本文主要是介绍OCP Java17 SE Developers 复习题08,希望对大家解决编程问题提供一定的参考价值,需要的开发者们随着小编来一起学习吧!

======================== 答案 ========================
======================== 答案 ========================
======================== 答案 ========================
A. This code is correct. Line 8 creates a lambda expression that checks whether the age is less than 5, making option A correct. Since there is only one parameter and it does not specify a type, the parentheses around the parameter are optional. Lines 11 and 13 use the Predicate interface, which declares a test() method.

======================== 答案 ========================
======================== 答案 ========================
======================== 答案 ========================
C. The interface takes two int parameters. The code on line 7 attempts to use them as if h is a String making option C correct. It is tricky to use types in a lambda when they are implicitly specified. Remember to check the interface for the real type.

======================== 答案 ========================
======================== 答案 ========================
======================== 答案 ========================
A, C. A functional interface can contain any number of non-abstract methods, including default, private, static, and private static. For this reason, option A is correct, and option D is incorrect. Option B is incorrect, as classes are never considered functional interfaces. A functional interface contains exactly one abstract method, although methods that have matching signatures as public methods in java.lang.Object do not count toward the single method test. For these reasons, option C is correct. Finally, option E is incorrect. While a functional interface can be marked with the @FunctionalInterface annotation, it is not required.

======================== 答案 ========================
======================== 答案 ========================
======================== 答案 ========================
A, F. Option B is incorrect because it does not use the return keyword. Options C, D, and E are incorrect because the variable e is already in use from the lambda and cannot be redefined. Additionally, option C is missing the return keyword, and option E is missing the semicolon. Therefore, options A and F are correct.

======================== 答案 ========================
======================== 答案 ========================
======================== 答案 ========================
A, C, E. Java includes support for three primitive streams, along with numerous functional interfaces to go with them: int, double, and long. For this reason, options C and E are correct. Additionally, there is a BooleanSupplier functional interface, making option A correct. Java does not include primitive streams or related functional interfaces for other numeric data types, making options B and D incorrect. Option F is incorrect because String is not a primitive but an object. Only primitives have custom suppliers.

======================== 答案 ========================
======================== 答案 ========================
======================== 答案 ========================
A, C. Predicate<String> takes a parameter list of one parameter using the specified type. Options E and F are incorrect because they specify the wrong type. Options B and D are incorrect because they use the wrong syntax for the arrow operator. This leaves us with options A and C as the answers.

======================== 答案 ========================
======================== 答案 ========================
======================== 答案 ========================
E. While there appears to have been a variable name shortage when this code was written, it does compile. Lambda variables and method names are allowed to be the same. The x lambda parameter is scoped to within each lambda, so it is allowed to be reused. The type is inferred by the method it calls. The first lambda maps x to a String and the second to a Boolean. Therefore, option E is correct.
======================== 答案 ========================
======================== 答案 ========================
======================== 答案 ========================

======================== 答案 ========================
======================== 答案 ========================
======================== 答案 ========================
E. The question starts with a UnaryOperator<Integer>, which takes one parameter and returns a value of the same type. Therefore, option E is correct, as UnaryOperator extends Function. Notice that other options don't even compile because they have the wrong number of generic types for the functional interface provided. You should know that a BiFunction<T,U,R> takes three generic arguments, a BinaryOperator<T> takes one generic argument, and a Function<T,R> takes two generic arguments.

======================== 答案 ========================
======================== 答案 ========================
======================== 答案 ========================
A, F. Option A is correct and option B is incorrect because a Supplier returns a value while a Consumer takes one and acts on it. Option C is tricky. IntSupplier does return an int. However, the option asks about IntegerSupplier, which doesn't exist. Option D is incorrect because a Predicate returns a boolean. It does have a method named test(), making option F correct. Finally, option E is incorrect because Function has an apply() method.

======================== 答案 ========================
======================== 答案 ========================
======================== 答案 ========================
A, B, C. Since the scope of start and c is within the lambda, the variables can be declared or updated after it without issue, making options A, B, and C correct. Option D is incorrect because setting end prevents it from being effectively final.

======================== 答案 ========================
======================== 答案 ========================
======================== 答案 ========================
D. The code does not compile because the lambdas are assigned to var. The compiler does not have enough information to determine they are of type Predicate<String>. Therefore, option D is correct.

======================== 答案 ========================
======================== 答案 ========================
======================== 答案 ========================
A. The a.compose(b) method calls the Function parameter b before the reference Function variable a. In this case, that means that we multiply by 3 before adding 4. This gives a result of 7, making option A correct.

======================== 答案 ========================
======================== 答案 ========================
======================== 答案 ========================
E. Lambdas are only allowed to reference final or effectively final variables. You can tell the variable j is effectively final because adding a final keyword before it wouldn't introduce a compiler error. Each time the else statement is executed, the variable is redeclared and goes out of scope. Therefore, it is not reassigned. Similarly, length is effectively final. There are no compiler errors, and option E is correct.

======================== 答案 ========================
======================== 答案 ========================
======================== 答案 ========================
B, D. Option B is a valid functional interface, one that could be assigned to a Consumer<Camel> reference. Notice that the final modifier is permitted on variables in the parameter list. Option D is correct, as the exception is being returned as an object and not thrown. This would be compatible with a BiFunction that included RuntimeException as its return type.
Options A and G are incorrect because they mix format types for the parameters. Option C is invalid because the variable b is used twice. Option E is incorrect, as a return statement is permitted only inside braces ({}). Option F is incorrect because the variable declaration requires a semicolon (;) after it.


======================== 答案 ========================
======================== 答案 ========================
======================== 答案 ========================
A, F. Option A is a valid lambda expression. While main() is a static method, it can access age since it is using a reference to an instance of Hyena, which is effectively final in this method. Since var is not a reserved word, it may be used for variable names. Option F is also correct, with the lambda variable being a reference to a Hyena object. The variable is processed using deferred execution in the testLaugh() method.
Options B and E are incorrect; since the local variable age is not effectively final, this would lead to a compilation error. Option C would also cause a compilation error, since the expression uses the variable name p, which is already declared within the method. Finally, option D is incorrect, as this is not even a lambda expression.

======================== 答案 ========================
======================== 答案 ========================
======================== 答案 ========================
C. Lambdas are not allowed to redeclare local variables, making options A and B incorrect. Option D is incorrect because setting end prevents it from being effectively final. Lambdas are only allowed to reference final or effectively final variables. Option C compiles since chars is not used.

======================== 答案 ========================
======================== 答案 ========================
======================== 答案 ========================
C. Line 8 uses braces around the body. This means the return keyword and semicolon are required. Since the code doesn't compile, option C is the answer
======================== 答案 ========================
======================== 答案 ========================
======================== 答案 ========================
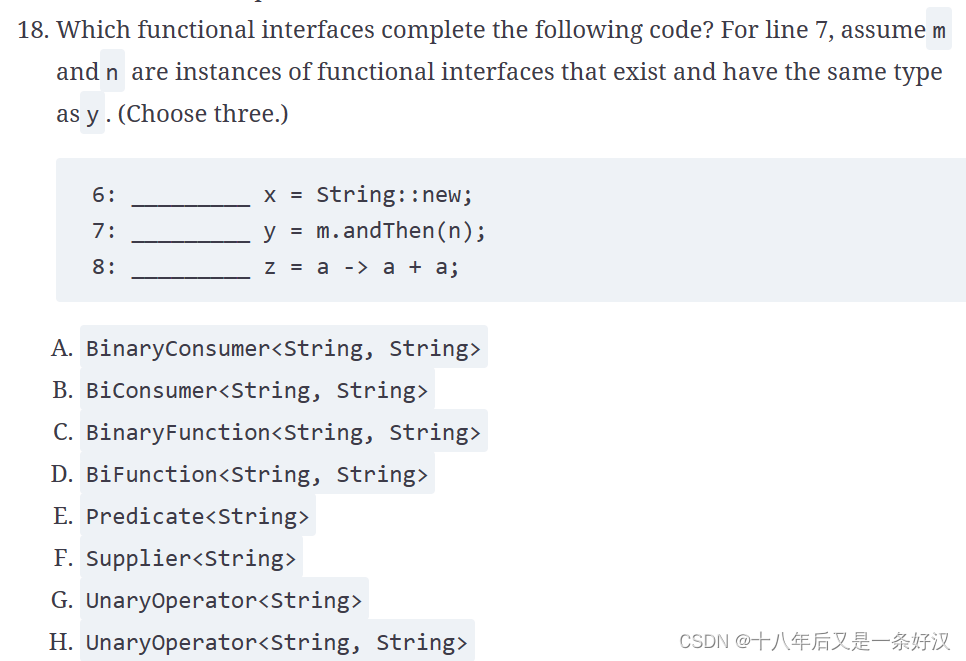
B, F, G. We can eliminate four choices right away. Options A and C are there to mislead you; these interfaces don't exist. Option D is incorrect because a BiFunction<T,U,R> takes three generic arguments, not two. Option E is incorrect because none of the examples returns a boolean.
The declaration on line 6 doesn't take any parameters, and it returns a String, so a Supplier<String> can fill in the blank, making option F correct. The declaration on line 7 requires you to recognize that Consumer and Function, along with their binary equivalents, have an andThen() method. This makes option B correct. Finally, line 8 takes a single parameter, and it returns the same type, which is a UnaryOperator. Since the types are the same, only one generic parameter is needed, making option G correct.

======================== 答案 ========================
======================== 答案 ========================
======================== 答案 ========================
F. While there is a lot in this question trying to confuse you, note that there are no options about the code not compiling. This allows you to focus on the lambdas and method references. Option A is incorrect because a Consumer requires one parameter. Options B and C are close. The syntax for a lambda is correct. However, s is already defined as a local variable, and therefore the lambda can't redefine it. Options D and E use incorrect syntax for a method reference. Option F is correct.


======================== 答案 ========================
======================== 答案 ========================
======================== 答案 ========================
E. Option A does not compile because the second statement within the block is missing a semicolon (;) at the end. Option B is an invalid lambda expression because t is defined twice: in the parameter list and within the lambda expression. Options C and D are both missing a return statement and semicolon. Options E and F are both valid lambda expressions, although only option E matches the behavior of the Sloth class. In particular, option F only prints Sleep:, not Sleep: 10.0.

======================== 答案 ========================
======================== 答案 ========================
======================== 答案 ========================
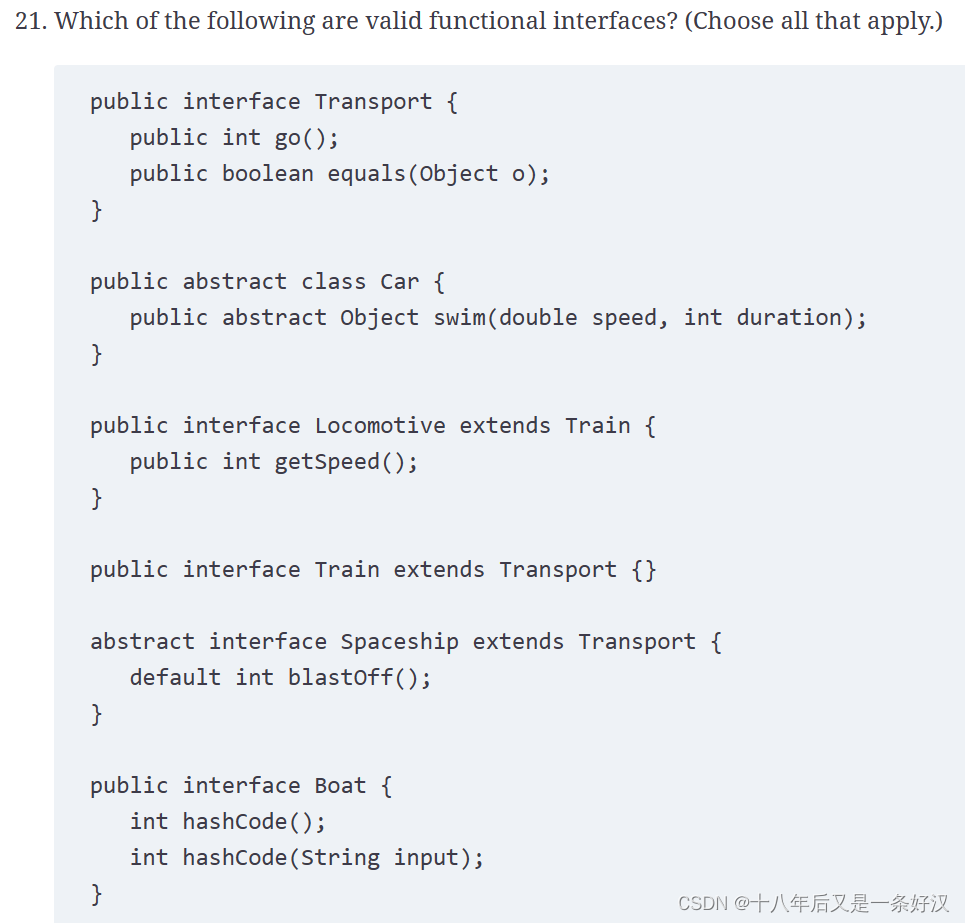
A, E, F. A valid functional interface is one that contains a single abstract method, excluding any public methods that are already defined in the java.lang.Object class. Transport and Boat are valid functional interfaces, as they each contain a single abstract method: go() and hashCode(String), respectively. This gives us options A and E. Since the other methods are part of Object, they do not count as abstract methods. Train is also a functional interface since it extends Transport and does not define any additional abstract methods. This adds option F as the final correct answer.
Car is not a functional interface because it is an abstract class. Locomotive is not a functional interface because it includes two abstract methods, one of which is inherited. Finally, Spaceship is not a valid interface, let alone a functional interface, because a default method must provide a body. A quick way to test whether an interface is a functional interface is to apply the @FunctionalInterface annotation and check if the code still compiles.
这篇关于OCP Java17 SE Developers 复习题08的文章就介绍到这儿,希望我们推荐的文章对编程师们有所帮助!




