本文主要是介绍ChibiOS简介5/5,希望对大家解决编程问题提供一定的参考价值,需要的开发者们随着小编来一起学习吧!
ChibiOS简介5/5
- 1. 源由
- 2. ChibiOS基础知识5/5
- 2.16 Chapter 16 - The OS Library
- 2.16.1 Memory Allocators
- 2.16.2 Binary Semaphores
- 2.16.3 Mailboxes
- 2.16.4 Objects FIFOs
- 2.16.5 Pipes
- 2.16.6 Delegate Threads
- 2.16.7 Jobs Queues
- 2.16.8 Objects Caches
- 2.16.9 Objects Factory
- 2.16.10 Notes on Testing
- 3. 参考资料
1. 源由
作为后续研读Ardupilot的ChibiOS的垫脚石,先了解下ChibiOS系统。
Ardupilot ChibiOS项目: https://github.com/ArduPilot/ChibiOS
Artery(AT32) porting项目: //Artery官网没有相关porting动作,不过开源github有相关项目。
- https://github.com/dron0gus/artery
- https://github.com/dron0gus/ChibiOS
2. ChibiOS基础知识5/5
2.16 Chapter 16 - The OS Library
The OS Library (OSLIB) is an optional set of RTOS features that can be added on top of both RT and NIL kernels. It is purely a source code architectural decision.
Requirements
- Features that only use the common RT and NIL common API.
- Features that cannot be optimized using tricks or details of the underlying RT or NIL kernels.
- Features that are CPU architecture agnostic.
- Features that are compiler agnostic.
- Features that have no dependencies on external modules other than RT or NIL kernels.
2.16.1 Memory Allocators
The 4 kinds of allocators are designed to work together:
- Core Allocator, for one-way memory allocation, memory cannot be freed.
- Pool Allocator, for allocating and freeing fixed-size objects.
- Guarded Pool Allocator, it is like the pool allocator but guarded by a semaphore. Trying to allocate an object causes the caller thread to wait if an object is not immediately available.
- Heap Allocator, for allocating and freeing arbitrary-size memory blocks.
The above mechanisms were previously in the RT kernel and have been moved into OSLIB.
Allocators Comparison
Here is a table summarizing the information:
| Allocator | Can Free | Constant Time | Variable Size | From ISR | Creates Fragments | Thread Safe |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Core Allocator | No | Yes | Yes | Yes | - | Yes |
| Pool Allocator | Yes | Yes | No | Yes | No | Yes |
| Guarded Pool Allocator | Yes | No | No | Yes1 | No | Yes |
| Heap Allocator | Yes | No | Yes | No | Yes | Yes |
| C Library Allocator | Yes | No | Yes | No | Yes | No2 |
- Without waiting.
- Depends on library implementation and integration with the RTOS.
- Can Free indicates the ability of the allocator to return blocks to the available memory.
- Constant Time is the ability to allocate/free blocks in a constant time, this is important for system determinism.
- Variable Size is the ability to allocate/free blocks of variable size.
- From ISR indicates that the allocator services can also be called from ISR context.
- Creates Fragments indicates if allocating and freeing memory can cause internal fragmentation.
- Thread Safe indicates that the allocator can be used in a multi-threaded environment.
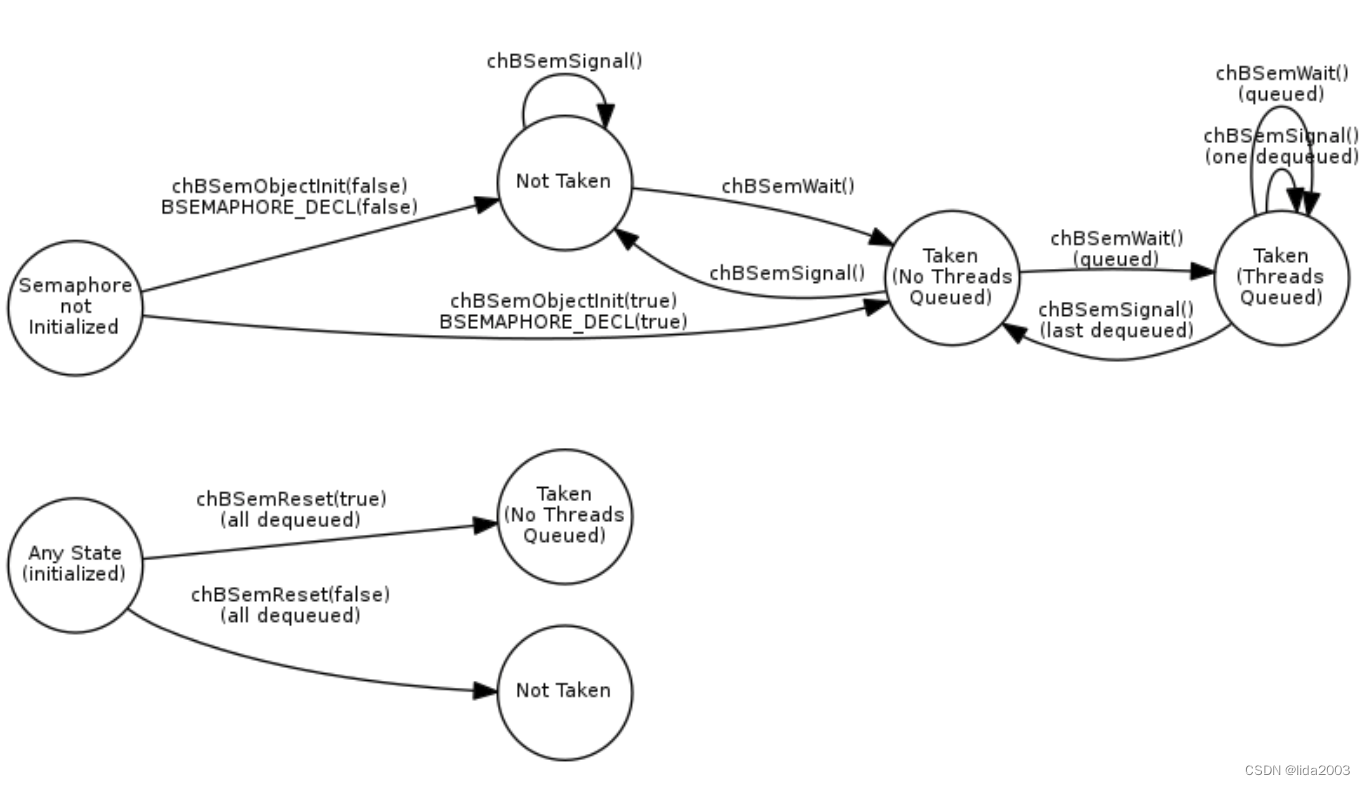
2.16.2 Binary Semaphores
A variation on the semaphore mechanism with only two internal states, this mechanism was previously in the RT kernel and has been moved into OSLIB.
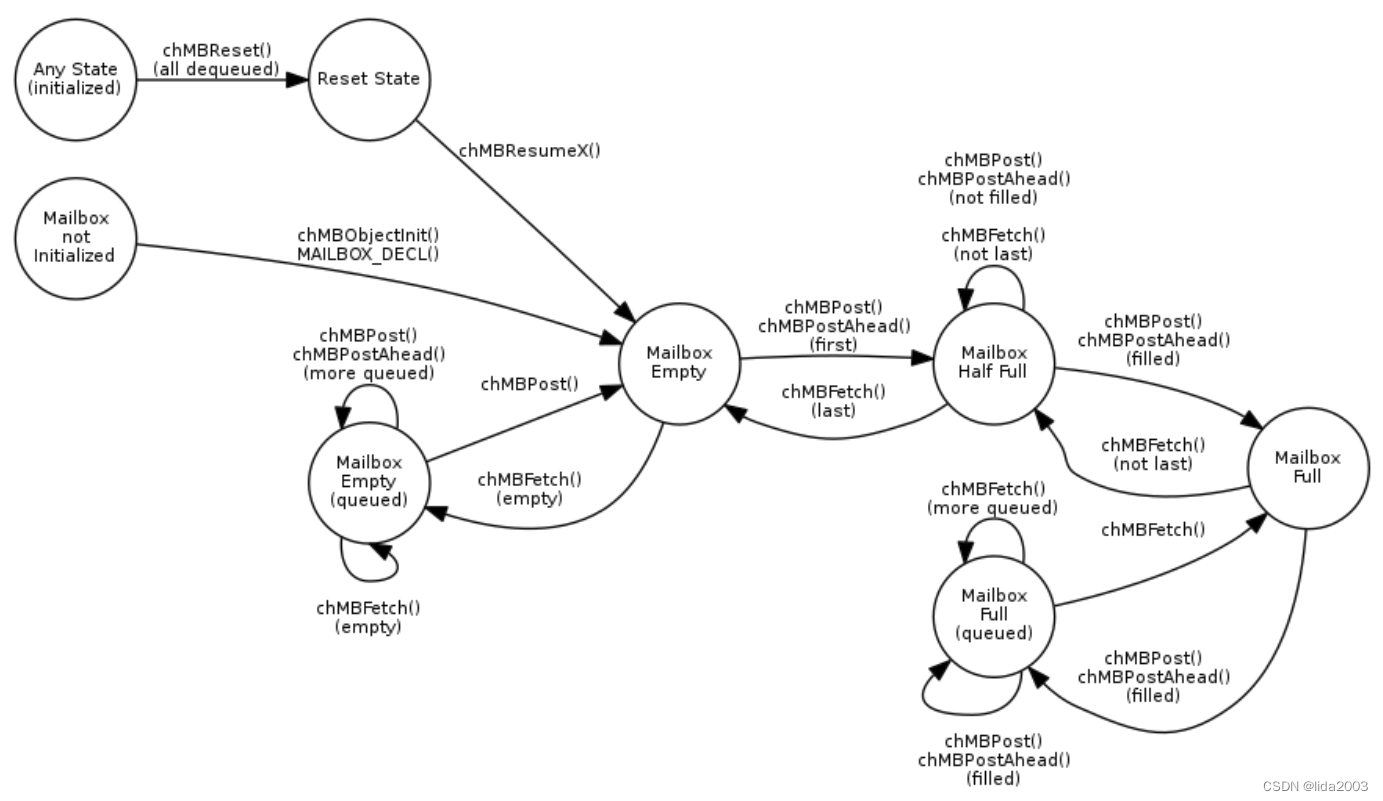
2.16.3 Mailboxes
Queues of asynchronous messages, this mechanism was previously in the RT kernel and has been moved into OSLIB.
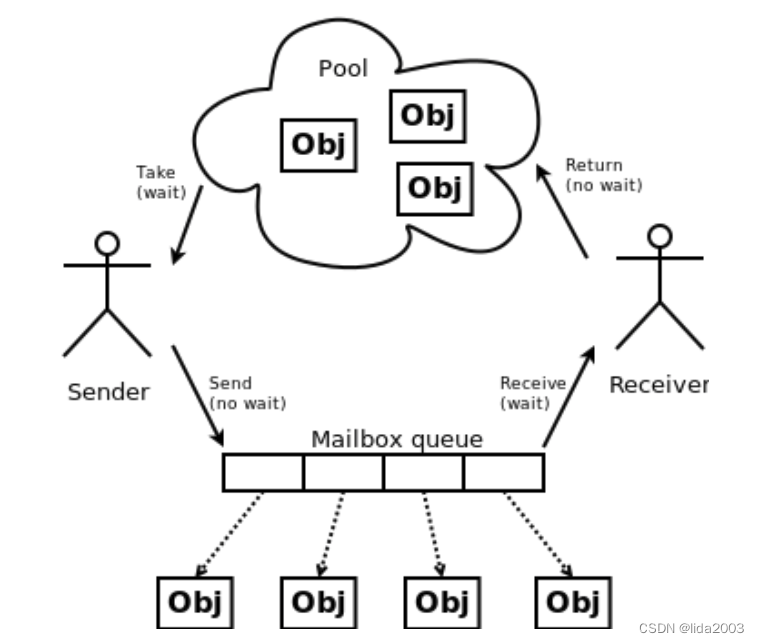
2.16.4 Objects FIFOs
Queues of objects composed by a pool of free object and a mailbox for pointers exchange. It is useful when there is the need to exchange fixed-size objects in a copy-less way.
2.16.5 Pipes
Structure-less streams of bytes exchanged between threads.
2.16.6 Delegate Threads
It is a mechanism that allows to perform function calls in the context of another thread which is acting as a “functions server thread”. Function calls are “delegated” to a dedicated thread which performs the call synchronously.
2.16.7 Jobs Queues
Implements a queue of “jobs” that are consumed and executed by a “jobs server thread” asynchronously. A job is simply a structure containing a function pointer and a pointer argument.
2.16.8 Objects Caches
Implements a cache of fixed-size objects which can be then retrieved by their numeric identifier. It could be used for a disk cache for example.
2.16.9 Objects Factory
A system that allows to allocate other objects dynamically and attribute them a name. Objects can be used by reference, references can be obtained by searching for name.
2.16.10 Notes on Testing
The OSLIB has its own suite of tests, the tests are performed on both RT and NIL host kernels.
3. 参考资料
【1】ArduPilot开源飞控系统之简单介绍
【2】Ardupilot开源飞控之ChibiOS简介
【3】 ChibiOS官方文档
这篇关于ChibiOS简介5/5的文章就介绍到这儿,希望我们推荐的文章对编程师们有所帮助!



