本文主要是介绍【C/PTA —— 15.结构体2(课外实践)】,希望对大家解决编程问题提供一定的参考价值,需要的开发者们随着小编来一起学习吧!
C/PTA —— 15.结构体2(课外实践)
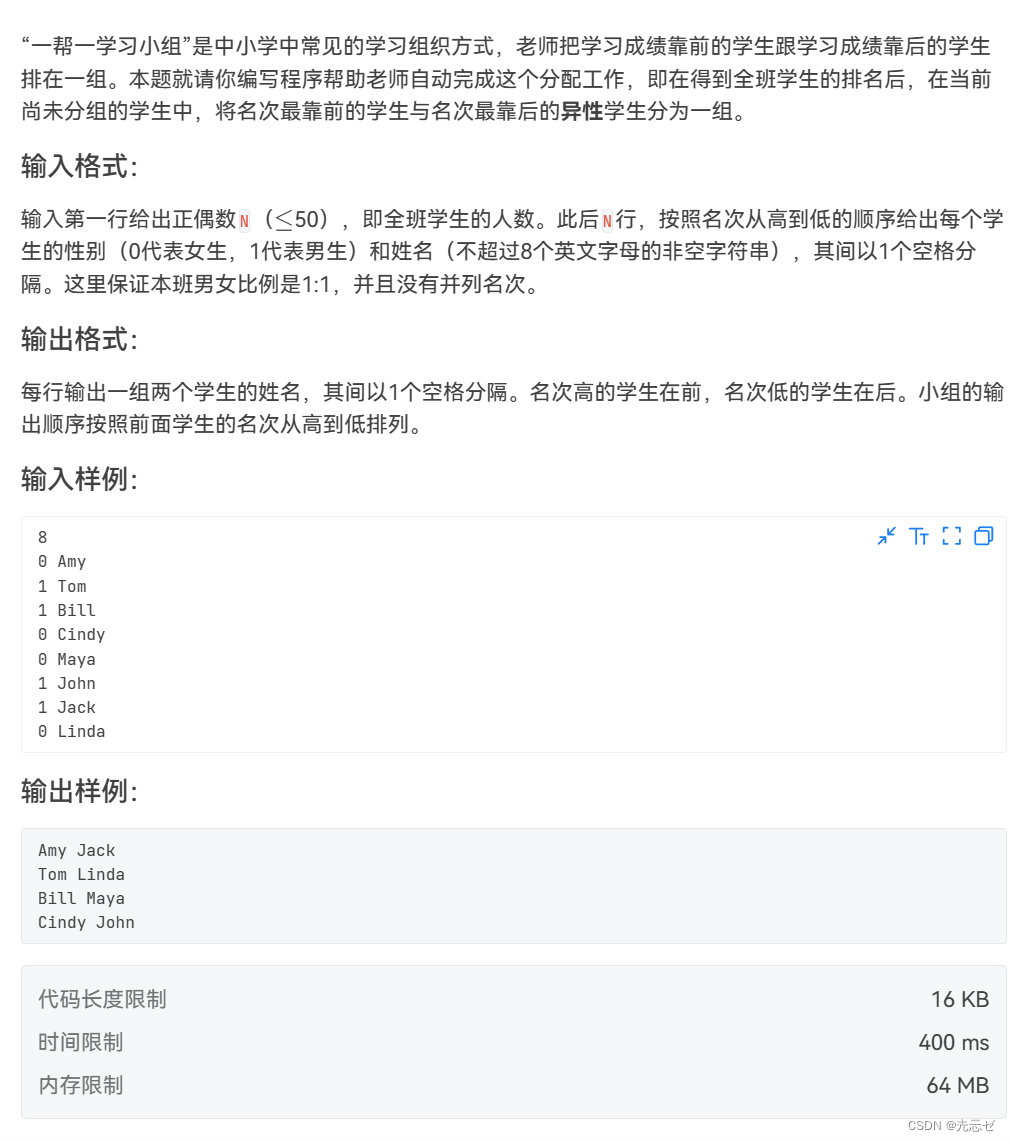
- 7-1 一帮一
- 7-2 考试座位号
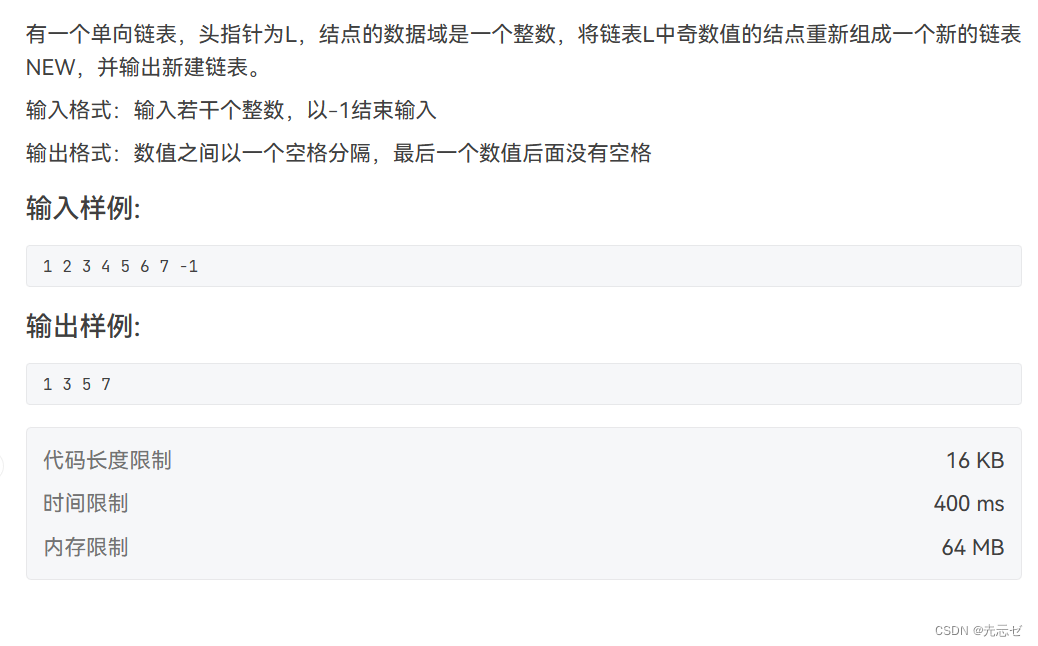
- 7-3 新键表输出
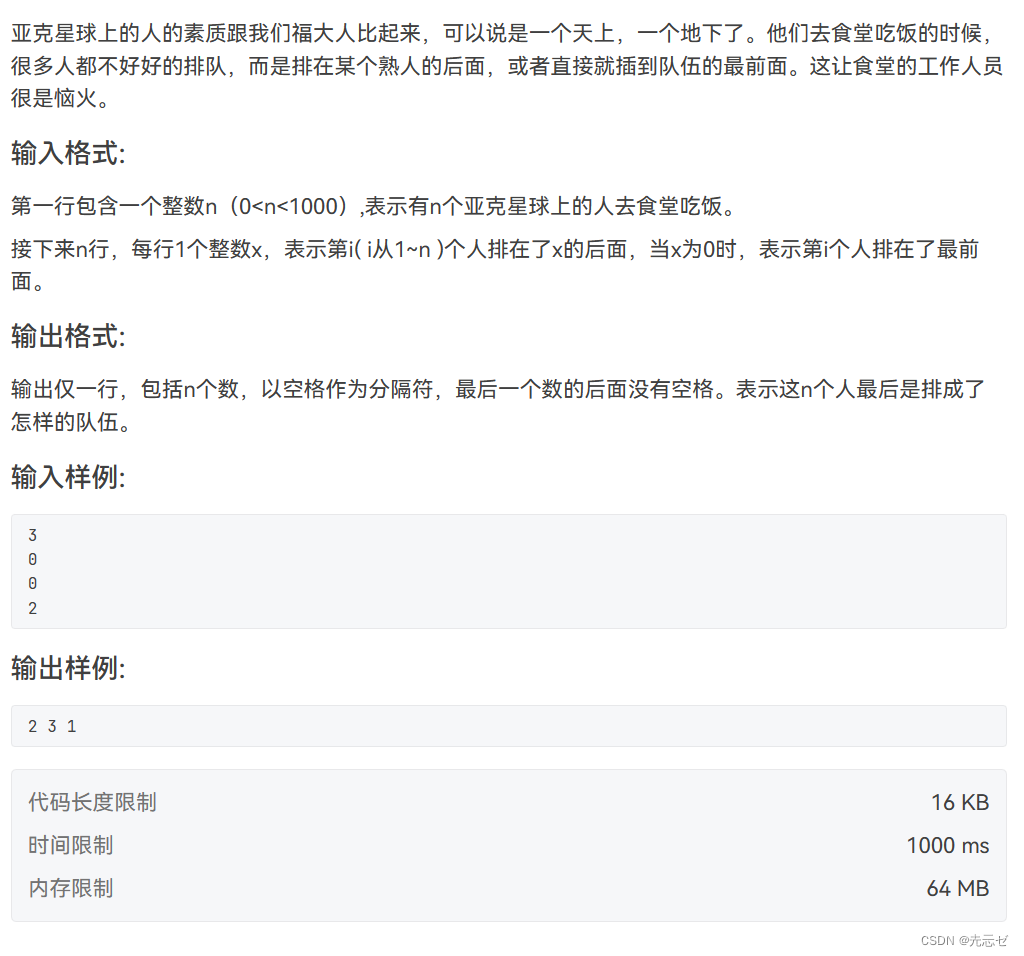
- 7-4 可怕的素质
- 7-5 找出同龄者
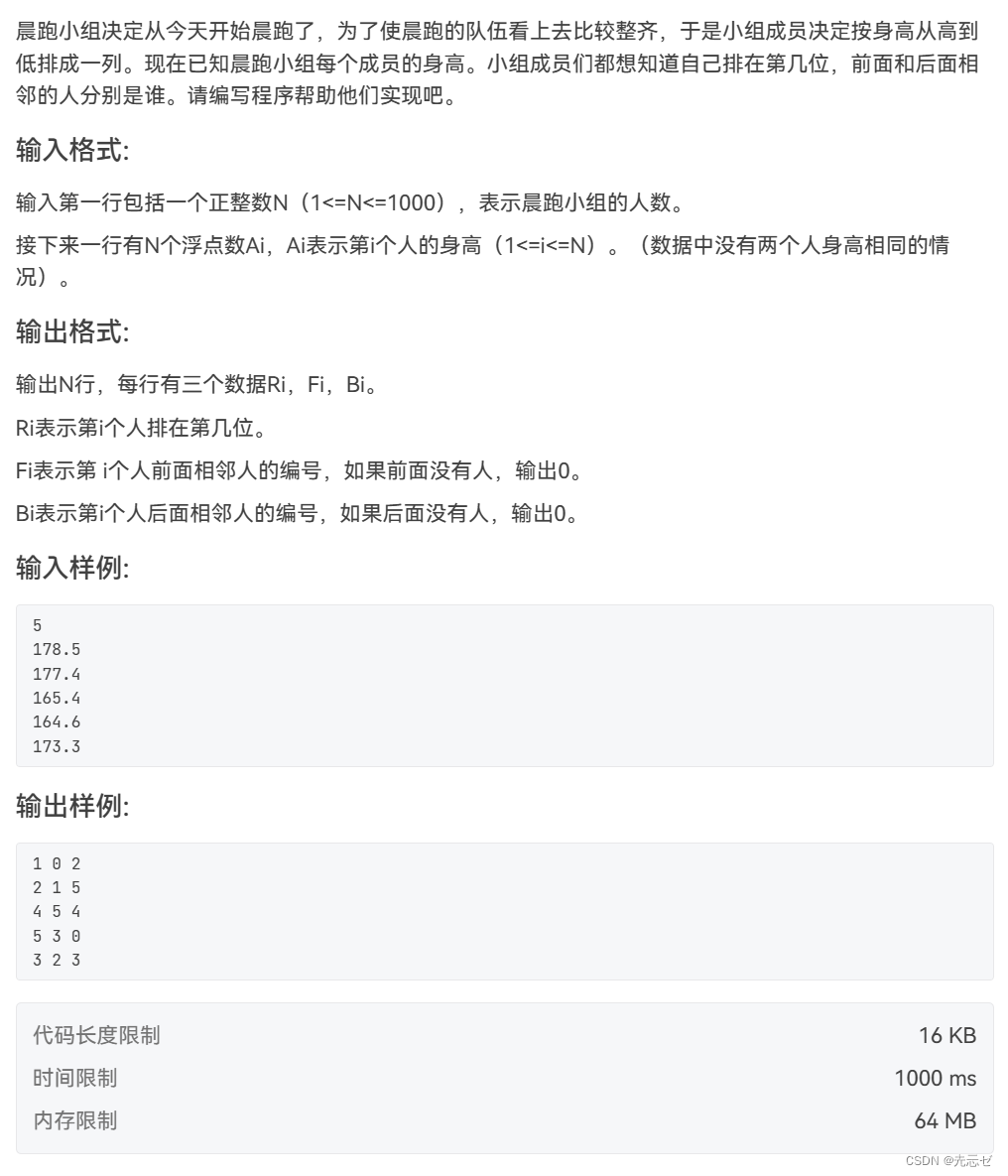
- 7-6 排队
- 7-7 军训
7-1 一帮一
#include<stdio.h>
#include<string.h>struct student
{int a;char name[20];
};struct student1
{int b;char name1[20];
};int main()
{struct student s1[50];struct student1 s2[50];struct student1 s3[50];int i, n, j = 0, t = 0, c, d;scanf("%d", &n);for (i = 0; i < n; i++){scanf("%d %s", &s1[i].a, s1[i].name);}for (i = 0; i < n; i++){if (s1[i].a == 1){s2[j].b = i;strcpy(s2[j].name1, s1[i].name);j++;}if (s1[i].a == 0){s3[t].b = i;strcpy(s3[t].name1, s1[i].name);t++;}}c = n / 2 - 1, d = n / 2 - 1;j = 0, t = 0;for (i = 0; i < n / 2; i++){if (s3[j].b < s2[t].b){printf("%s %s\n", s3[j].name1, s2[c].name1);j++;c--;}else{printf("%s %s\n", s2[t].name1, s3[d].name1);t++;d--;}}return 0;
}
7-2 考试座位号

#include<stdio.h>
struct student
{char num[17];int s;int k;
};int main()
{int n = 0;scanf("%d", &n);struct student stu[1000]={0};for (int i = 0; i < n; i++){scanf("%s %d %d", stu[i].num, &stu[i].s, &stu[i].k);}int m = 0,ret; scanf("%d", &m);for (int i = 0; i < m; i++){scanf("%d", &ret);int j=0;for (j = 0; j < n; j++){if (ret == stu[j].s){printf("%s %d\n", stu[j].num, stu[j].k);}}}return 0;
}
7-3 新键表输出
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>// 定义链表节点结构体
typedef struct ListNode {int val;struct ListNode* next;
} ListNode;// 定义头节点指针
ListNode* createList() {ListNode* head = NULL;int num;while (1) {scanf("%d", &num);if (num == -1) {break;}ListNode* newNode = (ListNode*)malloc(sizeof(ListNode));newNode->val = num;newNode->next = NULL;if (head == NULL) {head = newNode;} else {ListNode* cur = head;while (cur->next != NULL) {cur = cur->next;}cur->next = newNode;}}return head;
}// 遍历链表,将奇数值节点插入新链表
ListNode* createNewList(ListNode* head) {ListNode* newHead = NULL;ListNode* cur = head;while (cur != NULL) {if (cur->val % 2 != 0) {ListNode* newNode = (ListNode*)malloc(sizeof(ListNode));newNode->val = cur->val;newNode->next = NULL;if (newHead == NULL) {newHead = newNode;} else {ListNode* temp = newHead;while (temp->next != NULL) {temp = temp->next;}temp->next = newNode;}}cur = cur->next;}return newHead;
}// 打印链表
void printList(ListNode* head) {ListNode* cur = head;printf("%d", cur->val);cur = cur->next;while (cur != NULL) {printf(" %d", cur->val);cur = cur->next;}printf("\n");
}int main() {// 创建链表ListNode* head = createList();// 创建新链表ListNode* newHead = createNewList(head);// 打印新链表printList(newHead);return 0;
}
7-4 可怕的素质
#include <stdio.h>
#include<stdlib.h>
typedef struct student student;
struct student{int ret;struct student *next;
};
student *insert(int n);
void prin(student*,int n);
int main(){int n;student *stu1;scanf("%d", &n);stu1=insert(n);prin(stu1, n);return 0;
}
void prin(student*stu1,int n){student *p = stu1->next;while(p!=NULL){if(p->next!=NULL)printf("%d ", p->ret);elseprintf("%d", p->ret);p = p->next;}
}
student *insert(int n){student *head;head = (struct student*) malloc(sizeof(student));head->next = NULL;student *p = head, *q;int pos = 0;for (int i = 1; i <= n;i++){scanf("%d", &pos);q = (struct student *)malloc(sizeof(student));q->ret = i;q->next = NULL;if(i==1){head->next = q;}else if(pos==0){q->next = head->next;head->next = q;}else if(pos!=0){p = head->next;while(p->ret!=pos){p = p->next;}q->next = p->next;p->next = q;}}return head;
}
7-5 找出同龄者

#include<stdio.h>
typedef struct student
{char name[10];int age;
}student;
int main()
{int n = 0;student stu[100];scanf("%d", &n);for (int i = 0; i < n; i++){scanf("%s %d", stu[i].name, &stu[i].age);}int m = 0;scanf("%d", &m);int j = 0;for (int i = 0; i < n; i++){if (stu[i].age != m){printf("%s", stu[i].name);j = i;break;}}for (int i = j + 1; i < n; i++){if (stu[i].age != m){printf(" %s", stu[i].name);}}return 0;
}
7-6 排队
#include<stdio.h>
#include<stdlib.h>
typedef struct student student;
//还是双链表好用
struct student{student *prior;student *next;int ri, bi, fi,ret;double height;student *arret;
};
student* create(int n){student *head, *p, *q;head = (student*)malloc(sizeof(student));head->prior = NULL;head->next = NULL;head->arret = NULL;for (int i = 1; i <= n;i++){q = (student*)malloc(sizeof(student));scanf("%lf", &q->height);q->ret = i;if(i==1){head->next = q;head->arret = q;q->arret = NULL;q->prior = head;q->next = NULL;}else {p->next = q;p->arret = q;q->arret = NULL;q->prior = p;q->next = NULL;}p = q;}return head;
}
void swap(student *p1,student *p2){student *p1f, *p1b, *p2f, *p2b;p1f = p1->prior;p1b = p1->next;p2f = p2->prior;p2b = p2->next;p1f->next = p1b;p1b->prior = p1f;p1b->next = p2f;p2f->prior = p1b;p2f->next = p2b;if(p2b!=NULL)p2b->prior = p2f;
}
int main(){int n;scanf("%d", &n);student *stu1;stu1=create(n);student *p = stu1->next;for (int i = 1; i < n;i++){p = stu1->next;for (int j = 1; j < n - i + 1;j++){if(p->height<p->next->height){swap(p,p->next);}else p = p->next;}}p = stu1->next;for (int i = 1; i <= n;i++){if(i==1){p->fi = 0;p->bi = p->next->ret;}else if(i==n){p->bi = 0;p->fi = p->prior->ret;}else {p->fi = p->prior->ret;p->bi = p->next->ret;}p->ri = i;p = p->next;}p = stu1->arret;for (int i = 1; i <= n;i++){printf("%d %d %d\n", p->ri, p->fi, p->bi);p = p->arret;}return 0;
}
7-7 军训
#include<stdio.h>
#include<stdlib.h>
typedef struct queue queue;
struct queue{int rank;queue *prior;queue *next;int size;
};
void print(queue *queue1){queue *p = queue1->next;while(p!=NULL){if(p->next!=NULL)printf("%d ", p->rank);elseprintf("%d\n", p->rank);p = p->next;}
}
queue *delete_LB(queue *queue1){queue *k = queue1;queue1->prior->next = queue1->next;if(queue1->next!=NULL)queue1->next->prior = queue1->prior;queue1 = queue1->prior;free(k);return queue1;
}
queue *create(int n){queue *head;queue *p, *q;head = (queue*)malloc(sizeof(queue));head->prior = NULL;head->next = NULL;for (int i = 1; i <= n;i++){q = (queue *)malloc(sizeof(queue));q->rank = i;if(i==1){head->next = q;q->prior = head;q->next = NULL;}else {p->next = q;q->prior = p;q->next = NULL;}p = q;}return head;
}
int main(){int n;scanf("%d", &n);queue document[105];queue *a;for (int i = 1; i <= n;i++){int count;scanf("%d", &count);a = create(count);a->size = count;queue *p;while(a->size>3){p = a->next;for (int j = 1; j <= count; j++){if (j % 2 == 0)//这里无需判断是否size>3,因为无论是否满足,都必须在进行的一轮内将所有2的报数删除;{p=delete_LB(p);a->size--;}p = p->next;}count = a->size;p = a->next;if(a->size>3)//这里加上size>3的判断才能保证n=40的情况下37不会被删除,否则还会进行一次j=3时的删除操作;特殊情况(即处理完上一轮2的报数后size恰好为3,但是此时没有加入判断的话循环会继续运行,会多删除1项){for (int j = 1; j <= count; j++){if (j % 3 == 0) {p = delete_LB(p);a->size--;}p = p->next;}}count = a->size;}document[i] = *a;}for (int i = 1; i <= n;i++){print(&document[i]);}return 0;
}
这篇关于【C/PTA —— 15.结构体2(课外实践)】的文章就介绍到这儿,希望我们推荐的文章对编程师们有所帮助!


