本文主要是介绍ChibiOS简介1/5,希望对大家解决编程问题提供一定的参考价值,需要的开发者们随着小编来一起学习吧!
ChibiOS简介1/5
- 1. 源由
- 2. ChibiOS基础知识1/5
- 2.1 Chapter 1 - Introduction
- 2.1.1 Priciple(设计原则)
- 2.1.2 Fundamental requirements(基本需求)
- 2.2 Chapter 2 - Real Time Systems Concepts
- 2.2.1 System(系统)
- 2.2.2 Classification(分类)
- 2.2.3 Jitter(抖动)
- 2.3 Chapter 3 - Embedded RTOSes
- 2.3.1 Priorities(优先级)
- 2.3.2 Scheduling(调度)
- 2.3.3 Interrupts(中断)
- 2.3.4 Tasks and Threads(任务和线程)
- 2.3.5 Task Types(任务类型)
- 2.3.6 Synchronization(同步)
- 2.3.7 Atomic Operations(原子操作)
- 2.3.8 Critical Sections(临界区域)
- 3. 参考资料
1. 源由
作为后续研读Ardupilot的ChibiOS的垫脚石,先了解下ChibiOS系统。
Ardupilot ChibiOS项目: https://github.com/ArduPilot/ChibiOS
Artery(AT32) porting项目: //Artery官网没有相关porting动作,不过开源github有相关项目。
- https://github.com/dron0gus/artery
- https://github.com/dron0gus/ChibiOS
2. ChibiOS基础知识1/5
2.1 Chapter 1 - Introduction
2.1.1 Priciple(设计原则)
- Elegant
- Fast
- Small
- Static
2.1.2 Fundamental requirements(基本需求)
- Focus for code elegance and consistency, it must be a pleasure to work with the code.
- Fully, unambiguously static.
- Short code paths for all operations, it has to be really fast.
- Compact.
- Feature complete.
- Strong abstraction.
2.2 Chapter 2 - Real Time Systems Concepts
2.2.1 System(系统)
A complex systems can always be decomposed in a set of elementary processes connected in a network, the system has a set of input and output signals, we can still consider them events and reactions but on a system level. A system can also have a global state, information that can optionally be accessed by the various processes in the system.
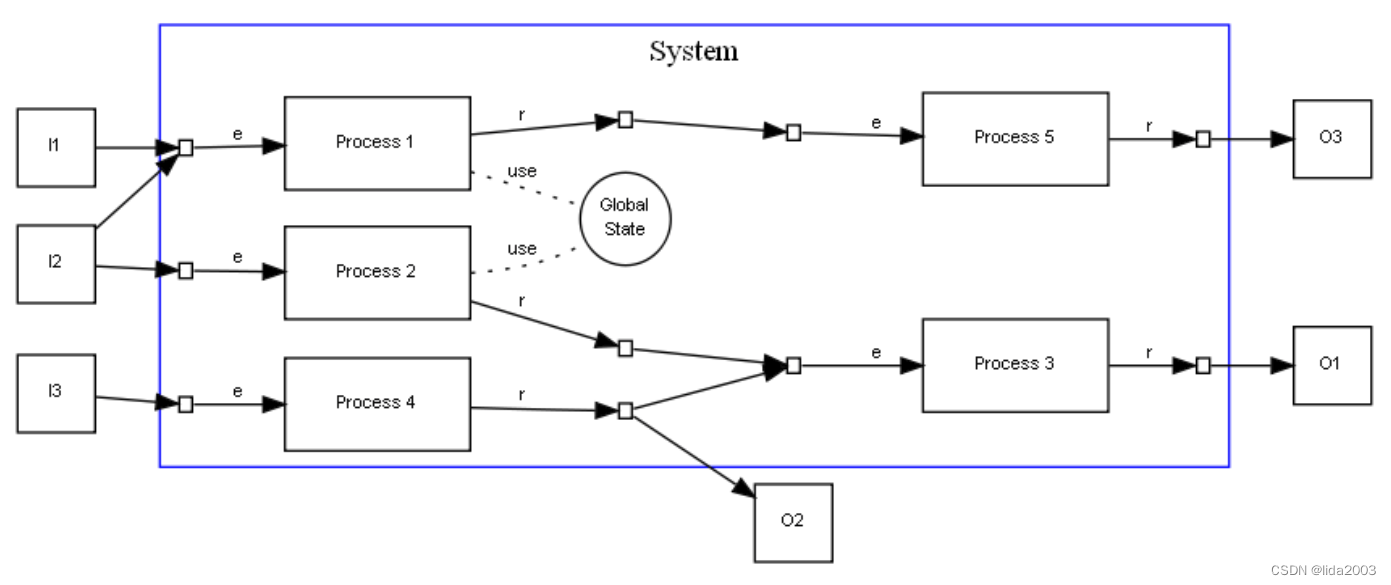
2.2.2 Classification(分类)
- Non Real Time(非实时). A non real time system is a system where there are no deadlines involved. Non realtime systems could be described as follow:
“A non real time system is a system where the programmed reaction to an event will certainly happen sometime in the future”.
- Soft Real Time(软实时). A Soft Real Time (SRT) system is a system where not meeting a deadline can have undesirable but not catastrophic effects, a performance degradation for example. Such systems could be described as follow:
“A soft real time system is a system where the programmed reaction to an event is almost always completed within a known finite time”.
- Hard Real Time(硬实时). An Hard Real Time (HRT) system is a system where not meeting a deadline can have catastrophic effects. Hard realtime systems require a much more strict definition and could be described as follow:
“An hard real time system is a system where the programmed reaction to an event is guaranteed to be completed within a known finite time”.
2.2.3 Jitter(抖动)
Processes never react in a constant time, at a sufficiently small time scale any physical process is bound to have jitter. Unbounded or not assessed jitter is not compatible with an hard realtime system.
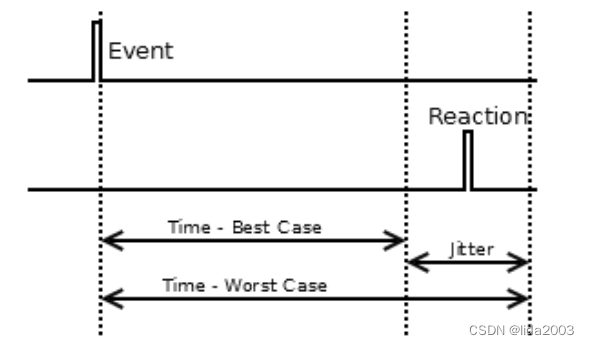
2.3 Chapter 3 - Embedded RTOSes
2.3.1 Priorities(优先级)
-
Static Priorities are usually assigned statically and cannot be changed at runtime.
-
Modifiable Priorities allow for priority to change at runtime in order to implement particular scheduling strategies.
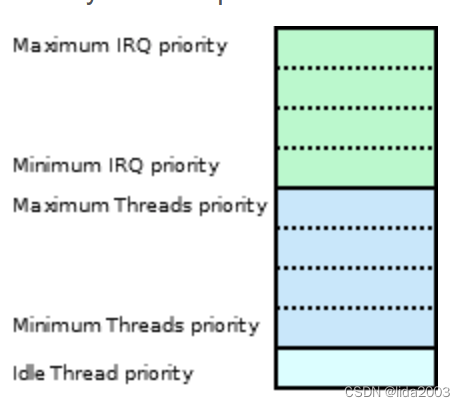
2.3.2 Scheduling(调度)
The scheduling rule is very simple: in any instant, the task being executed is the ready task with the highest priority level. This is true for both tasks and ISRs in the proposed model.
2.3.3 Interrupts(中断)
Interrupts trigger directly ISRs which in turn can wakeup tasks.

 Note: If interrupts processing is an important requirement for your system then you should look for an RTOS/core combination able to efficiently handle nested interrupts on a dedicated interrupts stack.
Note: If interrupts processing is an important requirement for your system then you should look for an RTOS/core combination able to efficiently handle nested interrupts on a dedicated interrupts stack.
2.3.4 Tasks and Threads(任务和线程)
Tasks are the fundamental entities in an RTOS environment. A task can be seen as a virtual CPU inside the system with its own registers bank and stack area. Tasks are scheduled by the RTOS based on their priority as described before. Some RTOSes, like ChibiOS for example, use the term threads for their tasks.
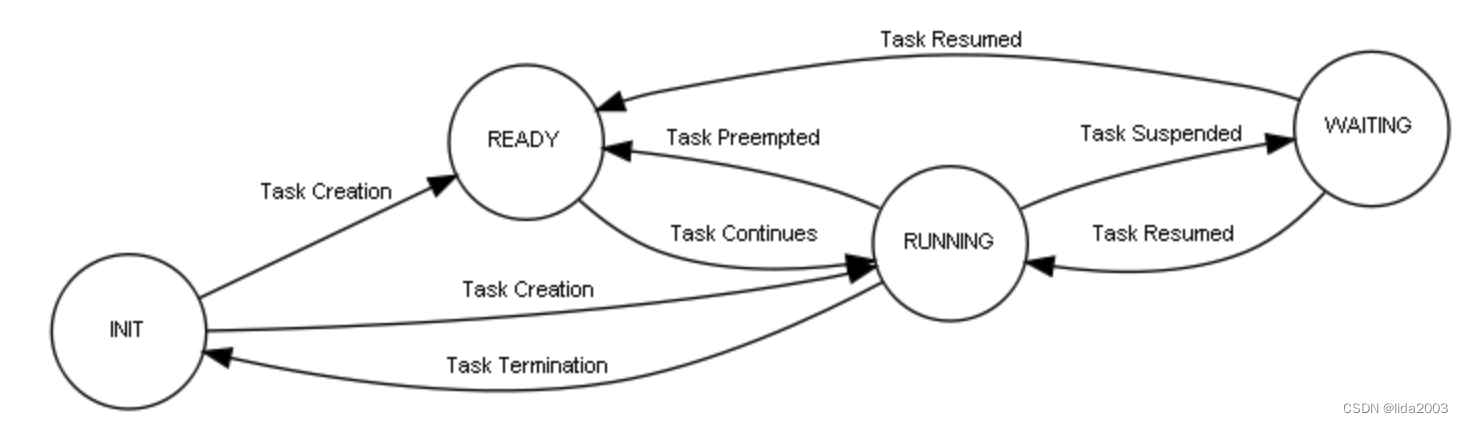
2.3.5 Task Types(任务类型)
-
Periodic Tasks, a periodic task is a task triggered periodically with a fixed time interval. The task is mostly waiting and becomes ready for execution when its internal timer triggers it. The task then performs a brief action and returns to the waiting state.
-
Non-periodic Tasks, this kind of tasks are triggered by an external event, for example an ISR, and are thus not periodic. After performing its programmed action the task returns to the waiting state.
-
Continuous Tasks, tasks should never take the CPU indefinitely, a task running an empty loop would not allow the execution of tasks at lower priority level. The rule is that tasks should wait for events, do their programmed action and then go back to waiting for events. If there are tasks that never release the CPU resource then those must be placed at lowest priority level in the system.
2.3.6 Synchronization(同步)
Usually tasks can use areas of memory as shared data, usually also called Shared Resources, the concurrent access to resources can lead to corruption of said data because the operations performed by tasks may be not atomic.
2.3.7 Atomic Operations(原子操作)
The safest approach is to consider everything not atomic. Failure to understand atomicity and implement proper mutual exclusion is the recipe for disaster, errors are usually random in nature and very hard to detect and debug. Ideally the problem must be resolved in the analysis and design phases by carefully defining the shared resources and defining correct protocols for concurrent access.
Most RTOSes have a specific API for handling of critical sections, the right approach is to use the RTOS-provided API and not make assumptions about how critical sections are or should be implemented. A good RTOS should take care about the best implementation on any given architecture.
2.3.8 Critical Sections(临界区域)
Critical Sections (or critical zones) are probably the most simple and common way to make a non-atomic sequence of code behave atomically.
3. 参考资料
【1】ArduPilot开源飞控系统之简单介绍
【2】 ChibiOS官方文档
这篇关于ChibiOS简介1/5的文章就介绍到这儿,希望我们推荐的文章对编程师们有所帮助!




