本文主要是介绍week07_day06_Map,希望对大家解决编程问题提供一定的参考价值,需要的开发者们随着小编来一起学习吧!
Map接口概述:
将键映射到值的对象。(我们可以根据键快速地查找到值)
Map 中键是唯一的 (不能包含重复的键)
每个键最多只能映射到一个值。
关于映射:
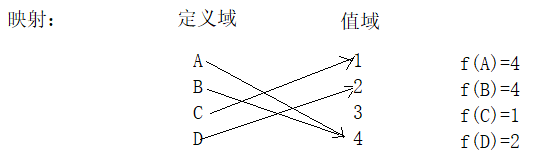
Map接口API:

- V put(K key, V value)
将指定的值与此映射中的指定键关联(可选操作)。如果此映射以前包含一个该键的映射关系,则用指定值替换旧值(当且仅当 m.containsKey(k) 返回 true 时,才能说映射 m 包含键 k 的映射关系)。
返回以前与 key 关联的值,如果没有针对 key 的映射关系,则返回 null。(如果该实现支持 null 值,则返回 null 也可能表示此映射以前将 null 与 key 关联)。 - void putAll(Map<? extends K,? extends V> m)
从指定映射中将所有映射关系复制到此映射中(可选操作)。
如果key已经存在就会更新value,key不存在就会添加进去。 - V remove(Object key)
如果存在一个键的映射关系,则将其从此映射中移除(可选操作)。
返回此映射中以前关联该键的值,如果此映射不包含该键的映射关系,则返回 null。
key对应的value可以为null,所以不能通过get(key) != null来判断key是否存在,应当通过containsKey(Object key) 来判断。
- Set<Map.Entry<K,V>> entrySet()
返回此映射中包含的映射关系的 Set 视图。
关于Map.Entry<K,V>,是Map接口的内部接口:

····················································································································································································································
HashMap概述:
基于哈希表的Map接口实现。
允许null键和null值。
不保证映射的顺序,特别是它不保证该顺序恒久不变。
不同步。
HashMap和HashSet的构造方法一样:

HashMap是基于哈希表的 Map 接口的实现。此实现提供所有可选的映射操作,并允许使用 null 值和 null 键。(除了非同步和允许使用 null 之外,HashMap 类与 Hashtable 大致相同。)此类不保证映射的顺序,特别是它不保证该顺序恒久不变。
HashMap VS Hashtable
相同点:
底层的数据结构都是哈希表
不同点:
a. HashMap是不同步的, Hashtable是同步的
b. HashMap可以允许null键和null值,Hashtable不允许null键和null值
····················································································································································································································
LinkedHashMap概述:
HashMap的子类
Map 接口的哈希表和链表实现,具有可预知的迭代顺序.
链表定义了迭代顺序,该迭代顺序就是键值对的插入顺序。
不同步。
LinkedHashMap是Map 接口的哈希表和链接列表实现,具有可预知的迭代顺序。此实现与 HashMap 的不同之处在于,后者维护着一个运行于所有键值对的双重链接列表。此链接列表定义了迭代顺序,该迭代顺序通常就是将键插入到映射中的顺序(插入顺序)。注意,如果在映射中重新插入 键,则插入顺序不受影响。(如果在调用 m.put(k, v) 前 m.containsKey(k) 返回了 true,则调用时会将键 k 重新插入到映射 m 中。)
为什么要注意这一点呢?
在week06_day02中讲过LRU算法,

改进:能不能够在O(1)的时间复杂度内完成所有操作?
LRU:哈希表+双向链表
但LRU应当将最近使用的结点删除,然后重新插入到head位置,而LinkedHashMap仅仅只是改变结点的value值,并不会改变结点的位置,所以,不能直接使用LinkedHashMap当做LRU的缓存。
····················································································································································································································
TreeMap概述:
底层的数据结构是红黑树。
如果创建对象时,没有传入 Comparator 对象,键将按自然顺序进行排序。
如果创建对象时,传入了 Comparator 对象,键将按 Comparator 进行排序。
不同步。
和TreeSet一样,我们将它的两个构造方法
- TreeMap()
使用键的自然顺序构造一个新的、空的树映射。 - TreeMap(Comparator<? super K> comparator)
构造一个新的、空的树映射,该映射根据给定比较器进行排序。
····················································································································································································································
练习:存储自定义对象
代码一:String类为key,Student类为value
Student类:
public class Student01 {private String name;private int age;public Student01() {}public Student01(String name, int age) {this.name = name;this.age = age;}public String getName() {return name;}public int getAge() {return age;}@Overridepublic String toString() {return "Student01{" +"name='" + name + '\'' +", age=" + age +'}';}}测试类:
public class TreeMapDemo1 {public static void main(String[] args) {TreeMap<String, Student01> map = new TreeMap<>();Student01 s1 = new Student01("Allen", 22);Student01 s2 = new Student01("Beyonce", 23);Student01 s3 = new Student01("Catalina", 24);Student01 s4 = new Student01("Diana", 25);map.put("Allen",s1);map.put("Beyonce",s2);map.put("Catalina",s3);map.put("Diana",s4);System.out.println(map.size()); // 4System.out.println(map);}
}之前写TreeSet的代码时,会发现不在Student类中写implements Comparable的话就没法存入TreeSet,但是现在却存入了,为啥?
因为TreeSet的add方法存入的是TreeMap的key,key必须唯一,可比较,但是现在的代码中,key存的是String,String本身就实现了Comparable接口,而Student是value,value可以相同,也就不需要实现Comparable接口。
····················································································································································································································
代码二:
Student类:
public class Student02 implements Comparable<Student02> {private String name;private int age;public Student02() {}public Student02(String name, int age) {this.name = name;this.age = age;}public String getName() {return name;}public int getAge() {return age;}@Overridepublic String toString() {return "Student01{" +"name='" + name + '\'' +", age=" + age +'}';}@Overridepublic int compareTo(Student02 s) {int cmp = this.age - s.age;cmp = cmp != 0 ? cmp : this.name.compareTo(s.name);return cmp;}
}测试类:
public class TreeMapDemo02 {public static void main(String[] args) {Map<Student02, String> map = new TreeMap<>();Student02 s1 = new Student02("Allen", 22);Student02 s2 = new Student02("Beyonce", 23);Student02 s3 = new Student02("Catalina", 24);Student02 s4 = new Student02("Diana", 25);map.put(s1, "Allen");map.put(s2, "Beyonce");map.put(s3, "Catalina");map.put(s4, "Diana");System.out.println(map.size()); // 4System.out.println(map);}
}····················································································································································································································
代码三:
Student类同代码一
测试类:
public class TreeMapDemo03 {public static void main(String[] args) {Map<Student01, String> map = new TreeMap<>(new Comparator<Student01>() {@Overridepublic int compare(Student01 s1, Student01 s2) {int cmp = s1.getAge() - s2.getAge();cmp = cmp != 0 ? cmp : s1.getName().compareTo(s2.getName());return cmp;}});Student01 s1 = new Student01("Allen", 22);Student01 s2 = new Student01("Beyonce", 23);Student01 s3 = new Student01("Catalina", 24);Student01 s4 = new Student01("Diana", 25);map.put(s1, "Allen");map.put(s2, "Beyonce");map.put(s3, "Catalina");map.put(s4, "Diana");System.out.println(map.size());System.out.println(map);}
}
····················································································································································································································
TreeMap特有的API:
-
K ceilingKey(K key)
返回大于等于给定键的最小键;如果不存在这样的键,则返回 null。 -
K floorKey(K key)
返回小于等于给定键的最大键;如果不存在这样的键,则返回 null。 -
K higherKey(K key)
返回严格大于给定键的最小键;如果不存在这样的键,则返回 null。 -
K lowerKey(K key)
返回严格小于给定键的最大键;如果不存在这样的键,则返回 null。 -
K firstKey()
返回此映射中当前第一个(最低)键。 -
K lastKey()
返回映射中当前最后一个(最高)键 -
Map.Entry<K,V> pollFirstEntry()
移除并返回与此映射中的最小键关联的键-值映射关系;如果映射为空,则返回 null。 -
Map.Entry<K,V> pollLastEntry()
移除并返回与此映射中的最大键关联的键-值映射关系;如果映射为空,则返回 null。 -
NavigableMap<K,V> subMap(K fromKey, boolean fromInclusive, K toKey, boolean toInclusive)
返回此映射的部分视图,其键的范围从 fromKey 到 toKey。
代码演示
public class TreeMapDemo04 {public static void main(String[] args) {TreeMap<Character, String> map = new TreeMap<>();map.put('A', "Allen");map.put('B', "Beyonce");map.put('C', "Catalina");map.put('D', "Diana");map.put('F', "Frances");map.put('X', "Xenia");// K ceilingKey(K key)/*System.out.println(map.ceilingKey('C')); // 'C'System.out.println(map.ceilingKey('E')); // 'F'System.out.println(map.ceilingKey('Z')); // null*/// K floorKey(K key)/*System.out.println(map.floorKey('C')); // CSystem.out.println(map.floorKey('E')); // DSystem.out.println(map.floorKey('0')); // null*/// K higherKey(K key)/*System.out.println(map.higherKey('C')); // 'D'System.out.println(map.higherKey('E')); // 'F'System.out.println(map.higherKey('Z')); // null*/// K lowerKey(K key)/* System.out.println(map.lowerKey('C')); // BSystem.out.println(map.lowerKey('E')); // DSystem.out.println(map.lowerKey('0')); // null*/// K firstKey()/* System.out.println(map.firstKey());System.out.println(map);*/// K lastKey()/*System.out.println(map.lastKey());System.out.println(map);*/// Map.Entry<K,V> pollFirstEntry()/*System.out.println(map.pollFirstEntry());System.out.println(map);*/// Map.Entry<K,V> pollLastEntry()/*System.out.println(map.pollLastEntry());System.out.println(map);*/// 视图技术// NavigableMap<K,V> subMap(K fromKey, boolean fromInclusive, K toKey, boolean toInclusive)NavigableMap<Character, String> subMap = map.subMap('C', true, 'X', false);System.out.println(subMap);subMap.pollFirstEntry();System.out.println(subMap);System.out.println(map);}
}····················································································································································································································
Properties概述:
Hashtable<Object, Object> 的子类
Properties 类表示了一个可持久的属性集。
Properties 可保存在流中或从流中加载。
Properties 中每个键及其对应值都是一个字符串(Sring类型)。
注意事项:不要使用Hashtable里面定义的方法添加键值对!因为它们可以插入不是String 类型的数据。
如果一个Properties中含有非String的键值对,那么这样的Properties是”不安全”的。调用 store 或者 save 方法将失败。

构造方法:
- Properties()
创建一个无默认值的空属性列表。 - Properties(Properties defaults)
创建一个带有指定默认值的空属性列表。
API:
- String getProperty(String key)
用指定的键在此属性列表中搜索属性。 - String getProperty(String key, String defaultValue)
用指定的键在属性列表中搜索属性。
key存在的话返回对应的value,不存在的话返回defaultValue - Object setProperty(String key, String value)
调用 Hashtable 的方法 put。 - Set<String> stringPropertyNames()
返回此属性列表中的键集,其中该键及其对应值是字符串,如果在主属性列表中未找到同名的键,则还包括默认属性列表中不同的键。
public class PropertiesDemo1 {public static void main(String[] args) {Properties info = new Properties();info.setProperty("刘强东", "章泽天");info.setProperty("文章", "马伊利");info.setProperty("贾乃亮", "李小璐");info.setProperty("罗志祥", "周扬青");// System.out.println(info);/*Properties properties = new Properties(info);System.out.println(properties);System.out.println(properties.size());*//*System.out.println(properties.containsKey("刘强东"));System.out.println(properties.getProperty("刘强东"));System.out.println(properties.getProperty("文章"));System.out.println(properties.getProperty("谢霆锋"));*//*properties.setProperty("文章", "");System.out.println(properties.getProperty("文章"));*/// String getProperty(String key)/*System.out.println(info.getProperty("刘强东"));System.out.println(info.getProperty("谢霆锋"));// String getProperty(String key, String defaultValue)System.out.println(info.getProperty("刘强东", "default"));System.out.println(info.getProperty("谢霆锋", "default"));*/Set<String> names = info.stringPropertyNames();for(String key : names) {String value = info.getProperty(key);System.out.println(key + "=" + value);}}
}····················································································································································································································
- void load(InputStream inStream)
从输入流中读取属性列表(键和元素对)。 - void load(Reader reader)
按简单的面向行的格式从输入字符流中读取属性列表(键和元素对)。 - void loadFromXML(InputStream in)
将指定输入流中由 XML 文档所表示的所有属性加载到此属性表中。 - void store(OutputStream out, String comments)
以适合使用 load(InputStream) 方法加载到 Properties 表中的格式,将此 Properties 表中的属性列表(键和元素对)写入输出流。 - void store(Writer writer, String comments)
以适合使用 load(Reader) 方法的格式,将此 Properties 表中的属性列表(键和元素对)写入输出字符。 - void storeToXML(OutputStream os, String comment)
发出一个表示此表中包含的所有属性的 XML 文档。 - void storeToXML(OutputStream os, String comment, String encoding)
使用指定的编码发出一个表示此表中包含的所有属性的 XML 文档。
package com.cskaoyan.map;import java.io.*;
import java.util.Properties;/*
和流相关的API// void store(OutputStream out, String comments)void store(Writer out, String comments)// void load(InputStream inStream)void load(Reader read)注意事项:字节流默认使用 ISO 8859-1 字符编码(无法表示汉字),所以不建议使用第一个和第三个API。void storeToXML(OutputStream os, String comment)void loadFromXML(InputStream in)注意事项:默认采用UTF-8编码。*/
public class PropertiesDemo2 {public static void main(String[] args) {/*Properties info = new Properties();info.setProperty("刘强东", "章泽天");info.setProperty("文章", "马伊利");info.setProperty("贾乃亮", "李小璐");info.setProperty("罗志祥", "周扬青");// void store(Writer out, String comments)try(Writer writer = new FileWriter("a.txt")) {info.store(writer, "...");} catch (IOException e) {e.printStackTrace();}*/// void load(Reader read)/*Properties info = new Properties();try (Reader reader = new FileReader("a.txt")) {info.load(reader);} catch (IOException e) {e.printStackTrace();}System.out.println(info);*/// void storeToXML(OutputStream os, String comment)/*Properties info = new Properties();info.setProperty("刘强东", "章泽天");info.setProperty("文章", "马伊利");info.setProperty("贾乃亮", "李小璐");info.setProperty("罗志祥", "周扬青");try(OutputStream out = new FileOutputStream("b.xml")) {info.storeToXML(out, "...");} catch (IOException e) {e.printStackTrace();}*/// void loadFromXML(InputStream in)Properties info = new Properties();try(InputStream in = new FileInputStream("b.xml")) {info.loadFromXML(in);} catch (IOException e) {e.printStackTrace();}System.out.println(info);}
}····················································································································································································································
PPT上的三道题:
- “aababcabcdabcde”,获取字符串中每一个字母出现的次数要求结果:a(5)b(4)c(3)d(2)e(1)
大致思路同LeetCode之根据字符出现频率排序
public class Homework01 {public static void main(String[] args) {String s = "aababcabcdabcde";String ret = charCount(s);System.out.println(ret);}public static String charCount(String s) {Map<Character, Integer> map = new TreeMap<>();for (int i = 0; i < s.length(); i++) {//if (map.containsKey(c)) map.put(c, map.get(c) + 1);//else map.put(c, 1);map.put(s.charAt(i), map.getOrDefault(s.charAt(i), 0) + 1);}StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder();Set<Map.Entry<Character, Integer>> entries = map.entrySet();for (Map.Entry<Character, Integer> e : entries) {Character key = e.getKey();Integer value = e.getValue();sb.append(key).append("(").append(value).append(")");}return sb.toString();}
}- LeetCode之两数之和
这道题用到了哈希表,工作中更常用的是HashMap,底层是哈希表,增删查时间复杂度都是O(1),而TreeMap底层是红黑树,增删查的时间复杂度是O(logN),也就是树的高度。 - 请设计一个猜数字小游戏,可以试玩5次。试玩结束之后,给出提示:游戏试玩结束,请付费。
package com.cskaoyan.exercise;import java.io.*;
import java.util.Properties;
import java.util.Scanner;/*** @author shihao* @create 2020-05-24 17:33*/
public class ex01 {public static void main(String[] args) {Properties properties = new Properties();try (Reader r = new FileReader("count.txt")) {properties.load(r);} catch (Exception e) {e.printStackTrace();}String value = properties.getProperty("count");int num = Integer.valueOf(value);if (num > 5) {System.out.println("试玩结束,请付费");System.exit(0);} else {num++;properties.setProperty("count",String.valueOf(num));try(Writer w = new FileWriter("count.txt")){properties.store(w,null);} catch (IOException e) {e.printStackTrace();}GuessNumber.start();}}
}class GuessNumber {public static void start() {int count = 0;while (true) {//一定要将(Math.random() * 100)强换为int//而不是只讲Math.random()强转为intint num = (int) (Math.random() * 100) + 1;Scanner in = new Scanner(System.in);System.out.println("请输入数据(1-100):");int guessNumber = in.nextInt();count++;if (guessNumber > num) {System.out.println("你猜的数字" + guessNumber + "大了");} else if (guessNumber < num) {System.out.println("你猜的数字" + guessNumber + "小了");} else {System.out.println("恭喜你," + count + "次猜中了");break;}}}
}
count.txt
#Sun May 24 18:12:45 CST 2020
count=1
····················································································································································································································
Map总结:
Map|-- HashMap|-- LinkedHashMap|-- Hashtable|-- Properties|-- TreeMap
这篇关于week07_day06_Map的文章就介绍到这儿,希望我们推荐的文章对编程师们有所帮助!



