本文主要是介绍Spring大略学习(二),希望对大家解决编程问题提供一定的参考价值,需要的开发者们随着小编来一起学习吧!
Spring大略学习(一)
文章目录
- Spring大略学习(一)
- 7. Bean的自动装配
- 1. byName自动装配
- 2. byType自动装配
- 3. 注解自动装
- @Autowired
- @Autowired + @Qualifier 的组合
- @Resource
- 4. 存在的问题
- 8. 使用注解开发
- 环境配置
- @Component
- @Scope
- 9. Java配置Spring
- @Configuration
- @ComponentScan("com.lzj.entity")
- @Import
- @Bean
- 例子
- 10. 代理模式
- 1. 静态代理
- 2. 动态代理
- 两种常用的动态代理
- 基于接口的动态代理
- 11. AOP
- 1. 什么是AOP?
- 2. AOP在Spring中的作用
- 3. Spring实现AOP
- 1. Spring的API接口 实现
- 流程
- 例子
- 2. 自定义类(切面)来实现AOP
- 流程
- 例子
- 3.使用注解来实现
7. Bean的自动装配
什么是自动装配?
Spring会根据上下文自动寻找,自动给bean装配属性
自动装配的方式
Spring有三种装配方式
- xml中显示配置
- java中显示配置
- 隐式 的自动装配bean 【重点】
1. byName自动装配
当bean的id的名字跟java类的属性名一致的时候,就会调用set注入赋值
People
package com.lzj.entity;import lombok.AllArgsConstructor;
import lombok.Data;
import lombok.NoArgsConstructor;@Data
@AllArgsConstructor
@NoArgsConstructor
public class People {private String name;private Dog dog;} <bean id="People" class="com.lzj.entity.People" p:name="先驱" autowire="byName"/><bean id="dog" class="com.lzj.entity.Dog"><property name="name" value="大欢"/><property name="size" value="18"/></bean><bean id="dog2" class="com.lzj.entity.Dog"><property name="name" value="大黄"/><property name="size" value="29"/></bean>
这边会吧id="dog"的注入到属性
2. byType自动装配
会根据bean的class自动装配,但是有一个坏处,出现两个同样类型的属性时无法注入,需要用byName
Dog
package com.lzj.entity;import lombok.Data;@Data
public class Dog {private String name;private String size;
}People
package com.lzj.entity;import lombok.AllArgsConstructor;
import lombok.Data;
import lombok.NoArgsConstructor;@Data
@AllArgsConstructor
@NoArgsConstructor
public class People {private String name;private Dog dog;}注入
<bean id="People" class="com.lzj.entity.People" p:name="先驱" autowire="byType"/><bean id="Dog" class="com.lzj.entity.Dog"><property name="name" value="大欢"/><property name="size" value="18"/></bean>test
@Testpublic void test01(){ApplicationContext context = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("applicationContext.xml");System.out.println((People)context.getBean("People"));}但是当有两条狗名字id不一样的时候
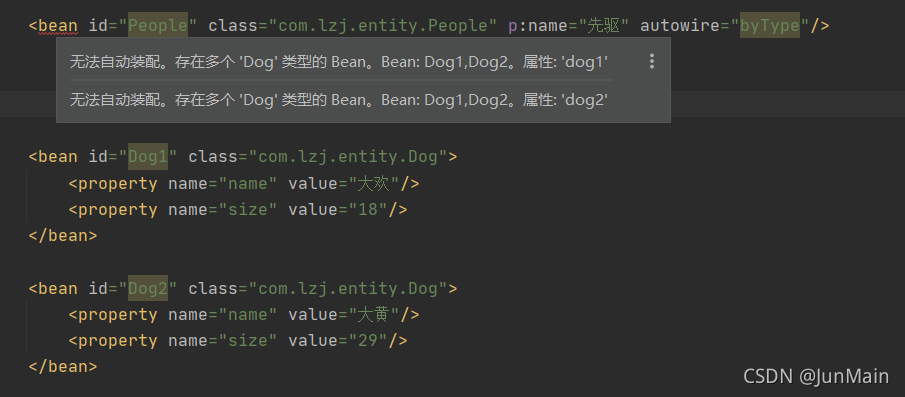
<bean id="People" class="com.lzj.entity.People" p:name="先驱" autowire="byType"/><bean id="Dog1" class="com.lzj.entity.Dog"><property name="name" value="大欢"/><property name="size" value="18"/></bean><bean id="Dog2" class="com.lzj.entity.Dog"><property name="name" value="大黄"/><property name="size" value="29"/></bean>
package com.lzj.entity;import lombok.AllArgsConstructor;
import lombok.Data;
import lombok.NoArgsConstructor;@Data
@AllArgsConstructor
@NoArgsConstructor
public class People {private String name;private Dog dog;}这个时候我们在利用byType注入属性就会报错
不知道应该注入哪一个
3. 注解自动装
导入约束。搭建环境
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context"xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beanshttps://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsdhttp://www.springframework.org/schema/contexthttps://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context.xsd"><!--开启注解的支持 --><context:annotation-config/>
</beans>@Autowired
是spring的注解,可以使用在属性 、set、构造器中, 是通过内部byType的方式注入。
当放在javaBean的属性 (引用的时候)如果bean里面有该类型,会自动注入
其实不需要set方法也可以使用@Autowired来实现ref类的注入,底层通过反射可以获取类的任何东西,包括private
所以有无setXXX()方法不影响
xml配置
<bean id="Dog" class="com.lzj.entity.Dog"><property name="name" value="大欢"/><property name="size" value="18"/></bean><bean id="cat" class="com.lzj.entity.Cat"><property name="name" value="猫猫"/></bean><bean id="animal" class="com.lzj.entity.Animal"/>
Animal
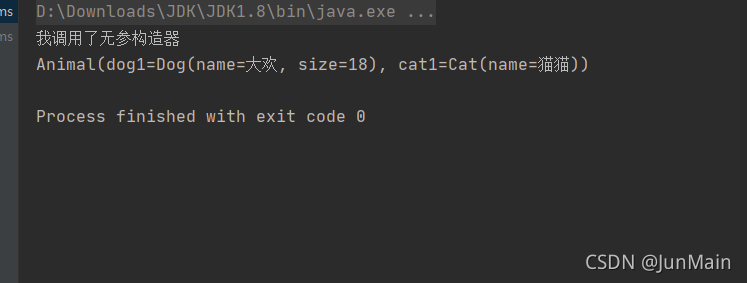
package com.lzj.entity;import lombok.Data;import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;@Data
public class Animal {@Autowiredprivate Dog dog1;@Autowiredprivate Cat cat1;}test
@Testpublic void test01(){ApplicationContext context = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("applicationContext.xml");System.out.println((Animal)context.getBean("animal"));}
注:@Autowired(required=false)放在属性上表示当在Spring容器里面找不到该类对象的时候不会报错,允许为null
@Autowired + @Qualifier 的组合
由于@Autowired是byType的,当有两个一样的bean类型,但是id不一样的时候,就会出现问题,于是就有@Qualifier
在举一个Dog1 Dog2的例子
Dog
package com.lzj.entity;import lombok.Data;@Data
public class Dog {private String name;private String size;
}
xml
<bean id="People" class="com.lzj.entity.People" p:name="先驱" autowire="byType"/><bean id="Dog1" class="com.lzj.entity.Dog"><property name="name" value="大欢"/><property name="size" value="18"/></bean><bean id="Dog2" class="com.lzj.entity.Dog"><property name="name" value="大黄"/><property name="size" value="29"/></bean>
Animal
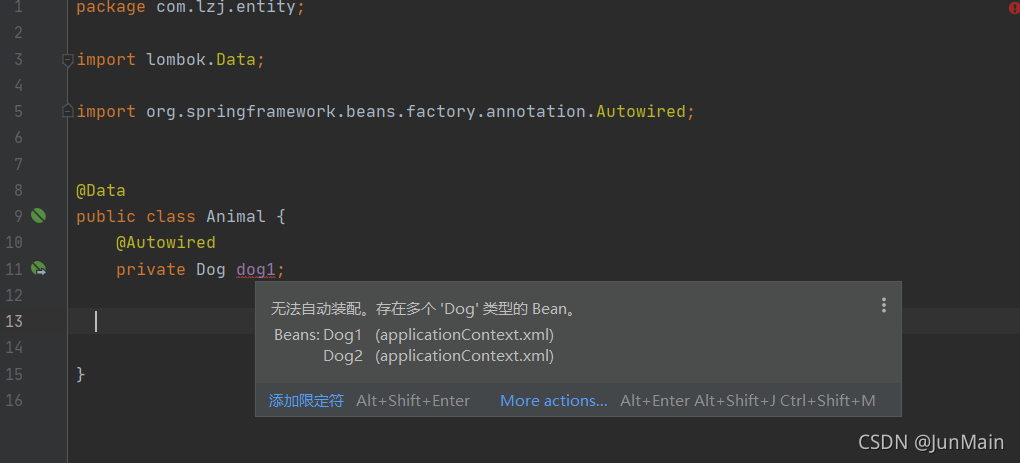
package com.lzj.entity;import lombok.Data;import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;@Data
public class Animal {@Autowiredprivate Dog dog1;}这个时候由于Autowired是byType的,但是此时容器里面有两个Dog的实例对象,这个时候就会不知道该注入哪一个从而报错
这个时候需要用@Qualifier来指定到底选哪一个Dog
package com.lzj.entity;import lombok.Data;import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Qualifier;@Data
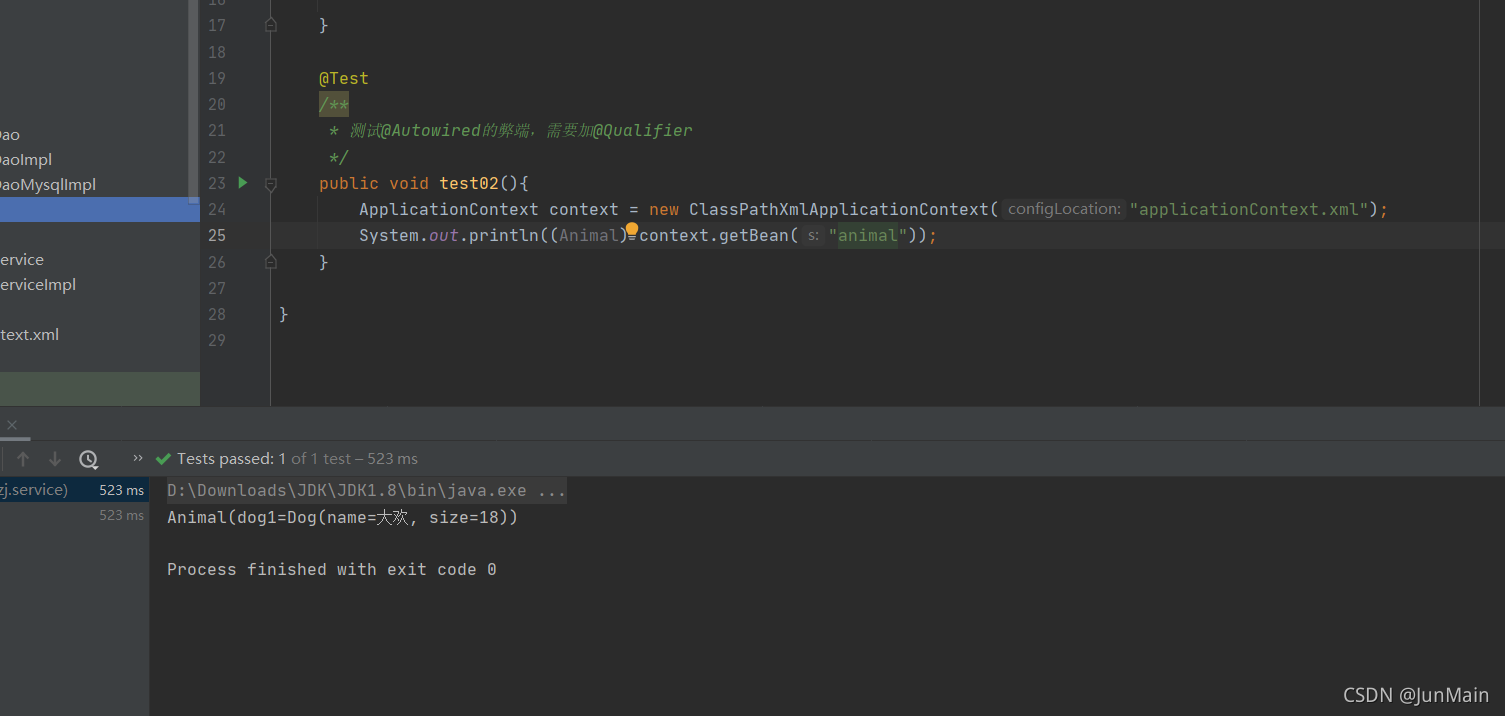
public class Animal {@Autowired@Qualifier("Dog1")private Dog dog1;}test
@Test/*** 测试@Autowired的弊端,需要加@Qualifier*/public void test02(){ApplicationContext context = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("applicationContext.xml");System.out.println((Animal) context.getBean("animal"));}
@Resource
是java的内部注解 可以使用在属性 、set、构造器中
优先byType, 冲突byName
King
package com.lzj.entity;import lombok.ToString;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Value;import javax.annotation.Resource;@ToString
public class King {@Value("大不列颠") //通过@Value注入普通类型private String name;@Resourceprivate Wife wife;
}
Wife
package com.lzj.entity;import lombok.ToString;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Value;@ToString
public class Wife {@Value("伊丽莎白") //通过@Value注入普通类型private String name;
}
xml
<bean id="animal" class="com.lzj.entity.Animal"/><bean id="Wife" class="com.lzj.entity.Wife"/><bean id="king" class="com.lzj.entity.King"/>
test
@Test/*** 测试@Resource* 例子:King, Wife*/public void test03(){ApplicationContext context = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("applicationContext.xml");System.out.println((King)context.getBean("king"));}
这边我们发现无论Wifebean的id怎么改,都能正确的注入,@Resource是先按照byName如果name不符合再byType
4. 存在的问题
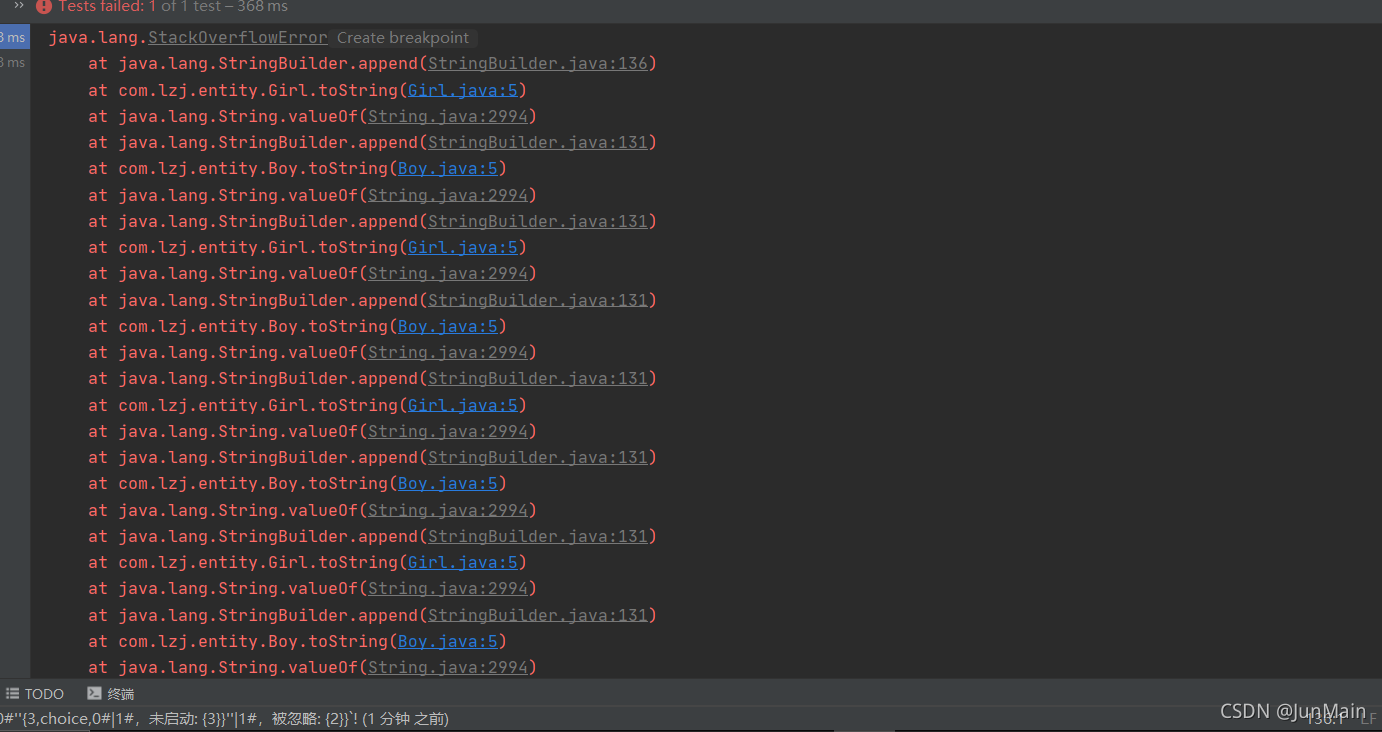
属性的循环依赖问题
Boy的属性依赖 Girl
package com.lzj.entity;import lombok.Data;@Data
public class Boy {private String name;private Girl girl;
}Girl的属性依赖Boy
package com.lzj.entity;import lombok.Data;@Data
public class Girl {private String name;private Boy boy;
}我们单个从Spring容器中获取Boy, Girl对象的时候没有任何问题,
但是我们一旦利用自动注入为其属性赋值的时候就出现了的时候就出现问题了(栈溢出错误)
<bean id="girl" class="com.lzj.entity.Girl" autowired="byType"><property name="name" value="sm"/></bean><bean id="boy" class="com.lzj.entity.Boy" autowired="byType"><property name="name" value="lzj"/></bean>
public void test01(){ApplicationContext context= new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("applicationContext.xml");System.out.println((Boy)context.getBean("boy"));}
8. 使用注解开发
环境配置
确保aop的包导入
xml约束配置
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?><beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context"xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beanshttps://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsdhttp://www.springframework.org/schema/contexthttps://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context.xsd"><!--开启注解的支持 --><context:annotation-config/><!--指定要扫描的包,这个包下的注解就会生效--><context:component-scan base-package="com.kuang"/><!--开启注解的支持 --><context:annotation-config/></beans>
@Component
@Controller 在controller层使用
@Service 在service层使用
@Repository 在dao层使用
这四个注解都是一个作用(放在类的上方让容器类名有她的实例化对象)相当于在applicationContext.xml里面 设置bean
这两个是自动注入属性(ref)
@Autowired
@Resource
@Value 这个是可以直接设置基本类型的值而不需要再bean的property里面设置了
@Scope
在javabean的类上面, 声明作用域 单例模式,原型模式等等
我们完全用注解来配置Father,和Son这两个类
Father
package com.lzj.entity;import lombok.ToString;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Value;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.ComponentScan;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;@ToString
@Component
/*** 等价在xml中* <bean id = "father" class = "com.lzj.entity.Father">* <property name = "name" value = "爸爸"/>* </bean>*/
public class Father {@Value("爸爸")private String name;
}Son
package com.lzj.entity;import lombok.ToString;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Qualifier;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Value;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.ComponentScan;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;@ToString
@Component
/*** 等价在xml中* <bean id="son" class="com.lzj.entity.Son">* <property name="name" value = "儿子"/>* <property name="father" ref = "father"/>* <bean/>*/
public class Son {@Value("儿子")private String name;@Autowired@Qualifier("father") //等价@Resourceprivate Father father;
}xml (需要加这个注解才生效)
<!--指定要扫描的包,这个包下的注解就会生效--><context:component-scan base-package="com.kuang"/><!--开启注解的支持 --><context:annotation-config/>test
@Test/*** 测试 @Component + @Value + @Autowired + @Qualifier / @Resource* 相当于 <bean id="类小写" class="全类名"/>* 例子:Father, Son*/public void test04(){ApplicationContext context = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("applicationContext.xml");System.out.println((Son)context.getBean("son"));}
9. Java配置Spring
基于纯java配置而不是xml 纯java配置在springboot中更常见一点
其中常见的注解
@Configuration
放在JavaConfig类上面表示这是配置类
@ComponentScan(“com.lzj.entity”)
放在JavaConfig类上面表示配置里面导入该包的注解生效
@Import
放在JavaConfig类上面,导入其他的JavaConfig配置类
@Bean
和@Component修饰位置范围不太一样@Bean是作用再方法上面的,让方法的返回类型new一个实例对象再Spring容器中
但是他们的效果都是一样的让Spring容器里面多一个实体对象
用法 方法名相当于bean的id 返回的类型相当于bean的class
例子
举一个例子来熟悉java配置 还是用刚才的父子例子
Father
package com.lzj.entity;import lombok.ToString;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Value;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.ComponentScan;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;@ToString
@Component
/*** 等价在xml中* <bean id = "father" class = "com.lzj.entity.Father">* <property name = "name" value = "爸爸"/>* </bean>*/
public class Father {@Value("爸爸")private String name;
}Son
package com.lzj.entity;import lombok.ToString;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Qualifier;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Value;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.ComponentScan;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;@ToString
@Component
/*** 等价在xml中* <bean id="son" class="com.lzj.entity.Son">* <property name="name" value = "儿子"/>* <property name="father" ref = "father"/>* <bean/>*/
public class Son {@Value("儿子")private String name;@Autowired@Qualifier("father") //等价@Resourceprivate Father father;
}JavaConfig
package com.lzj.config;import com.lzj.entity.Father;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.ComponentScan;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;@Configuration
@ComponentScan("com.lzj.entity") //这个包下面的@Component生效 装进容器中
public class JavaConfig {/**注册一个bean,就相当于我们之前写的一个bean标签这个方法的名字,就相当于bean标签中id属性这个方法的返回值,就相当于bean标签中的class属性**/@Beanpublic Father father(){return new Father();}}test
package com.lzj.service;import com.lzj.config.JavaConfig;
import com.lzj.entity.Son;
import org.junit.Test;
import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.AnnotationConfigApplicationContext;public class JavaConfigTest {@Testpublic void test01(){ApplicationContext context = new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext(JavaConfig.class);System.out.println(context.getBean("son", Son.class));System.out.println(context.getBean("father", Father.class));}
}这边我们发现我们其实完全不需要applicationContext.xml的配置文件,实现类“全注解配置”
10. 代理模式
1. 静态代理
静态代理再真正的决策者和适用者中介多了一层中介商,中间商可以完全复制决策者的操作,但是同时还可以自己增加一些(私货)给适用者,这样不会破坏决策者的真正意图,当其他中间商传达意思的时候还能自己再增加私货,提高了决策者代码的复用性
举一个例子,婚介所中介的,女方是真正的决策者,婚介所是中间商,男方是适用者。
IWoman
package com.lzj.entity;public interface IWoman {void say();
}Woman
package com.lzj.entity;public class Woman implements IWoman{public void say(){System.out.println("我想要高富帅");}
}Agency
package com.lzj.entity;public class Agency implements IWoman{private Woman woman;public Agency(Woman woman){this.woman = woman;}public void say(){woman.say();cost();}public void cost(){System.out.println("您需要支付中介费");}}Man
package com.lzj.service;import com.lzj.entity.Agency;
import com.lzj.entity.Woman;
import org.junit.Test;public class ProxyTest {@Testpublic void man(){Woman woman = new Woman();Agency agency = new Agency(woman);agency.say();}
}这边我们发现,当调用say()时候也调用了cost()方法,不用去Woman里面去修改,但是一旦Woman该类Agent也需要改
2. 动态代理
动态代理其实和静态代理一样都是代理,做中间商,但是比静态代理要方便许多,因为静态代理是写死的,当真正的决策者需要增加新的动作的时候,静态代理的中间商也要增加响应的方法去实现,当真正的决策者很多的时候,静态代理的成本就很高了,因此我们引入了动态代理的概念。
两种常用的动态代理
1、基于接口的动态代理
·提供者:JDK
·使用JDK官方的Proxy类创建代理对象
·注意:代理的目标对象必须实现接口
2、基于类的动态代理
·提供者:第三方 CGLib
·使用CGLib的Enhancer类创建代理对象
·注意:如果报 asmxxxx 异常,需要导入 asm.jar包
我们详细讲解基于接口的动态代理
基于接口的动态代理
Proxy和InvocationHandler这两个类
还是用婚介所的例子
IWoman
package com.lzj.entity;public interface IWoman {void say();
}Woman
package com.lzj.entity;public class Woman implements IWoman{public void say(){System.out.println("我想要高富帅");}
}AgentInvocation
package com.lzj.entity;import lombok.Data;import java.lang.reflect.InvocationHandler;
import java.lang.reflect.Method;
import java.lang.reflect.Proxy;public class AgencyInvocation implements InvocationHandler {//被代理的接口private IWoman woman;public void setWoman(Woman woman){this.woman = woman;}//生成代理类public Object getProxy(){return Proxy.newProxyInstance(this.getClass().getClassLoader(), woman.getClass().getInterfaces(),this);}public Object invoke(Object proxy, Method method, Object[] args) throws Throwable{Object result = method.invoke(woman,args);cost();return result;}public void cost(){System.out.println("我要收费10%");}}
Man
@Test/*** 动态代理实现的*/public void Man(){Woman woman = new Woman();AgencyInvocation agencyInvocation = new AgencyInvocation();agencyInvocation.setWoman(woman);IWoman iWoman = (IWoman) agencyInvocation.getProxy();iWoman.say();}
这边可以直接早调用say()的时候,cost()也调用了
这边我们发现这个动态代理类可以代理多一个Woman类只要都是实现类IWoman的都可以代理
提取工具类
AgencyInvocation
public class AgencyInvocation implements InvocationHandler{//被代理的接口private Object target;public void setWoman(Object target){this.target = target;}//生成代理类public Object getProxy(){return Proxy.newProxyInstance(this.getClass().getClassLoader(), woman.getClass().getInterfaces(),this);}public Object invoke(Object proxy, Method method, Object[] args) throws Throwable{Object result = method.invoke(woman,args);log(method.getName());return result;}public void log(String msg){System.out.println("[Debug] 使用了一个"+msg+"方法");}}
11. AOP
1. 什么是AOP?
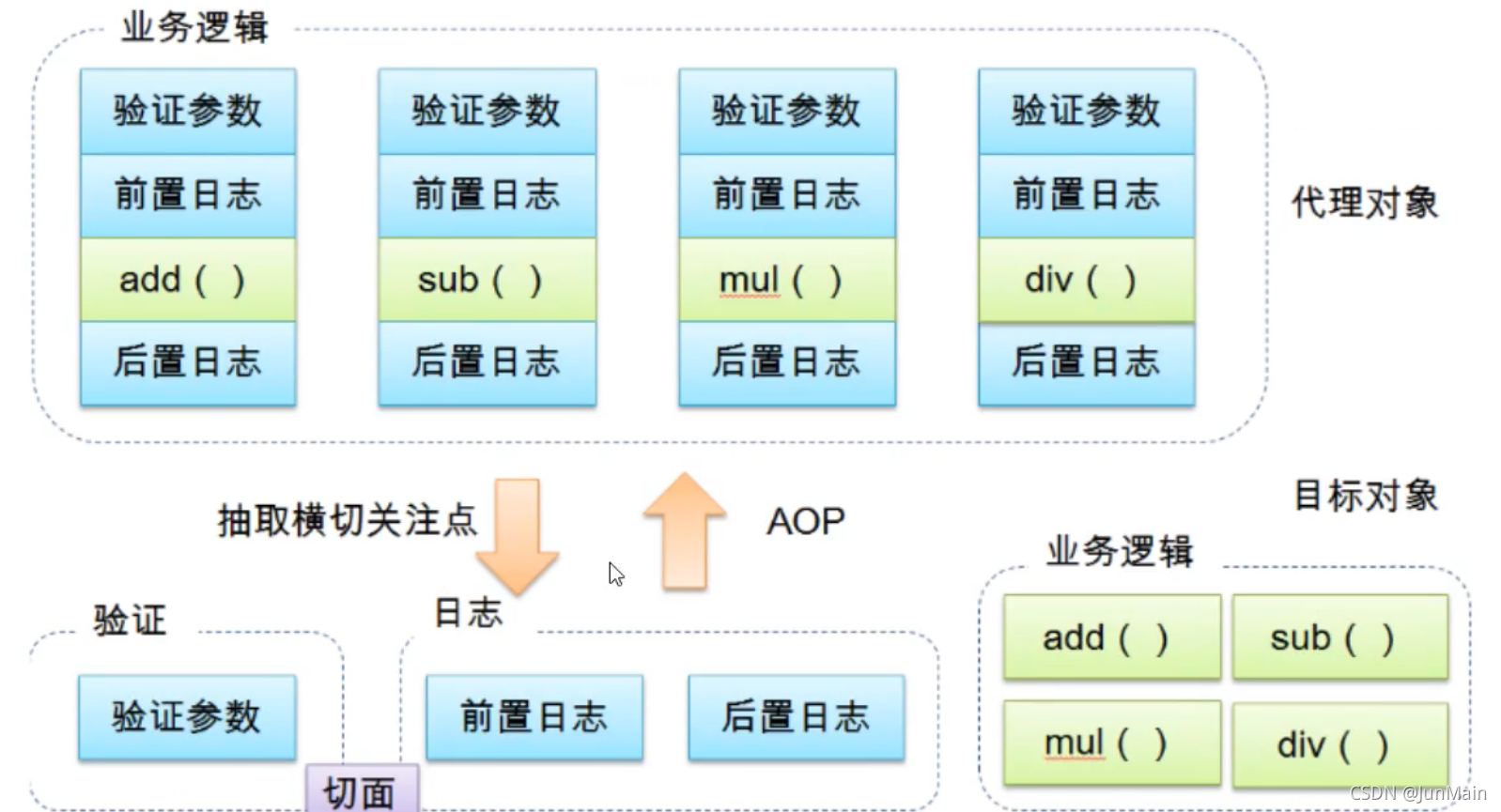
AOP(Aspect Oriented Programming)意为:面向切面编程,通过预编译方式和运行期动态代理实现程序功能的统一维护的一种技术。AOP是OOP的延续,是软件开发中的一个热点,也是Spring框架中的一个重要内容,是函数式编程的一种衍生范型。利用AOP可以对业务逻辑的各个部分进行隔离,从而使得业务逻辑各部分之间的耦合度降低,提高程序的可重用性,同时提高了开发的效率
2. AOP在Spring中的作用
提供声明式事务;允许用户自定义切面
横切关注点:跨越应用程序多个模块的方法或功能。即是,与我们业务逻辑无关的,但是我们需要关注的部分,就是横切关注点。如日志,安全,缓存,事务等等…
切面(ASPECT):横切关注点被模块化的特殊对象。即,它是一个类。
通知(Advice):切面必须要完成的工作。即,它是类中的一个方法。
目标(Target):被通知对象。
代理(Proxy):向目标对象应用通知之后创建的对象。
切入点(PointCut):切面通知执行的“地点”的定义。
连接点(JointPoint):与切入点匹配的执行点。
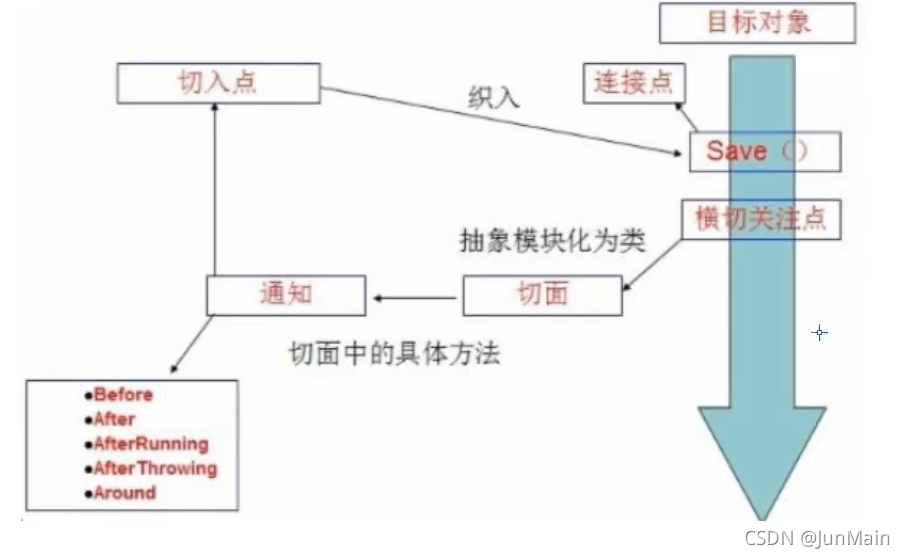
在SpringAOP中通过Advice定义横切逻辑,Spring支持五种Advice的逻辑
| 通知类型 | 连接点 | 实现接口 |
|---|---|---|
| 前置通知 | 方法前 | org.springframework.aop.MethodBeforeAdvice |
| 后置通知 | 方法后 | org.springframework.aop.AfterReturningAdvice |
| 环绕通知 | 方法前后 | org.aopalliance.intercept.MethodInterceptor |
| 异常抛出通知 | 方法抛出异常 | org.springframework.ThrowsAdvice |
| 引介通知 | 类中增加新的方法属性 | org.springframework.aop.IntroductionInterceptor |
3. Spring实现AOP
例如实现对增删改查增加log日志
添加依赖【重点】使用AOP织入
<!-- https://mvnrepository.com/artifact/org.aspectj/aspectjweaver -->
<dependency><groupId>org.aspectj</groupId><artifactId>aspectjweaver</artifactId><version>1.8.13</version>
</dependency>
Spring 的execution表达式
<aop:pointcut id="" expression="execution(void com.lzj.service.XX方法(String,Integer))"/>
1. void表示返回值类型,如果返回值类型设置为 * ,那么表示返回任意类型2. com.lzj.service.XX方法(String,Integer)表示com包下的lzj包下的XX方法,以及他的具体形参类型。3. 如果想要模糊表达,就可以使用通配符*,*代表任意字符,一个点代表某个包下的某个类,两个点表示某个包和他的子包路径下的所有类,两个点应用在形参中,表示所有形参。例子:
execution(* *..service..*.*(..))表示所有包中的service包中的所有类中的所有方法,他的返回值任意。
execution(* *..*Impl.doFirst(..)) 表示所有包中的任意以Impl结尾的类中的doFirst()方法,并且是任意形参,返回值也是任意的
execution(* *..ba02.*Impl.doOther(..)) 表示返回值任意,所有包中的ba02包中的以Impl结尾的类的doOther()方法,参数任意。
1. Spring的API接口 实现
导入的xml约束
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"xmlns:aop="http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop"xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beanshttps://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsdhttp://www.springframework.org/schema/aophttps://www.springframework.org/schema/aop/spring-aop.xsd">
</beans>
流程
先是业务的接口,业务接口的实现类
然后自定义类去实现五种Advice并实现方法,实现自己想要的逻辑
再XX.xml的注册bean,aop : pointcut自定义切点的具体位置到什么方法(execution表达式)
定义通知器 aop:advisor 在什么切点执行什么通知
然后测试的时候 getBean的时候要强转成接口,因为动态代理是基于接口实现的
例子
TableService
package com.lzj.service;public interface TableService {public void update();public void insert();public void delete();public void select();}TableServiceImpl
package com.lzj.service;import lombok.Data;@Data
public class TableServiceImpl implements TableService{public void update() {System.out.println("更新表");}public void insert() {System.out.println("表内插入数据");}public void delete() {System.out.println("表内删除数据");}public void select() {System.out.println("表内查询数据");}
}BeforeLog (前置通知实现类)
package com.lzj.log;import lombok.Data;
import org.springframework.aop.MethodBeforeAdvice;import java.lang.reflect.Method;@Data
public class BeforeLog implements MethodBeforeAdvice {//method: 要执行的目标对象的方法//args:参数//target:目标对象public void before(Method method, Object[] agrs, Object target) throws Throwable {System.out.println(target.getClass().getName() + "的" + method.getName() + "被执行了");}
}AfterLog (后置通知实现类)
package com.lzj.log;import lombok.Data;
import org.springframework.aop.AfterReturningAdvice;import java.lang.reflect.Method;@Data
public class AfterLog implements AfterReturningAdvice {//returnValue: 返回值public void afterReturning(Object returnValue, Method method, Object[] args, Object target) throws Throwable {System.out.println("执行了"+method.getName()+"方法,返回结果为:"+returnValue);}
}context.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"xmlns:aop="http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop"xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beanshttps://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsdhttp://www.springframework.org/schema/aophttps://www.springframework.org/schema/aop/spring-aop.xsd"><aop:config><!-- 切入点 expression="execution(* ..*(..))" 代切入的位置 细化到具体的方法 --><aop:pointcut id="pointcut" expression="execution(* com.lzj.service.TableServiceImpl.*(..))"/><!--执行环绕增加!--><aop:advisor advice-ref="afterLog" pointcut-ref="pointcut"/><aop:advisor advice-ref="beforeLog" pointcut-ref="pointcut"/></aop:config><bean id="tableServiceImpl" class="com.lzj.service.TableServiceImpl"/><bean id="beforeLog" class="com.lzj.log.BeforeLog"/><bean id="afterLog" class="com.lzj.log.AfterLog"/></beans>
test
@Testpublic void test01(){ApplicationContext context = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("context.xml");//注意这边是强转成接口,因为动态代理的是接口TableService tableService = (TableService) context.getBean("tableService");tableService.delete();}
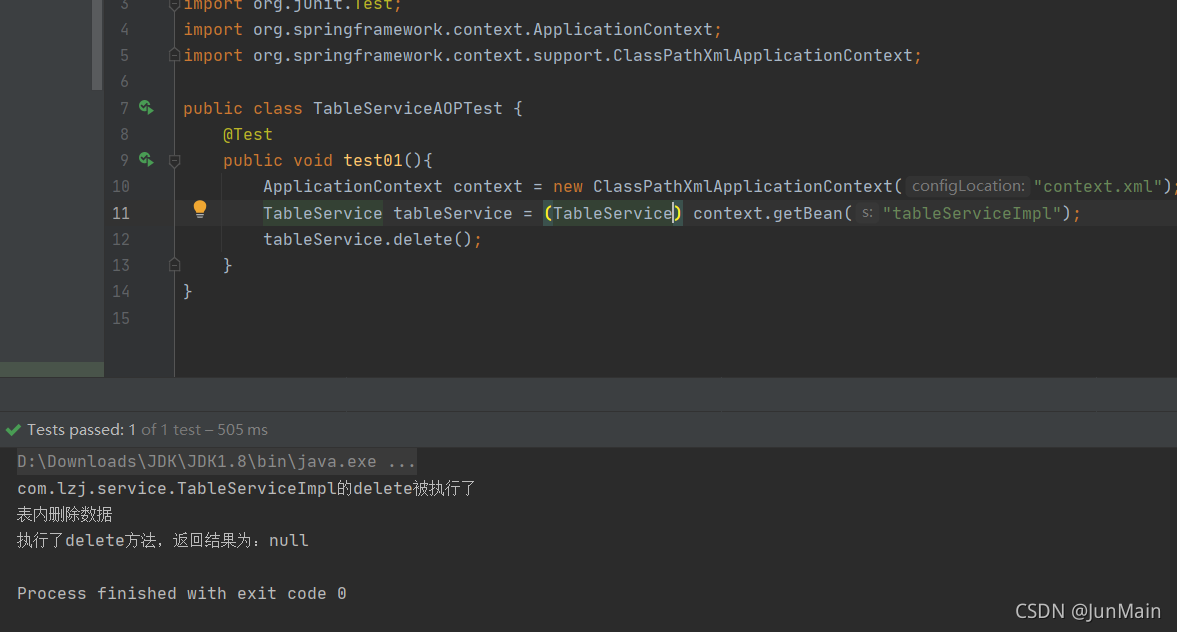
2. 自定义类(切面)来实现AOP
流程
先自己定义一个类(切面),定义方法(通知),就不需要向之前一样通知需要实现API接口
再aop:config 里面还是先定义切点,这个跟第一个一样 aop : pointcut
关键是aop : aspect 里面 先是ref绑定自定义切面,各种类型的通知跟自定义切面里面的方法绑定
例子
TableService
package com.lzj.service;public interface TableService {public void update();public void insert();public void delete();public void select();}TableServiceImpl
package com.lzj.service;import lombok.Data;@Data
public class TableServiceImpl implements TableService{public void update() {System.out.println("更新表");}public void insert() {System.out.println("表内插入数据");}public void delete() {System.out.println("表内删除数据");}public void select() {System.out.println("表内查询数据");}
}MyAspect
package com.lzj.aspect;public class MyAspect {public void before(){System.out.println("--------在方法执行前-----------");}public void after(){System.out.println("--------在方法执行后------------");}
}context.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"xmlns:aop="http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop"xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beanshttps://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsdhttp://www.springframework.org/schema/aophttps://www.springframework.org/schema/aop/spring-aop.xsd"><aop:config><!-- 切入点 expression="execution(* ..*(..))" 代切入的位置 细化到具体的方法 --><aop:pointcut id="pointcut" expression="execution(* com.lzj.service.TableServiceImpl.*(..))"/><aop:aspect ref="myAspect"><aop:before method="before" pointcut-ref="pointcut"/><aop:after method="after" pointcut-ref="pointcut"/></aop:aspect></aop:config><bean id="tableServiceImpl" class="com.lzj.service.TableServiceImpl"/><bean id="myAspect" class="com.lzj.aspect.MyAspect"/>
</beans>
test
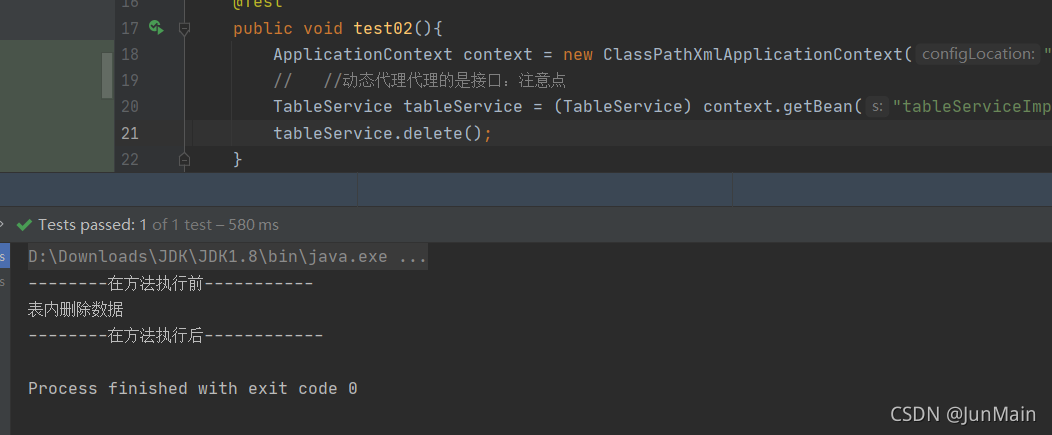
@Testpublic void test02(){ApplicationContext context = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("context.xml");// //动态代理代理的是接口:注意点TableService tableService = (TableService) context.getBean("tableServiceImpl");tableService.delete();}
3.使用注解来实现
@Aspect 标记哪个类是切面
@Before(“execution()”) 放在方法上
AnnotationAspect
package com.lzj.aspect;import org.aspectj.lang.ProceedingJoinPoint;
import org.aspectj.lang.Signature;
import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.After;
import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.Around;
import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.Aspect;
import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.Before;@Aspect
public class AnnotationAspect {@Before("execution(* com.lzj.service.TableServiceImpl.*(..))")public void before(){System.out.println("----------方法执行前-----------");}@After("execution(* com.lzj.service.TableServiceImpl.*(..))")public void after(){System.out.println("----------方法执行后------------");}@Around("execution(* com.lzj.service.TableServiceImpl.*(..))")public void around(ProceedingJoinPoint jp) throws Throwable{System.out.println("环绕前");Signature signature = jp.getSignature();// 获得签名System.out.println("signature:"+signature);Object proceed = jp.proceed(); //执行方法System.out.println("环绕后");System.out.println(proceed);}
}context.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"xmlns:aop="http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop"xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beanshttps://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsdhttp://www.springframework.org/schema/aophttps://www.springframework.org/schema/aop/spring-aop.xsd"><bean id="annotationAspect" class="com.lzj.aspect.AnnotationAspect"/><aop:aspectj-autoproxy/>
</beans>
test
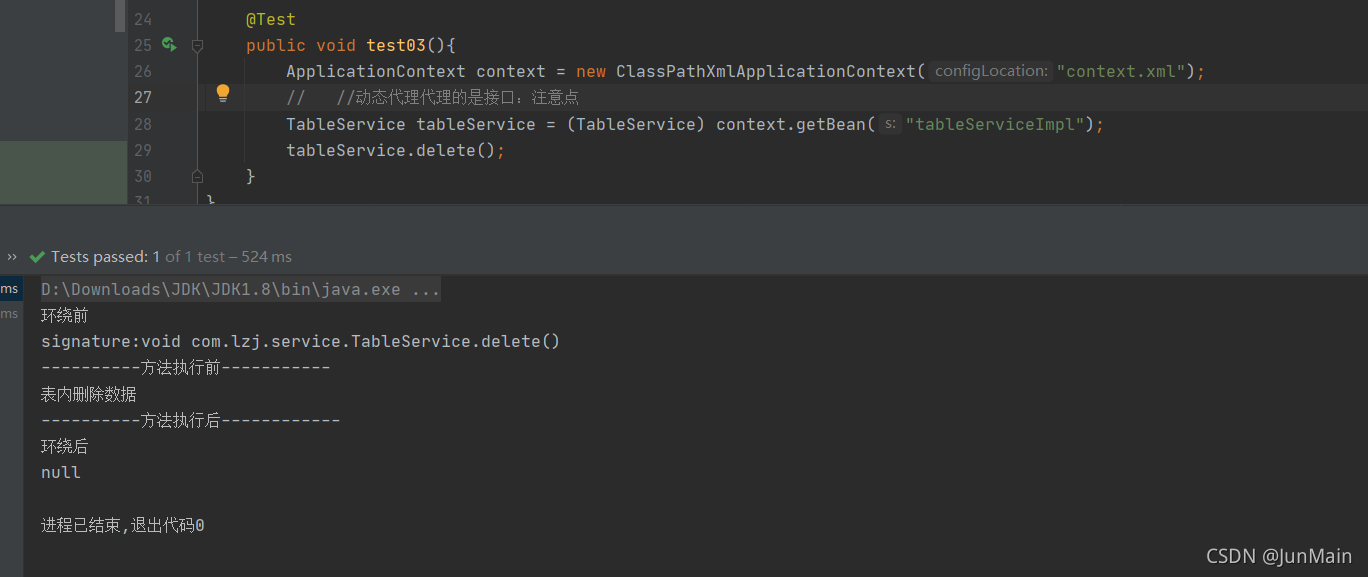
@Testpublic void test03(){ApplicationContext context = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("context.xml");// //动态代理代理的是接口:注意点TableService tableService = (TableService) context.getBean("tableServiceImpl");tableService.delete();}
这篇关于Spring大略学习(二)的文章就介绍到这儿,希望我们推荐的文章对编程师们有所帮助!





