本文主要是介绍arduino/mixly TFT显示SD卡的图片,希望对大家解决编程问题提供一定的参考价值,需要的开发者们随着小编来一起学习吧!
一、器材
SD卡模块
1.8寸TFT屏,ST7735
arduino uno开发板

SD卡

二、接线
| TFT屏 | arduino uno |
| GND | GND |
| VCC | 5V |
| SCL | D13 |
| SDA | D11 |
| RES | D8 |
| DC | D10 |
| CS | D9 |
| BL | D7 |
| SD卡模块 | arduino uno |
| GND | GND |
| VCC | 5V |
| MISO | D12 |
| MOSI | D11 |
| CLK | D13 |
| CS | D4 |
三、正式开始
首先我们从网上找到一张想要显示的图片,比如下面这一张
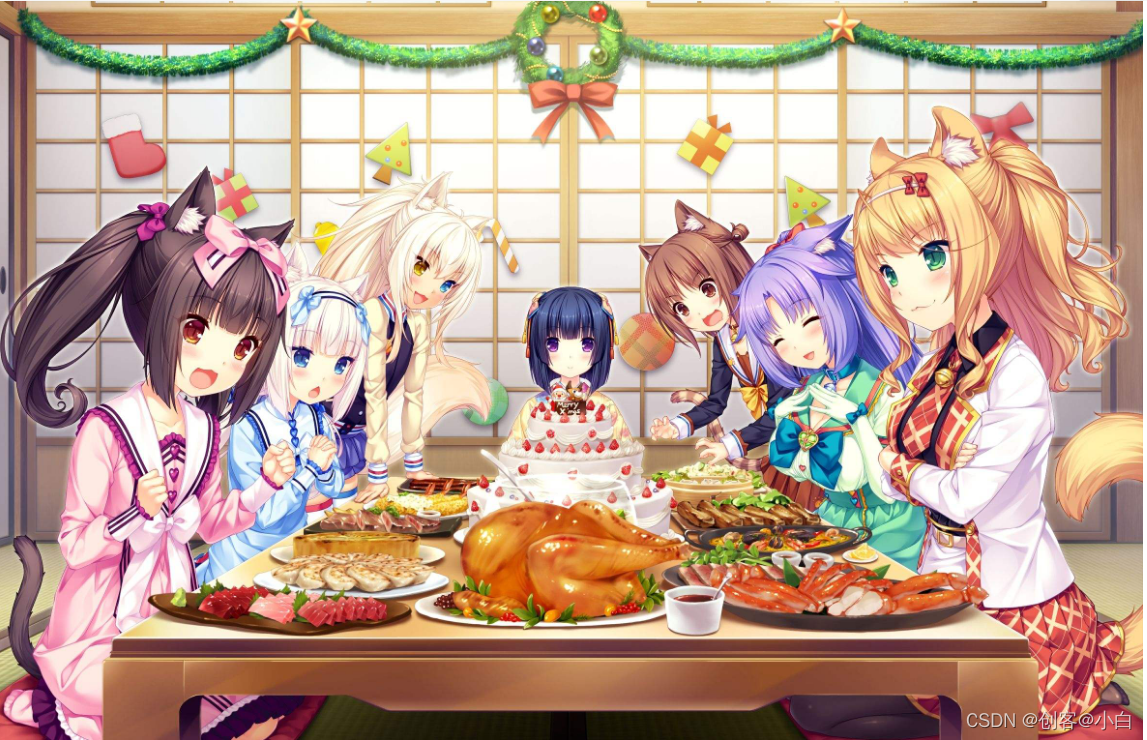

然后我们打开电脑自带的画图工具打开这张图片
然后重新调整像素大小到以下图所示160*128
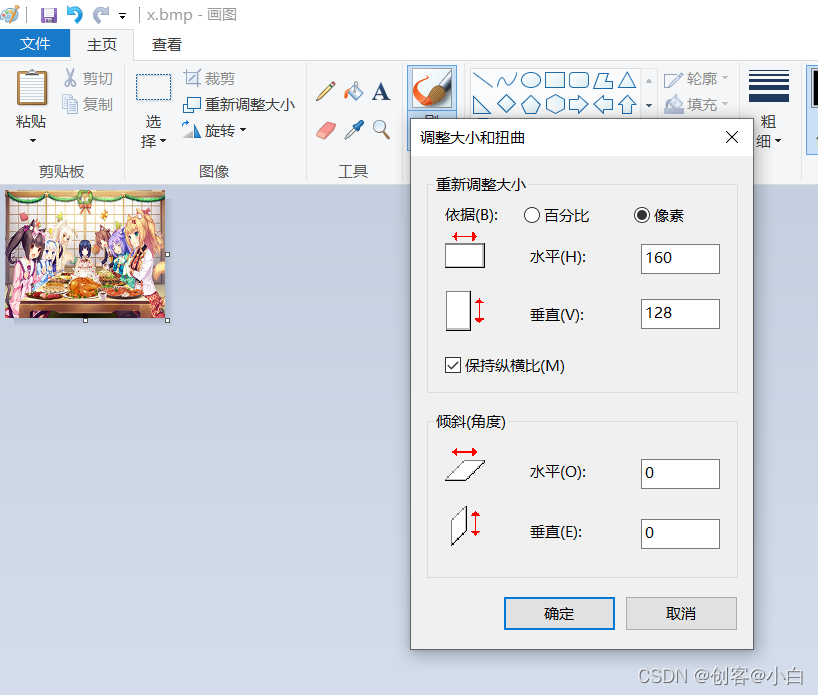
然后保存为。bmp格式的图片,这里我保存为x.bmp然后移动到SD卡中,再把SD卡插到SD卡模块中即可。
再复制以下程序,下载到arduino中
#include <Adafruit_GFX.h>
#include <Adafruit_ST7735.h>
#include <SD.h>
#include <SPI.h>#if defined(__SAM3X8E__)#undef __FlashStringHelper::F(string_literal)#define F(string_literal) string_literal
#endif// TFT display and SD card will share the hardware SPI interface.
// Hardware SPI pins are specific to the Arduino board type and
// cannot be remapped to alternate pins. For Arduino Uno,
// Duemilanove, etc., pin 11 = MOSI, pin 12 = MISO, pin 13 = SCK.
#define SD_CS 4 // Chip select line for SD card
#define TFT_CS 9 // Chip select line for TFT display
#define TFT_DC 10 // Data/command line for TFT
#define TFT_RST 8 // Reset line for TFT (or connect to +5V)Adafruit_ST7735 tft = Adafruit_ST7735(TFT_CS, TFT_DC, TFT_RST);#define BUFFPIXEL 20void bmpDraw(char *filename, uint8_t x, uint8_t y) {File bmpFile;int bmpWidth, bmpHeight; // W+H in pixelsuint8_t bmpDepth; // Bit depth (currently must be 24)uint32_t bmpImageoffset; // Start of image data in fileuint32_t rowSize; // Not always = bmpWidth; may have paddinguint8_t sdbuffer[3*BUFFPIXEL]; // pixel buffer (R+G+B per pixel)uint8_t buffidx = sizeof(sdbuffer); // Current position in sdbufferboolean goodBmp = false; // Set to true on valid header parseboolean flip = true; // BMP is stored bottom-to-topint w, h, row, col;uint8_t r, g, b;uint32_t pos = 0, startTime = millis();if((x >= tft.width()) || (y >= tft.height())) return;Serial.println();Serial.print("Loading image '");Serial.print(filename);Serial.println('\'');// Open requested file on SD cardif ((bmpFile = SD.open(filename)) == NULL) {Serial.print("File not found");return;}// Parse BMP headerif(read16(bmpFile) == 0x4D42) { // BMP signatureSerial.print("File size: "); Serial.println(read32(bmpFile));(void)read32(bmpFile); // Read & ignore creator bytesbmpImageoffset = read32(bmpFile); // Start of image dataSerial.print("Image Offset: "); Serial.println(bmpImageoffset, DEC);// Read DIB headerSerial.print("Header size: "); Serial.println(read32(bmpFile));bmpWidth = read32(bmpFile);bmpHeight = read32(bmpFile);if(read16(bmpFile) == 1) { // # planes -- must be '1'bmpDepth = read16(bmpFile); // bits per pixelSerial.print("Bit Depth: "); Serial.println(bmpDepth);if((bmpDepth == 24) && (read32(bmpFile) == 0)) { // 0 = uncompressedgoodBmp = true; // Supported BMP format -- proceed!Serial.print("Image size: ");Serial.print(bmpWidth);Serial.print('x');Serial.println(bmpHeight);// BMP rows are padded (if needed) to 4-byte boundaryrowSize = (bmpWidth * 3 + 3) & ~3;// If bmpHeight is negative, image is in top-down order.// This is not canon but has been observed in the wild.if(bmpHeight < 0) {bmpHeight = -bmpHeight;flip = false;}// Crop area to be loadedw = bmpWidth;h = bmpHeight;if((x+w-1) >= tft.width()) w = tft.width() - x;if((y+h-1) >= tft.height()) h = tft.height() - y;// Set TFT address window to clipped image boundstft.startWrite();tft.setAddrWindow(x, y, w, h);for (row=0; row<h; row++) { // For each scanline...// Seek to start of scan line. It might seem labor-// intensive to be doing this on every line, but this// method covers a lot of gritty details like cropping// and scanline padding. Also, the seek only takes// place if the file position actually needs to change// (avoids a lot of cluster math in SD library).if(flip) // Bitmap is stored bottom-to-top order (normal BMP)pos = bmpImageoffset + (bmpHeight - 1 - row) * rowSize;else // Bitmap is stored top-to-bottompos = bmpImageoffset + row * rowSize;if(bmpFile.position() != pos) { // Need seek?tft.endWrite();bmpFile.seek(pos);buffidx = sizeof(sdbuffer); // Force buffer reload}for (col=0; col<w; col++) { // For each pixel...// Time to read more pixel data?if (buffidx >= sizeof(sdbuffer)) { // IndeedbmpFile.read(sdbuffer, sizeof(sdbuffer));buffidx = 0; // Set index to beginningtft.startWrite();}// Convert pixel from BMP to TFT format, push to displayr = sdbuffer[buffidx++];g = sdbuffer[buffidx++];b = sdbuffer[buffidx++];tft.pushColor(tft.color565(r,g,b));} // end pixel} // end scanlinetft.endWrite();Serial.print("Loaded in ");Serial.print(millis() - startTime);Serial.println(" ms");} // end goodBmp}}bmpFile.close();if(!goodBmp) Serial.println("BMP format not recognized.");
}// These read 16- and 32-bit types from the SD card file.
// BMP data is stored little-endian, Arduino is little-endian too.
// May need to reverse subscript order if porting elsewhere.uint16_t read16(File f) {uint16_t result;((uint8_t *)&result)[0] = f.read(); // LSB((uint8_t *)&result)[1] = f.read(); // MSBreturn result;
}uint32_t read32(File f) {uint32_t result;((uint8_t *)&result)[0] = f.read(); // LSB((uint8_t *)&result)[1] = f.read();((uint8_t *)&result)[2] = f.read();((uint8_t *)&result)[3] = f.read(); // MSBreturn result;
}void setup(void) {pinMode(12,INPUT); // Set SD's MISO IO State, VERY IMPORTANT!Serial.begin(9600);// Initialize 1.8" TFTtft.initR(INITR_GREENTAB); // initialize a ST7735S chip, green tabtft.setRotation(3);Serial.println("OK!");tft.fillScreen(ST7735_BLACK);
}void loop() {Serial.print("Initializing SD card...");if (!SD.begin(SD_CS)) {Serial.println("failed!");tft.setTextSize(2);tft.fillScreen(ST7735_BLACK);tft.setCursor(0, 0);tft.setTextColor(ST7735_BLUE);tft.print("SD Card init error!");return;}bmpDraw("x.bmp", 0, 0);
}
效果

这篇关于arduino/mixly TFT显示SD卡的图片的文章就介绍到这儿,希望我们推荐的文章对编程师们有所帮助!





