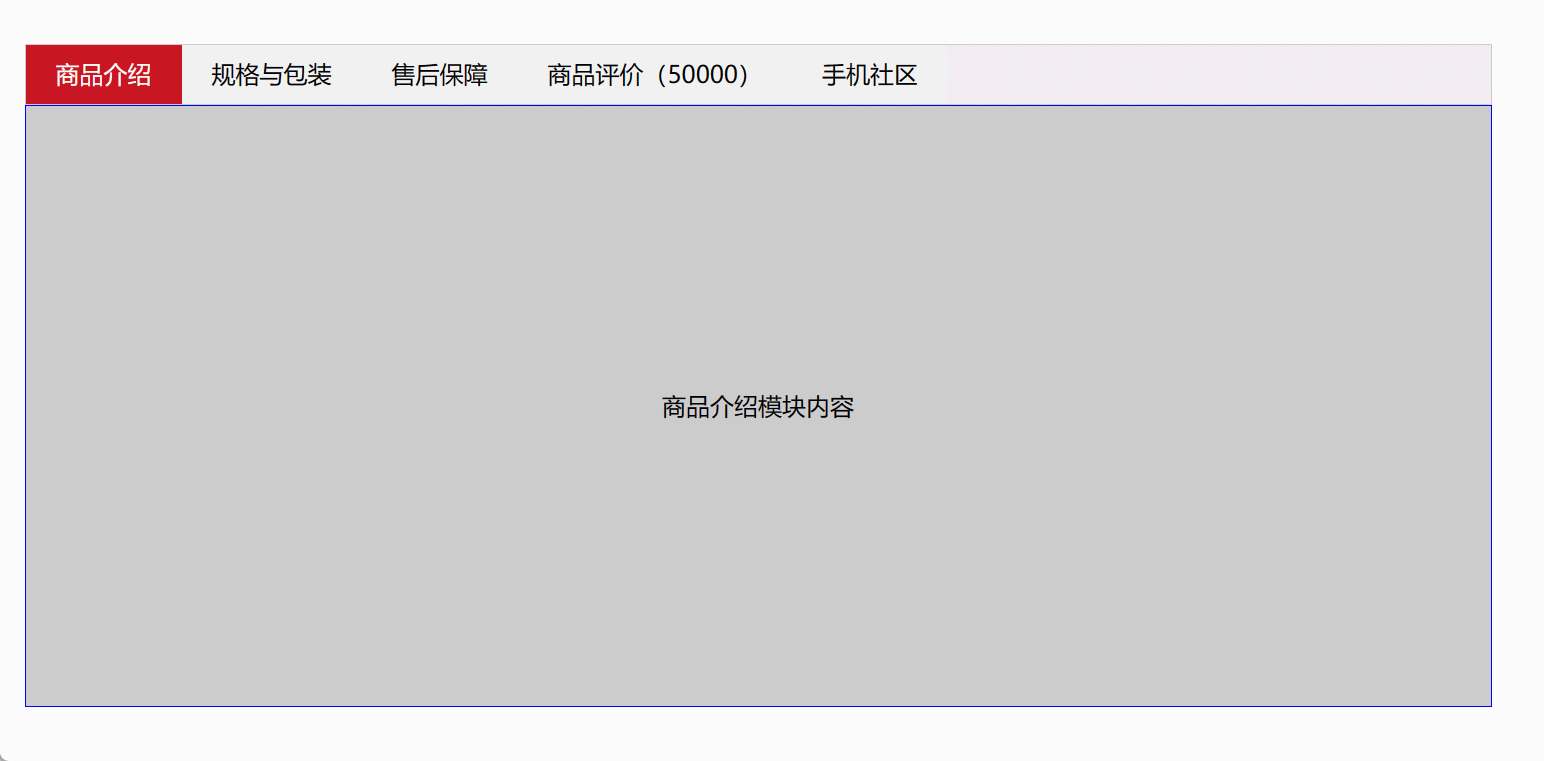
6、Tab栏切换
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html><head><meta charset="UTF-8"><title>Document</title><style>* {margin: 0;padding: 0;}li {list-style-type: none;}.tab {width: 978px;margin: 100px auto;}.tab_list {height: 39px;border: 1px solid #ccc;background-color: #f1f1f1;}.tab_list li {float: left;height: 39px;line-height: 39px;padding: 0 20px;text-align: center;cursor: pointer;}.tab_list .current {background-color: #c81623;color: #fff;}.item_info {padding: 20px 0 0 20px;}.item {display: none;height: 400px;background-color: #ccc;border:1px solid blue;text-align: center;line-height: 400px;}.item:nth-child(2n){background-color: pink;}</style></head><body><div class="tab"><div class="tab_list"><ul><li class="current">商品介绍</li><li>规格与包装</li><li>售后保障</li><li>商品评价(50000)</li><li>手机社区</li></ul></div><div class="tab_con"><div class="item" style="display: block;">商品介绍模块内容</div><div class="item">规格与包装模块内容</div><div class="item">售后保障模块内容</div><div class="item">商品评价(50000)模块内容</div><div class="item">手机社区模块内容</div></div></div><script>// 获取标签部分的所有元素对象var tab_list = document.querySelector('.tab_list');var lis = tab_list.querySelectorAll('li');// 获取内容部分的所有内容对象var items = document.querySelectorAll('.item');for (var i = 0; i < lis.length; i++) { // for循环绑定点击事件lis[i].setAttribute('index', i); // 开始给5个小li设置索引号lis[i].onclick = function () {for (var i = 0; i < lis.length; i++) {lis[i].className = '';}this.className = 'current';// 下面的显示内容模块var index = this.getAttribute('index');for (var i = 0; i < items.length; i++) {items[i].style.display = 'none';}items[index].style.display = 'block';};}</script></body>
</html>
效果
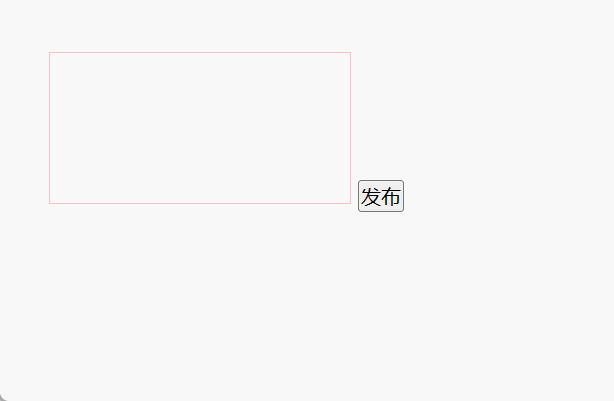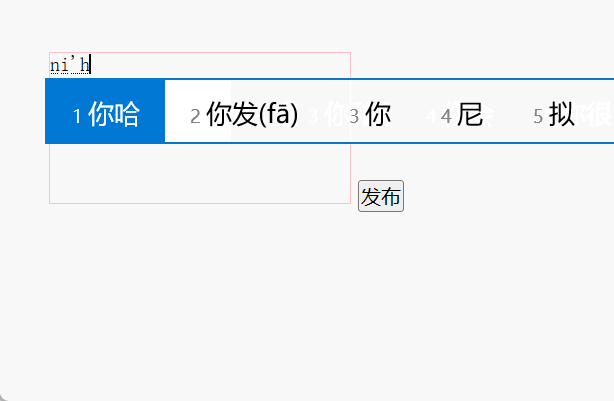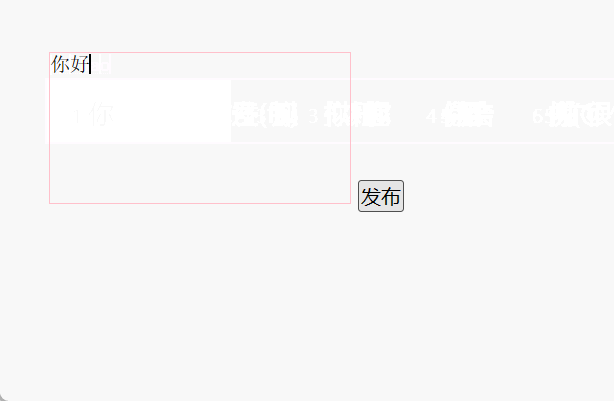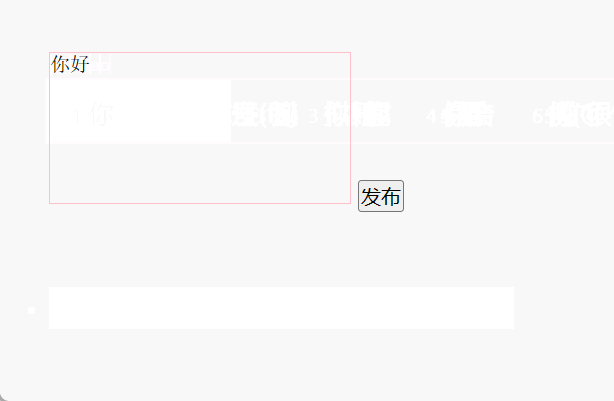
7、简易留言板
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html><head><meta charset="UTF-8"><title>Document</title><style>* {margin: 0;padding: 0;}body {padding: 100px;}textarea {width: 200px;height: 100px;border: 1px solid pink;outline: none;resize: none;}ul {margin-top: 50px;}li {width: 300px;padding: 5px;background-color: #eee;font-size: 14px;margin: 15px 0;}li a {float: right;}</style></head><body><textarea name="" id=""></textarea><button>发布</button><ul></ul><script>// 1. 获取元素var btn = document.querySelector('button');var text = document.querySelector('textarea');var ul = document.querySelector('ul');// 2. 注册事件btn.onclick = function () {if (text.value == '') {alert('您没有输入内容');return false;} else {// (1) 创建元素var li = document.createElement('li');// li.innerHTML = text.value;li.innerHTML = text.value + '<a href="javascript:;">删除</a>';// (2) 添加元素ul.insertBefore(li, ul.children[0]);var as = document.querySelectorAll('a');for (var i = 0; i < as.length; i++) {as[i].onclick = function () {ul.removeChild(this.parentNode);};}}};</script></body>
</html>
效果
更详细的js内容见下链接
链接:https://pan.baidu.com/s/1NDjYPcbzb1ApNq6Vh5j0MQ?pwd=19tk
提取码:19tk
这篇关于福建农林大学 html +css + JavaScript 期末复习 -- 保姆级的文章就介绍到这儿,希望我们推荐的文章对编程师们有所帮助!




